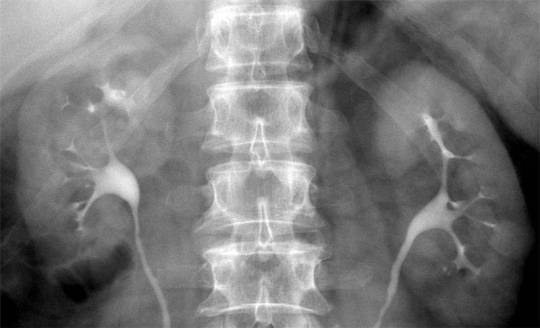
#Intravenous pyelogram
Text
Medical Abbreviations on Pharmacy Prescriptions
Here are some common medical abbreviations you may see on pharmacy prescriptions:
qd - once a day
bid - twice a day
tid - three times a day
qid - four times a day
qh - every hour
prn - as needed
pc - after meals
ac - before meals
hs - at bedtime
po - by mouth
IV - intravenous
IM - intramuscular
subQ - subcutaneous
mL - milliliter
mg - milligram
g - gram
mcg - microgram
stat - immediately, right away
NPO - nothing by mouth
cap - capsule
tab - tablet
susp - suspension
sol - solution
amp - ampule
inj - injection
Rx - prescription
C - Celsius
F - Fahrenheit
BP - blood pressure
HR - heart rate
RR - respiratory rate
WBC - white blood cell
RBC - red blood cell
Hgb - hemoglobin
Hct - hematocrit
PT - prothrombin time
INR - international normalized ratio
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
Cr - creatinine
Ca - calcium
K - potassium
Na - sodium
Cl - chloride
Mg - magnesium
PO2 - partial pressure of oxygen
PCO2 - partial pressure of carbon dioxide
ABG - arterial blood gas
CBC - complete blood count
BMP - basic metabolic panel
CMP - comprehensive metabolic panel.
ECG - electrocardiogram
EEG - electroencephalogram
MRI - magnetic resonance imaging
CT - computed tomography
PET - positron emission tomography
CXR - chest x-ray
CTX - chemotherapy
NSAID - nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
DMARD - disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
ACE - angiotensin-converting enzyme
ARB - angiotensin receptor blocker
SSRI - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
TCA - tricyclic antidepressant
ADHD - attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CAD - coronary artery disease
CHF - congestive heart failure
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
GI - gastrointestinal
UTI - urinary tract infection
OTC - over-the-counter
Rx - prescription
OD - right eye
OS - left eye
OU - both eyes.
TID - thrombosis in dementia
TDS - ter die sumendum (three times a day)
BOM - bilaterally otitis media (infection in both ears)
BT - body temperature
C&S - culture and sensitivity
D/C - discontinue or discharge
D/W - dextrose in water
ETOH - ethyl alcohol
FUO - fever of unknown origin
H&P - history and physical examination
I&D - incision and drainage
I&O - intake and output
KVO - keep vein open
N&V - nausea and vomiting
PERRLA - pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation
PR - per rectum
QAM - every morning
QHS - every bedtime
QOD - every other day
S/P - status post (after)
TPN - total parenteral nutrition
UA - urinalysis
URI - upper respiratory infection
UTI - urinary tract infection
VO - verbal order.
XRT - radiation therapy
YOB - year of birth
BRBPR - bright red blood per rectum
CX - cervix
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
GB - gallbladder
GU - genitourinary
HCV - hepatitis C virus
HPI - history of present illness
ICP - intracranial pressure
IVP - intravenous pyelogram
LMP - last menstrual period
MRSA - methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
MVA - motor vehicle accident
NKA - no known allergies
PEG - percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
PRN - pro re nata (as needed)
ROS - review of systems
SOB - shortness of breath
TAH - total abdominal hysterectomy.
TIA - transient ischemic attack
Tx - treatment
UC - ulcerative colitis
URI - upper respiratory infection
VSD - ventricular septal defect
VTE - venous thromboembolism
XR - x-ray
w/c - wheelchair
XRT - radiation therapy
ASD - atrial septal defect
Bx - biopsy
CAD - coronary artery disease
CKD - chronic kidney disease
CPAP - continuous positive airway pressure
DKA - diabetic ketoacidosis
DNR - do not resuscitate
ED - emergency department
ESRD - end-stage renal disease
FFP - fresh frozen plasma
FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone.
GCS - Glasgow Coma Scale
Hct - hematocrit
Hgb - hemoglobin
ICU - intensive care unit
IV - intravenous
JVD - jugular venous distension
K - potassium
L - liter
MCH - mean corpuscular hemoglobin
MI - myocardial infarction
Na - sodium
NGT - nasogastric tube
NPO - nothing by mouth
OR - operating room
PCN - penicillin
PRBC - packed red blood cells
PTT - partial thromboplastin time
RBC - red blood cells
RT - respiratory therapy
SOA - short of air.
SCD - sequential compression device
SIRS - systemic inflammatory response syndrome
STAT - immediately
T - temperature
TPN - total parenteral nutrition
WBC - white blood cells
ABG - arterial blood gas
A fib - atrial fibrillation
BPH - benign prostatic hypertrophy
CBC - complete blood count
CO2 - carbon dioxide
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CPR - cardiopulmonary resuscitation
CT - computed tomography
CXR - chest x-ray
D5W - dextrose 5% in water
Dx - diagnosis
ECG or EKG - electrocardiogram
EEG - electroencephalogram
ETO - early termination of pregnancy.
FHR - fetal heart rate
GSW - gunshot wound
H&P - history and physical exam
HCG - human chorionic gonadotropin
I&D - incision and drainage
IBS - irritable bowel syndrome
ICP - intracranial pressure
IM - intramuscular
INR - international normalized ratio
IOP - intraocular pressure
LFT - liver function test
LOC - level of consciousness
LP - lumbar puncture
NG - nasogastric
OA - osteoarthritis
OCD - obsessive-compulsive disorder
OTC - over-the-counter
P - pulse
PCA - patient-controlled analgesia
PERRLA - pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation.
PFT - pulmonary function test
PICC - peripherally inserted central catheter
PO - by mouth
PRN - as needed
PT - physical therapy
PT - prothrombin time
PTSD - post-traumatic stress disorder
PVC - premature ventricular contraction
QD - once a day
QID - four times a day
RA - rheumatoid arthritis
RICE - rest, ice, compression, elevation
RSI - rapid sequence intubation
RSV - respiratory syncytial virus
SBP - systolic blood pressure
SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus
SSRI - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
STAT - immediately
TB - tuberculosis
TIA - transient ischemic attack.
