#within the contextual confines of the comics and their references to the films
Photo

darth vader (2020-), #26 (pak/ienco)
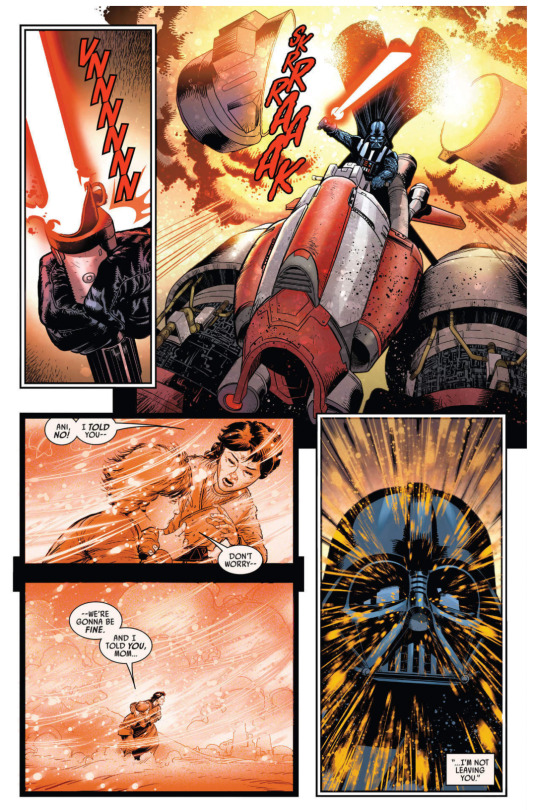
it’s a podrace! darth vader pilots a podracer through an artificial sandstorm to save sabé, the former double for queen amidala, who has been lost in its center. vader flies alone through a maelstrom manufactured by the empire; as he steers and slices his way past dark obstacles, his mind dwells on the podrace he won as a child slave to help queen amidala, then represented too by sabé while padmé masked herself as a handmaiden.
before he won that race, vader remembers, he could find his mother even in sandstorms, and promise her he would never leave her. in the subsequent panels, we see the contrasting results of winning: it meant separation from his mother, interrogation by the jedi council over his fear of losing her, his mother’s death, his own subsequent choice to murder the villagers who’d held her hostage, and finally, separation from padmé again because of jedi and sith. specifically, vader remembers how she’d fallen out of their ship into a sand dune, and his jedi master obi-wan ordering him to leave her behind (so they could pursue the sith lord count dooku instead). surrounded by sand with his mother, he was never closer to her; alone in the jedi temple, before his mother’s grave, a smattering of sand kernels was all he had left.
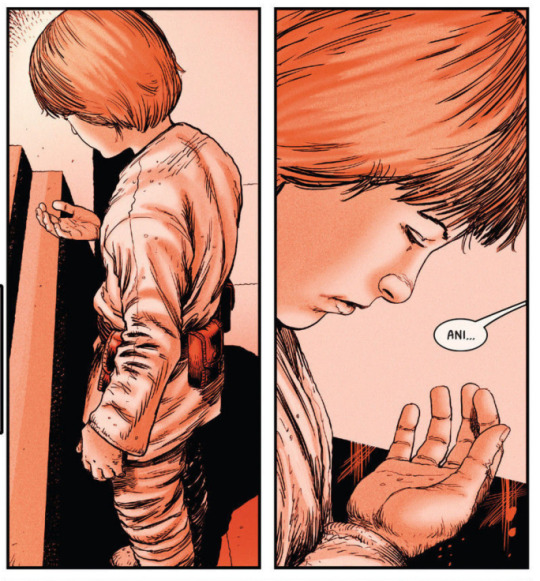


[image caption: panels from two different pages showing vader’s memories of losing his mother - first when he was taken to the temple, then when she died. anakin’s hand is shown in close-up, stray grains of sand in his palm.]
vader wins this race as well. as he once helped queen amidala and her handmaidens leave tatooine, so too does he now save the queen’s shadow. when he arrives at the site where sabé disappeared, he finds anakin’s childhood friend kitster (more context below), who learned how to build pods from anakin and put together the pod that vader has just raced. kitster shows him that sabé has been buried alive under a toppled cylinder. vader lifts it with the force; as she rises from the shallow grave, he remembers his power from before he won the tatooine race and was taken to the jedi - the power to tell his mother, “don’t worry, we’re going to be fine,” and, “I’m not leaving you.”

