#rbi monetary policy june 2022
Text

CENTRAL BANK CONUNDRUM.
Whenever there is a hike in the interest rate, the economist is apprehensive about its impact on growth. The recent rate hike by RBI also poses the same apprehensions among the economists that these decisions could be growth restrictive as the economy has not revived completely.
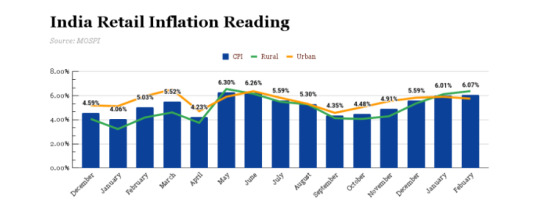
If we look at the inflation rate, it was seeing a continuous surge from October, and the recent data of May shows that it has reached 8.6% highest since 1981. This exponential increase in the inflation rate is attributed to the rise in food inflation. Various economists suggest that the R.B.I rate hike will not be able to tame this inflation because of the international phenomenon. Instead, it will hurt the growth prospects.
If we look at the data more carefully, we will find that a fast-forwarded rate hike was unavoidable because of five primary reasons- (Joshi, 2022)
Broad-based inflation- The recent inflation is not just the result of the international phenomenon; various factors have made it long-lasting and broad-based. It’s not just our headline inflation (which includes food and fuel) surging. Our core inflation, too, is hovering around 6.8%. Every commodity in RBI’s basket shows an increase in prices, making inflation broad-based.
Constitutional obligation- Monetary policy committee is constitutionally obligated to keep the interest rate at 4% (+/- 2%); if we look at the graph since January, it has been above the allowed limit, and even the recent R.B.I inflation expectation is showing that it will be 6.7% which means that this fiscal year inflation will be above the allowed threshold. R.B.I. has to give the government reasons for the same as the Monetary policy committee’s primary responsibility is to control inflation.
Negative Real Policy Rate- Our repo rate is still below the pre-pandemic level. If we see our real policy rate, i.e. interest rate minus inflation, we will find that it is negative, which means that the value of money deposited in our bank is getting eroded in real terms; this will have a direct impact on savings pattern.
Higher inflation expectation- The recent RBI inflation expectation survey and IIM Ahmedabad inflation expectation survey show that people feel that inflation will also remain high for the upcoming period. The different studies suggest that higher inflation expectations hurt household expenditure patterns; Juster and Wachter, in 1972, did the research and established that higher inflation expectations result in lower spending on durable goods. (Shankar, 2015)
Increase in interest rate by Federal reserve- With the increase in federal fund rate, India has seen a massive outflow of capital; till the 10th of June, 25 billion dollars had been withdrawn by the foreign portfolio investors. The Fed is expected to increase its fund rate further; hence, RBI must increase its repo rate to tackle the impact.
Though the rate hike was unavoidable, that doesn’t mean we can negate the impact it will create on consumption patterns and demand in the economy. But the normal forecast of monsoon and increase in consumer confidence, as reflected in the RBI survey, does give the cushion to MPC to decide on a rate hike. Also, the allowance of credit cards to be linked to UPI will push the consumption of small, durable goods like laptops, smartphones and other small-ticket items. The risk that this unanchored inflation poses to macroeconomic stability is enormous, and the central bank must be ready to answer these complications.
Joshi, D. (2022, June Friday). Google. Retrieved from Indian express: Dharmakirti Joshi writes: RBI leans harder to rein in inflation, but rebound in services will put upward pressure on prices
Shankar, S. Y. (2015). Inflation Expectations and Consumer spending in India; evidence from consumer confidence survey. Reserve bank of India occasional papers, 41-43.
0 notes
Text
One year to the Russia-Ukraine War: Effects on the Indian Economy | BDBIPL
As 2023 begins, the world is still dealing with the 3 Cs (covid, conflict and climate) a set of risks
that feel both wholly new and eerily familiar. These concerns feel both entirely new and uncannily familiar. With the threat of these “older” risks—inflation, cost-of-living crises, trade wars, capital outflows from emerging markets, widespread social unrest, geopolitical conflict, and the spectre of nuclear war and constant climate changes.