TID - three times a day
TKO - to keep open
TNTC - too numerous to count
TPN - total parenteral nutrition
URI - upper respiratory infection
UTI - urinary tract infection
V-fib - ventricular fibrillation
V-tach - ventricular tachycardia
VA - visual acuity
WNL - within normal limits
AED - automated external defibrillator
ARDS - acute respiratory distress syndrome
BID - twice a day
BP - blood pressure
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
CAD - coronary artery disease
CHF - congestive heart failure
CVA - cerebrovascular accident
D/C - discontinue
DKA - diabetic ketoacidosis.
DM - diabetes mellitus
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
EGD - esophagogastroduodenoscopy
ER - emergency room
F - Fahrenheit
Fx - fracture
GI - gastrointestinal
GTT - glucose tolerance test
HCT - hematocrit
Hgb - hemoglobin
HRT - hormone replacement therapy
ICP - intracranial pressure
IDDM - insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
IBS - irritable bowel syndrome
IM - intramuscular
IV - intravenous
K - potassium
KVO - keep vein open
L&D - labor and delivery
LASIK - laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis.
ROM - range of motion
RT - radiation therapy
Rx - prescription
SCD - sequential compression device
SOB - shortness of breath
STD - sexually transmitted disease
TENS - transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
TIA - transient ischemic attack
TSH - thyroid-stimulating hormone
UA - urinalysis
US - ultrasound
UTI - urinary tract infection
VD - venereal disease
VF - ventricular fibrillation
VT - ventricular tachycardia
WBC - white blood cell
XRT - radiation therapy
XR - x-ray
Zn - zinc
Z-pak - azithromycin (antibiotic).
AAA - abdominal aortic aneurysm
ABG - arterial blood gas
ACS - acute coronary syndrome
ADL - activities of daily living
AED - automated external defibrillator
AIDS - acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
ALS - amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
AMA - against medical advice
AML - acute myeloid leukemia
APAP - acetaminophen
ARDS - acute respiratory distress syndrome
ASCVD - atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
BPH - benign prostatic hyperplasia
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
CABG - coronary artery bypass graft
CBC - complete blood count
CHF - congestive heart failure
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CPAP - continuous positive airway pressure
CRF - chronic renal failure.
CT - computed tomography
CVA - cerebrovascular accident
D&C - dilation and curettage
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
ECG/EKG - electrocardiogram
EEG - electroencephalogram
ESRD - end-stage renal disease
FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone
GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease
GFR - glomerular filtration rate
HbA1c - glycated hemoglobin
Hct - hematocrit
HIV - human immunodeficiency virus
HPV - human papillomavirus
HTN - hypertension
IBD - inflammatory bowel disease
IBS - irritable bowel syndrome
ICU - intensive care unit
IDDM - insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
IM - intramuscular.
IV - intravenous
LFT - liver function test
MI - myocardial infarction
MRI - magnetic resonance imaging
MS - multiple sclerosis
NPO - nothing by mouth
NS - normal saline
OCD - obsessive-compulsive disorder
OSA - obstructive sleep apnea
PCOS - polycystic ovary syndrome
PMS - premenstrual syndrome
PPD - purified protein derivative
PSA - prostate-specific antigen
PT - prothrombin time
PTT - partial thromboplastin time
RA - rheumatoid arthritis
RBC - red blood cell
RSV - respiratory syncytial virus
SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus
TB - tuberculosis.
It is important to remember that medical abbreviations can vary based on location and specialty.
Healthcare professionals should use medical abbreviations with caution and only when they are familiar with their meanings.
Patients should always communicate any questions or concerns they have about their medications or medical care to their healthcare provider or pharmacist to ensure they receive safe and accurate medical care.

7 notes
·
View notes
Text
How is hematuria diagnosed and evaluated?
X-ray: If you experience nausea and vomiting, your doctor may prescribe an abdominal x-ray to check for stones. Most causes of hematuria cannot be detected by an x-ray.
MR/CT Urography: CT or MR urography may be used to evaluate the urinary system, bladder, ureters, and kidneys.
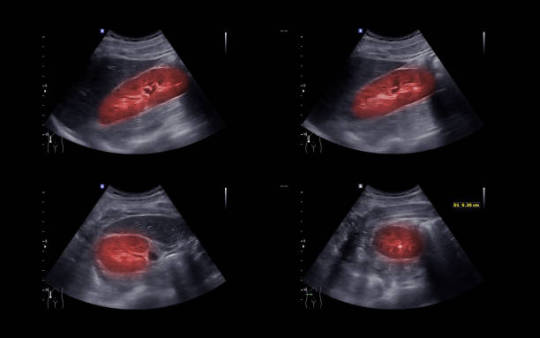
Your doctor may use abdominal ultrasonography to check your kidneys and bladder for potential causes of blood in the urine.
IVP (intravenous pyelogram): An IVP x-ray exam allows your doctor to see your kidneys, bladder, and ureters. It can help detect urinary system abnormalities and show how efficiently your system works.
Prostate MRI: doctor may prescribe MRI to examine your prostate and seminal vesicles.
For more information, consult Dr. Amit Doshi one of the best Urologist in Vadodara
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Urinary Bladder Stones: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment

When you urinate, do you feel pain? Do you notice a difference in the colour of your urine? Do you have an ongoing urge to urinate? These could be signs of bladder stones in the urine. They go by the name "bladder calculi."
What Exactly Are Bladder Stones in thfeele Urine?
Urinary bladder stones are solid growths that form in the bladder and are frequently made of salts and minerals. Their size and shape can vary. While some bladder stones can develop to incredible dimensions, the smallest ones are hardly visible to the human eye.
How Are They Created?
When the bladder is not empty and pee remains inside for too long, urinary bladder stones typically develop. This urine becomes more concentrated over time, and its minerals harden and crystallise.
Dehydration or an inability to empty your bladder are the two most common causes of concentration in urine. These circumstances could be to blame for this.
1. Increasing Prostate Gland Size
Your prostate gland surrounds your urethra, a little tube that transfers pee from your bladder when you urinate. By pressing against the urethra, prostate enlargement might cause problems when urinating.
2. An Injured Urethra
A damaged or injured urethra due to an illness, disease, or trauma can be another issue. It might get narrowed and infected, hindering your body from regularly eliminating urine.
3. UTIs (infection)
Bacteria and other microbes can cause bladder infections or inflammation. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the most frequent cause of bladder stones. Bladder infections are more prevalent in women, while bladder stones are more common in men. Women's urethras are shorter, making it more straightforward for bacteria to enter the bladder.
