#Journals on Biomedical Intervention
Text
Sustainability of Biologic Therapy is Less in Ulcerative Colitis than Crohn’s Disease Patients, Independent of Prior Biologic Experience
Sustainability of Biologic Therapy is Less in Ulcerative Colitis than Crohn’s Disease Patients, Independent of Prior Biologic Experience in Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
https://biomedres.us/fulltexts/BJSTR.MS.ID.006071.php
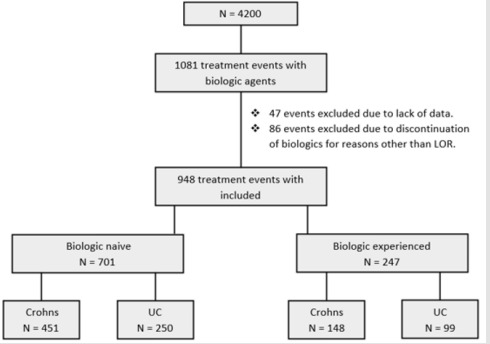
Background: Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) with biologics is effective but loss of response to treatment limits long-term treatment success. Few studies have examined what determines sustainability of biologic treatment. Objective: The aim of our study was to determine factors associated with sustainability of biologic therapy in IBD. Methods: We performed a retrospective study of 4,200 patients in a single healthcare network. Primary outcome was time to biologic treatment discontinuation (due to inadequate treatment response or adverse effects). Results: A total of 948 independent biologic treatment episodes were identified in 712 patients. Mean follow-up was 2.3years (range 0.0028 – 5.00). • Group 1: 701 biologic-naïve treatment episodes were included. 329 patients (47%) were treated with infliximab, 337(48%) with adalimumab and 32(5%) with golimumab. 250 (36%) had UC. Mean time to discontinuation in UC was 2.9 years compared to 3.6 years in CD (p = <0.001). • Group 2: 247 treatment episodes of biologic-experienced patients were included. 83(33%) were treated with infliximab, 57(23%) with adalimumab, 40(16%) with vedolizumab, 26(11%) with golimumab and 41(16.6%) with ustekinumab. 99(40 %) had UC. Mean time to discontinuation in UC was 2.3 years compared to 3.1 years in CD (p = 0.03). Conclusion: Our real-world data indicates sustainability of biologic treatment is less in UC than in CD patients and is not strongly determined by prior biologic exposure. These findings suggest the need for better understanding of the differing mechanisms for loss of biologic response which will assist in sequencing of therapies in the future.
For more articles in Journals on Biomedical Sciences click here bjstr
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/Biomedres01
Follow on Blogger :https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/
Like Our Pins On : https://www.pinterest.com/biomedres/
#Journals on Biomedical Intervention#Journals on Emergency Medicine#Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation#journal of biomedical research and reviews#journal of biomedical sciences research review
0 notes
Text
Biomed Grid | Biological Applications of Platinum-Based Nanoclusters
Introduction
Nanomaterials are materials which exist on a nanometer scale in at least one dimension. These materials, especially noble metal nanoparticles, exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties compared to their bulk counterparts due to the high surface to volume ratio and the quantum confinement effect, which make them highly compatible in materials science and biological applications. When the sizes are less than 2nm, nanoparticles become nanoclusters, whose electronic structures change from a continuous band into a discrete molecular-like orbital levels. Such unique electronic properties combined with the good biocompatibility and photostability, suggesting promising potentials of these noble metal nanoclusters for biological applications [1]. This mini review will focus on Platinum (Pt) nanoclusters and the corresponding biological applications specifically in biological imaging, enzymelike properties and cancer treatment.
Discussion
Biological Imaging
Biological imaging provides unique advantages in cancer identification and drug delivery [2]. One of the most critical factors for successful biological imaging is the use of stable, biocompatible and sensitive markers [3]. Traditional markers including organic dyes and fluorescent proteins often experience stability concerns for long-term experiments. Quantum dots markers have disadvantages such as biocompatibility issues for in vivo use. In contrast, Pt nanoclusters illustrate high sensitivity in long-term experiments and biocompatibility, making them highly suitable for biological imaging. For example, it has been reported that Pt nanoclusters attached by polyamine could be used for staining in hematopoietic system [4]. In addition, cell membranes have been imaged by blue mercaptoacetic acid protected Pt nanoclusters, where the antibody receptors were expressed [5].
Enzyme-Like Activities
Except for the excellent photoluminescence properties for bioimaging, protein capped Pt nanoclusters have also illustrated enzyme-like properties, i.e. peroxidase, oxidase and catalase [6]. Peroxidases are type of enzymes that reduce the lipid peroxide or hydrogen peroxide, and high peroxidase activities of Pt-based nanoclusters have been reported by Wei and coworker [7]. Based on the inhibition behavior of the peroxidase enzymatic activities between Pt and Hg, Pt nanoclusters have been proposed and utilized for the detection of toxic metal ions [8]. Oxidases are type of enzymes that promote oxidation by molecular Oxygen (O2).
Tseng and coworkers have shown that lysozyme ligand protected Pt nanoclusters could catalyze the oxidation reactions of organic substances such as dopamine and the degradation mechanism of organic pollutants by Pt nanoclusters have also been proposed [9]. Catalases are type of enzymes that decompose hydrogen peroxide into O2 and H2O. Nie, et al. have reported that the Platinum-ferritin nanoclusters could catalyze the decomposition of H2O2, which further reduce the 5-Diethoxyphosphoryl-5-methyl- 1-pyroline-N-oxide (DEPMPO)/OH˙ adduct signal in a H2O2/UV DEPMPO spin trap system [10].
Cancer Treatment
Platinum-Based drugs are widely used compounds for treatments of head, neck, cervical and lung cancers [11]. DNAPt adducts produced by cisplatin and other analogues are wellknown for their anti-tumor activities decades ago. However, these drugs demonstrate little effect on breast, liver, and prostate cancers, as well as similar tumor sensitivity and susceptibility to tumor resistance. To overcome this, demethylcantharidin has been employed to introduce the selectivity of anti-tumor behavior towards liver cancer cells [12]. Additionally, demethylcantharidinplatinum complexes have also shown to be free from cross resistance with cisplatin. Chien et al. have reported a dendrimercapped Pt nanocluster for targeting breast cancer cells [13]. Xia et al. have demonstrated polypeptide protected Pt nanoclusters could accelerate the release of Pt ions and overcome the cisplatin resistance problems [14].
