#converted grain mill
Text

Welcome to The Flour Tower. It's a 5 story, single family, converted 1910 former grain mill in Bridgeport, Washington. 4bds, 8ba, $945K.

First things, first. It has an elevator, b/c it's so high.

The "Grand Salon," as they call the first floor, houses the shop, garage, green house, half bath, family room & additional kitchen.

There's also a wine room.


The family room is nice. Looks like there's a walk-in freezer there on the left.
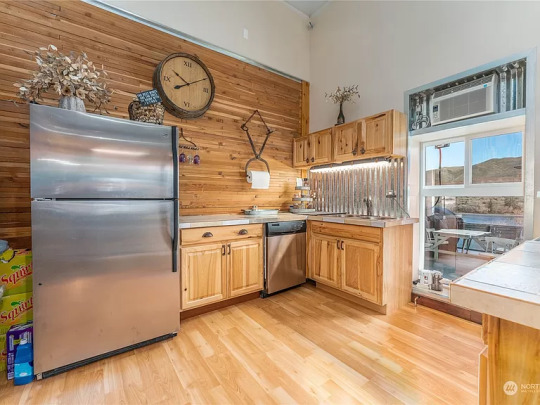

The downstairs kitchen and deck on the waterfront.

Very large sun room also on the water.

If you'd rather take the stairs.

This must be the primary suite. It's huge.

The en-suite.

Closet in with the water heater.

Large laundry room.

The main kitchen is big, too.

Down a few stairs is a dining area.
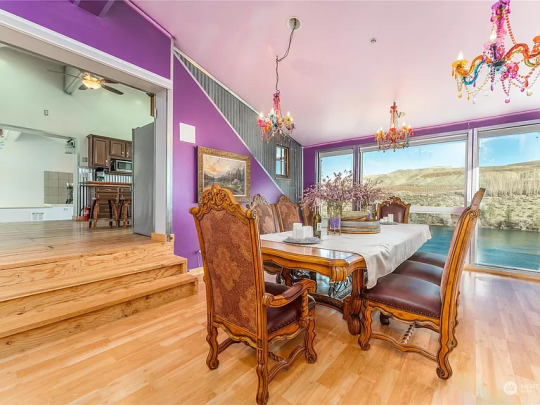

And, on the other side of the kitchen is the formal dining room.

Plus, a formal living room. This house is so large, you can decorate it a lot better.

Spacious pantry.

Perfect views of the Columbia River.
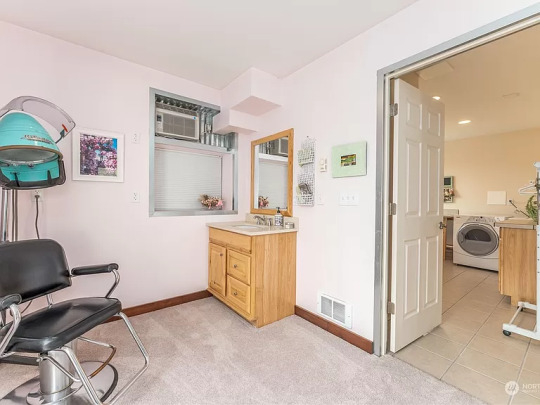


This secondary bedroom is large and it even has a little hair salon.

Ascending to the next level, they've got a TV area on the landing.

There's a separate apt. over the garage.


So, this could be rental income.

A long staircase goes down to a dock on the river.

The river bank property measures .67 acre.
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
The warped flooring of the lair and soundconducting walls thereof, to say nothing of the uprights and imposts, were persianly literatured with burst loveletters, telltale stories, stickyback snaps, doubtful eggshells, bouchers, flints, borers, puffers, amygdaloid almonds, rindless raisins, alphybettyformed verbage, vivlical viasses, ompiter dictas, visus umbique, ahems and ahahs, imeffible tries at speech unasyllabled, you owe mes, eyoldhyms, fluefoul smut, fallen lucifers, vestas which had served, showered ornaments, borrowed brogues, reversibles jackets, blackeye lenses, family jars, falsehair shirts, Godforsaken scapulars, neverworn breeches, cutthroat ties, counterfeit franks, best intentions, curried notes, upset latten tintacks, unused mill and stumpling stones, twisted quills, painful digests, magnifying wineglasses, solid objects cast at goblins, once current puns, quashed quotatoes, messes of mottage, unquestionable issue papers, seedy ejaculations, limerick damns, crocodile tears, spilt ink, blasphematory spits, stale shestnuts, schoolgirl’s, young ladies’ milkmaids’, washerwomen’s, shopkeepers’ wives, merry widows’, ex nuns’, vice abbess’s, pro virgins’, super whores’, silent sisters’, Charleys’ aunts’, grandmothers’, mothers’-in-law, fostermothers’, godmothers’ garters, tress clippings from right, lift and cintrum, worms of snot, toothsome pickings, cans of Swiss condensed bilk, highbrow lotions, kisses from the antipodes, presents from pickpockets, borrowed plumes, relaxable handgrips, princess promises, lees of whine, deoxodised carbons, convertible collars, diviliouker doffers, broken wafers, unloosed shoe latchets, crooked strait waistcoats, fresh horrors from Hades, globules of mercury, undeleted glete, glass eyes for an eye, gloss teeth for a tooth, war moans, special sighs, longsufferings of longstanding, ahs ohs ous sis jas jos gias neys thaws sos yeses and yeses and yeses, to which, if one has the stomach to add the breakages, upheavals distortions, inversions of all this chambermade music one stands, given a grain of goodwill, a fair chance of actually seeing the whirling dervish, Tumult, son of Thunder, self exiled in upon his ego a nightlong a shaking betwixtween white or reddr hawrors, noondayterrorised to skin and bone by an ineluctable phantom (may the Shaper have mercery on him!) writing the mystery of himsel in furniture.
James Joyce, Finnegans Wake
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
The word “processed” has become something of a slur.
Say “processed food” and most of us picture unhealthy, cheap junk. Fresh food straight from the garden or the field is good. Once we’ve put it through a processing plant or a laboratory, we’ve removed its halo qualities and added a bunch of bad ones. That means meat substitutes are no better than junk food.
But this perspective is short-sighted. We’re not going to feed billions a nutritious diet sustainably without food processing. The growing backlash against processing is one that neither people nor the planet can afford.
The benefits of processed food
Processed food is more than Coca-Cola, Dairy Milk chocolate, and ready meals. Most plant and animal products go through some form of processing to convert them into something that we can—and want to—eat. We mill grain into flour to make bread. We butcher and debone animals to get meat. We pasteurize milk.
Processed foods have brought us countless benefits, many of which we quickly forget. Iodized salt is just one example; iodine deficiencies used to be common across the world, leading to increased risks of stillbirths and miscarriages, significant reductions in IQ, and reduced cognitive development. Most of the world now consumes salt with iodine added, and many countries have eliminated this deficiency. By adding nutrients to food, we’ve been able to address a number of other micronutrient deficiencies.
We’ve been able to preserve food and increase its shelf life, reducing food waste. We’ve reduced the spread of food-borne diseases. Those with food allergies and intolerances can now eat a balanced diet. We don’t need to spend the day preparing food—this has been particularly important for the educational and career development of women. Last but not least: taste. Our shelves are now lined with great-tasting foods.
Of course, when people talk about “processed” food they’re often talking about ultra-processed food (UPF). These snacks and prepared meals are designed to have a longer shelf life and be more convenient and palatable. Corporations work hard to find the “Goldilocks” flavor profile we can’t resist by adding sugar and fat to make food as tasty as possible. Many describe these finely tuned combinations as addictive.
It’s true that increased consumption of ultra-processed food has been linked to poor health outcomes. It has been associated with lower consumption of essential nutrients, such as vitamins C, D, and B12. The more of these foods we eat, the more likely we are to be overweight or obese. This puts us at higher risk of health conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Ultra-processed foods are easy to overconsume.
The problem with most UPFs is that they are higher in calories, sugar, and fat. And they’re lower in protein and fiber, the nutrients that keep us full.
But this isn’t inherent to food processing itself. What matters is what corporations add to our food. They can create healthier foods if they want to—or if we demand it.
The growing backlash against meat substitutes
One area where I see the biggest backlash against processing is with meat substitutes.
These products try to emulate the experience of meat and include plant proteins such as soy-based sausages; Impossible and Beyond Meat burgers; proteins made from fermentation, such as Quorn, and lab-grown meat.
Passionate meat eaters and vegans don’t always see eye to eye, but they do often agree that natural is best. Vegans push back against meat substitutes because they’d rather people go straight to natural plant foods like peas, beans, and lentils. Meat eaters push back on these products for their artificiality, calling them “Frankenfood.”
Headlines critical of these foods go something like this: “People have told you that meat substitutes are super healthy, but they’re lying to you.”
So are meat substitutes better for your health or are they part of an elaborate con?
Well, “healthy” compared to what?
Are they better than meat equivalents? Are you better off going for an Impossible or Beyond Meat burger than a beefburger? Or a soy-based sausage over a pork one? Possibly.
I crunched the numbers on the nutritional profile of meat substitute products and compared them to meat. (You can find a graph of this comparison here.) To their credit, meat substitutes tend to be lower in calories and saturated fat and higher in fiber. To their detriment, some are lower in protein, and importantly, often contain lower-quality protein, meaning they contain less of the essential amino acids that we need.
When it comes to sodium, it’s a bit of a mixed bag. Substitute burgers tend to be comparable to beef. Substitute sausages look bad, but they contain less salt than their pork equivalents.
Many substitute products are now fortified with Vitamin B12, iron, and calcium. The Impossible burger actually has more Vitamin B12 and iron than beef. Many plant-based milks are fortified too. (I compared the nutrition of dairy and plant-based milks here.)
On balance, they’re probably a bit better for our health than their meat equivalents.
Are they better than whole, plant-based foods? Less likely, but possible, depending on the nutrients you’re trying to optimize for. They are higher in protein and have micronutrients added that plants don’t have much of, such as Vitamin B12. But they are also higher in saturated fat and salt.
However, this showdown between natural plant foods and meat substitutes is kind of beside the point. People who want a whole, plant-based diet aren’t the target for these products. If people want to switch to plant proteins such as peas and lentils, great. But this group is a minority. What meat substitutes offer is an easy swap for people who want “meat-like” meals. Many want an experience similar to meat: Substitutes try to give them this without killing animals—and without the high environmental cost of farming meat.
To have a chance of meeting our global climate targets, ending deforestation, and protecting the world’s wildlife, we need to eat much less meat. Both plant foods and meat substitutes have a much lower carbon footprint, use much less land, and cause less water pollution than meat. The environmental toll can be 10 to 100 times lower than that of beef or lamb.
Meat substitutes are our best shot at feeding the world without destroying it. The backlash to these products is counterproductive. And the blanket dismissal of such foods as “ultra-processed” isn’t helping. Most are defined as ultra-processed based on the methods used to produce them. But if we list the reasons UPFs are bad for our health, meat substitutes have almost none of those qualities. As shown above, they are generally not high in calories—most are lower than meat. They have less saturated fat, almost no added sugars, and are higher in fiber.
What they do have are additives. Impossible Foods adds them to give its burgers a juicy, meat-like texture. Many companies add binding agents and preservatives to extend their products’ shelf lives. People get freaked out by lists of ingredients they don’t recognize. But the notion that how pronounceable something is can determine whether we should eat it is not scientifically sound. You can probably pronounce “lead” and “mercury,” but I don’t recommend seasoning your dinner with them.
This is still an area that needs more research, but I’ve seen little good evidence that additives or sweeteners consumed within regulatory guidelines have negative health impacts.
We shouldn’t be eating them all the time, but as part of a diverse diet, there is little to suggest meat substitutes are bad for our health. In fact, some can be a nutritional plus.
Food processing could alleviate malnutrition for billions
Meat substitutes are mostly targeted at wealthy consumers. But the implications of a backlash to processed food are just as harmful for people with less money—if not more so.
More food processing, not less, could improve health and nutrition in developing countries.
Billions of people in the world suffer from “hidden hunger”—they don’t get enough of the micronutrients that are necessary for good health. The preferred way to address this would be for them to eat a more diverse diet.
That’s a nice pipe dream, but it’s decades away. These billions can’t afford a healthy, balanced diet even if they spend all of their income on food. The goal is to make sure their incomes rise, but this will take time.
What are we going to do in the meantime? Accept that billions are left malnourished and billions of children will never reach their potential?
We could solve this problem quickly and cheaply with more food processing. Simply add micronutrients to staple foods. Micronutrient fortification—the addition of key vitamins and minerals to foods such as flour, salt, bread, and cereals—is incredibly cost-effective. It can cost mere cents or a few dollars per person per year. To move from a diet that meets an individual’s energy needs—eating cheap staples that are high in calories—to a nutritionally complete or healthy diet will cost someone at least a few dollars per day. Micronutrient fortification would cost just a few dollars per person per year.
This is also true of meat and dairy products. In richer countries, we consume a lot of meat, and most people could easily cut back. Poorer countries eat very little meat, if any. Without nutritious alternatives, eating more animal products might actually be good for health. The problem is that meat is expensive—economically as well as environmentally. It’s hard to get cheap meat without sacrificing welfare and environmental standards. So we face a dilemma: Increasing meat consumption for those with lower incomes would improve nutrition but result in a larger environmental footprint.
But if meat substitutes become cheaper, we have the opportunity to make low-cost, high-quality protein available for everyone. People will be able to improve their nutrition long before they can afford to buy more meat. What’s even more promising is that consumers in low- and middle-income countries seem to be more accepting of meat alternatives. We don’t have a lot of data on these markets, but large surveys across China, India, and the US suggest that Chinese and Indian consumers would be much more likely to buy plant-based substitutes and lab-grown meat than Americans.
I’m all for a predominantly whole-food diet. But used in the right way and in moderation, processed foods could be a big boon for global nutrition. Stigma against them hinders such efforts, so rather than shunning food processing, we should embrace it in the appropriate contexts.
It’s not the process; it’s what we add that matters
I’m not here to defend ultra-processed foods or big food corporations. They’ve hijacked our food system in many ways and have created a plethora of health problems. But we need to stop throwing all processed foods into one group.
The problem is not the process itself; it’s what we add and how we do it. We can use processing to enhance nutrition or hinder it. We can embrace it where it adds value and boycott it where it doesn’t.
The backlash against food processing is a luxury that the world can’t afford to embrace. It’s not good for people or the planet. Nutritionally sound processed foods are one of many tools that will help nourish billions without destroying the environment.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the steps of beer brewing process?
Brewing refers to the process of producing beer through the fermentation of malted grains, typically barley, using yeast. It is a combination of art and science that involves various steps, including malting, mashing, lautering, boiling, cooling, fermentation, conditioning, carbonation, filtration and packaging, and maturation.
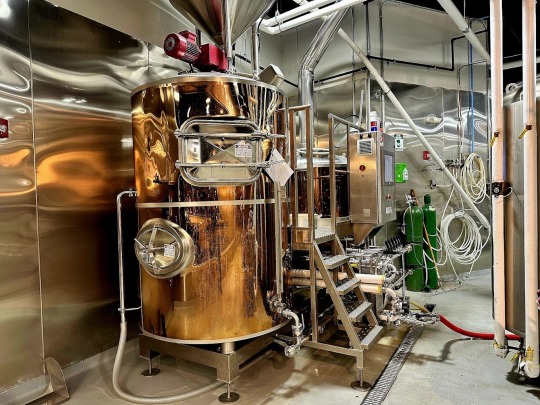

