#openbsd faq
Text
Xbox account hacker tool 2017

Uses Look-up table with +15 billion entries.
The service cracks password hashes by using pre-computed lookup tables consisting of over 15-billion entries that have been extracted from various online resources. This technique is a variation of the Dictionary Attack that contains both dictionary words and passwords from public password dumps. Review of the Password Cracking tools: #1) CrackStationīest for password hash cracking for free online.ĬrackStation is a free online service for password hash cracking.
Supports multi-core processing and GPU acceleration.
Optimized memory trade-off tool for table creation, conversion, and lookup.
Monitoring, analyzing, and testing Wi-Fi connection.
Windows, OS X, Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, and eComStation2
Uses Look-up Table with +15 billion entriesįTP, HTTP, POP3, SMB, Telnet, NetBus, IMAP, NNTP, and other platforms.
But it’s illegal to use a password cracking tool for hacking into another person’s account or data. Q #4) Is it legal to use a Password Cracking tool?Īnswer: You can use this tool for recovering stolen or forgotten passwords. Web application developers can also use password cracking tools to find out about security issues. It can help them to secure the authentication algorithm to protect the app against online attacks. The tool can also be used by security experts to detect vulnerabilities. You can also use the tool for recovering social media accounts that have been stolen. Q #3) What are the uses of a Password Cracking application?Īnswer: Password cracking software can be used to recover passwords that have been forgotten. Common techniques used include Dictionary Attack, Brute Force Attack, Rainbow Table Attack, Cryptanalysis, and simply guessing the password. Q #2) How does Password Cracking apps work?Īnswer: These applications make use of different methods for recovering passwords. Additionally, password cracking tools also help in finding out vulnerabilities in web applications. Others recover the passwords from a file stored in a local or remote location.

FAQs About Password Cracking ToolsĪnswer: These tools use different techniques to recover forgotten passwords. If a free trial is available, you should try the software to test the features of the application. The best password cracking tools use sophisticated techniques for recovering their passwords. Pro Tip: You should look at the techniques used for recovering passwords.

0 notes
Text
Lego avengers pc phantom lego brick


While it is important to be mindful of UV rays’ potential for skinĭamage, responsible sun exposure is an important part of a healthy This may be why colds and flu often occur during the winter months when people are indoors for the majority of the day.

People at risk for heart disease should probably look intoĬhecking their vitamin D levels (ask your doctor for a 25-hydroxyvitaminĭ test) and possibly supplement with a vegan form of vitamin D3.Ī deficiency of vitamin D can actually contribute to the suppression of the immune system. High blood pressure is a huge risk factor for these types of healthĬonditions, both of which account for 30 percent of annual deaths across
If sun exposure reduces blood pressure, it may also be able to prevent heart disease and stroke. The odds are that you will suffer from high blood pressure and heart Other studies have found that people tend to have lower blood pressureĭuring the summer, and the further you live from the equator, the higher According to a recent study conducted at the University of Edinburgh, 30 minutes of UV exposure may lower blood pressure by triggering natural stores of nitric oxide in the skin, which causes small blood vessels to dilate. Research has consistently shown that there is a direct correlation between vitamin D deficiency and high blood pressure. Some of the effects related to vitamin D deficiency include: Extreme measures to avoiding sunlightĮxposure may deprive you of Vitamin D, which is believed to offer a Important for maintaining a healthy mood, regulating your sleep cycles,Īnd supporting your immune system. It sounds paradoxical,īut most things related to health usually are. Other hand can actually prevent these effects. Prolonged exposure to sunlight may increase disease risk as well as While thisĪdvice might’ve had good intentions, the results have been nothing but In preparation for even the briefest contact with the sun. Urged listeners to avoid sun exposure whenever possible and slather skin Related to UV exposure became widespread, individuals around the globeīegan shying away from natural sunlight. Life-giving warmth or shun it altogether. The old site (.org) is now obsolete, please use .Īll of the current libusb development team has moved to .įor additional information, please consult the FAQ or the Wiki.The sun is both loved and feared, and many people either worship its Once you have secured your access to the library and its header, please check the libusb API or the libusb samples. If you prefer, you can also access the source directly from github. If you are using Linux, chances are your distribution already includes libusb, so you probably just need to reference the libusb header in your source.įor other platforms, or if you want to use the very latest, you are encouraged to recompile from source. Linux, macOS, Windows (Vista and newer), Android, OpenBSD/NetBSD, Haiku, Solaris. It is version-agnostic: All versions of the USB protocol, from 1.0 to 3.1 (latest), are supported. It is user-mode: No special privilege or elevation is required for the application to communicate with a device. It is portable: Using a single cross-platform API, it provides access to USB devices on Linux, macOS, Windows, etc. It is intended to be used by developers to facilitate the production of applications that communicate with USB hardware. Libusb is a C library that provides generic access to USB devices.