Conclusion
Due to ultra-small size, Pt nanoclusters have illustrated distinct electronic properties compared to the bulk materials. Combined with the good biocompatibility and photoluminescence, Pt nanoclusters have demonstrated exciting potential for biological applications such as, biological imaging, enzyme-like property and cancer treatment. Future directions include synthesizing Pt nanoclusters with improved florescence character, enhancing enzyme activities and preparation of new ligand groups for targeting tumor cells with lower resistivity.

Read More About this Article: https://biomedgrid.com/fulltext/volume6/biological-applications-of-platinum-based-nanoclusters.001094.php
For more about: Journals on Biomedical Science :Biomed Grid | Current Issue
#biomedgrid#american journal of biomedical science & research#journals on biomedical intervention#biomedical journal impact factor
0 notes
Text
Transgender Women Athletes and Elite Sport: New Scientific Review Dismisses Trans Women’s Performance Advantage

A new report commissioned by the Canadian Centre for Ethics in Sport (CCES) says there's no reliable evidence pointing to a performance advantage in elite trans women who have suppressed their testosterone.
Via Running
Here’s the Executive Summary of the report:
Transgender Women Athletes and Elite Sport: A Scientific Review is an in-depth review of scientific literature on transgender athlete participation in competitive sport.
The inclusion criteria for this report were research articles published in the English language between 2011 and 2021 inclusive. Only peer-reviewed articles or syntheses of academic literature (e.g., meta-analyses) in reputable academic journals were included.
Grey literature, or non-academic literature, was included if it provided a summary of empirical data or if it described rules currently in place worldwide to include/exclude trans athletes.
(...)
On the biology of trans women
The biomedical perspective views the physiology of trans women’s bodies as the source of perceived unfairness, with medicalized interventions (such as estrogen supplementation and testosterone suppression) as the resolution.
More specifically, this perspective holds that sexual dimorphism between those assigned male at birth (AMAB) and those assigned female at birth (AFAB) is the reason for athletic differences. Testosterone measures and boundaries are typically chosen as defining characteristics of manhood and womanhood in the context of sport and are used as the predominant marker to predict and level sex-related athletic advantage and the means for inclusion criteria.
The research findings in the biomedical area are inconclusive. Studies which make conclusions on pre- and post-hormone replacement therapy (HRT) advantage held by trans women athletes have used either cis men or sedentary trans women as proxies for elite trans women athletes. These group references are not only inappropriate for the context but produce conclusions that cannot be applied to elite trans women athletes.
Further, there is little scientific understanding about the attributes or properties of HRT, namely testosterone suppression and estrogen supplementation, on the physiology and athletic ability of trans women athletes. This ignores the potential for estrogen supplementation to reduce Lean Body Mass (LBM), and for testosterone suppression to produce holistic health disadvantages.
The sociocultural perspective
The second perspective is a sociocultural one. Researchers in the sociocultural field of study argue that social factors contribute to performance advantages to a far greater extent than does testosterone and that assessing testosterone levels is another way to perpetuate the long history of policing women’s bodies in sport.
Researchers highlight the many social factors that contribute to differences in athletic performance, including, for example: discriminations, disparate resource allocations, inequities, and violence against women in sport in the forms of sexism and sexual violence in sport contexts, arbitrary differences in rules and equipment between men’s and women’s sport, as well as histories of barring women from certain sports.
This body of work also highlights the foundational histories of anti-Blackness, anti-Global Southness, and misogyny which maintain inequities in sport.
Arguments are made that the use of testosterone to exclude trans women athletes represents another phase in the long history of policing women’s bodies in sport. Once women were allowed into competitive sport in the early 20th century, those whose athletic ability was on par with their male counterparts, or whose physique was too manly, were disqualified from competition as deviants of the gender order.
Through the history of women’s sport, female athletes have been exposed to intrusive gender verification processes including medical inspection of external genitalia and chromosome testing that produced many false positives and had catastrophic impacts on athletes’ careers.
The current climate is one that focuses on testosterone levels of those athletes whose gender is deemed to be ‘suspicious.’ In the context of sport policy development, biomedical and physiological data have todate been privileged over other aspects such as social factors. Many policies cite biomedical studies to explain their conditions of inclusion, or their exclusion.
(...)
Conclusion
There is no firm basis available in evidence to indicate that trans women have a consistent and measurable overall performance benefit after 12 months of testosterone suppression.
(...)
For pre-suppression trans women it is currently unknown when during the first 12 months of suppression that any advantage may persist. The duration of any such advantage is likely highly dependent on the individual's pre-suppression LBM which, in turn varies, greatly and is highly impacted by societal factors and individual circumstance.
Full report here.
The review was carried out by E-Alliance, a research hub for gender equity in sport led by Dr. Gretchen Kerr of the University of Toronto and Dr. Ann Pegoraro of the University of Guelph (pictured below).


Photo of transgender athlete: Phtographia Inc.
43 notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Shape-shifting ultrasound stickers detect post-surgical complications - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/shape-shifting-ultrasound-stickers-detect-post-surgical-complications-technology-org/
Shape-shifting ultrasound stickers detect post-surgical complications - Technology Org
Researchers led by Northwestern University and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a new, first-of-its-kind sticker that enables clinicians to monitor the health of patients’ organs and deep tissues with a simple ultrasound device.
Three variations of the soft, flexible ultrasound sticker device displayed on a finger. Image credit: Jiaqi Liu
When attached to an organ, the soft, tiny sticker changes in shape in response to the body’s changing pH levels, which can serve as an early warning sign for post-surgery complications such as anastomotic leaks. Clinicians can then view these shape changes in real-time through ultrasound imaging.
Currently, no existing methods can reliably and non-invasively detect anastomotic leaks — a life-threatening condition that occurs when gastrointestinal fluids escape the digestive system. By revealing the leakage of these fluids with high sensitivity and high specificity, the non-invasive sticker can enable earlier interventions than previously possible. Then, when the patient has fully recovered, the biocompatible, bioresorbable sticker simply dissolves away — bypassing the need for surgical extraction.