Malting: The process begins with malting, where barley grains are soaked in water and allowed to germinate. This activates enzymes that convert the starches in the barley into fermentable sugars.
Mashing: The malted barley is then milled and mixed with hot water in a process called mashing. This allows the enzymes in the malt to break down the starches into sugars. The mixture, known as the mash, is held at specific temperatures to promote enzyme activity and sugar extraction.
Lautering: After mashing, lautering involves separating the liquid portion of the mash (known as the wort) from the solid grain material. This is typically done by rinsing the mash with hot water and collecting the wort.
Boiling: The wort is transferred to a kettle where it is boiled. During this process, hops are added to provide bitterness, aroma, and flavor to the beer. The boiling also sterilizes the wort and helps to clarify it by precipitating proteins.
Cooling: Following the boiling process, the wort needs to be rapidly cooled to a temperature suitable for yeast fermentation. This can be achieved using a heat exchanger or by transferring the wort to a fermentation vessel and employing cooling equipment.
Fermentation: Once the wort has been cooled, yeast is added to the fermentation vessel. Yeast consumes the sugars in the wort and produces alcohol, carbon dioxide, and various flavor compounds. Fermentation can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the beer style and yeast used.
Conditioning: After primary fermentation, some beers may undergo a secondary fermentation or conditioning phase. This allows the flavors to mellow, and any remaining yeast or sediment to settle. Conditioning can take place in the same fermentation vessel or in a separate vessel.
Carbonation: Carbonation adds the desired level of carbon dioxide to the beer, creating bubbles. Carbonation can be achieved through natural carbonation (where priming sugar is added to the beer before bottling) or forced carbonation (using carbon dioxide gas).
Filtration and Packaging: Before packaging, the beer may undergo filtration to remove any remaining solids or haze. The filtered beer is then packaged into bottles, cans, or kegs, ensuring proper sealing to maintain freshness and prevent oxidation.
Maturation: Some beer styles benefit from a period of maturation, allowing flavors to develop and mellow further. This can take place in the bottle, can, or keg.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Production Process of Barley Malt Extract
Malt extract, which the barley malt extract manufacturers produce via the process of malting, has gone a long way over time. The current malt extract, when applied appropriately, may improve any recipe, but beer, in particular, and the extracts that are available today can produce great brews.
What is the Process for Making Malt?
There are primarily three stages to the malting process. The first thing that needs to be done to bring the grain out of dormancy is to soak or steep it. After that, it's time for the grain to start sprouting. The barley's color and taste are finally achieved by heating it, a process known as kilning.
The production process of Barley Malt Extract
Malt extract powder manufacturer use malt to create confectionery malt extract and malt extract powder. To start the manufacturing process, first choose high-quality barley grains. Then, soak them in water until they begin to germinate. Drying and roasting the sprouted grains brings out their flavor and color. The last step in making malt extract is milling the grains into a powder, which is then dissolved in water.
Exploring the Incredible History of Malting Barley
You can't just use any old barley. Malting barley is the specific kind that is being used by companies. This malting barley is the product of centuries of selective breeding, which has made it even better. Enzymes found in diastatic malt are capable of converting starches into sugars. This makes it a good baking ingredient since it accelerates the rising process and imparts a sweeter taste to dough. There are two types of malt: diastatic and non-diastatic. Breads, bagels, and other baked items often use diastatic malt due to its enzyme content.
Food-Grade Extracts vs. Brewing Extracts
Only the finest brewing malts are used when crafting brewing-grade malt extracts. Specialty malts are added for enhanced color and taste. They get a taste that works well in beer and other goods, and they play a prominent role in the flavor profile. Confectionery Malt Extract is often a tiny component derived from malt that is not suitable for brewing or distillation. Malted barley products used in cuisine sometimes have corn syrup and caramel color added to them.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of food and other items uses a far greater quantity of malt extract powder in India than the manufacturing of beer on a global scale. A natural grain-based sweetener, malt extract predated contemporary corn syrup by hundreds of years and was produced using modern technologies.
For more information about: Malt Extract Powder Please visit at https://www.mahalaxmimaltextract.com/
#malt extract powder#malted barley powder manufacturers#barley malt powder#barley malt extract#malt extract powder manufacturer#barley malt extract manufacturers#liquid malt extract#malt extract liquid#malt extract#barley malt flour
0 notes
Text
What Is Reclaimed Wood, and How Can You Use It?
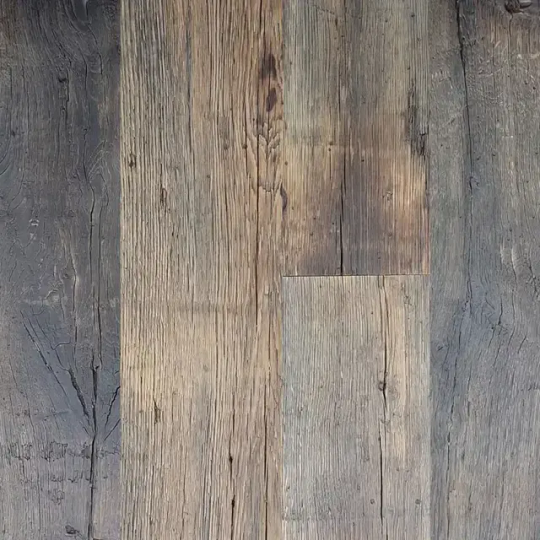

