#Supreme Court History
Note
Could you recommend books on the Supreme Court? I honestly didn’t think there were any.
There are countless numbers of books about the Supreme Court, so it really depends on what exactly you're interested in reading about, whether that might be a general history of the Court itself, biographies of the most influential justices, landmark cases, and so on.
By no means is this a complete list, but here's some suggestions that I can recommend:
GENERAL HISTORY OF THE SUPREME COURT
•A People's History of the Supreme Court: The Men and Women Whose Cases and Decisions Have Shaped Our Constitution by Peter Irons (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•Nine Scorpions in a Bottle: Great Judges and Cases of the Supreme Court by Max Lerner and edited by Richard Cummings (BOOK)
•The Supreme Court by William H. Rehnquist (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO) -- This history of the Court is especially interesting because it was written by the incumbent Chief Justice.
•The Nine: Inside the Secret World of the Supreme Court by Jeffrey Toobin (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
BOOKS ABOUT SPECIFIC JUSTICES OR COURTS
•The Oath: The Obama White House and the Supreme Court by Jeffrey Toobin (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•Leaving the Bench: Supreme Court Justices at the End by David N. Atkinson (BOOK) -- A unique book about Justices at the end of their time on the Court and how they ultimately left the Court. Most of them died in office because the Court is a lifetime appointment, but the book looks at how some Justices held on to their seats and remained on the bench despite failing health or faltering cognitive abilities.
•First: Sandra Day O'Connor by Evan Thomas (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•Sisters In Law: How Sandra Day O'Connor and Ruth Bader Ginsburg Went to the Supreme Court and Changed the World by Linda Hirshman (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO) -- An excellent dual biography about the first two women ever appointed to the Supreme Court and the impact they had on American law.
•The Brethren: Inside the Supreme Court by Bob Woodward and Scott Armstrong (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO) -- The legendary journalist from the Washington Post gives the Woodward treatment to the Supreme Court presided over by Chief Justice Warren E. Burger.
•The Showdown: Thurgood Marshall and the Supreme Court Nomination That Changed America by Wil Haygood (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO) -- The remarkable life of Thurgood Marshall, who was already a legendary figure in the annals of American justice as a civil rights lawyer who successfully argued the case the led to the Supreme Court striking down Brown v. the Board of Education. Marshall's place in history became even more important when President Lyndon B. Johnson nominated him as the first-ever Black Supreme Court Justice.
