#1792 france
Text

Over two years since original announcement, Neflix finally sets Castlevania: Nocturne release date.
The series will follow Richter Belmont during the French Revolution.
And according to Collider, there’s a chance Richard and Alejandra Reynoso might reprise their roles from the original series via flashbacks.
Castlevania: Nocturne premieres September 28 on Netflix.
#richard armitage#trevor belmont#alejandra reynoso#sypha belnades#richter belmont#james callis#alucard#adrien fahrenheit tepes#graham mctavish#vlad dracula tepes#dracula#wallachia#castlevania#castlevania nocturne#netflix#castlevania spin off#spin off#france#french revolution#1792#kevin kolde#clive bradley#samuel deats#adam deats#powerhouse animation#frederator studios#animation studio#collider#september 2023#news
320 notes
·
View notes
Text

Napoleon standing in the ruins of the Tuileries palace in Paris goes kind of hard ngl
#Napoleon#job#Jacques Onfroy de Bréville#Jacques Marie Gaston Onfroy de Bréville#napoleon bonaparte#frev#French Revolution#1792#tuileries#Tuileries palace#napoleonic era#19th century#first french empire#french empire#napoleonic#bonaparte#France#la révolution française#art#illustration#cartoon#palace#1790s#1700s#18th century#first french republic
174 notes
·
View notes
Text



Okay fine Netflix I won't cancel my subscription just yet fuck you
#holy fuck finally#God i love Richter's design he looks like a combination of Trevor and Sypha#im excited to see where they take the story now that its in 1792 Revolutionary France unlike Rondo where its just Wallachia bit in 1792#Give Richter some Vampire killing flintlocks that he can use alongside his whip please and thank you#Castlevania#Castlevania Nocturne#castlevania netflix
158 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let me talk Church and the Revolution

Okay, let me post this preemptively. Because I already know that soon enough those people looking for reasons to hate on Castlevania Nocturne because it is not like the games will also come to cry a river about "they depict the church as evil!!!!"
So, let me quickly talk about the role of the church in the French Revolution. Because there is something you gotta understand about the Church during the French revolution: That there was not THE Church.
Basically within the Catholic church in France there was a fracture over the entire revolution happening. A lot of the higher ranked clergy men stood on the side of the nobles and royals, while a lot of the lower ranked clergymen stood with the revolutionaries. The reason behind that mostly was money.
See, before the revolution the church was allowed to collect taxes themselves, while also being tax exempt. So they did not have to pay taxes on all the stuff they sold and made to the nobility. Which was why the bishops and general higher ups within the church could have the lavish lifestyle of nobility themselves, often of course ignoring their vows.
Meanwhile a lot of lower clergy (and especially certain groups of monks - especially the franciscans) were like: "We are all equal in the eyes of god. Rich folks do not get into heaven. Equality is what god wanted from us" and supported the revolution because of it.
But of course there was also the thing that the show mentioned: Given the show is set in summer it seems (probably just before the Reign of Terror) it would have been not even a year before that a lot of clergy got slaughtered. Why did they get slaughtered?
Well, short explanation: Royalists and also some of the bishops provoked the war with Prussia in an attempt to overthrow the revolutionary forces with the help of the Prussian military. This of course failed and the revolutionaries were out for blood. So nobles fled into the churches for sanctuary. And in retaliation a lot of clergy died for haboring the nobles in question.
And, yeah. There is of course the other aspect: The church at the time for a lot of historcal and religious reasons very much supported slavery. Meanwhile this is already a point where the revolution at large had decided that slavery should be done away with. And that leads to what we see in the show here: Clergy going on about the revolution being against "the natural order".
(Being frank: I LOVE that they brought this into the show. Which is almost like a whole other thing I could write about. The entire idea of the revolution and the "natural order" and how it is all linked to colonialism.)

Another interesting part here is the order the abbot and Mizrak are from. On the Castlevania discord server I already went into a whole thing trying to figure that out, but my last idea was right: They are from the Knights Hospitaller. The order of St. John.
This order arose during the crusades and as the name Knights Hospitaller suggests: Yeah, they mostly created hospitals (though historically those were not only to cure the sick, but also to be a home - "hospitality" - for those on the road). They were based in Jerusalem for a while, but ended up moving to Malta, which was of course for a long while ruled by France. They referenced here that the Abbot came to France from Malta, which is the reason.
But yeah, they actually were about helping people for the most part. But they also made money from it. And when the revolution came, they seized all the assets from the order, which made the order join into the ranks of clergy who stood against the revolution by 1792.
#castlevania#castlevania netflix#castlevania nocturne#french revolution#european history#christianity#knights hospitaller#france#malta
450 notes
·
View notes
Text
hey i’ve got an ap euro project so for data, which rébellion in france do you guys think les misérables took place during?
if you don’t know just guess based on the dates
(for reference the french revolution began in 1789)
pls let me know in the tags why you think it’s that time
321 notes
·
View notes
Text

'Monssonia Speciosa' (Butterfly Flower).
Botanical illustration taken from 'Le Jardin du Roi' by Pierre-Joseph Buc'hoz.
Published 1792.
Bibliothèque nationale de France, département Réserve des livres rares.
250 notes
·
View notes
Note
Can you tell me the story of the relationship between saint-just and desmoulins? . ..
Because I couldn't understand it properly so yeah ...