4. Weak Bladder
The walls of your bladder may become weaker in some areas, resulting in pouches that project upward in the shape of bumps. These pouches can collect and hold urine, crystallising the liquid.
5. Kidney Stones
Small stones can form and move from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters. Although kidney stones develop differently, they can transform into bladder stones when they reach the bladder.
6. Neurogenic Bladder
The neurogenic bladder impacts the nerves that transmit commands from your brain to your bladder muscles. The brain's ability to communicate with your bladder muscles to contract and expand so that you can urinate will be impaired if these nerves are destroyed or injured.
Urinary Bladder Stones Symptoms
Some of the most common indications of kidney stones include the following:
1) A constant urge to urinate
2) Lower abdominal ache
3) burning or discomfort during peeing in the urethra
4) Bloody or murky urine
5) Unable to stop urinating
Bladder Stones Are More Common In Men Than In Women
Men in their 80s may exist. Additionally, residents of somewhat hotter regions and individuals who consume large amounts of sugar and fat are in danger.
Additionally, kids in developing countries are susceptible to bladder stones. They often consume subpar meals and frequently lack access to enough water to stay hydrated.
Diagnostic Techniques
Before any more diagnostic tests, you'll probably undergo a physical examination when you visit the doctor. If you're a man, your physical examination may include a test to see if you have an enlarged prostate. Numerous techniques can be used to diagnose bladder stones. The techniques are:
1. Urine testing
The most popular approach is urinalysis. This test checks your urine for infections, abnormalities, and crystals.
2. Sonography
Sound waves create images of your interior organs during a pelvic ultrasound. Your doctor can use these images to assess whether you have bladder stones. Sometimes it's essential to know the stone's precise dimensions and location.
3. Intravenous Pyelogram With X-rays
The bladder's interior and most abnormalities are seen on X-rays. A dye is injected into your veins during an intravenous pyelogram. Before it reaches your bladder, it passes through your blood vessels. Any unexpected structures are marked, and the X-rays are subsequently run on the highlighted findings.
4. Spiral CT Scan
According to this type of CT scan, anywhere in the body can have abnormalities, including the bladder. Compared to a standard CT scan, it is faster and more accurate.
How Are Urinary Bladder Stones Managed?
The size and placement of the stone determine the optimal course of treatment for bladder stones. Smaller rocks may occasionally pass by themselves. Larger stones, however, might need to be removed surgically.
1. Cystolitholapaxy is a procedure that doctors may use to treat bladder stones. During this process, your stones will be broken up into smaller bits for removal using laser light or ultrasonic waves.
2. Several non-surgical procedures, as well as surgical ones, may aid in preventing the development of bladder stones. These include taking prescription drugs, staying hydrated, and avoiding particular foods and beverages.
The Final Say
Drinking enough fluids early on and scheduling routine checkups can help treat urinary bladder stones. Future stone formation and the emergence of more severe problems can both be avoided with early treatment.
You must get medical assistance as soon as possible if you experience any symptoms of bladder stones. To receive the best care, go to the urology and neurosurgery department of Bansal Hospital in Bhopal.
About Bansal Hospital
Bansal Hospital is a multispeciality hospital and is one of the leading, reputable and reliable healthcare providers trusted by patients and their families across the region. It has all the central departments, including cardiology, neurology, oncology, orthopedics, gastroenterology, urology, liver transplant, bone marrow transplantation, nephrology, gynecology and more. The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and technology. It has a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors and medical staff who provide round-the-clock care to the patient.
Visit Our Website
0 notes
Text
What Are Urinary Bladder Stones, And How To Treat Them?
Do you feel pain while urinating? Do you observe any change of colour in your urine? Do you feel a constant need to urinate? These might be symptoms of Urinary bladder stones. They are also known as Bladder calculi.
What Exactly Are Urinary Bladder Stones?
Urinary bladder stones are solid formations that develop in the bladder, often composed of minerals and salts. They can vary in size and shape. The smallest bladder stones are barely visible to the naked eye, but some can grow to an impressive size.
How Do They Form?
Urinary bladder stones usually form when the bladder is not entirely empty, and urine sits there for too long. Over time this urine gets concentrated, and minerals present harden and form crystals in the urine.
Concentration in urine is usually a result of dehydration or the inability to empty your bladder. This may be due to the following conditions:
1) Enlarged Prostate Gland
Your urethra, a little tube that carries urine from your bladder when you urinate, is encircled by your prostate gland. Prostate growth can trouble urination by pressing up against the urethra.
2) Damaged Urethra
Another condition could be injured or damaged urethra from illness, disease, or trauma. It might get infected and narrow, preventing your body from excreting pee normally.
3) Infection (UTIs)
Bacteria and other organisms can bring on infections or inflammation of the bladder. The most typical cause of bladder stones is Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs).
While bladder stones are more common in men, bladder infections are more common in women. Because women’s urethras are shorter, bacteria can easily enter the bladder.
4) Weak Bladder
Your bladder’s walls could develop weak spots in some places, leading to pouches that form bumps outward. These pouches can catch and store urine which will cause the formation of crystals in urine.
5) Kidney Stones
Small stones can develop and pass through the ureters, from the kidneys to the bladder. Although kidney stones‘ development differs, they can turn into bladder stones when they get to the bladder.
6) Neurogenic Bladder
Neurogenic bladder affects the nerves that carry signals from your brain to your bladder muscles. If these nerves are injured or damaged, the brain will not be able to communicate with your bladder muscles to contract and expand to urinate.
Symptoms Of Urinary Bladder Stones
Some most common symptoms of Urinary Bladder Stones are:
1)frequent need to urinate
2)pain in the lower abdomen
3)burn or pain in the urethra while urinating
4)bloody or cloudy urine
5)unable to control urination
Bladder Stones Are More Common In Men Than Women!
Males are more likely than women to acquire bladder stones, particularly older men with prostate issues. Males in their 80s have a probability. Also, inhabitants of comparatively hotter areas and people who consume heavy sugar and fat are at risk.
Additionally, bladder stones can affect children who reside in underdeveloped nations. They frequently lack access to adequate water to stay hydrated, and they typically eat poor meals.
Diagnosis Methods
You’ll probably receive a physical examination when you visit the doctor before any further diagnostic testing. Your physical examination may involve a test to determine whether you have an enlarged prostate if you are a man.
Bladder Stones can be diagnosed through a variety of methods. The methods are:
1) Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the most common method. This test is performed to look for infections, anomalies, and crystals in your urine.
2) Ultrasound
During a pelvic ultrasound, sound waves produce images of your internal organs. Your doctor can determine if you have bladder stones using these photos. In some cases, it is necessary to determine the exact size and location of the stone.