The study will be published March 8 in the journal Science. The paper outlines evaluations across small and large animal models to validate three different types of stickers made of hydrogel materials tailored for the ability to detect anastomotic leaks from the stomach, the small intestine and the pancreas.
“These leaks can arise from subtle perforations in the tissue, often as imperceptible gaps between two sides of a surgical incision,” said Northwestern’s John A. Rogers, who led device development with postdoctoral fellow Jiaqi Liu. “These types of defects cannot be seen directly with ultrasound imaging tools. They also escape detection by even the most sophisticated CT and MRI scans. We developed an engineering approach and a set of advanced materials to address this unmet need in patient monitoring. The technology has the potential to eliminate risks, reduce costs and expand accessibility to rapid, non-invasive assessments for improved patient outcomes.”
“Right now, there is no good way whatsoever to detect these kinds of leaks,” said gastrointestinal surgeon Dr. Chet Hammill, who led the clinical evaluation and animal model studies at Washington University with collaborator Dr. Matthew MacEwan, an assistant professor of neurosurgery. “The majority of operations in the abdomen — when you have to remove something and sew it back together — carry a risk of leaking. We can’t fully prevent those complications, but maybe we can catch them earlier to minimize harm. Even if we could detect a leak 24- or 48-hours earlier, we could catch complications before the patient becomes really sick. This new technology has potential to completely change the way we monitor patients after surgery.”
A bioelectronics pioneer, Rogers is the Louis Simpson and Kimberly Querrey Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, Biomedical Engineering and Neurological Surgery, with appointments at the McCormick School of Engineering and Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. He also directs the Querrey Simpson Institute for Bioelectronics. At the time of the research, Hammill was an associate professor of surgery at Washington University. Rogers, Hammill and MacEwan co-led the research with Heling Wang, an associate professor at Tsinghua University in Beijing.
The importance of being early
All gastrointestinal surgeries carry the risk of anastomotic leaks. If the leak is not detected early enough, the patient has a 30% chance of spending up to six months in the hospital and a 20% chance of dying, according to Hammill. For patients recovering from pancreatic surgery, the risks are even higher. Hammill says a staggering 40-60% of patients suffer complications after pancreas-related surgeries.
The biggest problem is there’s no way to predict who will develop such complications. And, by the time the patient is experiencing symptoms, they already are incredibly ill.
“Patients might have some vague symptoms associated with the leak,” Hammill said. “But they have just gone through big surgery, so it’s hard to know if the symptoms are abnormal. If we can catch it early, then we can drain the fluid. If we catch it later, the patient can get sepsis and end up in the ICU. For patients with pancreatic cancer, they might only have six months to live as it is. Now, they are spending half that time in the hospital.”
In search of improved outcomes for his patients, Hammill contacted Rogers, whose laboratory specializes in developing engineering solutions to address health challenges. Rogers’ team had already developed a suite of bioresorbable electronic devices to serve as temporary implants, including dissolving pacemakers, nerve stimulators and implantable painkillers.
The bioresorbable systems piqued Hammill’s interest. The greatest odds of developing an anastomotic leak occur either three days or two weeks after surgery.
“We like to monitor patients for complications for about 30 days,” Hammill said. “Having a device that lasts a month and then disappears sounded ideal.”
Enhancing ultrasound
Instead of developing new imaging systems, Rogers speculated that his team might be able to enhance current imaging methods — allowing them to “see” features that otherwise would be invisible. Ultrasound technology already has many advantages: it’s inexpensive, readily available, does not require cumbersome equipment and does not expose patients to radiation or other risks.
But, of course, there is a major drawback. Ultrasound technology — which uses sound waves to determine the position, shape and structure of organs — cannot reliably differentiate between various bodily fluids. Blood and gastric fluid, for example, appear the same.
“The acoustic properties of the leaking fluids are very similar to those of naturally occurring biofluids and surrounding tissues,” Rogers said. “The clinical need, however, demands chemical specificity, beyond the scope of fundamental mechanisms that create contrast in ultrasound images.”
Ultimately, Rogers’ team devised an approach to overcome this limitation by using tiny sensor devices designed to be readable by ultrasound imaging. Specifically, they created a small, tissue-adhesive sticker out of a flexible, chemically responsive, soft hydrogel material. Then, they embedded tiny, paper-thin metal disks into the thin layers of this hydrogel. When the sticker encounters leaked fluids, it swells.
Making the invisible visible
The metal disks move apart as the hydrogel swells in response to changing pH. The ultrasound can then view these subtle changes in placement.
Watch the device expand in response to pH
“Because the acoustic properties of the metal disks are much different than those of the surrounding tissue, they provide very strong contrast in ultrasound images,” Rogers said. “In this way, we can essentially ‘tag’ an organ for monitoring.”
Because the need for monitoring extends only during a postsurgical recovery, Rogers team designed these stickers with bioresorbable materials. They simply disappear naturally and harmlessly in the body after they are no longer needed.
Computational collaborator Yonggang Huang, the Jan and Marcia Achenbach Professorship in Mechanical Engineering and professor of civil and environmental engineering at McCormick, used acoustic and mechanical simulation techniques to help guide optimized choices in materials and device layouts to ensure high visibility in ultrasound images, even for stickers located at deep positions within the body.
“CT and MRI scans just take a picture,” Hammill added. “The fluid might show up in a CT image, but there’s always fluid collections after surgery. We don’t know if it’s actually a leak or normal abdominal fluid. The information that we get from the new patch is much, much more valuable. If we can see that the pH is altered, then we know that something isn’t right.”
Rogers team constructed stickers of varying sizes. The largest measures 12 millimeters in diameter, while the smallest is just 4 millimeters in diameter. Considering that the metal disks are each 1 millimeter or smaller, Rogers realized that it might be difficult for radiologists to assess the images manually. To overcome this challenge, his team also developed software that can automatically analyze the images to detect with high accuracy any relative movement of the disks.