The war between Russia and Ukraine has already lasted a full year. Since then, both sides have been actively waging a full-fledged war against one another a number of infrastructures have been destroyed, the war is still raging. But the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has sent numerous shocks to the global economy, including that of India.
A year ago, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, there were concerns that the Indian economy would face increased uncertainty in at least three particular areas.
Increased inflation risks would provide additional difficulties for those in charge of overseeing India’s monetary policy.
The government’s fiscal consolidation plan would be in jeopardy if commodity prices increased, especially those of crude oil and fertilizers.
The external sector of the Indian economy would be under pressure due to an increase in import costs, while exports may suffer as a result of a potential slowdown in the world economy.
The war’s severe trade interruptions, spikes in food and fuel prices, and overall weakening of
the world economy are all factors in the rising inflation and accompanying tightening of financial
conditions worldwide. Conflict and a shift in geopolitics have created a new global alignment
that is upending the global economy, including India’s.
How did India handle the conflict between Russia and Ukraine?
The conflict in Ukraine will likely be the least anticipated of the economic surprises India is going
to encounter in 2023. There are no signs of a resolution, and it has been difficult to foresee how it would affect the different sections of the Economy.
India is in the incredibly fortunate position of almost surpassing China as the most populous nation on earth. Although far more drastic reforms would be necessary, its demographics indicate that it has the ability to grow at a rate closer to 8% annually over the next ten years.
There have been two direct effects for India and another, equally significant indirect effect that is it pushed up our import bill for both energy and fertilizers. Both these (and the rising price of wheat globally) have also contributed to rising inflation globally, promoting Indian policymakers to raise interest rates in tandem with the rise in global rates resulting in Higher inflation and lower growth for India in the initial phases of the conflict. The situation now has however come to a changing point for India with the changed policy and economic condition.
Domestic Equity Markets – The benchmark Sensex on the BSE lost 2,700 points and the Nifty50 on the NSE fell 815 points after Russia announced its military activities in Ukraine. The Sensex saw its steepest fall on February 24, 2022, since the Covid pandemic began in March 2020. That was also the fourth-worst fall in the index’s history. Sensex and Nifty fell to their 52-week low last year in June, due to rising concerns over the conflict and its impact on inflation, and the economy. Sensex touched a low of 51,360.42 on June 16 last year, while Nifty tumbled to 15,293.50. However, markets have also scaled new peaks over the past year. On November 30, Sensex crossed the 63,000 mark, and the Nifty breached 18,758 points, for the first time ever. The Index is not significantly impacted because of government policies and international support for the Indian market, even though recent stock market changes have caused instability.
India’s inflation and RBI’s rate hike – India’s GDP numbers have also been affected due to the ongoing conflict. According to experts, inflation will be a persistent issue for a while and the economy has been tackling a surge in prices for a while now. The conflict in Ukraine had a number of significant effects, one of which was the effort to keep domestic prices of important commodities in check, which widened demand-supply imbalances. The Russia-Ukraine conflict has crippled the global supply chain, triggering a global food shortage, and subsequently resulting in high inflation rates in countries. Retail inflation in India reached an 8-year high of 7.79% in April 2022, two months after Russia invaded Ukraine, and remained above the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) tolerance level of 2-6%. This was mostly fueled by the enormous rise in crude oil prices around the world, which exceeded $139 per barrel as a result of supply chain difficulties and numerous sanctions on Russia. Financial institutions have forecast that this year will see a slowdown in global economic development as inflation rates continue to rise in many countries. Yet analysts predict that India will continue to be a “bright
spot.” India is anticipated to grow 6.8% in FY23 as a result of digitalization, cautious fiscal policies, and large finance for capital investments announced in the Budget this year. Russian oil imports into India have significantly increased during the past few months. It has insisted that it has a fundamental responsibility to ensure that Indian consumers have the best possible access to international markets under the most favorable conditions.
India’s crude imports – India’s decision to increase crude oil trade and economic engagements with Russia would have huge diplomatic and economic repercussions. It is significant to remember that India mainly relies on imports to meet its needs for oil. Over 5 million barrels of the nation’s daily average need for crude oil—or about 85%—are imported. In February 2023, India’s imports of crude oil from Russia reached a record high of 1.6 million barrels per day, surpassing the sum of imports from its two main suppliers, Iraq and Saudi Arabia. For a sixth consecutive month, Russia maintained its position as the sole major supplier of crude oil, which is refined into gasoline and diesel. Russia provided more than one-third of all the oil that India bought. Prior to the start of the Russia-Ukraine conflict in February 2022, Russia had a market share of less than 1% of India’s imports; when the conflict began, that percentage increased to 1.62 million barrels per day.