Reclaimed wood has so much personality and character when made into flooring. One way to identify Reclaimed wide plank hardwood flooring is by looking at its distinctive gouges and scrapes.
Repurposed wood has more than aesthetic charm. Eco-friendly recyclable product. Despite its high cost, repurposed wood adds charm to a space without taking down forests.
What is Reclaimed Wood?
Used wood from barns, warehouses, water storage tanks, and barrels is called "reclaimed wood". The wood undergoes processing to make it more appropriate for construction purposes.
Wood that is either no longer produced or is very rare can be accessed through reclaimed wood. This includes non-renewable old-growth wood, wide-plank, and rare species of wood.
Converting storage facilities into flooring requires a lot of processing. After de-nailing, the wood is sawn, dried in a kiln, and re-milled. All of this work goes into making recycled wood affordable. Generally, Wide plank oak flooring is far more costly than brand-new, high-quality imported flooring.
Why Reclaimed Wood Is a Good Choice
Genuine Feeling
Nail holes, checks, scrapes, gouges, scuffs, blots, star-checked knots, and other historical markings are seen in reclaimed wood floors and other goods. These are seen as inherent characteristics of the recycled wood, rather than flaws, and contribute to its overall attractiveness.
Very Rare Woods
You can employ species of wood that are getting harder to source as new items by using salvaged wood in your flooring installation.
Reclaimed wide plank hardwood flooring is the only way to get your hands on this unique natural hardwood from the New England region.
Another species of hardwood that is hard to come by in its fresh form is hickory. The majority of hickory flooring is salvaged from old barns.
Old-Growth Wood
Access to Old Hemlock can be achieved through wood reclamation. It is not possible to extract old-growth timber sustainably. Some reclaimed timber is as old as two hundred to three hundred years. Reclaimed wood is the sole option for sourcing old-growth timber in the United States.
Wide Plank
Two and a half to four inches is the typical width of a wood floor's strip. Depending on species, wide-plank hardwood flooring boards can be 4–10 inches wide.
Due to the shortage of old-growth trees, Wide plank oak flooring is unusual. This is why ceramic tile, vinyl, and laminate imitations are common.
An exception to this rule is reclaimed wood. Wide plank oak flooring in the necessary widths of 4 to 6 inches and 6 to 10 inches can be made from the wide beams, floors, and sheathing in older structures.
Durability
In most cases, reclaimed wood outperforms modern wood in strength and durability. Its timber is more durable and weatherproof than younger, more recently cut wood because it comes from older, slower-growing trees.
Used wood doesn't warp easily under typical circumstances since its grain is denser and more solid than newer wood. Although it is often air-and kiln-dried, salvaged timber does not require seasoning like new wood.
Environmentally friendly Finding vendors
Salvaged wood is an eco-friendly option. Because the wood was already cut for another purpose, no new trees are felled to make salvaged wood. Reusing wood has two benefits: it reduces the need to cut down more trees and eliminates unused wood from certain places.
Reclaimed wide plank hardwood flooring is better for the environment because it cuts out a lot of the energy-sucking processes involved in cutting down trees: falling, delimbing, debarking, bucking, chipping, collecting, loading, and transporting the wood.
Conclusion
These one-of-a-kind items were sent to illustrious locations all over the globe under the labels of "The Beauty of Recycling" by The Joinery Company. Exemplifying the best that America's Virgin Forests had to offer in Longleaf Pine, the Reclaimed Heart Pine from the Sears, Roebuck and Company complex was of outstanding quality. According to the Joinery, reclaiming and recycling the Sears & Roebuck Complex was the biggest reclamation effort ever undertaken.
0 notes
Text
Converted 5-Story 'Flour Tower' on the Columbia River Wades Onto the Market for $945K http://dlvr.it/T2pz3W
#BestRealEstateAgentElkGrove
http://dlvr.it/T2pz3g
http://dlvr.it/T2pz3m
http://dlvr.it/T2pz3t
0 notes
Text
How Can I Add Value To My Crops Through Processing Or Packaging?
If you’re a farmer or an aspiring entrepreneur in the agricultural industry, you may have found yourself wondering how to maximize the value of your crops. Well, fret not, because there are two remarkable ways you can achieve just that – by exploring the potential of processing and packaging. By engaging in innovative processing techniques or investing in attractive packaging designs, you can elevate your crops from mere commodities to desirable products with added value. In this article, we will delve into the various strategies and benefits of processing and packaging, empowering you to make informed decisions that will enhance the profitability and success of your agricultural endeavors. So, let’s explore how you can add value to your crops through processing or packaging!
Learn more.
Processing crops
Understanding the benefits of crop processing
Crop processing refers to the transformation of raw agricultural products into value-added products. This process offers numerous benefits for farmers, including increased market opportunities, higher profitability, and reduced post-harvest losses. Through processing, crops can be transformed into various forms such as flour, oil, juice, or even snacks, which can appeal to a wider range of consumers.
Processing crops also enables farmers to extend the shelf life of their products, making it easier to transport and store them for longer periods. Additionally, crop processing allows for the utilization of by-products or waste materials, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. By adding value through processing, farmers can enhance their competitiveness in the market and differentiate their products from others.
Exploring different crop processing methods
There are various crop processing methods available, depending on the type of crop and desired end-product. Some common methods include drying, milling, grinding, baking, fermenting, and canning. Drying is particularly useful for crops such as herbs, fruits, and vegetables, as it removes moisture from the product and extends its shelf life. Milling and grinding are commonly used for grains, such as wheat or corn, to produce flour or meal.
Baking and fermenting are popular methods for crops like grains or fruits, where yeast or bacteria are used to convert sugars into carbon dioxide and alcohol, giving rise to products like bread, beer, or wine. Canning involves the preservation of crops in airtight containers through heat treatment, ensuring their long-term storage and safety.
Determining the optimal processing techniques for your crops
Selecting the most suitable processing techniques for your crops requires careful consideration of factors such as crop type, intended end-product, available resources, and market demand. It is essential to assess the characteristics of your crops, including their moisture content, sturdiness, and nutritional properties, as these factors can impact the processing methods that are most effective.
Consulting with experts, such as food scientists or agricultural extension officers, can provide valuable insights and guidance on the most appropriate processing techniques for your specific crops. Additionally, market research and consumer demand analysis can help determine whether there is a niche for particular value-added products, enabling you to make informed decisions about the processing methods to employ.
Ensuring food safety during crop processing
Food safety is a critical aspect of crop processing, as improper handling and processing techniques can lead to contamination, spoilage, and health risks. To ensure food safety during crop processing, farmers must follow good manufacturing practices (GMPs) and adhere to established food safety regulations.
This includes maintaining proper hygiene and sanitization practices, implementing effective pest control measures, and conducting regular equipment maintenance and cleaning. Farmers should also monitor and control critical control points (CCPs) throughout the processing line to prevent contamination.
Additionally, investing in proper training and education for yourself and your staff can enhance food safety knowledge and practices. This provides assurance to consumers that your processed crops meet the highest safety standards, building trust and loyalty in your brand.
Investing in the right processing equipment
Investing in the right processing equipment is crucial for efficient and effective crop processing. The choice of equipment will depend on the scale of your operations, the type of crops being processed, and the desired end-products. Some commonly used processing equipment includes dryers, mills, ovens, blenders, canning machines, and packaging machinery.
When considering equipment, factors such as equipment quality, durability, maintenance requirements, and compatibility with your crops should be taken into account. It is advisable to seek recommendations from reliable suppliers or consult experts in the field to make informed decisions on the most suitable equipment for your specific processing needs.
Furthermore, regular maintenance and calibration of the equipment are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This will minimize downtime and production losses, maximizing the return on your investment.
Packaging crops
Importance of effective crop packaging
Effective crop packaging plays a critical role in preserving product quality, enhancing shelf appeal, and ensuring consumer satisfaction. Proper packaging not only protects crops from physical damage, moisture, and contamination but also extends their shelf life by minimizing exposure to air, light, and temperature fluctuations.
Packaging also serves as a marketing tool, catching the attention of consumers and conveying essential information about the product. It creates a visual identity for your brand and can differentiate your crop products from competitors. Additionally, packaging serves as a convenient means of transportation and storage, making it easier for both farmers and consumers to handle and store the crops.
Exploring different crop packaging options
There are various crop packaging options available, ranging from traditional materials like plastic bags, cardboard boxes, and glass containers to innovative, eco-friendly alternatives such as biodegradable films, compostable containers, and reusable packaging.
The choice of packaging material depends on factors such as the nature of the crop, the desired shelf life, environmental considerations, and consumer preferences. For example, certain crops may require breathable packaging to prevent spoilage, while others may benefit from airtight packaging to preserve freshness.
Exploring different packaging options can also be an opportunity to align with sustainable practices and reduce environmental impact. Using recyclable or compostable materials can appeal to eco-conscious consumers and contribute to a positive brand image.
Understanding the role of packaging in marketing and branding
Packaging plays a significant role in marketing and branding, as it is often the first point of contact between consumers and your crop products. The design, color scheme, and labeling on the packaging should capture the essence of your brand and resonate with your target market.
Investing in attractive and informative packaging design can make your products stand out on store shelves and attract consumer attention. Clearly communicating key product information such as nutritional content, certifications, and traceability details can build trust and credibility with customers.
Furthermore, packaging can be utilized as a platform to tell your brand’s story, highlighting the unique qualities of your crops, sustainable farming practices, or social responsibility initiatives. Utilizing different packaging sizes or formats can also cater to various consumer needs and preferences, enhancing convenience and versatility.
Ensuring proper labeling and compliance
Accurate and compliant labeling is essential to ensure consumer safety, regulatory compliance, and brand transparency. All packaged crop products should include clear and legible labels that provide vital information such as product name, ingredients, allergens, nutritional facts, storage instructions, and expiration dates.
Proper labeling helps consumers make informed choices, especially individuals with dietary restrictions or allergies. Additionally, adhering to labeling requirements set by regulatory bodies ensures legal compliance and avoids potential penalties or recalls.
It is critical to stay updated on labeling regulations and requirements specific to your target market or distribution destinations. Regularly auditing and reviewing your labeling practices can help identify any necessary adjustments or updates to remain compliant with evolving regulations.
Evaluating the sustainability of packaging materials
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration for consumers, evaluating the environmental impact of packaging materials is crucial. Sustainable packaging aims to minimize resource consumption, reduce waste generation, and promote circular economy principles.
When selecting packaging materials, assess their life cycle impacts, including the sourcing, production, use, and end-of-life stages. Consider materials that are recyclable, compostable, or made from renewable resources. Opt for lightweight materials that minimize carbon emissions during transportation.
Collaborating with packaging suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices or participating in industry initiatives focused on sustainable packaging can provide access to innovative solutions and support a more sustainable future.
youtube
Value-added crop products
Identifying potential value-added products
Value-added crop products are those that have undergone processing or have been transformed in a way that enhances their market value, desirability, and versatility. Identifying potential value-added products requires understanding market trends, consumer preferences, and your crop’s unique qualities.
Conducting market research and staying informed about emerging consumer demands can help identify opportunities for value addition. For example, trends such as plant-based foods, health-conscious snacks, or artisanal products can inspire the development of value-added crop products that cater to these specific consumer preferences.
Additionally, carefully assessing the characteristics and potential uses of your crops can uncover new possibilities for value addition. For example, surplus or imperfect crops can be transformed into juices, sauces, or jams, reducing waste and creating additional revenue streams.
Exploring processing techniques for value-added products
Transforming crops into value-added products requires exploring and applying various processing techniques. This can include techniques such as juicing, baking, fermenting, freeze-drying, or extracting essential oils.
For example, fruits and vegetables can be juiced to create refreshing beverages, while grains can be milled and baked to produce artisanal bread or pastries. Fermenting crops like cabbage can lead to the creation of sauerkraut or kimchi, which have gained popularity for their probiotic benefits.
Innovative processing techniques, such as freeze-drying, can preserve the nutritional content and flavors of crops, enabling the creation of instant soups, fruit powders, or freeze-dried snacks. Exploring these techniques and experimenting with different combinations can result in unique and appealing value-added crop products.
Creating innovative and unique crop-based products
Creating innovative and unique crop-based products involves thinking creatively and pushing the boundaries of traditional processing methods. This can include experimenting with flavor combinations, incorporating novel ingredients, or exploring unconventional packaging formats.
For example, infusing herbs or spices into oils or vinegar can create flavorful dressings or marinades. Blending fruits and vegetables can lead to colorful smoothies or fruit purees that can be used in various culinary applications. Combining different crops with grains or nuts can result in nutritionally rich and satisfying snack bars.
Innovation can also extend to packaging design, where attention-grabbing shapes, colors, or branding elements can differentiate your product on store shelves. Considering the overall sensory experience and convenience of your product can further enhance its uniqueness and appeal.
Testing and evaluating the market viability of value-added products
Before launching a value-added crop product, it is important to test and evaluate its market viability. This involves conducting small-scale trials, obtaining consumer feedback, and assessing market demand.
Engaging in market research, focus groups, or surveys can provide insights into consumer preferences, willingness to pay, and potential barriers to adoption. Testing the product with a targeted audience can help gauge its acceptance, taste preferences, and overall satisfaction.
Additionally, collaborating with retailers, distributors, or local food establishments can provide opportunities for trial runs or limited market testing. Monitoring sales performance and collecting data on consumer feedback will help refine the product and make necessary adjustments before scaling up production.
Developing a marketing strategy for value-added crop products
A comprehensive marketing strategy is essential for the successful promotion and sale of value-added crop products. Start by identifying your target market and understanding their needs, preferences, and purchasing behaviors. This knowledge will help tailor your marketing efforts to effectively reach and engage your intended audience.
Develop a clear and compelling brand story that articulates the unique qualities, benefits, and values of your value-added crop products. Utilize various marketing channels such as social media, e-commerce platforms, farmers’ markets, or traditional advertising to showcase your products and engage with potential customers.
Collaborating with influencers or brand ambassadors who align with your brand values can help increase brand visibility and build credibility. Offering product samples, organizing tastings or cooking demonstrations, and participating in relevant industry events can also generate buzz and create opportunities for direct customer interaction.
Implementing a robust digital marketing strategy, including search engine optimization, email marketing, or content creation, can expand your reach and maintain a strong online presence. Monitoring and analyzing marketing performance metrics will provide insights to optimize your marketing efforts and adapt to changing consumer preferences.
Increasing shelf life
Understanding the importance of shelf life for crop value
Shelf life refers to the length of time a crop product can be stored without significant deterioration in quality or freshness. Increasing the shelf life of your crops is crucial as it enhances product availability, reduces post-harvest losses, and allows for extended marketing and distribution periods.
Consumers value fresh, high-quality produce, and longer shelf life increases the chances of your crops reaching the market in optimal condition. It also reduces the need for frequent restocking, making it easier for retailers to manage inventory levels and minimize waste.
Exploring preservation techniques to extend shelf life
Preservation techniques are essential for extending the shelf life of crop products. These techniques aim to slow down the natural biochemical processes that lead to spoilage, such as enzymatic reactions, microbial growth, and oxidative reactions.
Some common preservation techniques include cooling and refrigeration, freezing, canning, drying, and vacuum packaging. Cooling and refrigeration slow down spoilage by inhibiting microbial growth and enzyme activity. Freezing preserves the quality of crops by preventing the growth of microorganisms and enzymatic reactions. Canning uses heat treatment to destroy spoilage microorganisms and create airtight containers, ensuring long-term preservation.
Drying removes water, inhibiting microbial growth and enzymatic reactions, thus extending shelf life. Vacuum packaging removes oxygen, retarding the oxidation of fats and the growth of spoilage microorganisms. Exploring and utilizing the most suitable preservation technique for your crops will depend on factors such as crop type, market demand, and available resources.
Determining the optimal packaging methods to preserve crops
Packaging plays a crucial role in preserving crops by providing protection from physical damage, moisture, and microbial contamination. The choice of packaging method should align with the preservation technique employed and the desired shelf life of the crops.
For example, if utilizing a cooling or refrigeration method, packaging should provide adequate airflow and allow for proper cooling. If using a vacuum packaging method, ensuring air-tightness and barrier properties to prevent oxygen entry is essential. For dried crops, packaging should effectively exclude moisture and maintain their dry state.
Considering the specific characteristics of your crops and their preservation requirements, such as temperature sensitivity or vulnerability to physical damage, will help determine the optimal packaging methods. Consulting with packaging experts or conducting trials can assist in selecting the most appropriate packaging materials and formats.
Implementing proper handling and storage practices
Proper handling and storage practices are crucial for maximizing the shelf life of crops. This includes rigorous quality control measures throughout the production and supply chain, from harvest to packaging and distribution.
During harvesting, crops should be handled with care to minimize bruising, damage, or contamination. Promptly cooling harvested crops to the optimal storage temperature slows down the degradation process and preserves freshness.