0 notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Ntfs 3g For Mac Os X

Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X Dmg
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 10.12.5
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 2010.10.2
NTFS-3G for Mac adds drivers to your OS X installation that allow you to read and write to NTFS-formatted thumb and external hard drives as if you're using a Windows machine. The software comes. On October 5, 2009, NTFS-3G for Mac was brought under the auspices of Tuxera Ltd. And a proprietary version called Tuxera NTFS for Mac was made available. On April 12, 2011, it was announced that Ntfsprogs project was merged with NTFS-3G. NTFS-3g added TRIM support in version 2015.3.14. Follow this process to enable NTFS Write Support on Mac OS X Yosemite for FREE. We install three free applications to achieve that. Here are the links for th.
UPD: There is even better way to solve the same issue with native Mac OS X drivers, but it has its own pros and cons. Read at the end for details. UPD (IMPORTANT): Native driver makes NTFS unusable. Read below for details. Mac OS X Lion (10.7) was released recently, in the end of July 2011. And many users had started to complain that their NTFS disks stopped working.
While OS X can natively read and write FAT-formatted drives, it’s a one-way (read-only) street with NTFS—that is, without a little help from Paragon. NTFS for Mac 14 installs a preference pane.
NTFS-3GDeveloper(s)Tuxera Inc.Stable releaseWritten inCOperating systemUnix-like, HaikuTypeLicenseDual-licensed GNU GPL/Proprietary[citation needed]Websitewww.tuxera.com/community/open-source-ntfs-3g/
NTFS-3G is an open-sourcecross-platform implementation of the Microsoft WindowsNTFS file system with read/write support. NTFS-3G often uses the FUSEfile system interface, so it can run unmodified on many different operating systems. It is runnable on Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenSolaris, illumos, BeOS, QNX, WinCE, Nucleus, VxWorks, Haiku,[1]MorphOS, Minix, macOS[2] and OpenBSD.[3][4] It is licensed under the GNU General Public License. It is a partial fork of ntfsprogs and is under active maintenance and development.
NTFS-3G was introduced by one of the senior Linux NTFS developers, Szabolcs Szakacsits, in July 2006. The first stable version was released on February 21, 2007, as version 1.0. The developers of NTFS-3G later formed a company, Tuxera Inc., to further develop the code. NTFS-3G is now the free 'community edition',[1][failed verification] while Tuxera NTFS is the proprietary version.
Features[edit]
NTFS-3G supports all operations for writing files: files of any size can be created, modified, renamed, moved, or deleted on NTFS partitions. Transparent compression is supported, as well as system-level encryption.[5] Support to modify access control lists and permissions is available.[6] NTFS partitions are mounted using the Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) interface. NTFS-3G supports hard links, symbolic links, and junctions. With the help of NTFS reparse point plugins, it can be made to read chunk-deduplicated files, system-compressed files, and OneDrive files.[7] NTFS-3G provides complete support and translation of NTFS access control list (ACL) to POSIX ACL permissions. A 'usermap' utility is included to record the mapping from UIDs to Windows NT SIDs.
NTFS-3G supports partial NTFS journaling, so if an unexpected computer failure leaves the file system in an inconsistent state, the volume can be repaired. As of 2009, a volume having an unclean journal file is recovered and mounted by default. The ‘norecover’ mount option can be used to disable this behavior.[8]

Performance[edit]
Benchmarks show that the driver's performance via FUSE is comparable to that of other filesystems' drivers in-kernel,[9] provided that the CPU is powerful enough. On embedded or old systems, the high processor usage can severely limit performance. Tuxera sells optimized versions of the driver that claims to have improved CPU utilization for embedded systems and MacOS.[10]
The slowness of NTFS-3G (and FUSE in general) on embedded systems is attributed to the frequent context switching associated with FUSE calls. Some open-source methods provided to reduce this overhead include:[11]
The underlying FUSE layer has an option called big_writes to use larger blocks when writing. Using a larger block means fewer context switches. This is in fact a solution recommended by Tuxera.[12] A patch is available to use an even larger block.[13]
There is also a Linux kernel option called lazytime to reduce the writes on file access.