Impact on exports – In its monthly economic report, the ministry of finance highlighted that the country’s major export markets are anticipated to experience steep declines in 2023, which could result in lack lustre growth for India’s exports this year. The volume and value of trade are likely to continue to drop in 2023 as a result of slowing global output, which caused a decline in global trade growth in 2022. The slowdown in international trade, particularly from the US and two of India’s top export destinations, may have a big effect on the country’s exports as well. Lower demand for Indian goods would result from a slowdown in their economy. India’s exports have grown significantly in the last few years due to robust manufacturing across a number of industries and supportive policy conditions. India’s merchandise exports soared to a new high of US$417.81 billion in the fiscal year (FY) 2022, above the government’s target of US $400 billion. According to government projections, India will reach its US$450 billion export goal in FY 2023.
India’s currency devalued – The rupee has declined against the US dollar by over 800 paise (9.8%) in the year since Russia invaded Ukraine. The depreciation has been almost 11% lower overall in 2022 than it was in all of 2013. The external industry has demonstrated resilience on numerous fronts despite the downturn being the most severe since the taper tantrums of 2013. The Reserve Bank had to repeatedly draw from its reserves as a result of the currency market’s volatility, which was brought on by a rise in world oil prices after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, making it difficult for policymakers to address imported inflation.
Russia became India’s 5th largest trade partner – During the period of April through
December 2022, according to data from the ministry of commerce, Russia became India’s fifth-largest trading partner. Russia moved up the list of India’s top commercial partners this was because of an increase in oil imports, from position 25. China and Russia are the only two of India’s top five trading partners whose shipments declined in the first half of the year, despite a 17% increase in overall exports. Despite pressure from the US and other nations to limit imports after the start of the conflict in Ukraine, the government has allowed oil corporations to acquire additional petroleum from Russia, which in October became the largest supply of crude for India.

BDBIPL, a prominent engineering products company, recognizes the significance of partnering with a strategy consulting company in India to fuel its growth and expansion plans. By engaging a reputable consulting firm with a deep understanding of the Indian market landscape, BDBIPL can tap into expert guidance and strategic insights. This collaboration enables BDBIPL to refine its business strategies, explore new market opportunities, optimize its operations, and effectively navigate the complexities of the Indian business environment. Leveraging the consulting company's expertise, BDBIPL can make data-driven decisions, strengthen its competitive position, and achieve sustainable growth in the ever-evolving Indian market.
0 notes
Text
India's Q2 GDP Grows At 6.3% Vs 8.4% A Year Ago
India’s Q2 GDP Grows At 6.3% Vs 8.4% A Year Ago
India’s Q2 GDP Growth: India’s gross domestic product (GDP) grew 6.3 per cent in the September 2022 quarter (Q2FY23) as compared with 8.4 per cent in the corresponding quarter last year, according to the official data released on Wednesday. The Indian economy had grown 13.5 per cent in the June 2022 quarter (Q1FY23).
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee had also expected GDP to grow 6.3 per cent…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Chandigarh University closed till Saturday amid protests
India reported 4,858 new Covid cases on Monday, taking the nation's tally to 44,539,046. With 18 new deaths, including eight reconciled by Kerala, India's toll from the pandemic has reached 528,355. A total of 4,735 people recovered from the Covid infection in the last 24 hours, taking the nation's tally of recovered cases to 43,962,664.
A poll by Business Standard showed that the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI’s) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is likely to lift the policy repo rate by 35-50 basis points (bps) on September 30 as it seeks to bring back elevated domestic inflation within its target range. Analysts said that a heightened pace of policy tightening by central banks in advanced economies is also seen as increasing pressure on the RBI to continue front-loading rate hikes to maintain adequate interest rate differentials.