When packaging crops, maintaining cleanliness and proper hygiene practices is important to avoid contamination. Crops should be sorted and graded to remove damaged or spoiled ones, ensuring only high-quality produce enters the packaging process.
In storage, maintaining the appropriate temperature, humidity, and light conditions is critical. Temperature and humidity controls can slow down enzyme activity, microbial growth, and respiration rates. Avoiding exposure to direct sunlight or extreme temperature fluctuations helps preserve the quality of the crops.
Monitoring and managing post-harvest diseases and pests
Post-harvest diseases and pests pose a significant threat to crop quality and shelf life. Implementing proper monitoring and management practices is essential to minimize losses and ensure food safety.
Regular inspections of your crops, both pre and post-harvest, can help identify signs of disease or pest infestation. Promptly removing and properly disposing of any affected crops can prevent the spread of diseases or pests to other crops.
Applying appropriate pest control measures, such as biological control methods or approved pesticides, can help manage pest populations. Regular sanitation of storage facilities and equipment, as well as proper hygiene practices, minimize the risk of contamination and the growth of spoilage microorganisms.
Investing in education and training on post-harvest disease and pest management can enhance your understanding of potential risks and equip you with the knowledge to implement effective control measures. Collaborating with agricultural extension services or plant pathologists can provide additional guidance and support in managing post-harvest diseases and pests efficiently.
Maximizing nutritional value
Understanding the impact of processing on nutritional value
Processing crops can have varying effects on their nutritional value. Some processing methods, such as heating or exposure to light, can lead to nutrient loss or degradation. On the other hand, certain processing techniques, like fermentation or fortification, can enhance or preserve the nutritional content of crops.
It is important to understand the nutritional vulnerabilities of your crops and consider how different processing methods may impact their nutrient composition. Collaboration with nutrition experts or conducting laboratory analysis can provide insights into the changes in nutritional value resulting from processing.
Exploring techniques to preserve and enhance nutritional content
Preserving and enhancing the nutritional content of processed crop products is achievable through careful selection and application of processing techniques. For example, minimal processing methods such as blanching or steam cooking can help retain more nutrients compared to prolonged heating or deep frying.
Fermentation is a valuable technique that not only preserves crops but also enhances their nutritional value. Fermented products, such as yogurt, pickles, or sourdough bread, can provide probiotics, increase vitamin availability, and improve digestibility.
Another approach to enhancing nutritional content is through fortification, where essential nutrients are added to processed products. This can include adding vitamins, minerals, or protein sources to improve the nutritional profile of the crop-based product.
Balancing the need for preservation and the desire to maximize nutritional value requires careful consideration of processing techniques, timing, and temperature control. Collaborating with nutrition experts or conducting research on the impact of different processing methods on specific nutrients can guide your choices.
Incorporating value-added ingredients for added nutritional benefits
Incorporating value-added ingredients into crop-based products can provide additional nutritional benefits and diversify product offerings. These ingredients can enhance the nutritional profile of the product and cater to specific dietary needs or preferences.
For example, adding nutrient-dense nuts, seeds, or dried fruits to snack bars or breakfast cereals can increase their fiber and antioxidant content. Including plant-based protein sources like legumes or quinoa in pasta or baked goods can make the products more nutritionally balanced.
Incorporating functional ingredients, such as superfoods or herbal extracts, can also provide targeted health benefits. These ingredients, known for their antioxidant properties or specific health-promoting qualities, can be incorporated into beverages, snacks, or other processed crop products.
Identifying the nutritional needs and preferences of your target market can guide your selection of value-added ingredients. Monitoring consumer trends and health claims regulations will ensure compliance with applicable labeling and marketing restrictions.
Developing partnerships with nutrition experts and researchers
Developing partnerships with nutrition experts and researchers can provide valuable insights and support in maximizing the nutritional value of your processed crop products. These experts can offer guidance in selecting appropriate processing methods, preserving nutrients, and incorporating functional ingredients.
Collaborating with nutrition experts can help identify gaps in the nutritional profile of your products, suggest ingredient additions or fortifications, and ensure adherence to dietary guidelines and recommendations.
Research institutions or universities may also offer resources and facilities for evaluating the nutritional content of your crop products before and after processing. Nutritional analysis can provide data on the presence and concentration of essential vitamins, minerals, macronutrients, and other beneficial compounds.
By establishing partnerships and maintaining an open dialogue with nutrition experts and researchers, you can continuously improve the nutritional quality of your processed crop products and adapt to evolving consumer needs and scientific advancements.
Communicating the nutritional benefits to consumers
Effectively communicating the nutritional benefits of your processed crop products to consumers is vital in creating awareness and building trust. Your product labeling, marketing materials, and digital presence should clearly and accurately present the nutritional qualities and positive health impacts of your crop-based products.
Clearly highlight the key nutrients and functional ingredients in your product labeling and packaging. Consider incorporating nutrition claims or symbols that are compliant with local regulations and recognized by consumers. For example, using symbols denoting gluten-free, organic, low sodium, or high fiber can help consumers quickly identify the beneficial qualities of your product.
Investing in clear and accurate product descriptions, both on packaging and online platforms, can further educate consumers about the specific nutritional benefits they can expect from your processed crop products.
Utilize digital marketing channels, social media platforms, and your brand’s website to provide educational content, recipe ideas, or dietary tips, reinforcing the nutritional value of your products. Incorporating testimonials from satisfied consumers or collaborating with nutrition influencers can also enhance the credibility and appeal of your product’s nutritional benefits.
Ensuring product quality
Implementing quality control measures during processing and packaging
Implementing robust quality control measures during processing and packaging is essential to consistently deliver high-quality crop products to the market. Quality control begins with setting quality standards and implementing quality assurance protocols at every stage of the production process.
Developing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) that outline specific quality control checkpoints and procedures will ensure consistency and adherence to desired quality standards. This may include regular inspections, monitoring critical control points, and conducting laboratory testing for physical, chemical, and microbiological parameters.
Regular calibration and maintenance of equipment, such as scales, temperature monitors, or pH meters, is necessary to ensure accuracy and reliability. Additionally, investing in training and education for employees involved in the processing and packaging stages will enhance their understanding of quality control protocols and their role in maintaining product quality.
Establishing quality standards for crop products
Establishing quality standards for your crop products involves determining specific criteria and benchmarks that define what constitutes a high-quality product. Quality standards should be based on industry guidelines, regulations, and consumer expectations.
Consider factors such as physical appearance, taste, texture, aroma, nutritional composition, and safety parameters when establishing quality standards. Work with experts, such as quality control professionals or agricultural extension services, to identify the appropriate quality indicators for your specific crops and end-products.
Regularly monitoring and evaluating product quality against established standards through inspection, sensory analysis, and laboratory testing will help ensure that your crop products consistently meet or exceed customer expectations.
Monitoring and managing factors that impact product quality
Numerous factors can impact the quality of crop products throughout the production and supply chain. Proper monitoring and management of these factors are essential to maintain product quality and minimize the risk of quality deterioration.
Factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure can affect the sensory attributes, nutritional content, and shelf life of your crop products. Implementing appropriate storage and transportation practices, including refrigeration, temperature monitoring, and protection from sunlight, can mitigate potential quality risks.
Managing factors that contribute to spoilage or contamination, such as pests, microbial growth, or cross-contamination, is crucial for maintaining product quality. Implementing pest control measures, sanitation protocols, and hygienic handling practices will help safeguard product integrity.
Monitoring market feedback, conducting regular sensory evaluation, or using advanced testing methods, such as shelf life studies or microbiological analysis, can help identify potential quality issues and continuously improve product quality.
Utilizing technology for quality assurance
Technology plays a significant role in enhancing quality assurance processes for crop products. Utilizing advanced tools, sensors, and monitoring systems can provide real-time data and insights that enable proactive quality control and quick response to potential issues.
For example, temperature monitoring systems can provide continuous and remote monitoring of cold storage facilities, ensuring consistent temperature control. Sensors can measure and track essential parameters such as humidity, pH levels, or oxygen levels, enabling early detection of any variations that may impact product quality.
Automation and digitalization of quality control processes can streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting, reducing human errors and enhancing efficiency. Implementing software or mobile applications for quality management, such as electronic record-keeping or traceability systems, can enable better tracking, identification of potential bottlenecks, and quick resolution of quality issues.
Embracing technology-driven quality assurance practices can improve product consistency, reduce quality-related risks, and provide valuable data for process optimization and continuous improvement.
Investing in training and education for quality management
Investing in training and education for yourself and your staff is crucial to ensure effective quality management. Providing comprehensive training on quality control protocols, good manufacturing practices, and regulatory compliance will equip employees with the necessary knowledge and skills.
Training programs focused on sensory evaluation, quality assessment techniques, and lab analysis can enhance the ability to identify and address quality issues at various stages of production. Employees should also receive training on food safety practices, hygiene protocols, and understanding of cross-contamination risks.
In addition to initial training, continuous professional development and refresher sessions are important to stay updated on evolving quality standards, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements. This ongoing investment in training and education will contribute to a culture of quality excellence and continuous improvement within your organization.
Market research and consumer preferences
Conducting market research to understand consumer demands
Conducting market research is vital for understanding consumer demands, preferences, and trends, enabling you to tailor your products and marketing strategies accordingly. Market research provides insights into consumer behavior, purchasing patterns, competitor analysis, and emerging market trends.
Surveys, focus groups, and interviews can help identify consumer preferences regarding crop products, processing methods, packaging formats, and nutritional expectations. Understanding consumer demographics, lifestyles, and values can guide the development of products and marketing messages that resonate with your target market.
Analyzing market data, industry reports, and conducting competitor analysis will help identify market gaps and potential niches where your value-added crop products can thrive. It is important to stay up-to-date with evolving consumer demands and preferences to ensure your products remain relevant and competitive.
Identifying market trends and opportunities
Identifying market trends and opportunities is crucial for capitalizing on emerging consumer demands and staying ahead of competitors. Monitor industry publications, attend trade shows, and engage with industry associations to keep a pulse on the latest market developments.
Trends such as plant-based diets, clean label products, or sustainable packaging have gained significant traction in recent years. Adapting your crop products to align with these trends and incorporating them into your marketing messages can enhance their market appeal.
Additionally, understanding the impact of current events, cultural shifts, or macroeconomic factors on consumer behavior can uncover new market opportunities. Rapidly changing consumer preferences, such as the demand for convenience, healthier alternatives, or unique flavor experiences, can open doors for innovative value-added crop products.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing market data, integrating feedback from customers, and monitoring competitor activities will help identify potential market trends, gaps, and opportunities for growth.
Assessing consumer preferences for processed or packaged crops
Assessing consumer preferences for processed or packaged crop products requires gathering insights into their expectations, perceptions, and purchasing habits. Understanding the specific values and motivations driving consumer choices can inform your product development and marketing strategies.
Conducting surveys, focus groups, or consumer panels can provide direct feedback on what consumers seek in processed or packaged crop products. This includes factors such as convenience, taste, nutritional attributes, sustainability, or brand reputation.
Assessing consumer preferences regarding packaging formats, materials, labeling clarity, or product claims can help optimize your packaging design and enhance its appeal. For example, some consumers may prefer grab-and-go packaging options, while others may prioritize eco-friendly materials or minimalistic designs.
Monitoring online consumer reviews, social media conversations, or engaging with customers directly through customer service channels can also yield valuable insights into consumer preferences and areas for improvement.
Incorporating consumer feedback into product development
Incorporating consumer feedback into product development is essential for creating crop products that resonate with target markets and meet consumer expectations. Actively listening to consumer preferences and integrating their suggestions can foster brand loyalty and drive innovation.
Engaging with consumers through surveys, taste tests, or product trials allows them to voice their opinions and provide valuable feedback on flavors, textures, packaging, or other product attributes. This feedback can guide the refinement of existing products or inspire the development of new value-added crop products.
Establishing feedback loops and utilizing customer relationship management systems can facilitate ongoing communication with consumers. Monitoring online reviews, social media comments, or customer service interactions can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiments and expectations.
By incorporating consumer feedback into your product development process, you demonstrate responsiveness to consumer needs, build trust, and establish a customer-centric approach that creates long-term loyalty.
Adapting to changing consumer preferences and demands
Adapting to changing consumer preferences and demands is crucial for sustained success in the crop product market. Consumer preferences can be influenced by a range of factors, including evolving health trends, environmental concerns, cultural shifts, economic conditions, or technological advancements.
Regularly monitoring market trends, conducting consumer surveys, or engaging in open dialogues with customers can provide insights into shifting preferences and anticipate changing demands. Continuously evaluating and adjusting your product offerings, processing methods, packaging formats, or marketing strategies will help ensure your crop products remain relevant and desirable to consumers.
Remaining agile and responsive to emerging market trends allows you to stay ahead of competitors and capture new opportunities. This includes exploring new ingredients, experimenting with novel processing methods, or embracing sustainable packaging solutions.
Collaborating with industry experts, attending conferences, or participating in industry forums can provide additional perspectives and guidance on navigating the ever-changing consumer landscape. By maintaining a customer-centric mindset and adaptability, you can successfully meet evolving consumer preferences and demands.
Branding and marketing strategies
Developing a strong brand identity for your crop products
Developing a strong brand identity is essential for positioning your crop products in the market and connecting with consumers on a deeper level. Your brand identity encompasses your brand story, values, mission, and the emotional connections you establish with your target audience.
Start by defining your brand’s unique qualities, such as sustainable farming practices, locally sourced ingredients, or social responsibility initiatives. Craft a compelling brand story that effectively communicates these qualities, resonates with your target market, and differentiates your crop products from competitors.
Consistency in branding elements, such as your logo, color scheme, typography, and packaging design, establishes visual recognition and reinforces your brand identity. Incorporating these elements across various touchpoints, from packaging to marketing materials to digital presence, will help build a strong and cohesive brand identity.
Furthermore, cultivating a strong brand personality through your communication style, tone of voice, and interactions with customers fosters trust, loyalty, and emotional connections. Authenticity and transparency in your brand messaging and actions will solidify your position in the market and create a strong foundation for future growth.
Creating attractive and informative packaging design
Creating attractive and informative packaging design is key to capturing consumer attention, communicating your brand’s unique qualities, and promoting your crop products effectively. Packaging design serves as a visual representation of your brand identity, instantly conveying the essence and quality of your products.
Investing in professional packaging design services or collaborating with graphic designers experienced in food packaging can ensure your packaging stands out on store shelves. Consider factors such as color psychology, typography legibility, and overall aesthetic appeal that align with your brand identity and attract your target market.
The packaging should clearly and accurately communicate key product information such as product name, ingredients, nutritional facts, certifications, and brand story. Utilizing symbols or icons to highlight product attributes, such as organic, gluten-free, or sustainable, can quickly convey important information to consumers.
Choose packaging formats that are convenient, functional, and suitable for your crop products. Additionally, incorporating sustainable packaging materials or design elements that minimize waste and environmental impact can enhance the perceived value of your products.
Implementing effective marketing strategies
Implementing effective marketing strategies is crucial for generating awareness, driving sales, and establishing a strong presence for your crop products in the market. Marketing strategies encompass various channels, techniques, and campaigns that communicate your brand’s value proposition, benefits, and unique qualities.
Start by identifying your target market, understanding their preferences, and determining the most effective marketing channels to reach them. This could include social media platforms, digital advertising, traditional media, farmers’ markets, or collaborations with retail partners.
Crafting persuasive and targeted marketing messages that highlight the unique selling points of your crop products is crucial. Emphasize factors such as taste, freshness, sustainability, nutritional benefits, or local sourcing to differentiate your products and align with consumer desires.
Utilize storytelling and visual content to engage consumers and create a memorable brand experience. Sharing your brand’s origin story, highlighting your farming practices, or showcasing behind-the-scenes processes can foster emotional connections and build trust.