Synology Inc. uses a modified NTFS-3G on their NAS systems. It replaces the ntfs-3g inode caching CACHE_NIDATA_SIZE with a different mechanism with unsure benefit. (It also includes an alternative Security Identifier translation for the NAS.)
History[edit]

NTFS-3G forked from the Linux-NTFS project on October 31, 2006.
On February 21, 2007, Szabolcs Szakacsits announced 'the release of the first open-source, freely available, stable read/write NTFS driver, NTFS-3G 1.0.'
On October 5, 2009, NTFS-3G for Mac was brought under the auspices of Tuxera Ltd. and a proprietary version called Tuxera NTFS for Mac was made available.[14]
On April 12, 2011, it was announced that Ntfsprogs project was merged with NTFS-3G.[15]
NTFS-3g added TRIM support in version 2015.3.14.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
^ abc'STABLE Version 2017.3.23 (March 28, 2017)'. Tuxera. Tuxera. 2017-03-23. Retrieved 2017-03-23.
^NTFS-3G for Mac OS X ('Catacombae')
^'OpenBSD adds fuse(4) support for adding file systems in userland'. OpenBSD Journal. 2013-11-08. Retrieved 2013-11-08.
^'ntfs_3g-2014.2.15 – FUSE NTFS driver with read/write support'. OpenBSD ports. 2014-01-05. Retrieved 2015-02-14.
^NTFS-3G FAQ
^NTFS-3G: NTFS Driver with Ownership and permissions
^André, Jean-Pierre (March 1, 2019). 'NTFS-3G: Junction Points, Symbolic Links and Reparse Points'. jp-andre.pagesperso-orange.fr.
^'NTFS-3G 2009.2.1 changelog'. Archived from the original on 2009-03-23. Retrieved 2012-09-10.
^Comparing NTFS-3G to ZFS-FUSE for FUSE Performance
^Performance at Tuxera
^Gothe, Markus. 'On Linux NTFS Performance'. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
^'NTFS-3G Questions'. Tuxera. Workaround: using the mount option “big_writes” generally reduces the CPU usage, provided the software requesting the writes supports big blocks.
^Wang, M. 'linux - Disadvantages of ntfs-3g `big_writes` mount option'. Unix & Linux Stack Exchange. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
^NTFS-3G for Mac OS X is now Tuxera NTFS for Mac
^Release: NTFS-3G + NTFSPROGS 2011.4.12
External links[edit]
Retrieved from 'https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=NTFS-3G&oldid=958820922'
3 Free NTFS Solution
UPD 21.08.2011: There is even better way to solve the same issue with native Mac OS X drivers, but it has its own pros and cons. Read at the end for details.
UPD 12.09.2011 (IMPORTANT): Native driver makes NTFS unusable. Read below for details.
Mac OS X Lion (10.7) was released recently, in the end of July 2011. And many users had started to complain that their NTFS disks stopped working. And the much worse problem is that “old” solutions do not work well.
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X Dmg
But after one or two weeks of researching of this issue, I’ve managed to make NTFS work in Mac OS X Lion (10.7). The key here is a proper combination of software versions.
So I will shortly describe the usual choices for external data storages, and what problems arises with each of them. And later I will show how you can get the most universal way — NTFS — to work where it does not work by default, with links and pictures.
Data Storages
The only reason to worry about this problem is an ability to access external storage drives. Even if these are your own drives and you can select a filesystem to use, that choice is not easy.
There are few possible choices for large (~1TB) file storages, but each has very unpleasant limitations and issues:
* HFS+/HFSX (or “Mac OS Extended”/”Mac OS Extended (case sensitive)”) — okay with big volumes and big files, but works natively under Mac OS X and Linuxes only. Windows need third-party software, which is either free file browser/extractor or paid low-level drivers.