Chandigarh University was closed till Saturday amid the raging controversy over the alleged leaked objectionable videos of students. The university authorities on Sunday claimed that no objectionable video was made of the girl students except a personal video shot by a girl, which she shared with her boyfriend. The woman has been arrested and accused of voyeurism under the IT Act. Her 23-year-old boyfriend, Sunny Mehta, who works with a travel agency, has also been arrested from Shimla. A second man has also been arrested from Shimla.
Outstanding dues of power distribution companies towards gencos declined sharply to Rs 713.29 crore on Friday from Rs 5,085.30 crore as of August 17 following a strict action against defaulter utilities. The defaulter utilities were barred from trading at power exchanges under the Electricity (Late Payment Surcharge and related matters), Rules 2022 notified by the power ministry in June 2022.
0 notes
Text
Gold -- a source of return on investments amid monetary policy tightening: WGC

Aug 10, 2022 15:22 IST
New Delhi , August 10 (Always First): Against the backdrop of monetary policy tightening by several central banks including the Reserve Bank of India, gold as an asset may offer investors a source of return on their investments and effective diversification of the portfolio, said World Gold Council in its latest Investment Update.
Gold is widely considered a safe-haven asset and a hedge against volatility in financial markets.
"Interest rate hikes are driven by rising inflation. In the short term, higher rates are a headwind for gold, but in the current environment they remain historically low - in real terms mostly negative across developed markets," the council said.
Historical data, the council said, shows that gold has offered attractive returns during India's monetary-tightening cycles. In five rate-hiking cycles since 2004 gold in Indian rupees averaged an annualised return of 19.5 per cent, outperforming other major assets.
For instance, over the past 41 years, gold has delivered an average annual return of 10 per cent in rupees, clearly outperforming retail inflation, which grew by an average of 7.3 per cent over the same period.
Gold's performance has also been particularly strong in periods of high inflation, increasing by 12 per cent on average when inflation rose above 6 per cent, it said.
Central banks around the world have responded to rising inflation. The US, the UK and Canada have raised interest rates, while the US Federal Reserve and European Central Bank (ECB) have rolled back their emergency pandemic support for the economy, it added.
For the record, faced with an over four-decade high inflation in the country, the US Federal Open Market Committee had in its latest meeting raised the key policy interest rate by 75 basis points to 2.25-2.50 per cent. Hiking interest rates typically cool demand in the economy, thereby putting a brake on the inflation rate.
The monetary policy committee of the Reserve Bank of India has raised the repo rate by 50 basis points to 5.40 per cent in order to contain the persistently high inflation. The latest hike takes the repo rate above pre-pandemic levels of 5.15 per cent. RBI has so far hiked the key repo rates -- the rate at which the central bank of a country lends money to commercial banks -- by 140 basis points.
In India, retail inflation has been over the RBI's upper tolerance band of 6 per cent for the sixth consecutive month in a row in June. Retail inflation was at 7.01 per cent in June. Inflation data for July is due on Friday. (Always First)
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
RBI Hikes Repo Rate To 5.4%; Curbing Inflation To Remain Focus

Published by
BOOM LiveBy BOOM Team The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) hiked the repo rate by 50 basis points on Friday to 5.4 per cent, its third hike in the current financial year continuing its fight to tame stubbornly high inflation. The decision of the six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the RBI, which met on August 3 to Aug 5, 2022 was largely in line with expectations. Financial markets were largely unchanged at mid day as the hike was on expected lines. June 2022 was the sixth consecutive month when headline CPI (consumer price inflation) inflation remained at or above the upper tolerance level of 6 p...Read More
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Monetary Policy will remain focused on withdrawing accommodation while supporting growth
Kotak Editorial Team

To combat persistently high inflation, the RBI Governor-led Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) on 5th August 2022 raised the repo rate by 50 basis points to 5.40 per cent. Following a 40 and 50 basis point rise in May and June respectively this year, this is the third consecutive rate hike. Despite raising rates, MPC has decided to maintain its real GDP growth projections.
Here are Kotak leaders' thoughts on the announcement of RBI monetary policy announcement.
Continue reading...