Implementing promotions, discounts, or loyalty programs can incentivize trial and repeat purchases. Collaborating with influencers, bloggers, or chefs to create recipe content or product reviews can expand your reach and leverage their engaged audiences.
Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of your marketing strategies through metrics such as sales data, website traffic, social media engagement, or customer feedback will help optimize your efforts and refine future campaigns.
Utilizing digital marketing channels for product promotion
Utilizing digital marketing channels is crucial for reaching a wide audience, engaging with consumers, and driving product promotion for your crop products. Online platforms offer numerous opportunities to build brand awareness, showcasing your products, and interacting with potential customers.
Establishing a strong online presence through a website or e-commerce platform allows consumers to access information about your crop products, make purchases conveniently, and stay updated on your latest offerings. A well-designed and user-friendly website that incorporates search engine optimization (SEO) techniques can help your brand rank higher in online searches and drive organic traffic.
Social media platforms provide an avenue to share visually appealing content, engage with consumers, and build a community around your brand. Utilize platforms such as Instagram, Facebook, or YouTube to share product images, recipes, behind-the-scenes stories, or customer testimonials.
Implementing targeted digital advertising campaigns can help reach specific demographics, geographic areas, or interest groups. Utilize platforms like Google Ads or social media advertising tools to create campaigns that align with your marketing objectives and maximize reach.
Utilize email marketing to establish direct communication with customers, providing them with exclusive offers, product updates, or valuable content. Collecting customer information through opt-in forms or loyalty programs can help build your email subscriber list and nurture customer relationships.
Regularly monitoring and analyzing digital marketing metrics, such as website traffic, click-through rates, conversion rates, or engagement levels, will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your digital marketing efforts and allow for continuous optimization.
Collaborating with influencers and ambassadors for brand awareness
Collaborating with influencers and brand ambassadors can significantly boost brand awareness, amplify your reach, and create social proof for your crop products. Influencers, whether they are bloggers, social media personalities, or industry experts, have established credibility and a following among your target market.
Identify influencers or ambassadors whose values, expertise, or audiences align with your brand and products. Engaging in collaborations, sponsored posts, or product reviews with these influencers can introduce your crop products to their engaged audience, foster trust, and generate interest.
When selecting influencers, consider their authenticity, engagement levels, alignment with your target market, and past collaborations. Long-term partnerships with influencers or brand ambassadors can create ongoing awareness and advocacy for your products.
Co-creating content with influencers, such as recipe collaborations, product showcases, or live demonstrations, can leverage their expertise, reach, and storytelling abilities. This partnership can generate engaging and compelling content that resonates with their audience and drives interest in your crop products.
Regularly evaluate the impact and effectiveness of influencer collaborations through metrics such as engagement levels, follower growth, website traffic, or sales. Collaborating with influencers should align with your overall marketing strategy and goals to ensure a meaningful and mutually beneficial partnership.
Packaging regulations and certifications
Understanding packaging regulations and requirements
Understanding packaging regulations and requirements is crucial to ensure compliance with food safety standards and legal obligations. Packaging regulations can vary across regions, and it is important to stay updated on the applicable regulations for your target market or distribution destinations.
Industry regulatory bodies often provide guidelines and requirements related to packaging materials, labeling, product claims, and overall safety. Familiarize yourself with these guidelines and ensure your packaging design, materials, and practices align with the specified requirements.
Regulations may cover aspects such as proper labeling of allergens, nutritional information, expiration dates, country of origin, or proper disposal instructions. Compliance with these regulations helps protect consumer health, prevent misleading information, and avoid potential penalties or product recalls.
Regularly review and monitor regulatory updates, engage with relevant industry associations or consult legal experts to ensure ongoing compliance with packaging regulations and requirements.
Ensuring compliance with food safety standards
Ensuring compliance with food safety standards is critical for protecting consumer health and maintaining the integrity of your crop products. Food safety standards encompass various aspects, including packaging materials, hygiene practices, pest control, and traceability.
Packaging materials should meet relevant food safety standards to prevent potential chemical migration or harm to consumers. Selecting packaging materials that are certified as food-grade or conform to recognized safety standards ensures product safety and minimizes potential risks.
Maintaining proper hygiene practices throughout the production and packaging processes is essential. This includes implementing appropriate sanitation protocols, personal protective measures, and effective cleaning procedures to prevent cross-contamination and microbial growth.
Effective pest control measures must be in place to prevent pest infestation, which can contaminate crop products and compromise food safety. Regular inspection, monitoring, and appropriate pest management practices, such as integrated pest management (IPM), should be employed.
Establishing traceability systems for packaging materials is crucial for ensuring product safety and enabling efficient recalls if necessary. Implementing proper record-keeping mechanisms, managing batch codes or lot numbers, and utilizing technologies like barcodes or RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags enable effective traceability and quick identification of potential sources of contamination.
Obtaining necessary certifications for packaging materials, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certification, BRCGS (Brand Reputation Compliance Global Standards), or HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), can provide assurance to consumers and business partners of your commitment to food safety.
Obtaining necessary certifications for packaging materials
Obtaining necessary certifications for packaging materials demonstrates your commitment to quality, safety, and sustainability. Certifications provide independent verification of your adherence to specific standards and can enhance consumer trust and confidence in your crop products.
Various certifications exist for different types of packaging materials and may cover areas such as quality management systems, environmental impact, or social responsibility. Some commonly recognized certifications for packaging materials include ISO 9001 (Quality Management System), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System), or FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certification for sustainable paper-based packaging.
Consider the specific requirements of your target market, industry expectations, and consumer demands when selecting certifications for your packaging materials. Certifications can also showcase your commitment to meeting international standards and facilitate trade in global markets.
Collaborating with packaging material suppliers or obtaining guidance from industry experts can help identify relevant certifications applicable to your specific packaging materials and production processes. Consultation with certification bodies or accreditation agencies can provide clarity on specific requirements and streamline the certification process.
Implementing traceability systems for packaging materials
Implementing traceability systems for packaging materials is crucial for ensuring product safety, complying with regulations, and maintaining supply chain transparency. Traceability systems enable efficient tracking and identification of packaging materials and their origins throughout the supply chain.
Traceability mechanisms, such as batch codes, lot numbers, or unique identifiers, should be incorporated into your packaging materials. These mechanisms facilitate identification of potential sources of contamination or quality issues, aiding quick recall actions if necessary.
Utilizing technologies like barcodes, RFID tags, or QR (Quick Response) codes can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of traceability systems. These technologies enable the capture and transfer of essential information about packaging materials, including origin, manufacturing date, or quality control data.
Implementing proper record-keeping practices, maintaining accurate inventory management systems, and collaborating with suppliers to ensure traceability of packaging materials are essential components of effective traceability systems.
Regular auditing of your traceability systems, conducting mock recalls, and performing traceability exercises can help identify any potential gaps or areas for improvement. Continually refining and optimizing your traceability systems will ensure their reliability and effectiveness in ensuring product safety.
Adhering to labeling and packaging regulations
Adhering to labeling and packaging regulations is crucial for ensuring transparency, avoiding false claims, and building consumer trust. These regulations specify requirements for product labeling, including elements such as product name, ingredient listing, allergen declaration, nutritional facts, and country of origin.
Labeling regulations also provide guidelines for the size, legibility, placement, and language of the required information. Compliance with these regulations ensures that consumers have accurate and easily accessible information to make informed choices.
Avoid making false or misleading claims on your packaging, such as health benefits not supported by scientific evidence, organic claims without certification, or exaggerated claims about nutritional content. These false claims can damage your brand reputation and result in legal consequences.
Regularly review and update your packaging labels to ensure compliance with evolving regulations. Collaborating with legal experts, engaging with regulatory bodies, or consulting industry associations can provide guidance on specific labeling and packaging requirements applicable to your crop products.
Efficiency and cost-effectiveness
Optimizing processing and packaging operations for efficiency
Optimizing processing and packaging operations for efficiency is crucial for maximizing productivity, minimizing costs, and meeting market demands. Improving operational efficiency reduces waste, increases output, and contributes to overall profitability.
Gaining a thorough understanding of your processing and packaging workflows, identifying potential bottlenecks, and streamlining processes are essential for achieving efficiency. This may involve reorganizing workstations, implementing automation or robotics, or optimizing workflow sequences to minimize unnecessary movement or idle time.
Investing in reliable and quality processing and packaging equipment can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Equipment that is well-maintained, calibrated, and operated by trained personnel ensures consistent product quality and reduces downtime.
Implementing standard operating procedures (SOPs), ensuring clear communication channels, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement among your staff can further enhance efficiency. Encouraging employee input and feedback can uncover valuable suggestions for process optimization and workflow simplification.
Regularly monitoring and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production rates, downtime, or waste levels can provide insights into operational efficiency and indicate areas for improvement. Utilize data-driven decision-making to guide your optimization efforts and measure the impact of implemented changes.
Minimizing product waste during processing and packaging
Minimizing product waste during processing and packaging is not only environmentally responsible but also contributes to cost-effectiveness and profitability. Reducing waste requires identifying waste sources, implementing waste management protocols, and optimizing processes to minimize losses.
Conduct a thorough analysis of your processing and packaging stages to identify potential waste sources, such as trimmings, imperfect crops, or packaging material scraps. Developing strategies to repurpose or minimize waste can create additional revenue streams or cost savings.
Implementing good manufacturing practices (GMPs) and adhering to quality control protocols help reduce waste associated with rejections, product recalls, or customer returns. Proper calibration and maintenance of equipment ensure accurate measurements, minimizing overfills or underfills.
Optimizing production planning to align with market demand and streamlining inventory management reduce the risk of stock expiration or obsolescence. Utilize forecasting techniques and collaborate closely with suppliers and distributors to optimize raw material procurement and eliminate waste due to overstocking or shortages.
Investing in employee training on waste reduction techniques, promoting a culture of waste consciousness, and establishing a waste management system for different waste streams contribute to an overall waste reduction strategy.
Regularly monitor waste generation and disposal data, conduct waste audits, and measure key waste-related KPIs to track progress and identify areas for improvement. Collaboration with waste management specialists, recycling companies, or industry associations can provide guidance on waste minimization practices specific to your crop processing and packaging operations.
Exploring cost-effective packaging solutions
Exploring cost-effective packaging solutions is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and maximizing profitability. Cost-effective packaging balances product protection, functionality, and visual appeal while minimizing material and production costs.
Collaborating with packaging material suppliers or consulting packaging experts can help identify cost-efficient materials that meet the required performance attributes. Assess the overall lifecycle costs, including sourcing, manufacturing, transportation, and disposal, to ensure the long-term cost-effectiveness of chosen packaging solutions.
Optimizing packaging design to minimize material usage, such as using lightweight materials or right-sizing package dimensions, reduces material costs and transportation expenses. However, it is crucial to balance this optimization with maintaining product protection and meeting regulatory requirements.
Consider utilizing eco-friendly or sustainable packaging materials that offer cost advantages in addition to environmental benefits. Some sustainable packaging options, such as compostable films or recycled paperboard, can be commercially competitive with conventional packaging materials, while showcasing your commitment to sustainability.
Evaluating different packaging formats or sizes that align with consumer preferences and market demands can optimize packaging efficiency. Offering multiple packaging options, such as bulk quantities or portioned sizes, allows consumers to choose what best suits their needs, reducing inventory costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Regularly review and analyze the costs associated with your packaging materials, production processes, and transportation to identify areas for cost-saving efforts. Collaborate with suppliers, attend packaging trade shows, or engage in industry forums to stay updated on cost-effective packaging solutions and emerging technologies.
Implementing streamlined supply chain processes
Implementing streamlined supply chain processes is critical for achieving cost-effectiveness, minimizing lead times, and ensuring a reliable flow of materials and products. A well-organized and efficient supply chain contributes to increased productivity, reduced inventory costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Collaborate closely with suppliers and establish long-term relationships to foster reliability, timely delivery, and knowledge sharing. Implementing supplier performance evaluation systems, monitoring service levels, and conducting regular supplier audits ensure alignment with your quality and delivery requirements.
Optimize procurement processes by adopting efficient ordering and inventory management techniques. Utilize demand forecasting methods, establish safety stock levels, and implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory management strategies to minimize carrying costs and overstocking.
Implementing efficient warehousing and distribution practices aids in reducing storage costs, order fulfillment time, and inventory obsolescence. Utilize inventory tracking systems, adopt automation technologies, and implement well-defined receiving and shipping protocols to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
Implementing advanced planning and scheduling technologies or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can integrate and streamline supply chain processes, improving coordination among different functional areas. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of inventory levels, demand fluctuations, and order progress, facilitating efficient decision-making.
Regularly evaluate and analyze key supply chain performance metrics, such as order fulfillment rate, on-time delivery, or inventory turnover. Collaboration with supply chain experts, attending industry seminars, or engaging with logistics providers can provide valuable insights into supply chain optimization opportunities.
Evaluating the return on investment for processing and packaging
Evaluating the return on investment (ROI) for processing and packaging investments is crucial for financial decision-making and assessing the effectiveness of implemented strategies. ROI analysis provides insights into the profitability, cost savings, and long-term viability of various processing and packaging initiatives.
Calculate the initial investment costs, including equipment purchases, packaging design development, or employee training programs. Additionally, consider ongoing operational costs such as energy consumption, maintenance, packaging material sourcing, and labor requirements.
Analyze the impact of your processing and packaging initiatives on factors such as production efficiency, waste reduction, product quality improvements, or market penetration. Quantify these impacts by measuring key performance indicators, such as increased output, reduced downtime, decreased waste levels, or improved customer satisfaction.
Estimate the financial benefits resulting from these impacts, including cost savings, revenue growth, or improved market share, and compare them against the initial investment costs. Consider both short-term and long-term financial returns to evaluate the sustainability and overall profitability of your processing and packaging investments.
Collaborating with financial consultants or conducting accurate cost analysis will provide a comprehensive understanding of the financial implications of processing and packaging decisions. These insights enable informed decision-making, resource allocation, and identification of areas for further optimization.
In conclusion, adding value to your crops through processing and packaging requires a comprehensive understanding of the benefits, methods, and techniques involved. By exploring different processing methods and packaging options, determining optimal techniques, ensuring food safety, and investing in the right equipment, you can enhance your crop products and expand market opportunities.
Value-added crop products offer unique opportunities to cater to consumer preferences, increase nutritional value, and test market viability. By incorporating innovative processing techniques, creating unique crop-based products, and developing marketing strategies, you can successfully introduce value-added products and captivate consumers.
To maximize shelf life, preservation techniques, optimal packaging methods, and proper handling practices are vital. Prioritizing nutritional value requires understanding the impact of processing, exploring different techniques, incorporating value-added ingredients, and effectively communicating benefits to consumers.
Ensuring product quality involves implementing quality control measures, establishing standards, monitoring impacting factors, utilizing technology, and investing in training. Understanding market preferences, trends, conducting research, incorporating consumer feedback, and implementing branding and marketing strategies are essential to meet consumer demands.
Compliance with packaging regulations, certifications, traceability systems, and adhering to labeling requirements guarantee product safety, transparency, and legal obligations. Optimizing efficiency, minimizing waste, exploring cost-effective packaging solutions, implementing streamlined supply chain processes, and evaluating ROI contribute to overall productivity and profitability.
By following these guidelines and continuously seeking opportunities for improvement, you can effectively add value to your crops through processing and packaging, ensuring success in the competitive market.
More info.
The article How Can I Add Value To My Crops Through Processing Or Packaging? first appeared on https://www.66thlondon.org.
https://pinkribbonmail.com/how-can-i-add-value-to-my-crops-through-processing-or-packaging/
0 notes
Link
Check out this listing I just added to my Poshmark closet: Small coach black hobo style purse.
0 notes
Text