Improving quality of life
To evaluate the efficacy of the new sticker, Hammill’s team tested it in both small and large animal models. In the studies, ultrasound imaging consistently detected changes in the shape-shifting sticker — even when it was 10 centimeters deep inside of tissues. When exposed to fluids with abnormally high or low pH levels, the sticker altered its shape within minutes.
Rogers and Hammill imagine that the device could be implanted at the end of a surgical procedure. Or, because it’s small and flexible, the device also fits (rolled up) inside a syringe, which clinicians can use to inject the tag into the body.
“These tags are so small and thin and soft that surgeons can easily place collections of them at different locations,” Rogers said. “For example, if an incision extends by a few centimeters in length, an array of these tags can be placed along the length of the site to develop a map of pH for precisely locating the position of the leak.”
“It’s obviously an early prototype, but I can envision the final product where, at the end of surgery, you just place these little patches for monitoring,” Hammill said. “It does its job and then completely disappears. This could greatly impact patients, their recovery time and, ultimately, their quality of life.”
Next, Rogers and his team are exploring similar tags that could detect internal bleeding or temperature changes. “Detecting changes in pH is a good starting point,” Rogers said. “But this platform can extend to other types of applications by use of hydrogels that respond to other changes in local chemistry, or to temperature or other properties of clinical relevance.”
Source: Northwestern University
You can offer your link to a page which is relevant to the topic of this post.
#Accessibility#advanced materials#applications#approach#bioelectronics#bleeding#blood#Cancer#challenge#change#chemical#chemistry#Civil and environmental engineering#Collections#computed tomography#course#detection#development#devices#digestive system#electronic#electronic devices#engineering#Environmental#equipment#Features#fluids#Fundamental#Health#Health & medicine news
0 notes
Text
Journal of Medical Case Reports

Journal of Medical Case Reports accepting case reports in medical science journal, medical case reports journal, journals accepting medical case reports, journals publishing medical case reports etc. Journal publishes methods of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases. The practice of medicine involves multidisciplinary study and application of concepts of several branches of biomedical sciences, genetics, microbiology, immunology etc. Furthermore, practice of medicine also requires a thorough knowledge of pharmaceutical sciences and surgery. It also takes the help of other therapies like physiotherapy, psychotherapy and preventive medicine. Medicine research is therefore, an intricate subject that has multiple facets, each of which needs to be addressed in great detail before a specific diagnostic or therapeutic method is standardized for large scale application.
Journal Homepage: https://www.literaturepublishers.org/
Manuscript Submission
Authors are requested to submit their manuscript by using Online Manuscript Submission Portal:
(or) also invited to submit through the Journal E-mail Id: [email protected]
American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics: American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics is an open access peer reviewed and monthly published research journal that publishes articles in the field of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics. It is an international journal to encourage research publication to research scholars, academicians, professionals and students engaged in their respective field.
Related Journals: Herbal Medicine: Open Access, Natural Products Chemistry & Research, American Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics
Translational Biomedicine
Translational Biomedicine: Translational Biomedicine is an international open access, peer-reviewed academic journal. The Journal publishes original science-based research that advances communication between the scientific discovery and health improvement. Translational Biomedicine publishes Original research and/or commentary on diseases with implications for treatment Clinical translation where scientific ideas are translated into clinical trials or applications, Nutrition research: the interaction and validation between research and application Perspectives and Reviews on current basic science or clinical science research topics Survey of recent significant published findings. Journal Highlights Includes: Translational Biomedical Research, Translational Research and Clinical Intervention, Translational Stroke, Translational Neurology, Translational Oncology, Translational imaging, Translational Psychiatry, Orthopedic Translation, Stem Cell Translation Medicine, Translation Proteomics, Translational Neuroscience, Translational Cancer Research, Discovery Biology, Medical Biotechnology.
0 notes
Text
Journal of Medical Case Reports

Journal of Medical Case Reports accepting case reports in medical science journal, medical case reports journal, journals accepting medical case reports, journals publishing medical case reports etc. Journal publishes methods of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases. The practice of medicine involves multidisciplinary study and application of concepts of several branches of biomedical sciences, genetics, microbiology, immunology etc. Furthermore, practice of medicine also requires a thorough knowledge of pharmaceutical sciences and surgery. It also takes the help of other therapies like physiotherapy, psychotherapy and preventive medicine. Medicine research is therefore, an intricate subject that has multiple facets, each of which needs to be addressed in great detail before a specific diagnostic or therapeutic method is standardized for large scale application.
Journal Homepage: https://www.literaturepublishers.org/
Manuscript Submission
Authors are requested to submit their manuscript by using Online Manuscript Submission Portal:
https://www.literaturepublishers.org/submit.html
(or) also invited to submit through the Journal E-mail Id: [email protected]
American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics: American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics is an open access peer reviewed and monthly published research journal that publishes articles in the field of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics. It is an international journal to encourage research publication to research scholars, academicians, professionals and students engaged in their respective field.
Related Journals: Herbal Medicine: Open Access, Natural Products Chemistry & Research, American Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics
Translational Biomedicine
Translational Biomedicine: Translational Biomedicine is an international open access, peer-reviewed academic journal. The Journal publishes original science-based research that advances communication between the scientific discovery and health improvement. Translational Biomedicine publishes Original research and/or commentary on diseases with implications for treatment Clinical translation where scientific ideas are translated into clinical trials or applications, Nutrition research: the interaction and validation between research and application Perspectives and Reviews on current basic science or clinical science research topics Survey of recent significant published findings. Journal Highlights Includes: Translational Biomedical Research, Translational Research and Clinical Intervention, Translational Stroke, Translational Neurology, Translational Oncology, Translational imaging, Translational Psychiatry, Orthopedic Translation, Stem Cell Translation Medicine, Translation Proteomics, Translational Neuroscience, Translational Cancer Research, Discovery Biology, Medical Biotechnology.
Related Journals: Translational Cancer Research, Orthopedic Translation, Translational Proteomics, Translational Biomedical Research, Translational Neuroscience, Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology, Molecular Therapy, Stem Cell Translation, Translational Biomedical Research, Translational Clinical Research
American Journal of Ethnomedicine
American Journal of Ethnomedicine: American Journal of Ethnomedicine is an open access, peer-reviewed, bimonthly, online journal that aims to promote the exchange of original knowledge and research in any area of ethnomedicine.