3) X-Rays and Intravenous Pyelogram
X-rays provide a clear view of the bladder’s interior and most abnormalities. In an Intravenous Pyelogram, a dye is put into your veins. It travels through your blood vessels until it reaches your bladder. Any unexpected structures are highlighted, and the highlighted findings are then subjected to X-rays.
Because not all bladder stones will be visible on an X-ray, this diagnostic procedure is no longer utilised frequently for bladder stones.
4) Spiral CT Scan
This kind of CT scan scans for problems anywhere in the body, including the bladder. Compared to a standard CT scan, it is faster and more accurate.
How Do You Treat Urinary Bladder Stones?
Treatment for bladder stones typically depends on the size and location of the stone. In some cases, smaller stones may pass on their own. However, larger stones may require surgical removal.
In the case of bladder stones, doctors may perform a cystolitholapaxy. This procedure uses laser energy or ultrasound waves to break your stones down into smaller pieces for removal.
In addition to surgical treatments, several non-surgical treatments may help prevent the formation of bladder stones. These include medications, drinking plenty of fluids, and avoiding certain foods and drinks.
The Final Say
Urinary bladder stones can be cured by drinking plenty of fluids at the initial stage and getting regular check-ups. Early treatment can help prevent the formation of future stones and prevent more severe complications from developing.
As soon as you experience bladder stones symptoms, you must seek medical help immediately. You can visit Bansal hospital Bhopal’s Urology and Urosurgery department to get the best treatment.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why Would You Need to Consult a Urologist?
Urologists deal with health issues that involve the urinary tract and the male reproductive system. They also treat conditions that affect the adrenal glands.
Men often seek a urologist for blood in their urine, urinary incontinence, or an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA). Prostate cancer is another common reason men see a urologist.
If you see blood in your urine, you must visit a urologist. Most hematuria is benign, but it can be a warning sign of a severe condition.
The kidneys filter blood to produce urine, which is made up of waste products and extra water. It then passes through the tubes called ureters to the bladder, where it is stored until urination occurs.
Sometimes, the urine is pink, red, or tea-colored (gross hematuria). In other cases, it is hard to spot blood in the urine with the naked eye.
Doctors usually perform a physical exam to look for bleeding and check the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. They will also order tests to help find the source of the hematuria and treat it. These include a urinalysis and an intravenous pyelogram.
Urinary incontinence is a common problem that affects millions of men and women. However, many people don’t see a doctor because they are embarrassed or think nothing can be done.
A urologist can help you get to the bottom of your incontinence and find solutions that work for you. Usually, they begin by asking you questions about your symptoms and the type of incontinence you have.
Your doctor will also ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam. This includes looking at your pelvic area for any signs of a problem, checking your prostate, and performing a pelvic ultrasound or renal ultrasound.
The doctor may also ask you to keep a bladder diary. This involves recording when you urinate, how much you urinate, and whether you have any incontinence episodes.
If you have pelvic pain, it could indicate an underlying medical condition. It can be challenging to pinpoint the cause of pelvic pain, but if you see a urologist, it could lead to a better diagnosis and treatment.
A urologist is a specialist doctor who treats conditions that affect both the urinary and reproductive systems. They may have to do tests, such as blood work or an X-ray, to diagnose the source of your pain.
For example, if your symptoms suggest that you have interstitial cystitis (IC), a urologist can do a cystoscopy, which uses a particular scope to look inside your bladder. Your urologist can also do other tests to rule out possible causes of your pelvic pain.
If you have difficulty achieving and maintaining an erection firm enough to allow sexual intercourse, you may need a consultation with a urologist. They specialize in disorders of the urinary tract and male reproductive system, so they can be an excellent resource for treating erectile dysfunction.
Your urologist will discuss your medical history and ask questions about sexual activity. They will also perform a physical examination to determine the cause of your ED.
Many times erectile dysfunction is the result of an underlying health problem, such as diabetes or low testosterone levels. Treating these conditions usually reverses ED.
Other times erectile dysfunction is a symptom of a more severe condition, such as vascular disease (hardening of the arteries). This can be treated by your GP or by taking medication.
Psychological issues, such as depression and stress, can also cause erectile dysfunction. These issues can lead to poor self-esteem and anxiety.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Are Kidney and Bladder Stones Diagnosed
Imaging is used to provide your doctor with valuable information about the kidney or bladder stones, such as location, size and effect on the function of the kidneys. How your doctor Diagnosed Kidney and Bladder Stones may be for the following kinds of imaging:
The quickest scanning procedure for finding a stone is abdominal and pelvic CT. This treatment may offer comprehensive pictures of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, as well as locate stones and determine if they are obstructing urine flow.
Intravenous pyelogram: An x-ray examination of the kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder that uses iodinated contrast material injected into veins to assess the urinary system. More information regarding x-rays may be found on the Safety page.
Abdominal and Pelvic ultrasound: These scans employ sound waves to create images of the kidneys and bladder, which may help discover urine flow blockages and stones.
Why Do Doctors Examine the Stone's Contents?
Stones are classified into four categories. Studying the stone may help you understand why you have it and how to limit your chances of getting more. Calcium is found in the most frequent sort of stone. Calcium is an essential component of a balanced diet.
The kidney normally eliminates excess calcium from the body. People who have stones often retain an excessive amount of calcium. This calcium, when combined with waste products such as oxalate, forms a stone. Calcium oxalate is the most prevalent combination.
Less frequent forms of stones include infection-associated struvite stones, which include magnesium and ammonia, and uric acid stones, which are generated from monosodium urate crystals and may be connected to obesity and dietary variables. The most unusual sort of stone is a cysteine stone, which runs in families.
How Does the Method Work?
X-rays, like light and radio waves, are forms of radiation. X-rays can penetrate most things, including the human body. The x-ray beam is precisely aimed at the region of interest by the technician.
The equipment emits a brief blast of radiation that travels through your body. The radiation creates a picture, which is then recorded on photographic film or a specific detector.
The x-rays are absorbed to differing degrees by different areas of the body. Dense bone absorbs a large portion of the radiation, while soft tissue allows more of the x-rays to flow through. As a consequence, bones look white on x-rays, soft tissue appears gray, and air appears black.
The majority of x-ray pictures are digital data that are electronically stored. Your doctor will have easy access to these saved photographs in order to diagnose and manage your disease.
0 notes
Link

#Cases of Vesico#Vaginal Fistulae#Vesico Vaginal Fistulae#Intravenous pyelogram#Transperitoneal transvesical repair
0 notes
Text
Duplicated collecting system
This week we will focus on congenital malformations of the genitourinary system. Such defects are common and can lead to recurrent infection, incontinence and other complications.