* FAT32 work in each and every OS now, but has limitation for file size up to 4GB (so, you cannot store DVD image, which is usually 4.5+ GB).
* FAT64 (exFAT) is a new solution, but it works natively only in Mac OS X and Windows 7. Older Windows systems (Vista, XP) require Service Packs and updates to support exFAT. Linuxes do not support exFAT yet at all. More on that, it has only one file table, so if this only place will be corrupted on write, I will get all the data lost.
* NTFS. Okay with big files an bug volumes. Works natively in all Windows systems. Works fluently in all Linux systems. Has native read-only support in Mac OS X. But has not write support under Mac OS X.
As you can see, in terms of cross-compativility, NTFS is the best choice: it works almost everywhere, and with no limitations. The only issue is write mode in Mac OS X.
Taking into account that you probably have a lot of friends with NTFS volumes, who can visit you and bring you something interesting there, you actually have no choice except as try to make NTFS working.
So, let’s do it.
Paid NTFS Solutions
But first, in case you want to make your own research, or you are looking for a solution that just works out of the box, and you are ready to pay for it, you can give a try to Paragon NTFS for Max OS X 9.0 for $19.99 (5-days trial). That is much cheaper than Tuxera NTFS for Mac for $36.02 (with 15-days trial).
The former one definitely works – I’ve tried it in trial. Just install and get everything ready: both read and write modes, auto-mount, and also NTFS formatting in Disk Utility, disk checking, etc.
I haven’t tested the latter one, so you can leave a comment here about your experience with Tuxera paid solution.
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 10.12.5
Free NTFS Solution
This free solution requires some efforts. Not so much, of course. Well, if you are going to make your own research, it can be lots of efforts, since the situation with NTFS-3G is not very clear now.
But if you are just about a ready, copy-n-install solution, it will be easy, and requires only these two or three steps:
* MacFUSE 64-bit.
* NTFS-3G stable.
* “15 seconds” error work-around (optional).
MacFUSE 64-bit
First, you need MacFUSE with 64 bit support. That is the main problem with Mac OS X Lion — it uses 64-bit kernel, and all previous version of Mac OS X used 32-bit one. So, old MacFUSE binaries won’t work anymore.
You can get Tuxera MacFUSE 2.2 image for free (could not find a page with it, just a download links) or try to compile OSXFUSE from sources. I’ve used the former one.
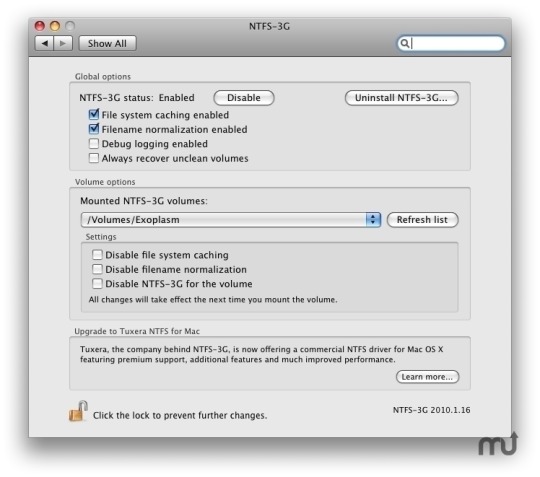
You can see MacFUSE preferences in “System Preferences”. Well, actually these are not preferences, but only “update” and “uninstall” actions, and current version info:
NTFS-3G stable
Second, you will need working copy of NTFS-3G. Long story short, NTFS-3G is either already dead or is going to die. There is its ancestor: Tuxera NTFS for Mac (paid).
But we are going to use old version of NTFS-3G — the one from 2010. I’ve got one from here. But you can try googling for it, or browse here for this exact version (not 2011 — I’m not sure they work).
I also tried to install later version from MacPorts, but it does not work too: mounts something that stills unreadable. That is in addition to an error in installation process (“mv” does not see the libntfs-3g file or so).
Now, when you have installed two binary packages, you can restart Mac OS X and try to attach the drive. It should work.
NTFS-3G preferences pane looks populated and interesting:
“15 seconds” error work-around
But it will show you the error message saying that there were not signal in 15 seconds:
This is not a big problem, because everything works fine. Only annoying message box is a problem.