0 notes
Text
Market Talk - July 25, 2022

ASIA:
China’s new household deposits grew more than a third year on year to a record USD 1.5tn in the first half of 2022, while individual bank borrowings plunged more than half over the same period, official data showed. The inversion in savings rates followed an increase in bank deposits as Chinese savers raced to find safe options for their assets, and an economic downturn weighed on personal spending. China’s economy narrowly escaped a contraction in the second quarter, expanding 0.4 percent year on year in the three months to the end of June. Long-term real estate development loans fell by a quarter in the first half of 2022 from a year ago after many property companies, mainly Evergrande, defaulted on debt payments. Infrastructure buildout, another significant source of long-term credit, is also lagging as debt-laden local governments, the main backer of roads and bridges, struggle to raise capital.
India’s central bank governor Shaktikanta Das said that India’s central bank has zero tolerance for volatile and bumpy movements of rupee against US dollar and ensured to engage with foreign exchange markets to stop the downfall of rupee and to find its appropriate level. The rupee touched its record low in history to cross the psychological 80 per dollar mark last week, which caused India’s central bank, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), for heavy dollar selling. Das said the rupee’s movements have been relatively smooth and orderly due to the RBI’s actions in the foreign exchange market. On Friday, the rupee was last trading at 79.90/91 to a dollar, compared to its Thursday’s close of 79.9450.
The major Asian stock markets had a mixed day today:
- NIKKEI 225 decreased 215.41 points or -0.77% to 27,699.25
- Shanghai decreased 19.59 points or -0.60% to 3,250.39
- Hang Seng decreased 46.20 points or -0.22% to 20,562.94
- ASX 200 decreased 1.60 points or -0.02% to 6,789.90
- Kospi increased 10.55 points or 0.44% to 2,403.69
- SENSEX decreased 306.01 points or -0.55% to 55,766.22
- Nifty50 decreased 88.45 points or -0.53% to 16,631.00
The major Asian currency markets had a mixed day today:
- AUDUSD increased 0.00376 or 0.54% to 0.69613
- NZDUSD increased 0.00165 or 0.26% to 0.62685
- USDJPY increased 0.626 or 0.46% to 136.696
- USDCNY decreased 0.00341 or -0.05% to 6.75369
Precious Metals:
l Gold decreased 5.45 USD/t oz. or -0.32% to 1,723.61
l Silver decreased 0.130 USD/t. oz or -0.70% to 18.492
No economic news from last night:
Some economic news from today:
Hong Kong:
Exports (MoM) (Jun) decreased from -1.4% to -6.4%
Imports (MoM) (Jun) decreased from 1.3% to 0.5%
Trade Balance decreased from -36.7B to -68.5B
Singapore:
CPI (YoY) (Jun) increased from 5.6% to 6.7%
EUROPE/EMEA:
The UK’s Industrial output grew at the slowest pace in over a year in three months to July. A survey conducted by the Confederation of British Industry found that there are tentative signs that some challenges around inflation and investment are easing, which may help in economic growth of the region. The Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) scheduled to meet next must decide to increase the interest rates by 50 basis points to tackle the highest inflation of 40 years. Quarterly inflation expectations – a key concern for the BoE as it judges how long high inflation will last – dropped sharply to +48 from April’s record high of +71. Monday’s CBI Industrial Trends Survey output balance dropped to +6 for July from +19 in April, its lowest since the three months to April 2021 but still above its long-run average of +2. The monthly CBI industrial orders balance dropped to +8 from +18, its lowest since October but above its long-run average of -13.
A survey conducted by the German IFO institute think tank, published on Monday showed morale among German businesses has fallen as rising prices for goods and fuel dampen growth prospects. The IFO business climate index fell almost four points from 92.2 in June to 88.6 in July. The index measures businesses’ confidence in the current climate in comparison to a reference point set in 2015. The survey was conducted of around 9000 managers from across the German business community. The fall in confidence represents a new downward trend following over a year of recovery since the lows seen in early 2020 when the coronavirus pandemic broke out. July’s confidence index number represents the lowest point since June 2020.