•Five Chiefs: A Supreme Court Memoir by John Paul Stevens (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO) -- This is probably my favorite of the recommendations. John Paul Stevens, the third longest-serving Justice in the history of the Supreme Court, writes about the five Chief Justices (Fred Vinson, Earl Warren, Warren E. Burger, William H. Rehnquist, and John Roberts) that he worked for or with throughout his long career, beginning as a law clerk under Chief Justice Vinson and eventually serving as Associate Justice alongside Chief Justice Burger, Chief Justice Rehnquist, and Chief Justice Roberts.
BOOKS ABOUT JOHN MARSHALL (Longest-serving Chief Justice of the United States and arguably the most important judge in American history)
•John Marshall: The Chief Justice Who Saved the Nation by Harlow Giles Unger (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•Without Precedent: Chief Justice John Marshall and His Times by Joel Richard Paul (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•John Marshall: The Man Who Made the Supreme Court by Richard Brookhiser (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
I also strongly recommend checking out James F. Simon's books about the Supreme Court and the Presidency, which focus on the impact that the Court and the Chief Justices at the time had on specific Presidential Administrations. These are all written by James F. Simon:
•Eisenhower vs. Warren: The Battle for Civil Rights and Liberties (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•Lincoln and Chief Justice Taney: Slavery, Secession, and the President's War Powers (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•What Kind of Nation: Thomas Jefferson, John Marshall, and the Epic Struggle to Create a United States (BOOK | KINDLE | AUDIO)
•FDR and Chief Justice Hughes: The President, the Supreme Court, and the Epic Battle Over the New Deal (BOOK | KINDLE)
#History#Supreme Court#Supreme Court History#Books#Book Suggestions#Book Recommendations#Supreme Court Books#Judiciary#Judicial Branch#Chief Justice of the United States#Chief Justices#John Paul Stevens#John Marshall#James F. Simon#Thurgood Marshall#William H. Rehnquist#Sandra Day O'Connor#Ruth Bader Ginsburg#RBG
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
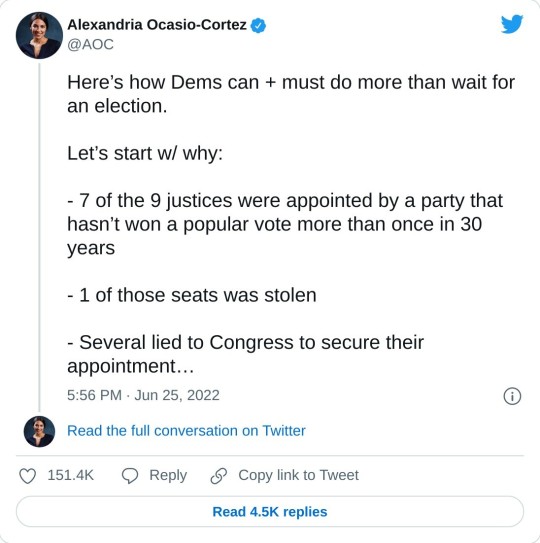
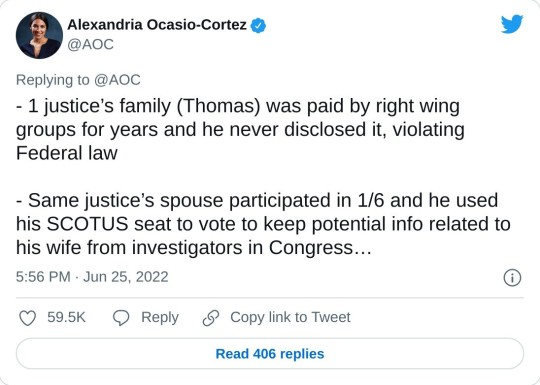
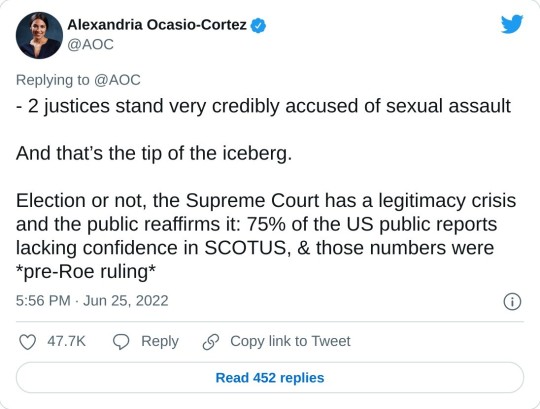
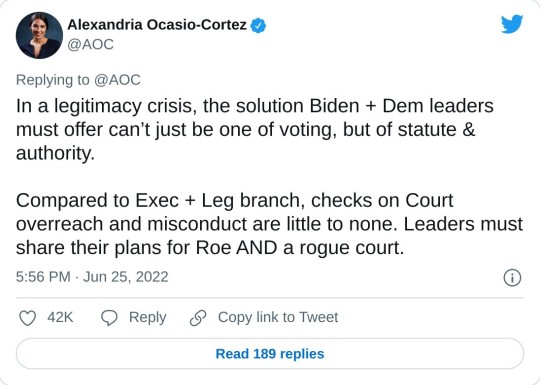
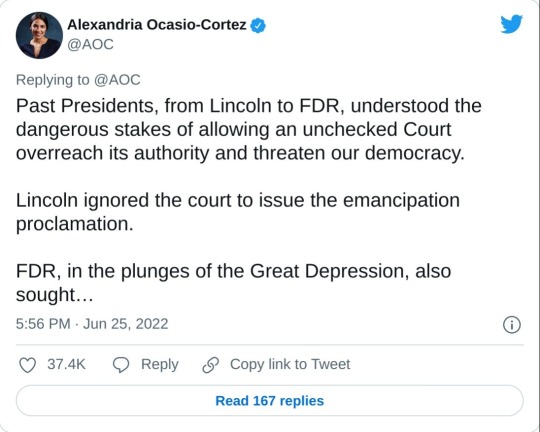
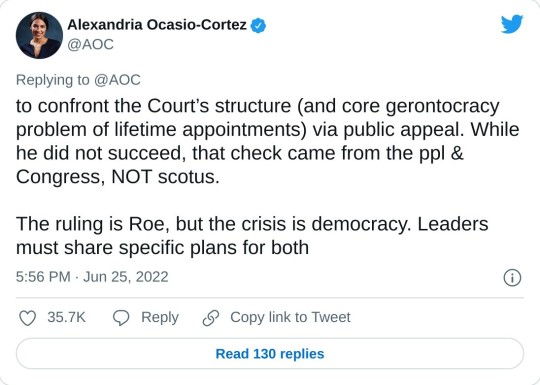
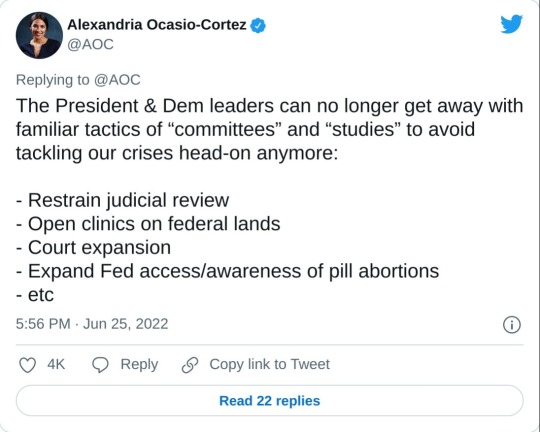
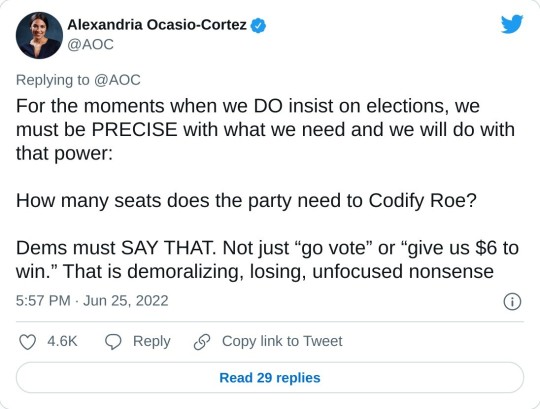
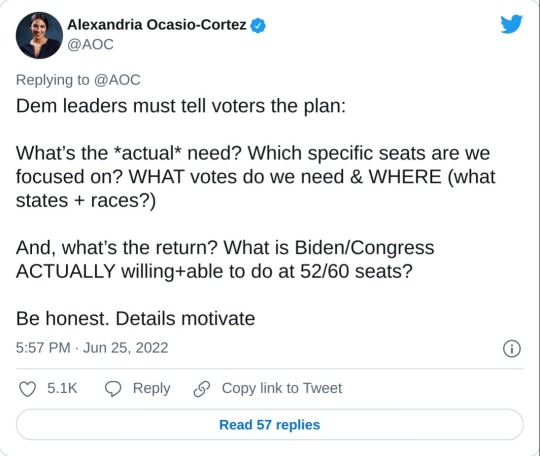
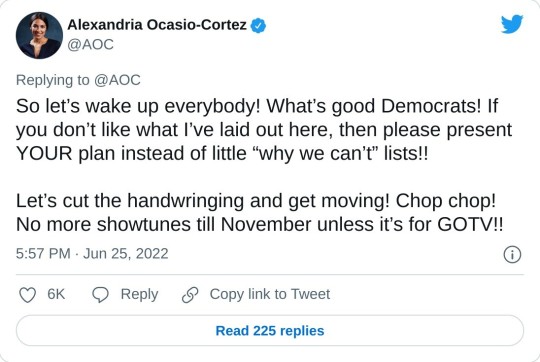
#us supreme court#2022 elections#2022 midterms#us congress#us house of representatives#us senate#biden administration#rep. alexandria ocasio cortez#new york#us history#President Franklin d. Roosevelt#president abraham lincoln#abortions#abortion bans#roe v. wade#scotus#us politics#news#twitter#tweet#2022#progressives#progressivism#democrats
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
On This Day In History