This is a case of duplicated collecting system, shown on intravenous pyelogram. Note complete duplication of the right collecting system and partial duplication on the left, with ureters joining at the level of L3. In complete duplication, the upper pole moiety tends to obstruct, while the lower pole moiety tends to reflux, placing patient at risk for infection. In this case, the left side shows eveidence of obstruction and/or reflux (VCUG or nuclear cystogram can be performed to demonstrate reflux). Case courtesy of Dr Aditya Shetty, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 27218
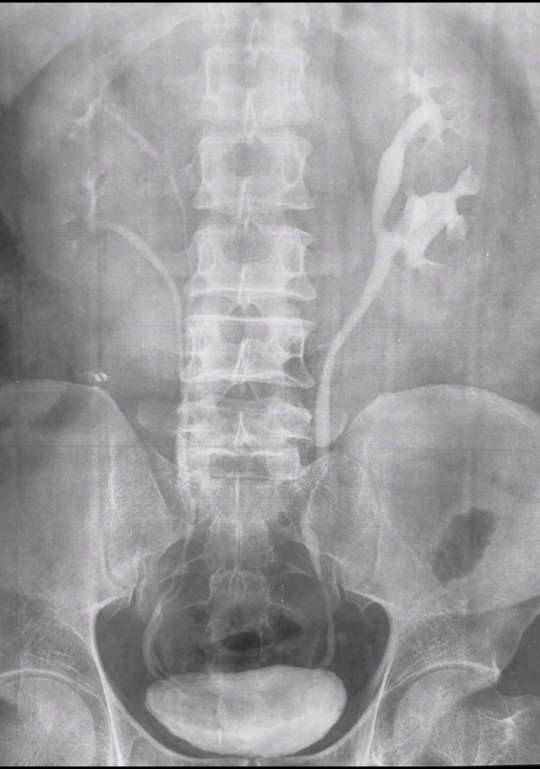
#teachingrounds#foamed#foamrad#pediatrics#peds#urology#pedsuro#radiology#pedsrad#gu#genitourinary#radiography
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ultra Max Rise Reviews, prices, benefits and where to buy
Ultra Max Rise a real assessment is head to the examination. Depending in your signs and indications, it can contain an assessment of the mid-region, rectum, crotch, or privates. Ladies with urinary signs will usually experience a pelvic test, while men can be given a computerized rectal assessment to physically assess the prostate gland.
Palpation (the contacting of shallow tissues) may likewise show an inguinal hernia or testicular twist, simultaneously as percussion (the mellow tapping of tissue) may furthermore help check urinary maintenance.
Blood checks
Blood tests are usually used to analyze genitourinary problems. Limit of the appraisals can't quickly analyze sickness yet are on the other hand used to help the guess. those comprise of:
Alpha-fetoprotein test (used to determine testicular cancer 4 related to have ldh and hcg tests)
Blood calcium investigate (used to screen for kidney infection)
keratinize and blood urea nitrogen (bun) appraisals (used to gauge kidney feature)five
Prostate-special antigen investigate (used to hit upon prostate most tumors)
Sexually transmitted disease screening (used to find explicitly sent contaminations)
Testosterone check (use to run over low testosterone levels)
Urinalysis is imperative to diagnosing urologic issues. the urinalysis may envelop a gross assessment of the tone, look, and scent of the example notwithstanding a substance and tiny assessment.

The synthetic investigation could degree components like protein and glucose, high levels of which can likewise support kidney infirmity or diabetes. Broadened nitrites or the presence of white platelets might be intriguing a bacterial contamination. the presence of blood in pee can be recognized outwardly or with a pee dipstick test. in the event that blood is distinguished, this at that point requires a particular workup, for example, additional pee research, cystoscopy, and imaging.
A minuscule assessment can be useful in identifying epithelial cells (floor cells by and large shed with kidney most malignancies). Urinary gems can likewise be spotted and used to affirm the presence of kidney stones. a pee custom will likewise be finished to check a bacterial defilement in any case undetected with the guide of blood appraisals.

while a difficulty isn't in every case easily noticeable, there are imaging methodologies normally used by urologists. those comprise of customary and specific innovations, alongside:
Kidney, urethra, and bladder (kub) x-beam (normally the main imaging examine achieved in an assessment)
Intravenous pyelogram (ivp) x-beam (which utilizes an infused color to diagram the frameworks of the urinary plot. this view is by and large completed now with processed tomography.
#Goketogenics
https://goketogenics.com/
#UltraMaxRise#UltraMaxRiseReview#UltraMaxRisePill#UltraMaxRiseReviews#UltraMaxRiseBenefits#UltraMaxRiseSharkTank#UltraMaxRiseReviewsPills#UltraMaxRiseMen’sHealth.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How is hematuria diagnosed and evaluated?
X-ray: If you experience nausea and vomiting, your doctor may prescribe an abdominal x-ray to check for stones. Most causes of hematuria cannot be detected by an x-ray.
MR/CT Urography: CT or MR urography may be used to evaluate the urinary system, bladder, ureters, and kidneys.
Your doctor may use abdominal ultrasonography to check your kidneys and bladder for potential causes of blood in the urine.
IVP (intravenous pyelogram): An IVP x-ray exam allows your doctor to see your kidneys, bladder, and ureters. It can help detect urinary system abnormalities and show how efficiently your system works.
Prostate MRI: doctor may prescribe MRI to examine your prostate and seminal vesicles.
for more information consult Dr. Amit Doshi one of the best Urologist in Vadodara
1 note
·
View note
Text
Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market to Grow at 4.4% CAGR to Reach US$1.98 billion by 2026
The Global Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market was valued at US$1.48 billion in the year 2018 and is expected to reach US$1.98 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 4.4%.
Urinary stones are mainly formed due to the inability of an individual to empty the urinary bladder. Due to urine accumulation, the minerals in the concentrated urine start crystalizing leading to the formation of stones. Depending on the location of the stone development it may be classified as a kidney stone, bladder stone or ureteral stone. These stones are diagnosed using, abdominal X-ray, CT scan, MRI scan, ultrasound, etc. During the early days, the stones were removed through surgical procedures. But the development of technologies such as lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, nephrolithotomy had reduced the hurdles in treatment and the removal of urinary stones. Also growing popularity of digital flexible ureteroscopes and rising focus on the development of lasers alternative to conventional once are the factors that contribute to the market growth.