The first connection between Desmoulins and Saint-Just is from 2 January 1790, when the former publishes an annonce for the latter’s recently published Organt in number 6 of Révolutions de France et de Brabant:
Organt, poem in twenty verses, with this epigraph: Vous, jeune homme, au bon sens avez-vous dit adieu ? And this preface: J’ai vingt ans, j’ai mal fait, he pourrai faire mieux.
A few months later, we find the following letter from Saint-Just to Desmoulins. It is undated, but can be traced to May 1790. The letter makes Desmoulins, alongside Robespierre, who he wrote a letter to the following year, the only revolutionaries Saint-Just is confirmed to have contacted prior to heading to Paris in 1792. Unlike in the case of Robespierre however, the letter to Desmoulins implies a correspondence was actually picked up between the two:
Monsieur,
If you were not so busy I would tell you some more details about the Chauni assembly where one can find men of considerable calibre and quality. I was received in spite of my youth. Sieur Gelli, your compatriot from Vermandois had denounced me. He was thrown out bodily. We saw your compatriots, M. Saulce, M. Violette and others, by whom I was received with great courtesy. There is no point telling you (because you are not fond of foolish praise) that your region is proud of you. You will have known before I did that the department is fixed at Laon. Is that good or is that bad for one or other of the towns? It seems to me that it is no more than a point of honour between the two towns and points of honour are of little importance. I took the tribune; I worked with the intention of carrying the day on the question of the chief place but I did not follow on, I left, weighed down with compliments like a donkey burdened with relics, having, however, the assurance that at the next legislature I could be with you in the national assembly. You had promised to write to me, but I see clearly that you will not have the time. I am free as of now. Should I return to you or remain amongst the foolish aristocrats in this part of the world. At the time of my return from Chauni the peasants from my region came to look for me at Manicamp. The Comte de Lauraguais was greatly astonished by this rustic-patriotic ceremony. I led them all to his house for a visit. They said that he was out in the fields, however, like Tarquin, I had a rod with which I cut off the head of a nearby fern beneath the window of the castle and without a word we made a volte face. Farewell my dear Desmoulins. Write to me if you have need of me. Your latest issues are full of excellent things. Apollo and Minerva are still with you and are not displeased. If you have anything to say to your people in Guise I will be seeing them again in eight days’ time from Laon where I will be going on specific business.
Goodbye again: glory, peace and patriotic rage.
Saint-Just
I will read you this evening since I have only spoken to you of your recent issues by saying yes.
Different feelings can however be found a year later, in a letter Saint-Just adressed to Villain Daubigny on July 20 1791 (it is dated 1792 in Oeuvres complètes de Saint-Just, but Saint-Just’s biographer Bernard Vinot points out that this is most likely an error, since all the events it makes allusions to took place the previous year):
…Go and see Desmoulins, embrace him for me, and tell him that he will never see me again, that I esteem his patriotism, but that I despise him, because I have penetrated his soul, and because he fears that I will betray him. Tell him to not abandon the good cause, and recommend it to him, because he does not yet possess the audacity of magnanimous virtue.
What exactly had happened between the two for Saint-Just to write this about Desmoulins is unknown. The same can be said about the question regarding where and when the meeting between them he alludes to here played out, since neither of them are confirmed to have left their respective cities in 1791.
Yet another year later, in September 1792, both Saint-Just and Desmoulins were elected deputies for the National Convention, meaning the former came to settle in Paris on Rue de Gaillon 7, around 2,5 km from the latter’s home on Rue du Théâtre 1 (today Rue de l’Odeon 28). Aside from the fact both were fervent montagnards, I have not been able to find any connection between them until the second half of the following year, with the release of Desmoulins’ Lettre de Camille Desmoulins, député de Paris à la Convention, August général Dillon en prison aux Madelonettes. In it, Saint-Just, who had accused Dillon of having been asked to lead an uprising to put the dauphin on the throne and declare Marie-Antoinette regent on June 2 1793, got described the following way in a footnote:
After Legendre, the member of the Convention who has the highest opinion of himself is Saint-Just. One can see by his gait and bearing that he looks upon his own head as the corner-stone of the Revolution, for he carries it upon his shoulders with as much respect and as if it was the Sacred Host. But what makes his vanity killing is, that some years ago he published an epic poem in twenty-four cantos entitled Argant [sic]. Rivarol and Champcenetz, from whose microscope, used in the interests of the Almanach des grands hommes, not a single verse, not a single hemistich in France has ever escaped, have in vain gone searching for this; they who have hunted up even the least little scrap of literature have not seen Saint-Just’s epic poem in twenty-four cantos. After such a misadventure, how can he show himself?