North Union Shaker Site
South Park Boulevard
Shaker Heights OH
North Union Shaker Site is a historic site along Shaker Run below Upper Shaker Lake in Shaker Heights, Ohio. The site was founded by Shakers in 1822 by Ralph Russell. Russell, originally from Connecticut, who converted neighbors and family to Shakerism. It was added to the National Register in 1974. The Shakers ran grist and grain mills from the lakes created when they dammed Doan Creek. The community ceased to exist in 1899. All of the buildings that had been part of the North Union Shaker community have been demolished, and 280 of the original 1,000 acres are Shaker Lakes parkland, which includes walking trails and a Shaker archaeological site, the Shaker Historical Museum and Library.
Ralph Russell convinced his family to convert to the Shaker sect and established the North Union Shaker Settlement in 1822 with just over 80 individuals on 1,000 acres of donated land to start the new community. In 1826, the group dammed Doan Brook, thus creating the Lower Lake and establishing a gristmill and a sawmill. The Mill family was established about 1826 to run the mills, which produced usable lumber and milled grain. By 1837 a third family unit, the Gathering Family, was established in the community. Later, in 1854, the community built a second dam creating the Upper Lake, the counterpart to Lower Lake., and constructed another mill. Also called 'The Valley of God's Pleasure,’ the colony peaked around 1850 with about 300 settlers.
There were approximately 200 Shaker songs, hymns and anthems composed at North Union. One of them was written in tribute to the Shaker leader, Ann Lee, on her arrival in New York City in 1774. It is titled, "On the Landing of Mother Ann in America." As the Shakers practiced celibacy, the colony faded away and was closed in 1889. In 1905, the land was bought by brothers M.J. and O.P. Van Sweringen who envisioned the first garden styled suburb in Ohio for the site and developed Shaker Heights, a garden-city suburb inspired by the Shaker landscapes. The brothers constructed homes, set aside land for churches and schools, and planted trees. None of the buildings from the North Union Shaker community remain.
In 1892, 280 acres of the Shaker Lakes Parklands were donated to the City of Cleveland. Today, all the buildings of the former Shaker village have been demolished, but their archeological resources remain. Public access to the archeological site is restricted to ensure its preservation. However, most of the parklands and the Shaker Lakes are accessible via walking trails. Located on land that was once the North Union apple orchard, the Shaker Historical Museum interprets the history of the Shakers who once lived here. The museum features furniture and artifacts from North Union and other Shaker National Register of Historic Places on August 13, 1974.
0 notes
Text