[image caption: vader saves sabé with kitster’s help, and remembers finding his mother in a sandstorm.]
but it’s not that easy. generated by an energy-eating machine (I think? again, don’t ask me about the lore), the storm doesn’t respond to vader’s attempts to quell it with the force. he realizes that sabé will be consumed by it - he thinks back to leaving padmé behind, her body half-buried in sand - if he fails to call on machine power.
using the cylinder-gravestone from which he’d just freed sabé as armor for himself, sabé, and kitster, vader directs his orbiting flagship to fire upon his location with maximum incinerating force. the result: all the sand in the storm fuses and flattens into a smooth ground of glass.
the sand still caught in his glove slides down his palm; vader looks at it, looks at it for a long time. this time, it seems, it is not all that he has left: he has saved sabé from death. letting the sand fall from his hand, he lifts sabé and carries her over the glass into the light horizon.

[image caption: vader steps out from an armored shell into a landscape he’s had incinerated; sand has transformed into black glass. some sand that was caught in his glove falls from his hand; he lets it, then takes sabé from kitster and walks towards a sunlit cloud.]
so ... why is kitster here? vader has come to this place because sabé is as haunted by his mother’s death as he is. troubled by the fact that anakin, a child slave, won a podrace to help royalty, and that his mother was nonetheless left behind in slavery, padmé had directed sabé to find shmi on tatooine. never having met shmi before, as queen amidala did not leave her starship on tatooine, sabé failed to locate shmi on that mission. she did manage to free a small number of slaves, however, including anakin’s childhood best friend kitster, and relocate them. the more immediate context is this: these ex-slaves are now under threat from a crimson dawn operative masquerading as an imperial, or something (don’t ask me about the lore-related details of the plot, I can only grasp at relationships between images). and since vader has vowed to end crimson dawn in the name of restoring “order”, sabé was able to convince him to visit this community, and work with people like kitster to destroy the imperial/dawn weapon that caused the sandstorm in the first place.
in summary. we are here because of shared grief over shmi and padmé, over shared grief about the results of that first podrace. we have a second race with a parallel result - vader has helped the former queen, again; helped padmé, in a way, again - and a contrast: there is no jedi betting on vader’s freedom, now. but in some sense this is another parallel. for as winning the race led vader to coruscant and the jedi temple, the comic now cuts to the former temple, now the imperial palace, on coruscant.

[image caption: it is night on coruscant; the former jedi temple, now the emperor’s palace, is shown in dark profile against a sky lit pink-purple from the city lights.]
the emperor is speaking, speaking to himself, ignoring his red-robed guards, who gaze at each other questioningly. vader, the emperor mutters, couldn’t save his mother, nor padmé. but now he thinks he can --
well, the emperor doesn’t finish the sentence. you might say the emperor is betting on failure; he is delighted by what he anticipates, for he closes the issue with his cackles. you can fill in the blanks.
#darth vader (2020)#darth vader#anakin skywalker#handmaiden sabé#kitster banai#greg pak#raffaele ienco#sw comics#comic analysis#these are just attempts to sort out relationships between images#in a very simple way#within the contextual confines of the comics and their references to the films#not character meta#this comic run is perhaps the most poetic of the three#where the internal plot - vader's mindscape - is concerned#i don't really understand the external plot#something something crimson dawn#anyway the way image and text are arranged in this run#what is said and especially what is left unsaid#the sheer amount left to the imagination to fill#speaks to me#long post
41 notes
·
View notes
Link
“BUTCH” HAS LONG been the name we’ve given a certain kind — that kind — of lesbian. The old adage applies: You know her when you see her. She wears men’s clothing, short hair, no makeup. Butch is an aesthetic, but it also conveys an attitude and energy. Both a gender and a sexuality, butchness is about the body but also transcends it: “We exist in this realm of masculinity that has nothing to do with cis men — that’s the part only we [butches] know how to talk about,” says the 42-year-old writer, former Olympic swimmer and men’s wear model Casey Legler. “Many people don’t even know how to ask questions about who we are, or about what it means to be us.”
Many of us wear the butch label with a certain self-consciousness, fearing the term doesn’t quite fit — like a new pair of jeans, it’s either too loose or too tight. The graphic novelist Alison Bechdel, 59, doesn’t refer to herself as butch but understands why others do. “It’s a lovely word, ‘butch’: I’ll take it, if you give it to me,” she says. “But I’m afraid I’m not butch enough to really claim it. Because part of being butch is owning it, the whole aura around it.”