June 26th, 2003: The Supreme Court of the United States rules in Lawrence v. Texas that gender-based anti-sodomy laws are unconstitutional, based on the same "right to privacy" that Roe v. Wade helped to establish. It is a 6-3 ruling.
June 26th, 2013: The Supreme Court of the Unites States rules in United States v. Windsor that Section 3 of the Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA) that denied federal recognition of same-sex marriages was unconstitutional, based on the Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment. It is a 5-4 ruling.
June 26th, 2015: The Supreme Court of the United States rules in Obergefell v. Hodges that the fundamental right to legally recognized marriages must be extended to same-sex couples, based on the Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment and the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. It is a 5-4 ruling.
#history#gay history#queer history#politics#supreme court#Lawrence v. Texas#sodomy#United States v. Windsor#gay marriage#gay rights#Obergefell v. Hodges#civil partnerships
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
the girlbossification of ruth bader ginsburg has to be one of the most just plain annoying aspects of white liberal feminism. like it's not as actively harmful as a lot of other shit obviously. but it is soooooo annoying. if I never see another notorious rbg tote bag as long as I live it will be too soon
#her opinions and amicus' in many cases were iconic! not denying that certainly. she is absolutely AMONG the better justices in us history#HOWEVER her record on policing/the carceral system is very bad! genuinely bad!#and she just would not hold the conservative justices accountable. her and kagan are way too placating#and then she refused to retire in 2009 when there was a sitting democratic president and a fucking DEMOCRATIC SUPER MAJORITY#saying basically that no one else could do the job as well as her which is insane because sotomayor and KBJ literally are better :/#its also unbelievably conceited and just incredibly fucking selfish to knowingly doom the country because you think youre hot shit#started ranting abt this at work bc literally any talk even adjacent to the supreme court will set me off abt all of us court history#and my coworker was like 'well i dont think its very fair that she had to have that much riding on her decision to retire'#it literally is fair because that is the fucking job that she signed up for. this has literally always been how it fucking works#its a lifetime appointment. you either die unexpectedly or retire strategically#she accepted a position in which the entire country would depend on her but its not fair for the entire country to depend on her???#bullshit#im not fucking buying it. she did this knowing roe would likely be struck down as a result#she should absolutely be held accountable for that lmfao. you can know that she had a hand in a lot of great decisions for this country#while also knowing that she did a fucked up and extremely selfish thing
84 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Supreme Court ruled that the Defense of Marriage Act was unconstitutional on June 26, 2013.