The major Europe stock markets had a mixed day:
- CAC 40 increased 20.73 points or 0.33% to 6,237.55
- FTSE 100 increased 29.93 points or 0.41% to 7,306.30
- DAX 30 decreased 43.36 points or -0.33% to 13,210.32
The major Europe currency markets had a green day today:
- EURUSD increased 0.00018 or 0.02% to 1.02163
- GBPUSD increased 0.0043 or 0.36% to 1.20474
- USDCHF increased 0.00369 or 0.38% to 0.96499
Some economic news from Europe today:
UK:
CBI Industrial Trends Orders (Jul) decreased from 18 to 8
Germany:
German Business Expectations (Jul) decreased from 85.5 to 80.3
German Current Assessment (Jul) decreased from 99.4 to 97.7
German Ifo Business Climate Index (Jul) decreased from 92.2 to 88.6
US/AMERICAS:
The markets are preparing for an important week with numerous earnings reports being released, GDP data, and the next Federal Reserve meeting. The GDP report is set to be released on Thursday. The White House has changed the definition of “recession,” and will no longer call two consecutive quarters of decline one – a potential indicator of what to expect. Yet, the markets may be pricing that in differently. The markets are also pricing in a 75 bps rate hike from the Federal Reserve, but June’s 9.1% inflation report may cause them to act more aggressively. The Federal Reserve will announce its next move on Wednesday.
Prospects for Boeing were looking up after Delta placed a large order last week. Now, 2,500 workers have announced that they will go on strike on August 1. Union workers claim that the company has failed to meet their demands. Boeing said they increased their 401K contributions to 10%, implemented additional workers’ pay over the next two years, and matched student loan payments for the children of their employees. The union is seeking a 7.2% wage increase as well as a $1,000 cash bonus. If the strike does occur, the company may not be able to fulfill its new orders on time, causing trouble for the aerospace company and potentially the Dow at large.
US Market Closings:
- Dow advanced 90.75 points or 0.28% to 31,990.04
- S&P 500 advanced 5.21 points or 0.13% to 3,966.84
- Nasdaq declined 51.45 points or -0.43% to 11,782.67
- Russell 2000 advanced 10.89 points or 0.6% to 1,817.77
Canada Market Closings:
- TSX Composite advanced 121.56 points or 0.64% to 19,104.48
- TSX 60 advanced 6.87 points or 0.6% to 1,156.35
Brazil Market Closing:
- Bovespa advanced 1,345.03 points or 1.36% to 100,269.85
ENERGY:
The oil markets had a green day today:
- Crude Oil increased 1.83 USD/BBL or 1.93% to 96.616
- Brent increased 1.38 USD/BBL or 1.34% to 104.713
- Natural gas increased 0.378 USD/MMBtu or 4.55% to 8.6570
- Gasoline increased 0.1515 USD/GAL or 4.70% to 3.3726
- Heating oil increased 0.079 USD/GAL or 2.29% to 3.5292
The above data was collected around 13:57 EST on Monday
- Top commodity gainers: Natural Gas (4.55%), Bitumen(3.06%), Gasoline (4.70%) and Cocoa (3.27%)
- Top commodity losers: Oat (-1.66%), Aluminum (-2.19%), Lumber (-4.05%) and Sugar (-2.35%)
The above data was collected around 14:09 EST on Monday.
BONDS:
Japan 0.201%(-1.8bp), US 2’s 3.03% (+0.042%), US 10’s 2.8197% (+3.87bps); US 30’s 3.05% (+0.051%), Bunds 1.0220% (-0.1bp), France 1.6150% (-0.5bp), Italy 3.384% (-3.6bp), Turkey 16.71% (-11bp), Greece 3.045% (-23.7bp), Portugal 2.184% (-0.7bp); Spain 2.275% (+1.5bp) and UK Gilts 1.9380% (-0.3bp).
Original Article
Original Article Here:
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Loan Interest Rate: Fixed or floating rate, which home loan customer should choose
Loan Interest Rate: Fixed or floating rate, which home loan customer should choose
Raj Khosla(MD, mymoneymantra.com)
The Reserve Bank has increased the repo rate by 40 basis points to control inflation. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of RBI took this decision suddenly, shocking everyone. Earlier, most economic experts were anticipating an increase in interest rates, but their estimate was that this increase will not happen before June 2022.
The reason behind this increase…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Fixed deposit (FD) interest rates comparison of ICICI, Axis, HDFC banks w.e.f. 21.06.22
From 21st June 2022, Fixed deposit (FD) interest rates have been increased by the major private banks like ICICI, Axis, HDFC banks. Check the comparison here.
#FDrate #FD #FDinterestrate #ICICI #AXIS #HDFC
Fixed deposit interest rates comparison of ICICI, Axis, HDFC banks:
ICICI bank, Axis bank, HDFC bank have revised their Fixed deposit or Term deposit interest rates in synchronization with latest RBI’s monetary policy. Again FD interest rates are in the downward trend.