What does owning it look like? Decades before genderless fashion became its own style, butches were wearing denim and white tees, leather jackets and work boots, wallet chains and gold necklaces. It isn’t just about what you’re wearing, though, but how: Butchness embodies a certain swagger, a 1950s-inspired “Rebel Without a Cause” confidence. In doing so, these women — and butches who don’t identify as women — created something new and distinct, an identity you could recognize even if you didn’t know what to call it.
By refuting conventionally gendered aesthetics, butchness expands the possibilities for women of all sizes, races, ethnicities and abilities. “I always think of the first butch lesbian I ever saw,” says the 33-year-old actor Roberta Colindrez. “This beautiful butch came into the grocery store and she was built like a brick house. Short hair, polo shirt, cargo pants and that ring of keys … It was the first time I saw the possibility of who I was.” And yet, to many people, “butch style” remains an oxymoron: There’s a prevalent assumption that we’re all fat, frumpy fashion disasters — our baseball caps and baggy pants suggest to others that we don’t care about self-presentation. But it’s not that we’re careless; it’s that unlike, say, the gay white men who have been given all too much credit for influencing contemporary visual culture, we’re simply not out to appease the male gaze. We disregard and reject the confines of a sexualized and commodified femininity.
ETYMOLOGICALLY, “butch” is believed to be an abbreviation of “butcher,” American slang for “tough kid” in the early 20th century and likely inspired by the outlaw Butch Cassidy. By the early 1940s, the word was used as a pejorative to describe “aggressive” or “macho” women, but lesbians reclaimed it almost immediately, using it with pride at 1950s-era bars such as Manhattan’s Pony Stable Inn and Peg’s Place in San Francisco. At these spots, where cocktails cost 10 cents and police raids were a regular occurrence, identifying yourself as either butch or femme was a prerequisite for participating in the scene.
These butches were, in part, inspired by 19th-century cross-dressers — then called male impersonators or transvestites — who presented and lived fully as men in an era when passing was a crucial survival tactic. We can also trace butchness back to the androgynous female artists of early 20th-century Paris, including the writer Gertrude Stein and the painter Romaine Brooks. But it wasn’t until the 1960s and early 1970s that butches, themselves at the intersection of the burgeoning civil, gay and women’s rights movements, became a more visible and viable community.
From their earliest incarnations, butches faced brutal discrimination and oppression, not only from outside their community but also from within. A certain brand of (mostly white) lesbian feminism dominant in the late ’70s and early ’80s marginalized certain sorts of “otherness” — working-class lesbians, lesbians of color and masculine-of-center women. They pilloried butchness as inextricably misogynist and butch-femme relationships as dangerous replications of heteronormative roles. (Such rhetoric has resurfaced, as trans men are regularly accused of being anti-feminist in their desire to become the so-called enemy.) Challenged yet again to defend their existence and further define themselves, butches emerged from this debate emboldened, thriving in the late ’80s and early ’90s as women’s studies programs — and, later, gender and queer studies departments — gained traction on North American and European college campuses.
The ’90s were in fact a transformative decade for the butch community. In 1990, the American philosopher Judith Butler published her groundbreaking “Gender Trouble: Feminism and the Subversion of Identity,” and her theories about gender were soon translated and popularized for the masses. In her academic work, Butler argues that gender and sexuality are both constructed and performative; butch identity, as female masculinity, subverts the notion that masculinity is the natural and exclusive purview of the male body. Soon after, butch imagery infiltrated the culture at large. The August 1993 issue of Vanity Fair featured the straight supermodel Cindy Crawford, in a black maillot, straddling and shaving the butch icon K.D. Lang. That same year, the writer Leslie Feinberg published “Stone Butch Blues,” a now classic novel about butch life in 1970s-era New York. In Manhattan, comedians such as Lea DeLaria and drag kings such as Murray Hill took to the stage; it was also the heyday of Bechdel’s “Dykes to Watch Out For,” the serialized comic strip she started in 1983. In 1997, Ellen DeGeneres, still the most famous of butches, came out. Two years later, Judith “Jack” Halberstam and Del LaGrace Volcano published “The Drag King Book” and the director Kimberly Peirce released her breakthrough film, “Boys Don’t Cry”; its straight cisgender star, Hilary Swank, went on to win an Oscar for her portrayal of Brandon Teena, a role that still incites contentious debates about the nebulous boundaries between butch and trans identity. These artists and their legacies are the cornerstones of our community. As Legler says, “This is where we’ve come from, and the folks we look back to. If you identify with that lineage, then we’d love to have you.”