Urolithiasis and Nephrolithiasis are the main conditions that contribute to the development of kidney stones in individuals and chiefly contribute to market growth. Besides, the recurrence of kidney stones in the adult population has also risen to 50% in recent decades due to enormous changes in the lifestyle, poor dietary habits, an increase in obesity, less intake of water and many other associated morbidities. Moreover, as recent research suggested, the probability of recurrence of nephrolithiasis in adolescents or children is about 50% within 3 years of the first occurrence. According to the National Kidney Foundation, over half a million people across the globe visit emergency rooms every year. International Federation of Kidney Foundations and the International Society of Nephrology are taking several initiatives to create awareness among the people regarding the equitable and inexpensive access to treatment options, screening, and diagnosis. This is set to drive the Urinary Treatment Devices market during the forecast period.

Implementation of imaging technologies for scanning urinary stones is expected to drive the growth in the upcoming years. Among diagnoses, the ultrasound segment emphasizes reducing the amount of ionizing radiation delivered to patients during routine imaging. It has also become a mainstay tool in the urologists' armamentarium for the diagnosis and management of nephrolithiasis. New advancements in ultrasound technology had also facilitated its use as a therapeutic and therapy guidance aid. Ultrasound is being used as the first line for the diagnosis of urinary stones for more than 14 years and is set to grow with a healthy CAGR of 5.1% during the forecast period. Other diagnostic techniques such as MRI, intravenous pyelogram, non-contrast CT are said to contribute very little when compared to ultrasound.
Adoption of an alternative way of treatment such as Chinese herbal medicine, Ayurveda, acupressure was minimal during the yesteryears. However, after the rediscovery of the ancient techniques, the options for treating urinary stones with herbal medicine, acupressure, etc. are being researched more and few options have also become successful in minimizing the urinary stones. This is set to hamper the market growth as WHO had already initiated a global level initiative to study and standardize the usage of medicinal plants including that of the folklore medicine.
However modern medicine offers an effective way of treatment. Among them, the lithotripsy segment has a huge demand in the market treating urinary stones and also to sidestep the invasive surgical procedures that were used for stone removal. Lithotripsy uses ultrasonic energy or shock waves focused directly on the stone to identify the place which was previously located with fluoroscopy or ultrasound of the stones. The patient is positioned in such a way so that the stones are targeted precisely. By using this lithotripsy, the complications, hospital stays, costs and recovery time are reduced. The treatment using lithotripsy is expected to fuel market growth until 2026.
Among stone types, the calcium oxalate segment has been reported to propel the urinary stones market till 2018. The formation of calcium oxalate stones is strongly linked to the consumption of foods consisting high amount of oxalate that naturally occurs in plants and animals. This includes beets, black tea, chocolate, nuts, potatoes, and spinach. Also, calcium in the form of supplements for several other bone-related disorders may increase the chances of forming new calcium oxalate stones in the urine. Also, consumption of more leguminous foods such as dried beans, peas, anchovies and drinking of beer may increase the chances of uric acid crystal formation due to the deposition of purines in the kidney.
North American region highly dominates the urinary stones treatment devices market due to extensive prevalence in the occurrence of urinary stones. The favorable conditions for research and development, increased healthcare expenditure and growing utilization of advanced technology for the treatment aspects are evident in this region. The US market holds a market share of about 65% to 35% whereas the Canadian market share is set to increase by around 2% during the forthcoming years due to more immigration from other countries. Further, government initiatives towards strengthening the healthcare infrastructure are accelerating the growth of the urinary stone treatment devices market in this region. Followed by the North American region is the European region, where Germany alone contributes to more than 27% of the total European market growth due to more occurrence of Urolithiasis among German individuals followed by France, the UK, Italy, and Spain. Besides, the Asia Pacific and the Middle East countries are also expected to contribute to the market growth having potential opportunities falling under the kidney stone belt of the world.
Some of the key players in the urinary stones treatment devices market are, Becton, Dickinson and Company, Boston Scientific Corporation, EDAP TMS S.A., Olympus Corporation, Coloplast A/S, Siemens Healthineers, Convergent Laser Technologies, Cook Medical Inc, Direx Group, Dornier MedTech GmbH, Elmed Electronics & Medical Industry & Trade Inc, KARL STORZ GmbH & Co. KG, Lumenis Ltd, Medispec LTD, Richard Wolf Medical Instruments Corporation, Allengers Medical Systems Ltd and E.M.S. Electro Medical Systems SA.
Request for Sample Pages @ https://www.optimainsights.org/sample-request/145-urinary-stones-treatment-devices-market
Key Updates:
FDA Approves Retrophin’s New Formula Thiola EC (tiopronin) for treating Cystine Kidney Stones
Dornier’s new Gemini stone-busting system: The pulverizer is both a step into the future and a blast from the past
Dornier launches AXIS™ Single-Use Digital Ureteroscope for treating Urinary Stones
Journal Summaries in Internal Medicine: Researchers examined the utility of experimental Thulium fiber laser (TFL) as an alternative to the gold standard Holmium: YAG laser for lithotripsy
The Report Provides Key Insights on
History of the Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market, 2015 to 2017
Forecast of the Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Growth till the year 2026
The key market drivers, restraints, challenges, future opportunities and the market dynamics driving the Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market
Analysis of potential growth segments which will drive the market
Landscape analysis of the major companies, and new market entrants and companies which possess disruptive technologies which can change the trend of the entire market
Key market approaches adopted by the organizations and in-depth intelligence of potential strategies which could alter the market dynamics
Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Based on Diagnosis (Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, (US$ Mn)
· Abdominal X-Ray
· Computed Tomography(CT) Scan
· Intravenous Pyelography (IVP)
· Ultrasound
· Abdominal MRI
Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Based on Treatment (Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, (US$ Mn)
· Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
· Ureteroscopy (URS)
· Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Based on Stone Type (Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, (US$ Mn)
· Calcium Phosphate
· Cystine
· Struvite
· Uric Acid
· Calcium Oxalate
Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Based on Geographic Region (Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, (US$ Mn)
· North America
· Europe
· APAC
· LAMEA
Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Competitive Analysis (Company Overview, SWOT Matrix, Financial, Product Overview, and Market Strategies)
· Siemens Healthineers
· Direx Systems Corp
· Dornier Medtech Gmbh
· Elmed Electronics & Medical Industry & Trade Inc
· Karl Storz Gmbh & Co. KG
· Lumenis Ltd
· Medispec Ltd
· E.M.S. Electro Medical Systems SA
Download Complete TOC of the Report @ https://www.optimainsights.org/request-toc/145-urinary-stones-treatment-devices-market
About Us
Optima Insights is an innovative research and insights-driven enterprise committed to offering actionable intelligence to the global life science and healthcare market. We believe that meaningful insights and improved strategic content hold the key to improved ROI for our clients. We strike an innovative engagement model with our clients to Co-Create Intelligence that would address very specific issues facing them within their functional areas. We continuously support clients through the entire journey map to enable them to make better business decisions towards attaining market leadership.