So the third, optional step is to address this issue. You can follow this link: https://gist.github.com/1100318 (see first and the only comment under the code). You just download this attached C file, run “gcc” command line from the comment, and replaces the “fuse_wait” binary as said there. Yes, you will need “gcc” here.
And voila! Now you have working NTFS filesystem for free with no “15 seconds” error message. Profit!
Problems
Nevertheless, Mac OS X is a Unix-based system. And Unix-based system is a big problem when they work as desktop OS (earlier I thought that on Linux-based system because of community-driven and crowd-based development concept). This solution has some problems too. Though they are not about the solution itself, but about the components used.
The most important problem now is the speed: with this NTFS-3G on MacBook Air (4GB, i7 CPU) write speed for USB 2.0 drive is about 3.3 MB/s. Just to compare, the same drive in the same port, but with exFAT/FAT64 partition can write with ~38 MB/s (or fast enough to make exact estimation; will try larger files later).
Also, immediately following the mount of a drive, there is a line in system log with an error message saying:
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 2010.10.2
8/21/1112:48:43.000AM kernel:NTFS-fs error(device/dev/disk1s1,pid4859):ntfs_system_inodes_get():$LogFile isnotclean.Mounting read-only.Mount inWindows.
All the “cons” can be solved by installing NTFS-3G and keeping it disabled all the time, except when you need to format new volume, or to mount a problematic volume. Actually, it is better to enable NTFS-3G, mount it with NTFS-3G, then unmount, disable NTFS-3G, and mount it with native drivers; or use “ntfsfix” if you are not afraid of command line after all these hacks ;-)
IMPORTANT UPD 12.09.2011: Please read comments below: people say that this driver makes NTFS filesystem corrupted and unusable.
I had the same experience: my NTFS volume become only partially readable in Mac OS X, and completely unusable in Windows. More on that, when I tried to attach the drive, Windows kernel started to use 100% CPU, and did not stop to do so even when the drive were detached. Drive letter never appeared.
Luckily for me, I had two backups of the whole volume (I do so when experimenting with new drives, since I once lost my whole photo archive due to burned out new drive). To solve the whole problem of NTFS@Mac, I’ve finally bought Paragon NTFS for Mac.

0 notes
Text
Introducing the OpenBSD Virtualization FAQ
https://undeadly.org/cgi?action=article;sid=20181029144519
Comments
0 notes
Text
Virtually every WiFi router affected by WPA2 security flaw
Researchers have discovered a key flaw in the WPA2 WiFi encryption protocol that could allow hackers to intercept your credit card numbers, passwords, photos and other sensitive information. The flaws, dubbed "Key Reinstallation Attacks," or "Krack Attacks," are in the WiFi standard and not specific products, according to the security team that discovered it. That means that just about every router and device out there could be impacted, though attacks against Linux and Android 6.0 or greater devices could be "particularly devastating," according to KU Leuven University's Mathy Vanhoef and Frank Piessens, who found the flaw.
Attackers create a script that finds a WPA2 network, then make a carbon copy of it and change the WiFi channel. This new, fake network then acts as a "man in the middle," so when a device attempts to connect to the original network, it can be forced to bypass it and connect to the rogue one. The problem is made worse by Android and Linux, which don't force the client to demand a dedicated certificate. In some cases, a script can also force a connection to bypass HTTPS, exposing usernames, passwords and other critical data.
The system takes advantage of a flaw in the "handshake" method to direct users to the malicious network. Neither WiFi passwords nor secret keys can be obtained, the researchers say, as the hack works by forging the entire network. As such, it can't be used to attack routers, but hackers can still eavesdrop on traffic, making it particularly dangerous for corporations. Some details are still unclear, but it appears that for the hack to work, you may need to have had previous access to the WPA2 network.
youtube
As shown above, the researchers did a proof-of-concept attack on Android, and were able to decrypt all the victim's transmitted data. The researchers point out that this will "not work on a properly configured HTTPS site," but will work on a "significant fraction" that are poorly set up. Other devices, like those running MacOS, Windows, OpenBSD and other operating systems, are affected to a lesser extent. "When attacking other devices, it is harder to decrypt all packets, although a large number of packets can nevertheless be decrypted," say the researchers.