Here we have compared 3 largest private sector banks’ fixed deposit interest rates for below Rs. 2 crore domestic deposits in…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
कल शुरू होगी मौद्रिक समीक्षा की बैठक, रेपो रेट्स में होगा इजाफा! जानें क्या है एक्सपर्ट की राय?
कल शुरू होगी मौद्रिक समीक्षा की बैठक, रेपो रेट्स में होगा इजाफा! जानें क्या है एक्सपर्ट की राय?
RBI Monetary Policy: रिजर्व बैंक ऑफ इंडिया (Reserve Bank of India) बुधवार को अपनी आगामी मौद्रिक समीक्षा नीति (MPC Meeting) की बैठक करेगा. इस समय मुद्रास्फीति में लगातार तेजी देखने को मिल रही है. ऐसी उम्मीद की जा रही है कि आगामी बैठक में सरकार नीतिगत दरों में इजाफा कर सकती है. एक्सपर्ट ने यह अनुमान जताते हुए कहा कि गवर्नर शक्तिकांत दास पहले ही इसके संकेत दे चुके हैं.
0.35 फीसदी की हो सकती है…
View On WordPress
#business news in hindi#RBI#rbi monetary policy 2022 dates#rbi monetary policy june 2022#rbi monetary policy meeting#RBI MPC#RBI MPC Meet#rbi repo rate 2022#repo rate#आरबीआई#आरबीआई एमपीसी#आरबीआई रेपो रेट#बिजनेस न्यूज इन हिंदी#मौद्रिक समीक्षा नीति#रिजर्व बैंक ऑफ इंडिया#रेपो रेट्स#शक्तिकांता दास
0 notes
Text
HDFC Hikes Lending Rates by 50 bps from Today; How Much Home Loans; EMIs to Increase
HDFC Hikes Lending Rates by 50 bps from Today; How Much Home Loans; EMIs to Increase
HDFC has hiked its retail prime lending rates by 50 basis points
RBI had increased repo rate by 50 basis points to 4.9 per cent in its June monetary policy
Last Updated:June 10, 2022, 09:33 IST
FOLLOW US ON:
Housing Development Finance Corporation or HDFC raised lending rates by 50 basis points a day after Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had hiked repo rate. To tame rising inflation, RBI had…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
HDFC raises Retail Prime Lending Rate on housing loans by 50 bps
Housing Development Finance Corporation Ltd (HDFC) on Thursday said it will raise Retail Prime Lending Rate on housing loans by 50 basis points from June 10, 2022.
"HDFC increases its Retail Prime Lending Rate (RPLR) on Housing loans, on which its Adjustable Rate Home Loans (ARHL) are benchmarked, by 50 basis points, with effect from June 10, 2022," the mortgage lender said in a stock exchange filing.
Following the RBI monetary policy committee's (MPC) decision to raise benchmark policy rate by 50 basis points, many lenders, including ICICI Bank and Bank Baroda have also raised their external benchmark linked loan rates by an equal amount.
ICICI Bank on Thursday raised its external benchmark lending rate by 50 basis points to 8.60 per cent while Bank of Baroda has increased its repo linked lending rate to 7.40 per cent. RBL Bank has also raised its repo-linked lending rate by 50 bps to 10 per cent, effective June 8, 2022. Another private sector lender, Federal Bank, has also factored in the increase in repo rate and increased the interest rates accordingly.
0 notes
Text
RBI Monetary Policy | Credit cards can now be linked to your UPI, starting with RuPay
RBI Monetary Policy | Credit cards can now be linked to your UPI, starting with RuPay
Until now customers could only link their bank accounts through debit cards to UPI.
June 08, 2022 / 10:47 AM IST
Shaktikanta Das (FIle image)
In a major shift in how the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) functions, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) today said that credit cards too will be allowed to be linked to the UPI accounts.
The implementation will begin with the indigenous RuPay credit…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Gold -- a source of return on investments amid monetary policy tightening: WGC

Aug 10, 2022 15:22 IST
New Delhi , August 10 (Always First): Against the backdrop of monetary policy tightening by several central banks including the Reserve Bank of India, gold as an asset may offer investors a source of return on their investments and effective diversification of the portfolio, said World Gold Council in its latest Investment Update.