Beautiful converted 1900 historic mill in Quakertown, Pennsylvania has the original mill stone on the lawn, that was used to crush and grind the wheat and grains for bread. 4bds, 3ba, $885K.

I do like the entrance hall- beautiful leaded glass door.


Through the door is a vast main living space with a long stone fireplace and what looks like another millstone for a coffee table.


One step up is a very large dining room area off the kitchen.



The large eat-in modern country kitchen.

Cute half bath with a barrel sink.


Interesting how they put a wall over the stairs.


The primary bedroom is huge and look at the fireplace and stone wall. The ceiling also looks original.

One of the other bedrooms. Smaller, but a good size.

The full baths are disappointingly plain.


The home is listed as a single family but there's another big living/dining room and a kitchen up here.

These are the original hand hewn and joined beams.


There are so many large rooms, I'm wondering how much it costs for heat in the cold Pennsylvania winters.


There are rooms of work areas. The home is huge.

The water trough that drove the mill is still here.

The stucco top coat on the house is wearing off and exposing the stone. Looks like a picture.

The garden is lovely.

The mill stream flows past the large redwood deck. There's a total of 4.51 acres of land.
156 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Magic of Malt-Based Drinks: From Grains to Goodness
Have you ever wondered what makes malt-based drinks/ malt drink mix so delightful and invigorating? Join GrowVita health drink on a whimsical journey through the world of malt-based beverages, where grains transform into a liquid symphony of flavour and nutrition.

What Are Malt-Based Drinks?
Malt-based drinks are a delightful concoction crafted from malted barley, wheat, or other grains. These beverages aren’t just about refreshment; they’re a fusion of nourishment and taste, often offering a rich, malty flavour coupled with essential nutrients.
The Marvellous Manufacturing Process
Malting the Grains: It all begins with the selection of high-quality grains like barley or wheat. These grains are soaked in water, allowing them to germinate. Once they start sprouting, the germination process is halted by drying them in a controlled environment.
Milling: The dried grains are then milled into a fine powder or crushed form known as "grist."
Mashing: Grist meets hot water in a process called mashing. This concoction forms a thick liquid called "mash" where enzymes break down starches into fermentable sugars.
Fermentation: The magic happens as yeast is introduced to the mash. Yeast works its enchantment, converting sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide, creating a malty, flavorful liquid known as "wort."
Boiling and Hopping: The wort undergoes boiling to sterilise and concentrate the flavours. Hops, the magical ingredient responsible for aroma and bitterness balancing, are added during this stage.
Filtration and Cooling: Once the boiling is complete, the liquid goes through filtration to remove impurities, followed by rapid cooling to halt any further enzymatic activity.
Packaging: The final step involves packaging the liquid goodness into bottles, cans, or other containers, ready to be shared and savoured by enthusiasts around the globe.
The Charm of Malt-Based Drinks
What makes these beverages truly special is their versatility. Whether enjoyed as a standalone drink or mixed with milk for a creamier texture, malt-based drinks offer a delectable taste while serving as a source of energy and essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals.
Embrace the Magic in Every Sip
So, the next time you savour a malt-based drink, remember the intricate process that transforms humble grains into a liquid symphony. It's not just a beverage; it's a testament to the artistry and science behind creating something both delicious and nourishing.
Cheers to the whimsy and wonder found in every sip of a GrowVita malt-based drink!
For more information about: Health drink Please visit at https://growvita.in/
#malt drink mix#health drink in india for children#best protein powder for kids#chocolate drink for kids#malt based drinks#health drink#health benefit for kids#nutrition and health drink in india for kids#best health drink for child growth#nuitrition
0 notes
Text
The single malt whisky process is a meticulous journey that transforms grains into a rich, flavorful spirit. It begins with carefully selected malted barley, which is soaked in water to trigger germination. The germinated barley is then dried using hot air in a process called malting, imparting distinct flavors to the grain. Once malted, the barley undergoes milling, crushing it into coarse flour known as grist. This grist is mixed with hot water in a mash tun, initiating enzymatic reactions that convert starches into fermentable sugars. The resulting liquid, known as wort, is drained off, leaving behind spent grains. Fermentation is the next step, as yeast is introduced to the wort, initiating the transformation of sugars into alcohol. This yields a liquid known as "wash" with low alcohol content. The wash is distilled in pot stills, where alcohol vapors are separated and collected. This double distillation process refines the spirit, concentrating flavors and increasing alcohol content. After maturation, the whisky is often blended or bottled as single malt, preserving the unique characteristics of that particular distillery. It's common for distilleries to release limited editions, showcasing exceptional casks or unique finishes. Before bottling, the whisky may be filtered or diluted to achieve the desired flavor profile. The single malt whisky process is a harmonious dance of science and art, where each stage contributes to the creation of a distinctive and memorable spirit. From the careful selection of ingredients to the patient maturation process, every detail is essential in crafting a single malt whisky that captivates the senses and delights the palate.
G-17, Ground Floor, JMD Pacific Square, Sector – 15 Part 2, Gurugram (Gurgaon) – 122002, Haryana, India
Call - +91-124-4300840, +91-9996558100
Email - [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Harnessing Wind Energy: A Look at the Power Converter Market
A wind power converter market is a machine designed to convert the energy of wind movement into mechanical power. Further, this mechanical energy is converted into electricity with wind turbine generators. The power converter is required for wind turbine generators to adjust the generator frequency and voltage. This energy is used to operate various equipment such as mill grains, drive machinery, and pumping water. In addition, a power electronic converter can convert the variable frequency output of an induction generator, driven by a variable speed wind turbine. Wind turbines are similar to propeller blades of aircraft, as they rotate converting kinetic energy to mechanical power. The system is recognized as renewable, as wind energy is ecofriendly and emits no carbon dioxide. Thus, multiple benefits associated with wind power converter are anticipated to boost the growth of the global market during the forecast period.
COVID-19 impact analysis
The global market for wind power converter system has witnessed gradual growth by the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. This is attributed to the fact that the pandemic has enhanced the demand of energy utilization worldwide, as one-third of global population is staying indoors. Thus, rise in energy consumption has improved the demand for wind power converter systems, despite of global disruption in financial and other commodity markets. However, the demand for energy requirements will be low due to shut down of industries and less demand for electricity. Owing to the lockdown implemented across various countries, national and international transport have been hampered, which has significantly impacted the supply chain of numerous industries across the globe, thereby increasing the supply–demand gap. Thus, insufficiency of raw materials hampers the production rate and supply chain of the wind power converter system market.
Top impacting factors: market scenario analysis, trends, drivers, and impact analysis
The need to replace current nonrenewable energy sources such as fossils fuels, gas, and coal is the major factor contributing toward the growth of the global wind power converter system market. The market is diverting toward the adoption of renewable sources of energy and considered safe environment a vital factor. Thus, wind energy has been widely used to generate electricity. This, in turn, accelerated the consumption of electricity in commercial and other industrial processes, thereby boosting the demand for renewable wind power energy. Power converter adopts to the changing speeds continuously with respect to the changing wind velocity; thus, they have been considered as high-efficiency technology for electricity generation.
New product launches to flourish the market
The major market players have taken the necessary steps to improve the accuracy of devices and overall functionality. Increase in installation rate of wind power convertor across the globe plays a significant role in the evolution of the market. More focus is given to the design and control of power converters. New technologies have been used to increase the overall performance of the wind power convertors and to develop innovative blade manufacturing techniques. Increase in adoption of wind-induced energy harvesting devices and smart rotors is an emerging trend in the wind power converter market, which augments the global market growth.
Surge in usage in commercial and industrial applications
Manufacturers have been focusing on producing new products for specific applications as there are varying demands based on the utilization. Leading market players such as Alstom and AMSC Windtec USA Suzhou have determined how improved accuracy can be influential in many applications. The need to generate electrical power with a wide range of speeds leading to high usage of wind power converter system notably contributes toward the growth of the overall market. Furthermore, this system has the ability to capture and transfer the energy to the grid or a load.
Key benefits of the report
This study presents the analytical depiction of the global wind power converter industry along with the current trends and market estimation to determine the imminent investment pockets.
The report represents information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities along with detailed analysis of the wind power converter market share.
The current market is quantitatively analyzed to highlight the wind power converter market growth scenario.
The report provides a detailed global market analysis depending on competitive and how the competition will take shape in coming years.
This report helps users in comprehending the key product segments and their future.
0 notes
Text
How to Increase Rice Mill’s Production
Processing is a crucial stage in the production of rice post-harvest. The essential objective of a rice processing framework is to eliminate the husk and the bran layers to produce an edible, white rice kernel that is adequately processed and liberated from impurities. In addition, contingent upon the client’s prerequisites, the rice should have a minimal number of broken pieces of kernels.
Most rice assortments are made out of 20% rice hull or husk, 11% grain’s bran layers, and 69% starchy and sticky endosperm, likewise alluded to as the total processed rice.