American Journal of Ethnomedicine invites research articles and reviews based on original interdisciplinary studies on the inextricable relationships between human cultures and nature/universe, Traditional Environmental/Ecological Knowledge (TEK), folk and traditional medical knowledge, as well as the relevance of these for environmental and public health policies.
Specifically, the journal will cover the following topics: ethnobotany, ethnomycology, ethnozoology, ethnoecology (including ethnopedology), ethnometereology/ ethnoclimatology, ethnoastronomy, ethnopharmacy, ethnomedicine, ethnoveterinary, traditional medicines, traditional healthcare in households and domestic arenas, migrant healthcare/urban ethnobiology, pluralistic healthcare in developing countries, evidence-based community health, visual ethnobiology and ethnomedicine, gender studies and ethnobiology, as well as other related areas in environmental, nutritional, medical and visual anthropology. Botanically-centered manuscripts must clearly indicate voucher specimens and herbaria.
Journal of Biomedical Sciences
Journal of Biomedical Sciences: Journal of Biomedical Sciences is an international, peer reviewed journals which publishes high quality of article and novel research contribution to scientific knowledge. The Journal of Biomedical Sciences is an open access, peer-reviewed journal that encompasses all fundamental and molecular aspects of basic medical sciences, emphasizing on providing the molecular studies of biomedical problems and molecular mechanisms. The Journal of Biomedical Sciences gives an area to share the information among the medical scientists and researchers
Journal highlights includes: Cognitive and neurosciences, Biochemical engineering, Molecular biology, Gas transport and metabolism, Cardiac assist devices, Vascular autoregulation, Protein science, Structural biology, Biomedical ultrasound, Neuroengineering, Heart mechanics, Biomedical science, Genetics
Related Journals: Biomedicine Journal, Biomedical Science and Engineering Journal, Medicine Journal, Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical sciences, Journal of Biomedical sciences and Research, Journal of Biomedical Research, Neurology Journal, Biomedical Engineering Journal, Cellular Biology Journal, Alzheimer?s Disease Journal, Clinical Immunology Journal, Genetics and Genomics Research Journal, Archives of Medicine Journal, Journal of Clinical & Biomedical Sciences, Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, Neuroscience Journals, Behavioral Sciences journal, Journal of Neuroscience & Cognition, Journal of Psychology, Journals of Gerontology
Journal of Regenerative Medicine
Journal of Regenerative Medicine: Regenerative Medicine journal covers wide range of topics such as regenerative medicine therapies, stem cell applications, tissue engineering, gene and cell therapies, translational medicine and tissue regeneration etc. The journal provides hybrid access platform to publish the original research articles, review articles, case reports, short communications, etc and provides the rapid dissemination of significant research in various disciplines encompassing all areas of stem cells and regenerative medicine.
Journal Highlights: Cell and Organ Regeneration, Cell Engineering, Cellular Therapies, Diagnostics and Imaging, Ethical and Legal Issues, Gene Therapies, Human Pathological Conditions, Immunotherapy, Models of Regeneration, Nanoscaffolds in Regenerative Medicine, Regenerative Biology, Rejuvenation, Stem Cell Transplantation, Stem Cell Treatments, Stem Cells, Tissue Engineering, Tissue Repair and Regeneration, Translational Medicine, Translational Medicines, Translational Science, etc.
Related Journals: Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, Journal of Regenerative Medicine & Tissue Engineering, International Journal of Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research, Journal of Stem Cell Research & Therapy, Stem Cell Biology and Research, Biomaterials, Cardiovascular Journals, Cell Biology Journals, Hematology Journals, Liver Journals
0 notes
Text
Heard Of The Take My Biology Class For Me Effect? Right Here It Is
Title: The Role of Molecular Biology Reports in Advancing Biomedical Research: A Case Study
Introduction:
Molecular biology reports play a crucial role in advancing biomedical research by providing critical insights into the intricate workings of biological systems at a molecular level. This case study aims to highlight the significance of molecular biology reports through a specific research project on a prominent disease.
Case Study: Unraveling the Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide, causing cognitive decline and memory loss. Despite extensive research efforts, a definitive cure or effective treatment for AD is still lacking. However, molecular biology reports have significantly contributed to our understanding of the disease's underlying mechanisms, potentially paving the way for groundbreaking therapeutic interventions.
One key molecular online biology homework help report, titled "Identification of Amyloid-beta as the Main Culprit in Alzheimer's Pathogenesis," has profoundly influenced AD research. This report, published in a renowned scientific journal, elucidated the role of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide accumulation in the brain as the primary trigger for AD progression.
The study utilized state-of-the-art techniques such as immunohistochemistry, genome-wide association studies, and bioinformatics analyses to identify the key molecular players involved in AD. By investigating post-mortem brain tissue samples from AD patients, the researchers demonstrated a significantly higher accumulation of Aβ peptide compared to healthy individuals.
This molecular biology report not only provided a better understanding of AD pathology but also opened avenues for potential therapeutic targets. Subsequent studies based on the initial findings have sought to develop novel AD treatments that can selectively target Aβ accumulation and/or enhance its clearance from the brain.
Furthermore, molecular biology reports have greatly assisted in discovering potential genetic risk factors associated with AD. Another landmark study, titled "Uncovering the Role of the APOE Gene in Alzheimer's Disease Susceptibility," highlighted the significant contribution of the Apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene to AD development.
Through comprehensive genomic profiling of AD patients and healthy controls, the researchers determined that the presence of a certain APOE variant, specifically E4 allele, increased the risk of developing AD. Consequently, this molecular biology report spurred further investigations into the functional role of APOE gene isoforms and their implications in AD pathogenesis.
Based on these molecular biology reports, several prospective treatments targeting Aβ accumulation, APOE variants, or related molecular pathways have entered clinical trials. Furthermore, these findings have also facilitated the development of biomarkers for early AD detection, allowing for timely interventions and potential disease-modifying therapies.