Contact
Optima Insights
Mr. Chucks G
+91 966 6620 365 (Asia) | +1 424 2554 365 (US)
Email: [email protected]
https://www.optimainsights.org
#Urinary stones treatment devices market#Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Analysis#Urinary Stones Treatment Devices Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
Urinary Bladder Stones: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment

When you urinate, do you feel pain? Do you notice a difference in the colour of your urine? Do you have an ongoing urge to urinate? These could be signs of bladder stones in the urine. They go by the name "bladder calculi."
What Exactly Are Bladder Stones in thfeele Urine?
Urinary bladder stones are solid growths that form in the bladder and are frequently made of salts and minerals. Their size and shape can vary. While some bladder stones can develop to incredible dimensions, the smallest ones are hardly visible to the human eye.
How Are They Created?
When the bladder is not empty and pee remains inside for too long, urinary bladder stones typically develop. This urine becomes more concentrated over time, and its minerals harden and crystallise.
Dehydration or an inability to empty your bladder are the two most common causes of concentration in urine. These circumstances could be to blame for this.
1. Increasing Prostate Gland Size
Your prostate gland surrounds your urethra, a little tube that transfers pee from your bladder when you urinate. By pressing against the urethra, prostate enlargement might cause problems when urinating.
2. An Injured Urethra
A damaged or injured urethra due to an illness, disease, or trauma can be another issue. It might get narrowed and infected, hindering your body from regularly eliminating urine.
3. UTIs (infection)
Bacteria and other microbes can cause bladder infections or inflammation. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the most frequent cause of bladder stones. Bladder infections are more prevalent in women, while bladder stones are more common in men. Women's urethras are shorter, making it more straightforward for bacteria to enter the bladder.
4. Weak Bladder
The walls of your bladder may become weaker in some areas, resulting in pouches that project upward in the shape of bumps. These pouches can collect and hold urine, crystallising the liquid.
5. Kidney Stones
Small stones can form and move from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters. Although kidney stones develop differently, they can transform into bladder stones when they reach the bladder.
6. Neurogenic Bladder
The neurogenic bladder impacts the nerves that transmit commands from your brain to your bladder muscles. The brain's ability to communicate with your bladder muscles to contract and expand so that you can urinate will be impaired if these nerves are destroyed or injured.
Urinary Bladder Stones Symptoms
Some of the most common indications of kidney stones include the following:
1) A constant urge to urinate
2) Lower abdominal ache
3) burning or discomfort during peeing in the urethra
4) Bloody or murky urine
5) Unable to stop urinating
Bladder Stones Are More Common In Men Than In Women
Men in their 80s may exist. Additionally, residents of somewhat hotter regions and individuals who consume large amounts of sugar and fat are in danger.
Additionally, kids in developing countries are susceptible to bladder stones. They often consume subpar meals and frequently lack access to enough water to stay hydrated.
Diagnostic Techniques
Before any more diagnostic tests, you'll probably undergo a physical examination when you visit the doctor. If you're a man, your physical examination may include a test to see if you have an enlarged prostate. Numerous techniques can be used to diagnose bladder stones. The techniques are:
1. Urine testing
The most popular approach is urinalysis. This test checks your urine for infections, abnormalities, and crystals.
2. Sonography
Sound waves create images of your interior organs during a pelvic ultrasound. Your doctor can use these images to assess whether you have bladder stones. Sometimes it's essential to know the stone's precise dimensions and location.
3. Intravenous Pyelogram With X-rays
The bladder's interior and most abnormalities are seen on X-rays. A dye is injected into your veins during an intravenous pyelogram. Before it reaches your bladder, it passes through your blood vessels. Any unexpected structures are marked, and the X-rays are subsequently run on the highlighted findings.
4. Spiral CT Scan
According to this type of CT scan, anywhere in the body can have abnormalities, including the bladder. Compared to a standard CT scan, it is faster and more accurate.
How Are Urinary Bladder Stones Managed?
The size and placement of the stone determine the optimal course of treatment for bladder stones. Smaller rocks may occasionally pass by themselves. Larger stones, however, might need to be removed surgically.
1. Cystolitholapaxy is a procedure that doctors may use to treat bladder stones. During this process, your stones will be broken up into smaller bits for removal using laser light or ultrasonic waves.
2. Several non-surgical procedures, as well as surgical ones, may aid in preventing the development of bladder stones. These include taking prescription drugs, staying hydrated, and avoiding particular foods and beverages.
The Final Say
Drinking enough fluids early on and scheduling routine checkups can help treat urinary bladder stones. Future stone formation and the emergence of more severe problems can both be avoided with early treatment.
You must get medical assistance as soon as possible if you experience any symptoms of bladder stones. To receive the best care, go to the urology and neurosurgery department of Bansal Hospital in Bhopal.
About Bansal Hospital
Bansal Hospital is a multispeciality hospital and is one of the leading, reputable and reliable healthcare providers trusted by patients and their families across the region. It has all the central departments, including cardiology, neurology, oncology, orthopedics, gastroenterology, urology, liver transplant, bone marrow transplantation, nephrology, gynecology and more. The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and technology. It has a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors and medical staff who provide round-the-clock care to the patient.
Visit Our Website
0 notes
Text
UK Bladder Cancer Market, Size, Share, Analysis Report & Forecast to 2026
UK bladder cancer market is estimated to grow considerably at a CAGR of around 9.8% during the forecast period. UK has one of the finest healthcare systems in the EU region which enables it to provide quality healthcare to the individual citizens. Numerous factors are affecting the prevalence of bladder cancer in the country, such as the increasing population and exposure to a specific type of chemicals among numerous others. As the lifestyle of the people across the region changes, thereby changing the eating habits, this is expected to increase the prevalence of bladder cancer in the coming years. Smoking is one of the key reasons for the rising prevalence of bladder cancer across the population. The percentage of population smoking in the UK is majorly between the age group of 25-34. Owing to this, the prevalence of bladder cancer is expected to increase, thereby creating opportunities for the growth of the market in the near future.
Get Free Sample Copy @
https://www.omrglobal.com/request-sample/uk-bladder-cancer-market
UK bladder cancer market is segmented into cancer type, diagnosis, and treatment. Based on cancer type, the market is segmented into transitional cell bladder cancer/ urothelial carcinoma, squamous cell bladder cancer, adenocarcinoma, and other rare types (sarcomas, carcinoma in situ). Based on the diagnosis, the market is segmented into cystoscopy, biopsy, urinalysis, urine cytology, intravenous pyelogram (IVP), and others. Based on treatment, the market is segmented into chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and other treatment which include targeted therapy.