In U.S. v Windsor, SCOTUS held that the federal government could not discriminate against same-sex couples.
Record Group 267: Records of the Supreme Court of the United States
Series: Appellate Jurisdiction Case Files
Transcription:
[Stamped: " FILE COPY "]
(Bench Opinion) OCTOBER TERM, 2012 1 [Handwritten and circled " 1" in upper right-hand corner]
Syllabus
NOTE: Where it is feasible, a syllabus (headnote) will be released, as is
being done in connection with this case, at the time the opinion is issued.
The syllabus constitutes no part of the opinion of the Court but has been
prepared by the Reporter of Decisions for the convenience of the reader.
See United States v. Detroit Timber & Lumber Co., 200 U.S. 321, 337.
SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
Syllabus
UNITED STATES v. WINDSOR, EXECUTOR OF THE
ESTATE OF SPYER, ET AL.
CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF APPEALS FOR
THE SECOND CIRCUIT
No. 12-307. Argued March 27, 2013---Decided June 26, 2013
The State of New York recognizes the marriage of New York residents
Edith Windsor and Thea Spyer, who wed in Ontario, Canada, in
2007. When Spyer died in 2009, she left her entire estate to Windsor.
Windsor sought to claim the federal estate tax exemption for surviv-
ing spouses, but was barred from doing so by §3 of the federal Defense
of Marriage Act (DOMA), which amended the Dictionary Act---a
law providing rules of construction for over 1,000 federal laws and
the whole realm of federal regulations-to define "marriage" and
"spouse" as excluding same-sex partners. Windsor paid $363,053 in
estate taxes and sought a refund, which the Internal Revenue Service
denied. Windsor brought this refund suit, contending that DOMA vi-
olates the principles of equal protection incorporated in the Fifth
Amendment. While the suit was pending, the Attorney General notified
the Speaker of the House of Representatives that the Department
of Justice would no longer defend §3's constitutionality. In re-
sponse, the Bipartisan Legal Advisory Group (BLAG) of the House of
Representatives voted to intervene in the litigation to defend §3's
constitutionality. The District Court permitted the intervention. On
the merits, the court ruled against the United States, finding §3 un-
constitutional and ordering the Treasury to refund Windsor's tax
with interest. The Second Circuit affirmed. The United States has
not complied with the judgment.
Held:
1. This Court has jurisdiction to consider the merits of the case.
This case clearly presented a concrete disagreement between oppos-
ing parties that was suitable for judicial resolution in the District
Court, but the Executive's decision not to defend §3's constitutionali-
[page 2]
2 UNITED STATES v. WINDSOR
Syllabus
ty in court while continuing to deny refunds and assess deficiencies
introduces a complication. Given the Government's concession, ami-
cus contends, once the District Court ordered the refund, the case
should have ended and the appeal been dismissed. But this argu-
ment elides the distinction between Article Ill's jurisdictional re-
quirements and the prudential limits on its exercise, which are "es-
sentially matters of judicial self-governance." Warth v. Seldin, 422
U. S. 490, 500. Here, the United States retains a stake sufficient to
support Article III jurisdiction on appeal and in this Court. The re-
fund it was ordered to pay Windsor is "a real and immediate econom-
ic injury," Hein v. Freedom From Religion Foundation, Inc., 551 U. S.
587, 599, even if the Executive disagrees with §3 of DOMA. Wind-
sor's ongoing claim for funds that the United States refuses to pay
thus establishes a controversy sufficient for Article III jurisdiction.
Cf. INS v. Chadha, 462 U. S. 919.
Prudential considerations, however, demand that there be "con-
crete adverseness which sharpens the presentation of issues upon
which the court so largely depends for illumination of difficult consti-
tutional questions." Baker v. Carr, 369 U. S. 186, 204. Unlike Article
III requirements---which must be satisfied by the parties before judi-
cial consideration is appropriate---prudential factors that counsel
against hearing this case are subject to "countervailing considera-
tions [that] may outweigh the concerns underlying the usual reluc-
tance to exert judicial power." Warth, supra, at 500-501. One such
consideration is the extent to which adversarial presentation of the
issues is ensured by the participation of amici curiae prepared to de-
fend with vigor the legislative act's constitutionality. See Chadha,
supra, at 940. Here, BLAG's substantial adversarial argument for
§3's constitutionality satisfies prudential concerns that otherwise
might counsel against hearing an appeal from a decision with which
the principal parties agree. This conclusion does not mean that it is
appropriate for the Executive as a routine exercise to challenge stat-
utes in court instead of making the case to Congress for amendment
or repeal. But this case is not routine, and BLAG's capable defense
ensures that the prudential issues do not cloud the merits question,
which is of immediate importance to the Federal Government and to
hundreds of thousands of persons. Pp. 5-13.