After earlier, more limited hacks, the WPA2 protocol has been suspect for a while, so many security folks were already bracing themselves for something more serious. If you still doubt the seriousness of it, Alex Hudson, for one, is actually advising Android users to "turn off WiFi on these devices until fixes are applied." He adds that "you can think of this a little bit like your firewall being defeated."
As such, you can protect yourself to a great extent by sticking with sites that have solid, proven HTTPS security. And of course, the attack won't work unless the attacker is nearby and can physically access your network.
The problem should be relatively easy to fix. A firmware change can force routers to require a dedicated certificate for each handshake, instead of relying on the one already generated. And, as the security researchers who discovered it say, "implementations can be patched in a backwards-compatible manner."
That means if you patch your Android device and not your router, you can still communicate and be safe, and vice-versa. Nevertheless, they also advise to patch all your devices as soon as security updates are available. For more details about the hack, check this very detailed FAQ from Aruba Networks.
Via: Ars Technica
Source: Krack Attacks
- Repost from: engadget Post
0 notes
Text
Did you lose your crucial data? Don’t worry there is still hope!
Top-Notch Hard Drive Data Recovery Services
Techchef is an industry leader in hard drive data recovery services. With state-of-art technology tools and experienced professionals, we are the most coveted choice of enterprises and individuals looking for successful hard drive data retrieval services. Having worked in the industry for over fifteen years, we have honed our skills and gained unparalleled expertise. Our recovery engineers are adept in recovering data from almost all kind of data loss situations including:
Accidental File Deletion or formatting.
Ransomware attacks.
Physical damages.
Environmental damages.
Data overwriting especially in CCTV/DVR storages.
Types of Hard Drive Recovery Services Supported
Techchef recovery specialists are proficient in performing data recovery from hard disk drives. Our technology and expertise enable us to carry out data recovery for almost all types of hard drives, irrespective of its issue or storage capacity.
We work with following hard drive manufacturers:
Western Digital
Seagate
Sony
HGST
Samsung
Toshiba
Additionally, we can also provide data recovery services for various hardware interfaces including:
IDE
SATA
SSD
SAS
ESATA
Advanced-Data Recovery Services for different operating systems
Regardless of your operating system, we provide reliable data recovery services. Operating systems tend to affect the logical part of your data recovery process. To cater to this we employ a team of skilled technicians to undertake your project and consider each case as effectively as possible. We offer featured data recovery solutions for operating systems like Mac, Windows, and Linux. Moreover, different file formats we support for data recovery include Little Endian Variants and Big Endian Variants of UFS1 & UFS2 (FreeBSD/NetBSD/OpenBSD/Solaris), NTFS, NTSF5, ReFS, FAT12/16/32, exFAT, HFS/HFS+, APFS (Macintosh) along with Ext2,Ext3 & Ext4 FS (Linux).
Reasons to Use Techchef Hard Drive Data Recovery Services
Advanced Data Retrieval Capabilities
Trained engineers with years of experience
Support for all operating systems and file systems
Emergency services
100 percent recovery success
Affordable services with no hidden fees.
Secure & Confidential data recovery
Schedule hard drive data recovery at Techchef hassle-free!
Techchef is here to help with all of your data loss issues. For information on how to send your storage device to us, call our representative at 1800–313–1737. You can also meet us in-person by visiting any of our offices in major cities.
FAQs
Why do hard drives fail?
Hard drives have mechanical components that tend to wear over time. The components such as spindle, read/write head, and actuator may become incapable of reading data even with minute offset. Moreover, physical damages, drops, user errors, and viruses may also affect the operation of your drive.
How do Techchef engineers recover my data from the hard drive?
We are an ISO certified data recovery company. Our team of experienced professionals conducts data recovery processes in the special environment of Class 100 cleanrooms. We retrieve data using advanced tools and technologies. We ensure your 100 percent data recovery success within faster turnaround time.
Can I use hard drive data recovery software to fix my system?
No. Using data recovery software will only elevate problems. Physical damages cannot be repaired using recovery software. This software only leads to an increase in further damage or cause data overwriting.
How does the hard drive recovery costs?
The hard drive recovery cost depends on various factors such as drive model, brand, and capacity. The extent of damage is also a crucial factor; it may also affect overall recovery charges. We at Techchef offer you a full drive assessment free of cost based on which we provide you with an estimated price quote and turnaround time.