Conclusion:
Molecular biology reports have played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of complex diseases, as demonstrated by the case study on Alzheimer's disease. By dissecting the molecular mechanisms underlying AD pathology, researchers have identified potential therapeutic targets, genetic risk factors, and biomarkers. These reports serve as a foundation for further investigations, shaping the landscape of biomedical research and ultimately aiming to improve patients' lives. The significant impact of molecular biology reports on Alzheimer's disease research underscores their broader importance in unraveling the intricate mysteries of human biology.
0 notes
Link
#ACE2DecoyBreakthrough#COVID-19TreatmentInnovation#EffectiveCOVID-19TherapeuticBreakthrough#High-AffinityACE2Therapy#InnovativeInhalationTreatment#PandemicReshapingSolution#PromisingPrimateModelResults#RevolutionaryCoronavirusTreatment#Virus-CounteringACE2Decoy#WorldwidePandemicTreatmentAdvancement
0 notes
Text
Medical Image Journal: Journal of Medical Images

Medical Image Journal: Journal of Medical Images publishes medical image articles, images in medical science, imaging in medical journal, imaging in medical science journal, images in clinical medicine journal, images in medical research, imaging in medical research, image case journal etc. Journal allows for the peer-reviewed communication and archiving of Clinical and Medical Research, as well as applications, focused on medical imaging, a field that continues to benefit from technological improvements and yield biomedical advancements in the early detection, diagnostics, and therapy of disease as well as in the understanding of normal conditions.
Journal Homepage: https://www.literaturepublishers.org/
Manuscript Submission
Authors are requested to submit their manuscript by using Online Manuscript Submission Portal:
(or) also invited to submit through the Journal E-mail Id: [email protected]
Medical Image Journal: Journal of Medical Images provides a forum for the dissemination of new research results in the field of Medical and Clinical Image Journal, with special emphasis on efforts related to the applications of computer vision, virtual reality and robotics to biomedical imaging problems. Medical Image Journal: Journal of Medical Images publishes the highest quality, original papers that contribute to the basic science of processing, analyzing and utilizing medical and biological images for these purposes. Medical Image Journal: Journal of Medical Images is interested in approaches that utilize biomedical image datasets at all spatial scales, ranging from molecular/cellular imaging to tissue/organ imaging. While not limited to these alone, the typical biomedical image datasets of interest include those acquired from.
The types of papers accepted include those that cover the development and implementation of algorithms and strategies based on the use of various models (geometrical, statistical, physical, functional, etc.) to solve the following types of problems, using biomedical image datasets: representation of pictorial data, visualization, feature extraction, segmentation, inter-study and inter-subject registration, longitudinal / temporal studies, image-guided surgery and intervention, texture, shape and motion measurements, spectral analysis, digital anatomical atlases, statistical shape analysis, computational anatomy (modelling normal anatomy and its variations), computational physiology (modelling organs and living systems for image analysis, simulation and training), virtual and augmented reality for therapy planning and guidance, telemedicine with medical images, telepresence in medicine, telesurgery and image-guided medical robots, etc.
#Medical Image Journal: Journal of Medical Images publishes medical image articles#images in medical science#imaging in medical journal#imaging in medical science journal#images in clinical medicine journal#images in medical research#imaging in medical research#image case journal
0 notes
Text

and a recruiter, an opportunity for the participant to ask questions, the mutual signing of a written agreement which describes the clinical trial, and the opening of a communication channel through which the participate may ask any questions about the trial at any time.
Clinical trials are a critical component of all pharmaceutical and medical intervention research. Many clinical trials themselves meet Wikipedia criteria for notability as at any given contemporary time there are several hundred clinical trials active worldwide which are consuming government, industry, and non-profit budgets totaling USD 100 million over the course of a few years. This vast financial expenditure creates many paper trails including government regulatory announcements, disclosures by any pharmaceutical company providing research drugs or devices, oversight reviews from nonprofit organizations, trial reports from the entity actually conducting the trial, and often journalism from the sector which publishes on clinical trials. Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as experimental medicine, encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research" (also called bench science or bench research), [1] - involving fundamental scientific principles that may apply to a preclinical understanding - to clinical research, which involves studies ofs CLONES
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Diagnostic Difficulties and The Delayed Identification of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in A Teenage Patient. A Review of Literature
The Diagnostic Difficulties and The Delayed Identification of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in A Teenage Patient. A Review of Literature in Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
https://biomedres.us/fulltexts/BJSTR.MS.ID.006067.php
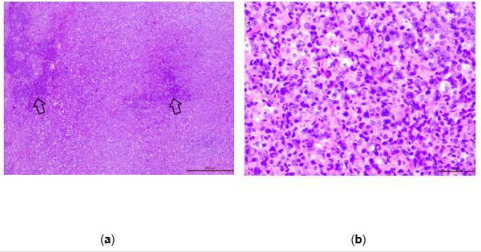
Systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma (S-ALCL) is a rare and aggressive lymphoma. In most cases it arises in cervical and axillary lymph nodes. At times, the disease may have an unusual course when the primary site appears in other locations, like skin, bone, lung liver. This may lead to diagnostic dilemmas. We report an unusual case of a 16-year-old boy with S-ALCL who presented with a nodular skin lesion located in the lower abdomen. Initially, based on the physical examination, he was misdiagnosed with an abscess. This resulted in the omission of diagnosing the neoplasm and caused the development of a systemic disease The diagnosis of ALCL is established in an advanced stage. This process relies on a histopathological and complex immunohistochemical examination of the collected material. To provide the best adjusted therapy, there is a requirement of a precise identification of neoplastic cells’ immunophenotype. It should be performed in the facility with the highest reference level. In the view of above, patient’s life depends on fast and exact diagnostic. Specialists, who are usually the first to encounter such patients, are crucial to initiate the relevant diagnostic processes and subsequently send the patient to the oncology unit.
For more articles in Journals on Biomedical Sciences click here bjstr
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/Biomedres01
Follow on Blogger :https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/
Like Our Pins On : https://www.pinterest.com/biomedres/
#Journals on Biomedical Intervention#Family Medicine#Behavioral Medicine Journals#journal of biomedical sciences research review#journal of biomedical research and reviews impact factor
0 notes
Text
Do NMN Boost the metabolism?