LIKE ANY QUEER subculture, butchness is vastly different now than it was three decades ago — though the codes have been tweaked and refined over the years, younger butches continue to take them in new and varied directions: They may experiment with their personas from day to day, switching fluidly between masculine and feminine presentation. There are “stone butches,” a label that doesn’t refer to coldness, as is often assumed, but to a desire to touch rather than to be touched — to give rather than receive — and is considered slightly more masculine than “soft butch” on the Futch Scale, a meme born in 2018 that attempted to parse the gradations from “high femme” to “stone butch.” (“Futch,” for “femme/butch,” is square in the middle.) And while there remains some truth to butch stereotypes — give us a plaid flannel shirt any day of the week — that once-static portrait falls apart under scrutiny and reflection. Not every butch has short hair, can change a tire, desires a femme. Some butches are bottoms. Some butches are bi. Some butches are boys.
Different bodies own their butchness differently, but even a singular body might do or be butch differently over time. We move between poles as our feelings about — and language for — ourselves change. “In my early 20s, I identified as a stone butch,” says the 45-year-old writer Roxane Gay. “In adulthood, I’ve come back to butch in terms of how I see myself in the world and in my relationship, so I think of myself as soft butch now.” Peirce, 52, adds that this continuum is as much an internal as an external sliding scale: “I’ve never aspired to a binary,” she says. “From day one, the idea of being a boy or a girl never made sense. The ever-shifting signifiers of neither or both are what create meaning and complexity.”
Indeed, butch fluidity is especially resonant in our era of widespread transphobia. Legler, who uses they/them pronouns, is a “trans-butch identified person — no surgery, no hormones.” Today, the interconnected spectrums of gender and queerness are as vibrant and diverse in language as they are in expression — genderqueer, transmasc, nonbinary, gender-nonconforming. Yet butches have always called themselves and been called by many names: bull dyke, diesel dyke, bulldagger, boi, daddy and so on. Language evolves, “flowing in time and changing constantly as new generations come along and social structures shift,” Bechdel says.
If it’s necessary to think historically, it’s also imperative to think contextually. Compounding the usual homophobia and misogyny, black and brown butches must contend with racist assumptions: “Black women often get read as butch whether they are butch or not,” Gay says. “Black women in general are not seen, so black butchness tends to be doubly invisible. Except for studs: They’re very visible,” she adds, referring to a separate but related term used predominantly by black or Latinx butches (though, unsurprisingly, white butches have appropriated it) who are seen as “harder” in their heightened masculinity and attitude. Gay notes that “people tend to assume if you’re a black butch, you’re a stud and that’s it,” which is ultimately untrue. Still, butch legibility remains a paradox: As the most identifiable of lesbians — femmes often “pass” as straight, whether they want to or not — we are nonetheless maligned and erased for our failure of femininity, our refusal to be the right kind of woman.
ANOTHER LINGERING stereotype, one born from “Stone Butch Blues” and its more coded literary forebears, particularly Radclyffe Hall’s “The Well of Loneliness” (1928), is the butch as a tragic and isolated figure. She is either cast out by a dominant society that does not — will not — ever see her or accept her, or she self-isolates as a protective response to a world that continually and unrelentingly disparages her.
When a butch woman does appear in mainstream culture, it’s usually alongside her other: the femme lesbian. Without the femme and the contrast she underscores, the butch is “inherently uncommodifiable,” Bechdel says, since two butches together is just a step “too queer.” We rarely see butches depicted in or as community, an especially sobering observation given the closure of so many lesbian bars over the past two decades. But when you talk to butches, a more nuanced story emerges, one of deep and abiding camaraderie and connection. Despite the dearth of representation, butch love thrives — in the anonymous, knowing glances across the subway platform when we recognize someone like us, and in the bedroom, too. “Many of my longest friendships are with people who register somewhere on the butch scale,” Peirce says. “We’re like married couples who fell in love with each other as friends.”
Legler, for their part, recognizes a “lone wolf” effect, one in which some young queers initially love “being the only butch in the room.” In organizing the group portrait that accompanies this essay over the past months, Legler was curious “what it would be like for butches to just show up together and to be able to display all of their power, all of their sexiness, all of their charisma, without having it be mitigated in some way.” And not only for butches of an older generation, but for those still figuring things out, transforming the scene in ways that both defy and inspire their elders. “It’s been centuries in the making, the fact that we are all O.K.,” Legler adds. “That our bodies get to exist: We have to celebrate that. You can do more than just survive. You can contribute.”
44 notes
·
View notes