2. DOMA is unconstitutional as a deprivation of the equal liberty of
persons that is protected by the Fifth Amendment. Pp. 13--26.
(a) By history and tradition the definition and regulation of mar-
riage has been treated as being within the authority and realm of the
separate States. Congress has enacted discrete statutes to regulate
the meaning of marriage in order to further federal policy, but
DOMA, with a directive applicable to over 1,000 federal statues and
[NEW PAGE]
Cite as: 570 U.S._ (2013) 3
Syllabus
the whole realm of federal regulations, has a far greater reach. Its
operation is also directed to a class of persons that the laws of New
York, and of 11 other States, have sought to protect. Assessing the
validity of that intervention requires discussing the historical and
traditional extent of state power and authority over marriage.
Subject to certain constitutional guarantees, see, e.g., Loving v.
Virginia, 388 U.S. 1, "regulation of domestic relations" is "an area
that has long been regarded as a virtually exclusive province of the
States," Sosna v. Iowa, 419 U. S. 393, 404. The significance of state
responsibilities for the definition and regulation of marriage dates to
the Nation's beginning; for "when the Constitution was adopted the
common understanding was that the domestic relations of husband
and wife and parent and child were matters reserved to the States,"
Ohio ex rel. Popovici v. Agler, 280 U. S. 379, 383-384. Marriage laws
may vary from State to State, but they are consistent within each
State.
DOMA rejects this long-established precept. The State's decision
to give this class of persons the right to marry conferred upon them a
dignity and status of immense import. But the Federal Government
uses the state-defined class for the opposite purpose---to impose re-
strictions and disabilities. The question is whether the resulting injury
and indignity is a deprivation of an essential part of the liberty
protected by the Fifth Amendment, since what New York treats as
alike the federal law deems unlike by a law designed to injure the
same class the State seeks to protect. New York's actions were a
proper exercise of its sovereign authority. They reflect both the
community's considered perspective on the historical roots of the in-
stitution of marriage and its evolving understanding of the meaning
of equality. Pp. 13--20.
(b) By seeking to injure the very class New York seeks to protect,
DOMA violates basic due process and equal protection principles ap-
plicable to the Federal Government. The Constitution's guarantee of
equality "must at the very least mean that a bare congressional de-
sire to harm a politically unpopular group cannot" justify disparate
treatment of that group. Department of Agriculture v. Moreno, 413
U. S. 528, 534-535. DOMA cannot survive under these principles.
Its unusual deviation from the tradition of recognizing and accepting
state definitions of marriage operates to deprive same-sex couples of
the benefits and responsibilities that come with federal recognition of
their marriages. This is strong evidence of a law having the purpose
and effect of disapproval of a class recognized and protected by state
law. DOMA's avowed purpose and practical effect are to impose a
disadvantage, a separate status, and so a stigma upon all who enter
into same-sex marriages made lawful by the unquestioned authority
[page 3]
4 UNITED STATES v. WINDSOR
Syllabus
of the States.
DOMA's history of enactment and its own text demonstrate that
interference with the equal dignity of same-sex marriages, conferred
by the States in the exercise of their sovereign power, was more than
an incidental effect of the federal statute. It was its essence. BLAG's
arguments are just as candid about the congressional purpose.
DOMA's operation in practice confirms this purpose. It frustrates
New York's objective of eliminating inequality by writing inequality
into the entire United States Code.
DOMA's principal effect is to identify and make unequal a subset of
state-sanctioned marriages. It contrives to deprive some couples
married under the laws of their State, but not others, of both rights
and responsibilities, creating two contradictory marriage regimes
within the same State. It also forces same-sex couples to live as mar-
ried for the purpose of state law but unmarried for the purpose of
federal law, thus diminishing the stability and predictability of basic
personal relations the State has found it proper to acknowledge and
protect. Pp. 20-26.
699 F. 3d 169, affirmed.
KENNEDY, J., delivered the opinion of the Court, in which GINSBURG,
BREYER, SOTOMAYOR, and KAGAN, JJ., joined. ROBERTS, C. J., filed a
dissenting opinion. SCALIA, J., filed a dissenting opinion, in which
THOMAS, J., joined, and in which ROBERTS, C. J., joined as to Part I.
ALITO, J., filed a dissenting opinion, in which THOMAS, J., joined as to
Parts II and III.