Numerous research initiatives have investigated how NAD precursors counteract the age-related loss in this key coenzyme involved in cellular energy metabolism and energy generation, with an emphasis on exercise metabolism and body composition. However, it has not been studied if NMN supplementation helps metabolism, much alone aging, in humans.
Klein and colleagues from the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis published a study in Science demonstrating for the first time that NMN metabolism enhances the insulin sensitivity of pre-diabetic women's skeletal muscles. They demonstrate that NMN achieves these beneficial metabolic benefits by improving the capacity of insulin to induce sugar absorption and the activation of genes involved in muscle structure and remodeling. However, the Missouri-based study team could not uncover evidence that NMN affects fat blood levels, blood sugar levels, or blood pressure. This article from Science gives tantalizing evidence that NMN may aid in the prevention of age-related diseases.
A May 2019 research published in the Journal of Biomedical Science reached the same outcome as the one referenced above. It was discovered that administering NMN or nicotinamide riboside (NR) to obese mice can prevent a decrease in NAD levels.
Along with NMN, NR is a NAD-booster (or precursor), which means that this molecule can assist in enhancing the level of NAD+ in all animal model studies, including our own. In this work, NR inhibited weight gain in mice fed a high-fat diet because it increased energy expenditure in a manner comparable to exercise. Mice with NMN used more energy, were more physically active, and did not undergo the average weight gain associated with aging.
The author concludes:
Thus, administration of NAD precursors [NR and NMN] can mitigate diet- and age-related weight increase, and nutritional intervention utilizing NMN and NR may be a viable therapy against [overweight].
I want to note that ProHealth Longevity carries its own brand of numerous NMN items in addition to an NR brand. We feel that the data clearly demonstrates that both of these NAD precursors are successful at increasing NAD levels as we age, which is extremely significant given that NAD is critical to our metabolic health yet decreases dramatically with age.
Scientists are convinced that NMN supplementation is safe for people, but human clinical trials that are now underway to assess if it is as useful to us as it is to other animals have not yet been published. It is essential to recognise that taking the most effective NMN supplement is a crucial aspect. There are several counterfeit items on the market that make bold promises but lack sufficient proof to support them. If you are worried about NMN and weight reduction, you will derive the maximum advantage from obtaining your NMN supplement from a reliable and trustworthy vendor.
Conclusion
From the discussion above, it can be inferred that NMN supplementation not only promotes slower aging and expression of longevity genes but is also a potent activator of weight-loss drugs. NMN may not immediately aid in weight reduction, but it will activate NAD+ and Sirtuin genes, which are essential for combating obesity and age-related weight gain.
Scientists think that food and exercise can reduce the likelihood of age-related weight increase. Therefore, NAD+ enhancement using NMN supplements may aid in exercise efficiency and weight reduction. Through Sirtuin gene activation, NMN supplementation, a balanced diet, and regular exercise may also relieve obesity-related illnesses.
0 notes
Text
Reductions associated with exterior massive efficiency rolloff inside organic and natural led lights simply by scavenging triplet excitons.
Comprehension mechanistic connections in between seagrass along with their enviromentally friendly stresses should be thought about pertaining to effective treatments for estuaries and may even notify in exactly why adjust provides transpired. All of us focused to formulate signs with regard to seagrass wellness as a result of sediment circumstances for your Swan-Canning Estuary, south-west Australia. This article identifies the introduction of a whole new sediment-stress indicator, relating facets of seagrass productivity along with sediment sulfur character. Sulfur dependable isotope percentage along with total sulfur ended up measured month-to-month inside the beginnings, rhizomes and instead gives off associated with Halophila ovalis, along with significantly different over web sites along with weeks. The development regarding seagrass in the summertime made an appearance restricted through sediment situation, along with increase of seagrass reduce while deposit extracted sulfur and/or full sulfur within rhizome associated with foliage flesh has been greater. L. ovalis appeared really loving toward sulfide invasion inside the actual compartment, however development ended up being sacrificed any time sulfide breached your root-rhizome hurdle. The tightest connection involving potential sulfur measurements as well as seagrass expansion ended up being observed to the ratio (delta S-34(leaf) + 30)Or(TSleaf), and it is this ratio we offer can be a useful sediment-stress sign with regard to seagrass. Case study also highlights in which sediment condition needs to be deemed with the field size. (H) The year 2013 Elsevier Limited. Just about all protection under the law set-aside.Heart diseases include the major reason behind demise worldwide; these are mainly because of vascular obstructions that, consequently, are mostly due to thrombi and atherosclerotic plaques. Even though a number of treatment strategies continues to be created for the regarded as items in the way, none of them is provided for free coming from limitations and conclusive. The current document analyzes the actual physical elements underlying state-of-art removal techniques and also classifies these into chemical substance, mechanical, laser and also a mix of both (specifically chemo-mechanical as well as mechano-chemical) strategies, whilst researching equivalent commercial/research tools/devices and operations. In addition, difficulties as well as options for interventional micro/nanodevices tend to be pointed out. Within this character, the present evaluation should help Shield-1 ic50 technicians, experts active in the micro/nanotechnology area, and also medical doctors inside the development of progressive biomedical solutions for the treatment general items in the way. Information ended up accumulated by using the ISI Internet of information web site, purchaser's guides and Food and drug administration listings; products certainly not described upon clinical journals, and also commercial gadgets forget about available for sale ended up discarded. Practically 70% from the recommendations have been posted since '06, 55% given that '08; these kind of percentages correspondingly boost in order to 85% as well as 65% as to the segment especially researching state-of-art removal tools/devices and operations.Objective: Phenotype centered modest chemical breakthrough discovery is often a sounding chemical substance anatomical study.
#Protease Inhibitor Library#Bcl-2 inhibitor#Pomalidomide#SB202190#Lenalidomide#Leupeptin#ML385#Cyclosporin A#U0126#IWP-2#Rigosertib#SP600125#PT2385#MPTP#IWR-1-endo#Hydroxychloroquine#4-Hydroxytamoxifen#Temsirolimus#Ro-3306#2-Deoxy-D-glucose#AK 7#Sulfopin#SBI-115#BGT226#Ziritaxestat#GSK650394#Semaglutide#Mavacamten#Oxidopamine#K03861
1 note
·
View note
Link
0 notes
Text
Cardiovascular Sciences | AHZ Associates

The curriculum has required teaching and research components. The things that are taught include how to write for a scientific audience, how to evaluate literature critically, and how to give presentations. There is also a research toolkit module that teaches basic experimental methods.