In optimal processing, this will result in the following divisions: 20% husk, 8−12% grain contingent upon the milling degree and 68−72% processed rice or white rice-edible form- fit for human consumption, depending on the assortment. Absolute processed rice contains whole grains or head rice and broken rice. The rice hull, rice germ and bran layers, and fine broken are the by-products of the rice milling process.
The quantity of outcome during milling is subject to various factors like the variety of paddy, the level or degree of milling process required, the quality of the milling mechanism utilized and other processing frameworks that perform processing of the paddy in stages. Therefore, the businesses of rice milling strive to lessen mechanical burdens and heat developed in the grain to limit grain breakage and produce consistently polished grain.
The excellent quality of the paddy and the accuracy of the rice milled are the two essential determiners for recovering the best quality rice. Thereby, to get high output, we need to follow the stringent procedures for the upkeep of the milling machinery, like:
1) Rice must not bounce back nor rotate within Bucket Elevator
The space between the elevator’s Bucket and tongue must be maintained at 2.5 – 3 mm, to be precise. If the distance between the two changes, a relatively some amount of recovery material rotates in the elevator repeatedly, affecting the machine’s productivity. Even 10 per cent of the disrupted output can cause a considerable disturbance, bringing down the production efficiency.
2) By Increasing Life of Elevator, Pulley and Belt and Bucket
The elevator’s belt must be placed accurately at the centre with respect to the pulleys located towards the two ends i.e. top and bottom of the vertical machine. Even if the belt shifts slightly to either side, the repercussion may be huge. It may cause damage to the belt, stressing down the motor of the machine and eventually reducing the possibility of achieving the optimum production level of the equipment.
3) Must maintain Uniform Air Suction level to properly separate Paddy/Rice and Stone
For the paddy destoner mechanism, the recommended air suction level is between 70-80 megapascal, which is a must. Failure to adjust to optimum pressure measurements may lead to inefficient machine functioning and low milling output. In low or high air pressure, sheer energy will be converted into heat, but the bran shall stay unremoved. In addition, it may result in a significant amount of paddy being discharged and discarded along with the stones separated by the machines.
The grease must be changed within 72 hours according to the machines’ use in the husker and paddy de-separator. A lapse in grease changing may adversely affect the bearings and rubber roll of the device, which decreases the machine’s life and increases the broken rice percentage.
4) Pass more material with less external weight in Whiteners for increasing head rice percentage
Whitener is a machine used for removing the bran layer from the rice, rendering it a white appearance. The load of the rice material and the external weight applied to hold the rice in place are inversely related. Therefore, to maximize the device’s efficiency and check the broken rice percentage, an optimal input load of the material must be maintained. Consequently, it reduces the use of external weights. Conversely, if the input load of material or rice is less than the requirement, the external weights are applied. Less load with less weight may increase the broken percentage, causing the material to flow off the machine with the bran layer still on it. In addition, the whitening process applies pressure to the grain, which may cause cracking and breakage of some kernels. Therefore, emphasis must be laid on more material with less external weight.
5) Must maintain more shining with less broken in Silky Polisher
Considering two-stage whitening – Having two stages in the polishing process will reduce the grain’s overheating and allow the operator to set independent machine settings for each step. In addition, it will ensure higher milling and head rice recovery. In the first silky polisher machine, the water level must be high with less material weight. For the second processing machine, vice versa of the first must be followed.
6) By removing sticked Bran layer into the inner walls of the whitener/polisher’s pipeline
The sticky and oily characteristics of the bran layers removed from the brown rice tend to stick into the inner walls of the whitener/polisher’s pipeline, reducing the output of the machines. Therefore, the pipeline needs regular and thorough cleaning to address this issue. Cleaning must be carried out once in a week for a new, well-maintained machine. With the machine’s increasing age, the interval between cleaning also reduces.
7) Must Give Proper Training to Operator/Foreman
The operator’s knowledge and skill for operating the high-graded technology machines are of utmost importance. Running your milling machine with the assigned method is vital for more output to follow. Furthermore, the rice processing equipment adjusts to explicit configurations, with the processing parts varying in plan and performance. With this, monitoring maintenance and replacing spare parts regularly, as and when required, is vital. Therefore, a good and efficient operator can add a few extra years to the life of machines.
8) Tanks of the whitener and polisher must be cleaned after every use
The tanks of the whitener and polisher must be cleaned after every use. There must not be any residue or leftover stock material in the tanks, as it may negatively impact production.
9) Increase production by regularly cleaning of machines
Keeping the machines clean always is an unstated mandate. Regular and consistent cleaning with proper oiling and greasing of the rice milling machines are necessary for their upkeep and ease the devices to reach their optimum production level.
Encouraging and enhancing the education and training allows the miller’s operations team to remain competitive to address the difficulties as they change and utilize the plant’s potential to the maximum.
Sona Machinery Ltd. is a leading Agro-processing machinery manufacturer and exporter specializing in rice mill projects in India and abroad and at the forefront of Rice Mill Turnkey Solutions. Specially trained Sona Machinery experts pass on their skills and expert knowledge in our innovation and training centres. Sona offers an encompassing array of training and consistent education options, either locally at the mill site or its instructional training centres. The consultancy service includes performance analysis of mills and machinery insights on improvements in machines and operations. The ready availability of reliable parts and spares of servicing mills ensures optimal and consistent output.
Sona Machinery offers optimized Rice Mill Machine Design, incorporating the best techno features ideal for modern innovative machines and solutions.
A 26+ years old association shining bright with a demonstrated history has explored advancement in every project it has been planning, designing, engineering, and executing that summing up to more than 10000 customers across the globe. With its immense experience, Sona Machinery Ltd. has the expert knowledge and skill to handle operational challenges even as it is at the forefront of modifying and customizing technology in the rice milling sector. Moreover, with a mission to deliver world-class, cutting edge technology products and services to its customers, Sona Machinery is readily available to provide project management support.
Source: https://www.sonamachinery.com/blog/6386f88e9cb1b0ed73980248
0 notes
Text
6 Types of Raw Materials Commonly Used in the Production of Feed and The Role of the Conditioner
The main raw materials of feed are mainly divided into the following types:
1. Feed ingredients that contain a lot of starch
These feeds are mainly composed of grains, seeds, and roots or tubers containing a large amount of starch. For example, all kinds of grains, potatoes, wheat, barley, beans, etc. These feeds mainly provide energy through polysaccharides and contain little protein. They are suitable for ruminants, poultry, and pigs, but feeds containing too much starch are not suitable for horses. After being processed by a pellet feed-making machine, their starch is converted into nutrients and absorbed by animals.
2. Oily-containing feed ingredients
These feeds are composed of oily seeds (rape, soybean, sunflower, peanut, cottonseed), etc. The energy of these feeds mainly comes from lipids, so their energy density is higher than that of feeds containing starch. The protein content of these feeds is also relatively low. Because these oils also have industrial uses, the popularity of such feed is not high.
The residue left after industrial oil pressing still contains quite a high oil content. Such residue can also be used as feed, especially for ruminants, and is also widely used. For example, adding rapeseed oil residue to the chicken feed machine to make chicken feed can improve the egg-laying rate.
3. Sugary-containing feed ingredients
These feeds are mainly straw feed or pellet feed based on "sweet sorghum straw". The sugar content of sweet sorghum straw is 18% - 23%, and the animal palatability is very good.



4. Protein-containing feed materials
These feeds are mainly plant protein feeds based on the protein mulberry. The plant protein of protein mulberry reaches 28% - 36% and is rich in 18 kinds of amino acids. It is the best raw material to replace plant protein.
5. Green feed ingredients
In these feeds, the whole plant is fed, such as grass, corn, grain, etc. These feeds contain a lot of carbohydrates, and the nutrition is very miscellaneous. For example, grass mainly contains carbohydrates, 15% to 25% protein, while corn contains more starch (about 20% to 40%) and less than 10% protein. The green feed can be fed fresh or stored after drying. They are more suitable for ruminants, horses, and waterfowl. You don't usually feed pigs. The green feed preserved after fermentation is called silage.
6. Other feed ingredients
In addition to the above-mentioned feeds, there are many other kinds of feeds, which can be directly from nature (such as the fish meal) or industrial replicas (such as rice bran, distiller grains, leftovers, etc.). Different livestock use different feeds, but these feeds are especially suitable for ruminants.
Function of conditioner


4. The conditioning equipment can improve the granulation of materials, increase the output, save the energy consumption of granulation, and improve the service life of the die and roller of the granulator. Through quenching and tempering, the material can be softened and more plastic. In the extrusion process with the die hole wall, the die inner wall, and the surface of the pressure roller, the friction is reduced, which avoids the transformation of a large amount of mechanical energy into heat energy in the granulation process, and slows down the wear of the die and the pressure roller.
Henan Herm Machinery Co., Ltd was established in 2010 and has been devoted to the research and development of Feed Mill Machinery ever since. With more than 10 years of experience, Herm® has become a leading manufacturer and supplier of animal feed machines and complete animal feed production lines, cattle feed plants, poultry feed plants, animal feed pellet production lines, etc. It always endeavored to improve the quality of products and aims to meet the new requirements of the international market.
If You Are Ready to Start a Feed Pellet Plant Business, please contact us for the feed mill machine. We Can Provide Professional Design and Comprehensive Guidance According to Your Needs. Get in touch with us now!
Welcome Contact Us!
Henan Herm Machinery Co., Ltd
Email: [email protected]
Phone/Whatsapp: 86-18037508651
0 notes