What if I only need certain files back instead of full data?
If certain files are more important to you, we will sure that we provide them a priority during the recovery process. However, we make ensure recovery full data, every time. We have a proven success rate of 100 percent for data recovery.
0 notes
Link
Explains how to download a file with curl http/ftp/sftp command line utility on a Linux, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD and Unix-like systems.
0 notes
Text
New top story on Hacker News: Introducing the OpenBSD Virtualization FAQ
Introducing the OpenBSD Virtualization FAQ
7 by sverige | 1 comments on Hacker News.
from Blogger https://ift.tt/2DlwHUX
0 notes
Link
Ubuntu Linux 16.04 / 18.04 LTS CentOS Linux 7 Debian Linux 9.x RHEL 7.x SUSE 12.x FreeBSD OpenBSD Prerequisite Please note that you must have Ansible version 2.7 to work with the reboot module: $ ansible --version If not using Ansible version 2.
0 notes
Text
KRACK, a flaw in Wi-Fi security protocol WPA2, leaves traffic open to eavesdropping, connection hijacking, and malicious injection; US CERT advisory issued (Dan Goodin/Ars Technica)
Aurich Lawson / Thinkstock
reader comments 210
Researchers have disclosed a serious weakness in the WPA2 protocol that allows attackers within range of vulnerable device or access point to intercept passwords, e-mails, and other data presumed to be encrypted, and in some cases, to inject ransomware or other malicious content into a website a client is visiting.
The proof-of-concept exploit is called KRACK, short for Key Reinstallation Attacks. The research has been a closely guarded secret for weeks ahead of a coordinated disclosure that was scheduled for 8am Monday, East Coast time. A website disclosing the vulnerability said it affects the core WPA2 protocol itself and is effective against devices running Android, Linux, and OpenBSD, and to a lesser extent macOS and Windows, as well as MediaTek Linksys, and other types of devices. The site warned that attackers can exploit the flaw to decrypt a wealth of sensitive data that's normally encrypted by the nearly ubiquitous Wi-Fi encryption protocol.
"This can be abused to steal sensitive information such as credit card numbers, passwords, chat messages, emails, photos, and so on," researcher Mathy Vanhoef, of the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven in Belgium wrote. "The attack works against all modern protected Wi-Fi networks. Depending on the network configuration, it is also possible to inject and manipulate data. For example, an attacker might be able to inject ransomware or other malware into websites."
Vanhoef provided the following video showing the attack against a device running Google's Android mobile operating system:
VIDEO
KRACK Attacks: Bypassing WPA2 against Android and Linux
It shows the attacker decrypting all data the phone sends to the access point. The attack works by forcing the phone into reinstalling an all-zero encryption key, rather than the real key. This ability, which also works on Linux, makes the attack particularly effective on these platforms.
The site went on to warn that visiting only HTTPS-protected Web pages wasn't automatically a remedy against the attack, since many improperly configured sites can be forced into dropping encrypted HTTPS traffic and instead transmitting unencrypted HTTP data. In the video demonstration, the attacker uses a script known as SSLstrip to force the site match.com to downgrade a connection to HTTP. The attacker is then able to steal an account password when the Android device logs in.
"Although websites or apps may use HTTPS as an additional layer of protection, we warn that this extra protection can (still) be bypassed in a worrying number of situations," the researchers explained. "For example, HTTPS was previously bypassed in non-browser software, in Apple's iOS and OS X, in Android apps, in Android apps again, in banking apps, and even in VPN apps."
The researcher went on to say that the weakness allows attackers to target both vulnerable access points as well as vulnerable computers, smartphones and other types of connecting clients, albeit with differing levels of difficulty and effectiveness. Neither Windows nor iOS are believed to be vulnerable to the most severe attacks. Linux and Android appear to be more susceptible, because attackers can force network decryption on clients in seconds with little effort.
Vanhoef said clients can be patched to prevent attacks even when connected to vulnerable access points. Linux patches have been developed, but it's not immediately clear when they will become available for various distributions and for Android users. Patches are also available for some but not all Wi-Fi access points.