[NEW PAGE]
Cite as: 570 U. S. _ (2013) 1
Opinion of the Court
NOTICE: This opinion is subject to formal revision before publication in the
preliminary print of the United States Reports. Readers are requested to
notify the Reporter of Decisions, Supreme Court of the United States, Washington,
D. C. 20543, of any typographical or other formal errors, in order
that corrections may be made before the preliminary print goes to press.
SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
No. 12-307
UNITED STATES, PETITIONER v. EDITH SCHLAIN
WINDSOR, IN HER CAPACITY AS EXECUTOR OF THE
ESTATE OF THEA CLARA SPYER, ET AL.
ON WRIT OF CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF
APPEALS FOR THE SECOND CIRCUIT
[June 26, 2013]
JUSTICE KENNEDY delivered the opinion of the Court.
Two women then resident in New York were married
in a lawful ceremony in Ontario, Canada, in 2007. Edith
Windsor and Thea Spyer returned to their home in New
York City. When Spyer died in 2009, she left her entire
estate to Windsor. Windsor sought to claim the estate tax
exemption for surviving spouses. She was barred from
doing so, however, by a federal law, the Defense of Mar-
riage Act, which excludes a same-sex partner from the
definition of "spouse" as that term is used in federal stat-
utes. Windsor paid the taxes but filed suit to challenge
the constitutionality of this provision. The United States
District Court and the Court of Appeals ruled that this
portion of the statute is unconstitutional and ordered the
United States to pay Windsor a refund. This Court granted
certiorari and now affirms the judgment in Windsor's
favor.
I
In 1996, as some States were beginning to consider the
concept of same-sex marriage, see, e.g., Baehr v. Lewin, 74
#archivesgov#June 26#2013#2010s#Pride#LGBTQ+#LGBTQ+ history#U.S. v Windsor#Defense of Marriage Act#same-sex marriage#Supreme Court#SCOTUS
143 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, this is REALLY important. Trump is hogging up so much GOP donor money that local GOP candidates are starving. The upcoming presidential election is an opportunity to really punish republicans IF YOU KIDS ALL VOTE. So please register and vote!!! We need you💙
#us history#trump#southern strategy#gqp#gop#republicans#abortion rights#civil rights#separation of church and state#fix the broken supreme court#lgbtq rights
68 notes
·
View notes
Note
I feel like FDR overplayed his hand after the 1936 Election when he proposed the Judicial Procedures Reform Bill of 1937, with not only were Southern Conservative Democrats opposed to it, but a good number of Northern Liberals opposed it as well. So my question is, if instead of proposing the JPRB, what do you think happens if he proposes a Constitutional Amendment to make his New Deal legislation unequivocally constitutional? Do you think it is passed and ratified?
I asked @warsofasoiaf, but I'm interested to see what you think.
Speaking as an expert on the New Deal, I think FDR's bigger mistake after the 1936 election was his decision to hit the breaks on New Deal spending programs in 1937, which caused a recession and seriously damaged the foundation of his political coalition at the same time that he was fighting his campaign against the Hughes Court.
That being said, I don't think a Constitutional Amendment would have been less controversial than the Judicial Procedures Reform Bill, and I agree with @warsofasoiaf that it would have been the heavier lift.
Even if the 1937 bill had been a straightforward expansion of the Supreme Court (in line with previous Judiciary Acts) without the stupid ageist mechanism of the OTL plan or if Roosevelt had pulled a Jackson and simply refused to enforce the Court's decision in Schecter, I think Roosevelt would have faced much the same opposition from Dixiecrats fearing that the Supreme Court might erode or outright strike down Jim Crow, and from liberals more devoted to proceduralism over consequentalism - any changes would have been at the margins, and unlikely to have changed the outcome of any votes.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

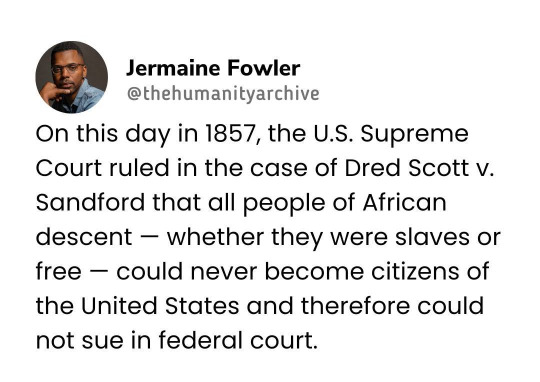

#racism#white racial hatred#white supremacy#white evil#dred scott v. sandford#u.s. supreme court#citizenship rights#racial discrimination#legal precedent#civil rights history#slavery#judicial activism#constitutional interpretation
16 notes
·
View notes
Photo

IN THESE TIMES
In mid-January, Montana state Senator Keith Regier floated the idea of a bill that would call on federal lawmakers to investigate alternatives to the tribal reservation system, created by federal legislation in 1851 in an effort to silo Native American people, remove them from their traditional way of life and create space for white settlers. Regier claimed he was motivated by genuine concern for the “lives and well-being” of Native Americans and all Montanans, asserting the system was built on race and that reservations are not “in the best interests of either the Indians inside our borders or for our common Montana citizen.” But Native lawmakers and tribal advocates saw it as something different: the latest, and perhaps most blatant, but far from only attempt to undermine tribal sovereignty.