Gold is widely considered a safe-haven asset and a hedge against volatility in financial markets.
"Interest rate hikes are driven by rising inflation. In the short term, higher rates are a headwind for gold, but in the current environment they remain historically low - in real terms mostly negative across developed markets," the council said.
Historical data, the council said, shows that gold has offered attractive returns during India's monetary-tightening cycles. In five rate-hiking cycles since 2004 gold in Indian rupees averaged an annualised return of 19.5 per cent, outperforming other major assets.
For instance, over the past 41 years, gold has delivered an average annual return of 10 per cent in rupees, clearly outperforming retail inflation, which grew by an average of 7.3 per cent over the same period.
Gold's performance has also been particularly strong in periods of high inflation, increasing by 12 per cent on average when inflation rose above 6 per cent, it said.
Central banks around the world have responded to rising inflation. The US, the UK and Canada have raised interest rates, while the US Federal Reserve and European Central Bank (ECB) have rolled back their emergency pandemic support for the economy, it added.
For the record, faced with an over four-decade high inflation in the country, the US Federal Open Market Committee had in its latest meeting raised the key policy interest rate by 75 basis points to 2.25-2.50 per cent. Hiking interest rates typically cool demand in the economy, thereby putting a brake on the inflation rate.
The monetary policy committee of the Reserve Bank of India has raised the repo rate by 50 basis points to 5.40 per cent in order to contain the persistently high inflation. The latest hike takes the repo rate above pre-pandemic levels of 5.15 per cent. RBI has so far hiked the key repo rates -- the rate at which the central bank of a country lends money to commercial banks -- by 140 basis points.
In India, retail inflation has been over the RBI's upper tolerance band of 6 per cent for the sixth consecutive month in a row in June. Retail inflation was at 7.01 per cent in June. Inflation data for July is due on Friday. (Always First)
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Rupee falls to a new low of 77.28 versus the US dollar.
The domestic currency was trading at 77.28 per dollar at 9.10 a.m., down 0.48 percent from its previous close of 76.93. The currency started at 77.06 and dropped to 77.31 per dollar. The Rupee last touched a low of 79.98 on March 7, 2022.
On Monday, the rupee fell to a new low against the US dollar, matching losses in global stocks amid inflation fears.
The domestic currency was trading at 77.28 per dollar at 9.10 a.m., down 0.48 percent from its previous close of 76.93. The rupee began trading at 77.06 per dollar and fell to 77.31. The rupee last fell to a low of 76.98 on March 7, 2022.
Traders questioned whether the Federal Reserve's interest rate boost would be sufficient to combat inflation, while Chinese officials warned against questioning their zero-COVID policy. While raising interest rates, the Bank of England warned of the possibility of a recession.
According to analysts, the worldwide inflationary pressure has been continued due to the persistence of high crude oil prices and uncertainty about the length of the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Foreign investors continued to sell the currency, causing the value to plummet. For the sixth straight month, FIIs were net sellers, selling $22.31 billion in stocks.
In India, the Reserve Bank of India may extend interest rate rises due to concerns that inflation may surpass its required objective in the next six months, albeit a three-quarter-point raise is unlikely at the June meeting.
The yield on the 10-year Treasury note increased 3 basis points to 7.484 percent. Following the RBI's unexpected rate hike last week, yields have climbed by more than 35 basis points.
"The Federal Reserve's planned interest rate rises and the positive outlook for the US economy may cause money to leave the domestic capital markets. The net withdrawals from domestic capital markets have totaled $19 billion since the Fed signaled a rate rise and starts decreasing its balance sheet in January 2021. Increased outflows and a growing trade imbalance might put more strain on the rupee "In a letter to clients, Edelweiss Wealth Research stated.
"In terms of monetary policy implications, the RBI's monetary policy action would be largely influenced by domestic inflation and growth concerns. Following on from yesterday's surprise interest rate hike, the RBI is poised to raise rates again in the coming months. Rate rises of 60–70 basis points are expected in FY23. Despite the upcoming rate hikes, we believe the chances of rates exceeding the pre-pandemic levels (5.15%) in FY23 are slim "According to Edelweiss research.
1 note
·
View note