A Full Report of UK Bladder Cancer Marketis Available at:
https://www.omrglobal.com/industry-reports/uk-bladder-cancer-market
The companies which are contributing to the growth of the UK bladder cancer market include AstraZeneca PLC, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Co., Eli Lilly & Co., GlaxoSmithKline PLC, Pfizer, Inc. The market players are considerably contributing to the market growth by the adoption of various strategies including new product launch, merger, and acquisition, collaborations with government, funding to the start-ups, and technological advancements to stay competitive in the market.
Market Segmentation
UK Bladder Cancer Market by Cancer Type
· Transitional Cell Bladder Cancer/ Urothelial Carcinoma
· Squamous Cell Bladder Cancer
· Adenocarcinoma
· Others (Sarcomas, Carcinoma in Situ)
UK Bladder Cancer Market by Diagnosis
· Cystoscopy
· Biopsy
· Urinalysis
· Urine Cytology
· Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
· Others (Biomarkers)
UK Bladder Cancer Market by Treatment
· Surgery
· Chemotherapy
· Immunotherapy
· Radiation Therapy
· Others (Targeted Therapy)
Company Profiles
· Astellas Pharma Inc.
· AstraZeneca PLC
· Bayer AG
· Bristol-Myers Squibb Co.
· Eli Lilly and Co.
· F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
For More Customized Data, Request for Report Customization @
https://www.omrglobal.com/report-customization/uk-bladder-cancer-market
About Orion Market Research
Orion Market Research (OMR) is a market research and consulting company known for its crisp and concise reports. The company is equipped with an experienced team of analysts and consultants. OMR offers quality syndicated research reports, customized research reports, consulting and other research-based services.
Media Contact:
Company Name: Orion Market Research
Contact Person: Mr. Anurag Tiwari
Email: [email protected]
Contact no: +91 780-304-0404
0 notes
Text
Polycystic kidney disease and its ayurvedic treatment
What is Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Polycystic kidney disease is defined as a genetic kidney disorder that causes cysts filled with fluids in the kidneys. The fist-sized organs - kidneys are personified as the whole balance of the human body.
Kidneys can manage multiple functions at the same time. They perform multiple duties and handle them as per physical requirements.
They balance the basic levels of electrolytes, regulate the blood pressure levels according to the body, and most importantly, these multi-tasking organs are responsible for purifying the blood and eliminating the waste products from the body. The cysts associated with PKD can trigger life-threatening outcomes as they begin to spread their maliciousness from the structural and functional units of the kidneys (nephrons). The growth of cysts causes renal enlargement and affects the functioning rate of kidneys. Considerable growth of cysts is harmful to the kidneys. Several complications arise, such as improper blood filtration, no reabsorption of essential substances, accumulation of waste products. The progression of polycystic kidney disease relies on the rate of growth of cysts. These cysts tend to metastasize in other parts of the body, like the liver.
Therefore, Polycystic kidney disease damages kidneys and surrounding organs. It is that type of disease that affects the kidneys and influences other parts of the body.
This genetic disorder can welcome a significant kidney disease if it reaches its extreme level. Chronic kidney disease occurs when the kidneys start losing their functional abilities over time due to the growth of PKD cysts. However, PKD can also be seen as a form of CKD (chronic kidney disease) as the kidney fails to function over time in both diseases.
What Are The Types of Polycystic Kidney Disease?
An insight into the types of polycystic kidney disease can help understand the causes of the disease. Two major types of PKD are as follows:
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD).
What causes Polycystic kidney disease?
The mutations in the genes are the primary cause of polycystic kidney disease. In some cases, a gene mutation occurs on its own, known as spontaneous gene mutation.
The two major types of PKD describes the causes of the disease:
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: ADPKD accounts for most of the cases. It is responsible for causing cysts within the kidneys only. The signs and symptoms occur within the age group of 30 to 40 years.
A single parent with the mutated gene can transport the disease to the child. The child can inherit the kidney disease with a 50% chance.
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: ARPKD is not as common as ADPKD is. The cysts growth in ARPKD spreads in both kidneys and the liver. Signs and symptoms become noticeable shortly after birth, or some cases do not experience symptoms until late childhood or during adolescence. Both the parents must be having defective genes to transfer this type of PKD. Each child will procure a 25% chance to inherit the kidney disorder.
What are the indications of polycystic kidney disease?
The identification of symptoms is linked with the growth of cysts in the kidneys. When kidneys become impaired and can not perform their duties, certain complications occur and causes symptoms that include:
Urinary tract infection (UTI).
Kidney stones.
Sensitive skin that bruises easily.
Back pain.
Unusual pale skin colour.
Fatigue.
Joint pain.
Nail abnormalities.
Abdominal pain.
Bloody urine.
Frequent urges to urinate.
Side pain.
Children having autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease can have symptoms like:
High blood pressure or hypertension.
Urinary tract infection.
Frequent urination.
How is Polycystic Kidney Disease Diagnosed?
If you are linked to PKD through family history or notice symptoms mentioned above, you need medical guidance. The doctor will review your family history by genetic testing. Other tests would also be performed to detect anaemia, red blood cells or protein in the urine.
Imaging tests used to diagnose polycystic kidney disease are as follows:
Intravenous pyelogram.
Abdominal ultrasound.
Abdominal CT scan.
Abdominal MRI scan.
Can Ayurvedic Treatment Reduce The Advancement of PKD?
Ayurveda is defined as the ancient medical treatment methods that have acquired significant experience and expertise in human anatomy. The theories of Ayurveda have proven to treat even major inherited kidney diseases like polycystic kidney disease.
The holistic approach to natural treatment does not rely on dialysis or renal transplants. Polycystic kidney disease treatment in Ayurveda does not involve drug-based medications and prescribes herb-based medications instead. As ayurvedic herbs have kidney-friendly properties and can help reduce the advancement of the disease and the cystic growth rate in the kidneys. These herbs are 100% natural and do not cause any side effects on the body's natural healing capabilities. According to the reports, a diet chart is also customized and comprises superfoods to boost your metabolism and immune system to help combat kidney disease.
However, Polycystic kidney disease treatment in Ayurveda can help reduce the progression of the genetic kidney disorder with natural and effective modes of Ayurveda. The limit of the natural healing system of Ayurveda can go from treating the disease with natural mediums and curing it of the core. The treatment is affordable and does not face any after-effects that enhance your mental and physical state.
#health#health & fitness#kidney problems#kidney failure#PKD Ayurvedic Treatment#polycystic kidney disease
0 notes