“They knew exactly what they were doing,” said Travis McAdam, who directs pro-democracy efforts at the Montana Human Rights Network. The text of Regier’s draft resolution refers to substance abuse, domestic violence, poverty and dependence on welfare systems. “It was really slandering them with these gross, racist stereotypes that have existed for a long time,” McAdam said. “The draft was an offensive piece of legislation.”
After swift pushback from the Montana American Indian Caucus and activists, political will for the legislation dissipated, and Rieger announced he would not formally introduce a bill.
Still, an even more serious threat to tribes across the entire country looms large. A decision on the Supreme Court case Brackeen v. Haaland—a direct assault on the constitutionality of the Indian Child Welfare Act (ICWA), and by extension, the very right of tribes to be classified as sovereign nations — is expected later this month.
Enacted in 1978, ICWA was part of the federal government’s efforts to rectify the incomprehensible harm it caused to Native families through the forcible removal of Native children from their communities into boarding schools or non-Native foster and adoptive homes. Between 1819 and 1969, hundreds of thousands of children were taken from their families and homes.
ICWA establishes minimum standards for a Native child to be removed from their home and empowers tribes to be more involved in adoption and custody procedures for kids enrolled or eligible to enroll in tribal nations. The law gives tribal courts exclusive jurisdiction over members who live on tribal land, in the hopes of keeping families together, and creates a process whereby they’re noticed and involved in cases outside of these boundaries.
For years, people and organizations hostile to ICWA have tried to erode the legislation through the court system. Should ICWA fall, it’s not only adoption and foster cases that will be gravely impacted; the basic foundations of tribal sovereignty could be unwound. Observers in Indian Country have long believed that attacks on the legislation have broader aims in mind than the wellbeing of children, and many anti-ICWA proponents are also perceived as gunning for access to natural resources, mineral rights and more.
(Continue Reading)
#politics#the left#in these times#native american rights#indigenous rights#supreme court#racial justice#discrimination#history
93 notes
·
View notes
Link
#Supreme Court#History#Judiciary#Judicial Branch#U.S. Supreme Court#Supreme Court Justices#Chief Justice of the United States#Supreme Court History#New York Times
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
This order is a colossal victory for Trump, and could potentially allow him to evade criminal responsibility for his attempts to overthrow the 2020 election altogether. Trump’s goal is to delay his trials until after Election Day. Should he prevail in that election, he can then order the Justice Department to drop all federal charges against him.
The Lowest Court in the land once again showed themselves to be nothing but Corrupt Political Hacks.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
On This Day In History
November 13th, 1922: Zucht v. King United States Supreme Court upholds mandatory vaccinations in public schools in a 9-0 ruling, even if there was no ongoing outbreak.
#history#world history#united states history#scotus#vaccinations#vaccines#zucht v king#supreme court#legislative history#smallpox
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
Welcome to Episode 3 of Hidden Medical History. Did you know that forced sterilization is still legal in the United States because of a 1927 Supreme Court case known as Buck v. Bell? There’s a history of eugenics being used on low-income people, people of color, disabled people and people deemed as “social deviants.” Let’s dive into the history of this Supreme Court case to better understand how laws continue to legalize this.
#tiktok#medical history#eugenics#us supreme court#reproductive rights#reproductive health#reproductive justice
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
It cannot be overstated just how earth-shattering Alito’s leaked Supreme Court opinion is - not simply for its dismantling of womens’ bodily autonomy (though that in itself is egregious enough) but also for how it goes about overturning the foundational precedent Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey are built on: the right to privacy and the due process clauses as outlined in the 14th Amendment.
Roe and Casey work on the precedent that the “privacy” of the 14th Amendment can be applied to a woman’s personal medical decisions. This is what’s called an “unenumerated right,” or a right that is implied to exist based off of what other laws say. For instance, the right to a public defender isn’t stated in the constitution at all, but was implied to exist because of a Supreme Court decision in 1963. Alito’s opinion however, asserts that a right must “must be deeply rooted in this Nation's history and tradition.”
The fuck does that mean?
Y’see, as an Originalist (like Amy Coney Barrett), Alito is concerned with the original public meaning of a law at the time it was written.
To an Originalist, since the 14th Amendment was drafted in 1868 - a time when most states criminalized abortion - to apply a “modern” interpretation of privacy to abortion like Roe did twists the 14th Amendment beyond what the drafters would have ever intended or even considered, which to Alito and other Originalists like him is Constitutional anathema.