In response to a FAQ item asking if the vulnerability signaled the need for a WPA3 standard, Vanhoef wrote:
No, luckily [WPA2] implementations can be patched in a backwards-compatible manner. This means a patched client can still communicate with an unpatched access point, and vice versa. In other words, a patched client or access points sends exactly the same handshake messages as before, and at exactly the same moments in time. However, the security updates will assure a key is only installed once, preventing our attacks. So again, update all your devices once security updates are available.
KRACK works by targeting the four-way handshake that's executed when a client joins a WPA2-protected Wi-Fi network. Among other things, the handshake helps to confirm that both the client and access points have the correct credentials. KRACK tricks the vulnerable client into reinstalling an already-in-use key. The reinstallation forces the client to reset packet numbers containing a cryptographic nonce and other parameters to their initial values. KRACK forces the nonce reuse in a way that allows the encryption to be bypassed. Ars Technica IT editor Sean Gallagher has much more about KRACK here.
Monday's disclosure follows an advisory the US CERT recently distributed to about 100 organizations described the research this way:
US-CERT has become aware of several key management vulnerabilities in the 4-way handshake of the Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2) security protocol. The impact of exploiting these vulnerabilities includes decryption, packet replay, TCP connection hijacking, HTTP content injection, and others. Note that as protocol-level issues, most or all correct implementations of the standard will be affected. The CERT/CC and the reporting researcher KU Leuven, will be publicly disclosing these vulnerabilities on 16 October 2017.
According to a researcher who has been briefed on the vulnerability, it works by exploiting a four-way handshake that's used to establish a key for encrypting traffic. During the third step, the key can be resent multiple times. When it's resent in certain ways, a cryptographic nonce can be reused in a way that completely undermines the encryption.
Although kept secret for weeks, KRACK came to light on Sunday when people discovered a Github page belonging to one of the researchers and a separate krackattacks.com website disclosing the vulnerability used the following tags:
WPA2
KRACK
key reinstallation
security protocols
network security, attacks
nonce reuse
handshake
packet number
initialization vector
Researchers briefed on the vulnerabilities said they are indexed as: CVE-2017-13077, CVE-2017-13078, CVE-2017-13079, CVE-2017-13080, CVE-2017-13081, CVE-2017-13082, CVE-2017-13084, CVE-2017-13086, CVE-2017-13087, CVE-2017-13088. One researcher told Ars that Aruba and Ubiquiti, which sell wireless access points to large corporations and government organizations, already have updates available to patch or mitigate the vulnerabilities.
The vulnerabilities are scheduled to be formally presented in a talk titled Key Reinstallation Attacks: Forcing Nonce Reuse in WPA2 scheduled for November 1 at the ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security in Dallas. It's believed that Monday's disclosure will be made through the site krackattacks.com. The researchers presenting the talk are Mathy Vanhoef and Frank Piessens of KU Leuven. The researchers presented this related research in August at the Black Hat Security Conference in Las Vegas.
The vulnerability is likely to pose the biggest threat to large corporate and government Wi-Fi networks, particularly if they accept connections from Linux and Android devices. And once again, attackers must be within Wi-Fi range of a vulnerable access point or client to pull off the attacks. Home Wi-Fi users are vulnerable, too, again especially if they connect with Linux or Android devices, but there are likely easier ways they can be attacked. Researcher and Errata Security CEO Rob Graham has useful information and analysis here.
If possible, people with vulnerable access points and clients should avoid using Wi-Fi until patches are available and instead use wired connections. When Wi-Fi is the only connection option, people should use HTTPS, STARTTLS, Secure Shell, and other reliable protocols to encrypt Web and e-mail traffic as it passes between computers and access points. As a fall-back users should consider using a virtual private network as an added safety measure, but users are reminded to choose their VPN providers carefully, since many services can't be trusted to make users more secure.
Post updated to add details from researchers.
from Techmeme http://ift.tt/2yMZsHs
0 notes
Link
Yay! Ansible 2.7 has been released. I was looking forward to this release for some time due to a reboot module that is useful when you need to update Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD kernel. Learn how to reboot a machine, wait for to come back.
#devops#sysadmin#centos#ubuntu#freebsd#macos#unix#devlife#programming#programmers#debian#openbsd#netbsd#python#python3
6 notes
·
View notes
Link
Want to learn more about Open TCP/UDP ports and established connections on a OpenBSD Unix system?
5 notes
·
View notes