You will also study a specific module on cardiovascular science. This is to make sure you have a good understanding of all parts of the field and to introduce the topics and research questions that will form the basis of your project.
Over the next twenty years, heart disease is likely to continue to be the leading cause of death, leading to a lot of disability and a lower quality of life.
The goal of this program is to teach about the biology and science of the heart, with a focus on the molecular, clinical, and genetic factors that cause heart problems and the drugs used to treat them.
BSc in Cardiovascular Sciences program in the UK
The BSc in Cardiovascular Sciences program teaches students all about the science behind cardiovascular disease and how it affects diagnosis and treatment. A substantial translational emphasis is placed on the course’s core areas of cardiovascular disease. Issues are covered, such as-
The goal of the program is to train academics and clinicians who can understand best practices, push the limits of common knowledge, and further medical knowledge. Also, it gives students a solid foundation in scientific methodology and analytical techniques, which can help them become skilled clinicians and clinical researchers who could go on to get graduate degrees in research.
BSc in Cardiovascular Sciences Program structure
Along with your research training in fundamental research knowledge and skills, the program will include a 12-week teaching block (Module 1) in which students will learn specialism-specific information and abilities. After that, there is a 5-week period of self-directed study with a concentration on evaluating the literature and clinical case studies. A 14-week study project follows that.
Best universities for Cardiovascular Sciences Program in UK
University of Glasgow
The University of Glasgow is famous across the world for its competence in cardiovascular science education and research. At Glasgow University, there are options for pursuing a PhD.
Their research teams are housed in the specifically designed Western Infirmary, the Royal Infirmary, and the British Heart Foundation Glasgow Cardiovascular Research Centre. Modern facilities allow us to concentrate on a broad research program.
University of Birmingham
The student will gain the knowledge and skills necessary to contribute to research in clinical cardiovascular medicine based on an understanding of key pathological events, such as coronary artery plaque rupture and thrombosis, or the vicious regulatory loops causing heart failure, and on a subsequent rigorous evaluation of new therapeutic interventions in large controlled clinical trials.
University of Leicester
They are known all over the world for their excellent work in cardiovascular science, which includes projects from the lab to the bedside. Their efforts have significantly influenced patient care both domestically and internationally.
They have close ties to the NHS, as evidenced by the designation of a Biomedical Research Center with a Cardiovascular Disease Topic by the National Institute for Health Research.
They are proud to have won the Athena SWAN Silver Award and to have a great track record of training students.
University of Bristol
The curriculum will be appealing to a wide range of students, including those in biological sciences, allied health professions, and clinical fields. You can choose to study on campus or through distance learning (full- or part-time). Each unit will include tutorials, lectures, homework assignments, and exam evaluations.
Students who live on campus will participate in lectures, tutorials, journal clubs, field trips to clinical settings, and practical.
Distance learners will have access to online lecture materials, and up to five days per year of optional workshops will be held in Bristol for part-time students and ten days per year for full-time students. These workshops will include tutorials, journal clubs, practical sessions, and trips to clinical sessions.
University of Sheffield
The well-known University of Sheffield is in the north of England. It was one of the first "red brick" universities and is a member of the Russell Group, which is made up of only a few universities. The University of Sheffield, which has 28,000 students enrolled from over 120 different countries and is ranked among the top 100 universities in the world by the QS World University Rankings, was established in 1905 through the amalgamation of three schools.
In a Times poll, students from Sheffield ranked the university as having the best student experience.
Five Nobel Prizes and six Queen's Anniversary Prizes have been given out by the University of Sheffield. Because of how good it is at engineering, and because many of its courses and departments have close ties to business, it is currently the world's top research university for systems engineering, smart materials, and stem cell technology. Companies like Boeing, Rolls-Royce, and The Welcome Trust are major investors.
Newcastle University
Newcastle University is a prestigious school that has been around since 1834 and is known around the world for its high academic standards. The Russell Group is an organization of 24 top-tier, heavily focused research universities in the UK that was founded with Newcastle University as a founding member.
The University is one of the most popular schools in the UK because of how well it teaches, how well it does research, and how well it helps its students.
Newcastle University is home to more than 28,000 students, including more than 5,400 foreign students from more than 115 countries. It is right in the middle of one of the UK's most lively student neighbourhoods.
The University puts a lot of emphasis on internationalization, and it works with some of the best universities and companies in the world, such as IIT Delhi, IIT Bombay, and IISc Bangalore in India, as well as Siemens, PwC, and IBM.
University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is one of the biggest universities in the UK, with approximately 9,000 international students and 10,000 staff members currently enrolled. It is located in the north of England. The university is a member of the Russell Group and is known for how well it does in school and research.
25 Nobel Prize winners have held positions at the University of Manchester in the past or present, and 91% of recent graduates from Manchester enter the workforce or pursue further education. In the respected Shanghai Jiao Tong Academic Ranking of World Universities, the University of Manchester is ranked 33rd worldwide and sixth in the UK.
Entry requirements for MSc in Cardiovascular Sciences in UK
With GCSEs or an equivalent Level 2 education, you could work in healthcare science as an associate or an assistant. Apprenticeship programs are rare in the healthcare science profession.
After getting an approved BSc in healthcare science, you need two or three A-levels, at least two of which must be in science, and a good mix of A-C GCSEs to get into the NHS Practitioner Training Program (PTP) as a healthcare science practitioner.
The National Health Service (NHS) offers a Scientist Training Program for recent college grads that has a cardiology concentration. You must have earned a first or a 2.1 in an undergraduate honors program or an integrated master's program in a pure or applied scientific field linked to the desired specialty.
You will also be considered if you have earned a Master's or Doctorate degree in a discipline related to the one for which you are applying and have a grade point average (GPA) of 3.0 or above.
0 notes