So why is this legalese important?
Simple: while Alito insists that Roe v. Wade is a special case because abortion is a unique issue, that doesn’t change the fact that his Originalist interpretation of the 14 Amendment will topple that privacy precedent, setting a brand new legal precedent that can be applied to a huge number cases that were also decided on the 14th’s Privacy and Due Process clauses. Rights that may also lack the “history and tradition” that Alito so treasures.
What other unenumerated rights does this endanger? To name a few:
Interracial marriage (Loving v. Virginia)
The right to a public defender (Gideon v. Wainwright)
“Miranda Rights,” or a person’s legal rights being read to them by police during arrest (Miranda v. Arizona)
The right to buy and use contraceptives (Griswold v. Connecticut)
The illegality of sodomy laws (Lawrence v. Texas)
Same-sex marriage (Obergefell v. Hodges)
Overruling Roe and Casey isn’t solely a horrible miscarriage of justice for women’s reproductive rights. If the legal logic of Alito’s draft carries into the Court’s final decision, then the legal precedence that toppled it will be legitimized and could theoretically be applied to...well. Pretty much all modern civil rights.
Now, Alito assures us that Roe is a special case and that other decisions such as interracial marriage (Loving) or contraception (Griswold) are in no danger of being overturned. They are decided law, so we have nothing to worry about.
Except...that’s exactly what a few recent Supreme Court nominees said about Roe, as well.
#alternative title: Samuel Alito is an Originalist Piece of Shit#Honestly the entire b.s. of Alito's ''history and tradition'' requirement for rights to be legally legitimate#is so enraging because it targets basically *all* unenumerated rights over the past half-century#not to mention Alito isn't a historian - he's a scholar of law#when he talks about history he is speaking as someone who has no credentials as a historian#so when he wields words like ''history'' and worse - ''tradition'' he is wielding them as ideological cudgels#because that's Originalism - it pretends to be unbiased but it chooses worship of the Law as a thing in and of itself#rather than a thing created by people trying to achieve fairness and justice#if this draft becomes precedent then it *WILL* be a domino#and will affect law and civil rights for generations#this is the culmination of a 50 year conservative project#this will be a generational fight Folks#so get ready#Supreme Court#Abortion#Originalism#Samuel Alito#Civil Rights#Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization#(also I am totally not a lawyer and I probably got a few details wrong - this is mostly broad strokes)
611 notes
·
View notes
Text

LITERARY DIGEST, March 26, 1927


8 notes
·
View notes
Note
What is your opinion on expanding the Supreme Court?
It's a perfectly cromulent response to a Supreme Court over-stepping its proper role. Article III of the U.S Constitution does not provide for a set number of justices, and Congress has the power to regulate the size of the Supreme Court through legislation. (It also has the right to regulate the appellate jurisdiction of the Supreme Court, and if it really came down to it, Congress could simply legislate that the Supreme Court doesn't have the authority to conduct judicial review.)
Indeed, at various times in our history, the U.S Supreme Court has had six, eight, ten, and was supposed to have seven at one point before it was expanded again to nine justices. (And no, I have no idea why the Judiciary Committees in their infinite wisdom kept establishing even numbers of justices.)
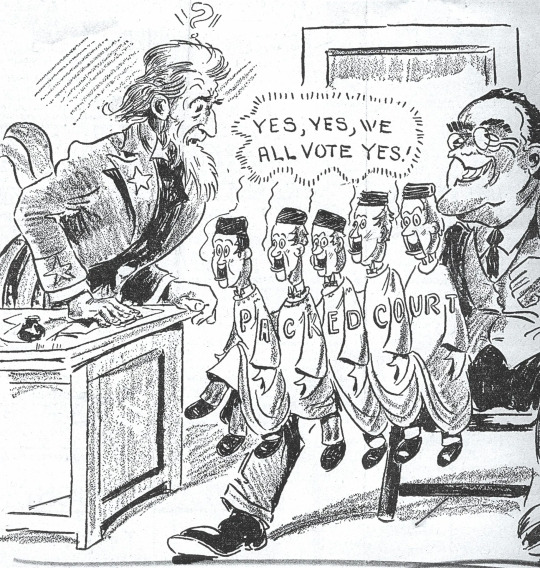

FDR's attempt in 1937 to expand the Supreme Court by adding justices in proportion to the number of sitting justices over age 70 was very politically divisive, although its actual legislative fate had far more to do with Southern Democrats afraid that an expanded Court would rule against segregation than it had anything to do with public opinion.
Ironically, FDR got his way in the end by intimidating the justices into compliance with the Legislative and Executive branches and then outliving a whole bunch of the aforesaid septuagenarians, and his appointees did end up ruling against segregation in a bunch of cases - setting up the precedents that the Warren Court would later use to dismantle Jim Crow.
62 notes
·
View notes