According to some sources, the ”he carries his head like the Sacret Host” comment was a reply to something Saint-Just had himself said about Desmoulins. Marcellin Matton published in 1834 an anecdote (which it is presumed he obtained from Desmoulins’ mother- or sister-in-law) in which Guillaume Brune has a meeting with the Desmoulins couple at the time of the numbers of the Vieux Cordelier being released. The following conversation would then have played out:
”…You [Brune said] are also read by Barère who recognizes himself; by Saint-Just, who promised to make you carry your head like Saint Denis.”
”That’s true,” [Desmoulins] replied, ”I remember it: it was a very bad joke, and my answer was much better. Have you seen my letter to Dillon? In the approach and posture of Saint-Just, we see that he regards his head as the cornerstone of the republic, and that he carries it on his shoulders with respect like a holy sacrament. Was I wrong, and do you think that for such a good joke he would want to kill me? I only ask him for one favor, and that is to wait until he has given a valid response.”
In 1851, the historian Nicolas Villiaume similarly claimed to have had the same story told to him multiple times by Desmoulins’ mother-in-law. Interestingly though, the ”I will make him carry his head like Saint Denis” comment already appeared in works dated 1816 and 1825 (in both cases without any source cited). There, it is instead portrayed as a response to Desmoulins having written ”Saint-Just carries his head like the Sacred Host” and not as the cause of it. In light of this, I think the idea of Saint-Just having actually said it is something that must be taken with a huge grain of salt.
The things more reliable sources can tell us about Saint-Just’s attitude towards Desmoulins at the time are less overwhelming. He was away from Paris during much of the period where Desmoulins released and got in trouble for the Vieux Cordelier (from October 17 to December 4, December 10 to December 30, and finally January 22 to February 13), and when he was there during said period, I cannot find him recorded to have spoken about Desmoulins or his journal a single time. Saint-Just also went unmentioned in all of the six numbers of the Vieux Cordelier that were released during the time they were both alive.
When the Committee of Public Safety decided to strike down Desmoulins and the other ”dantonists,” it was however Saint-Just who, like in the previous case with the hébertists, got tasked with writing a report against them. Here he obtained the help of Robespierre, who prepared around 65 notes for him to use as material against them. In said notes, Robespierre presented Desmoulins as less guilty than Danton and Fabre, having instead been more of their minion, a version of the story Saint-Just then stuck to when finishing his Rapport sur la conjuration ourdie pour obtenir un changement de dynastie; et contre Fabre d’Églantine, Danton, Philippeaux, Lacroix et Camille Desmoulins:
Bad citizen (speaking of Danton), you have conspired, you said, two days ago, bad things about Desmoulins, an instrument that you have lost, and you attributed to him shameful vices. […] For six months, a plan of palpitation and anxiety has been hatched within the government. Every day we were sent a report on Paris; we were flexibly insinuated, sometimes imprudent advice, sometimes misplaced fears; the tables were calculated on the feelings that it was important to arouse in us, so that the government would move in the direction that suited criminal plots; Danton was praised there, Hébert and Camille Desmoulins were accredited, and all their projects were assumed to be sanctioned by public opinion, to discourage us. […] What shall I say of those who claimed to be exclusively the old Cordeliers? They were precisely Danton, Fabre, Camille Desmoulins, and the ministry, author of the reports on Paris, where Danton, Fabre, Camille and Philippeanx are praised, where everything is directed in their direction and in the direction of Hébert. Danton had directed the last writings of Desmoulins and Philippeaux. […] Camille Desmoulins, who was initially duped and ended up being an accomplice, was, like Philippeaux, an instrument of Fabre and Danton. It was said, as proof of Fabre's good nature, that when he was at Desmoulins' house at the time when he read to someone a writing in which he requested a committee of clemency for the aristocracy and called the Convention the court of Tiberius, Fabre started to cry. The crocodile cries too. As Camille Desmoulins lacked character, his pride was used. As a rhetorician, he attacked the revolutionary government in all its forms; he spoke brazenly in favor of the enemies of the Revolution, proposed a committee of clemency for them; showed himself to be very inclement towards the popular party; attacked, like Hébert and Vincent, the representatives of the people in the armies; like Hébert, Vincent and Buzot, he himself treated them as proconsuls. He had been the defender of the infamous Dillon, with the same audacity that Dillon himself showed, when at Maubeuge he ordered his army to march on Paris, and take an oath of loyalty to the king. He fought the law against the English; he received thanks in England, in the newspapers of that time. Have you noticed that all those who were praised in England have betrayed their fatherland here?
According to an anecdote published in the pamphlet À Maximilien Robespierre aux enfers (1795), released a few months after thermidor by Taschereau de Fargues and Paul-Auguste-Jacques, Saint-Just and Robespierre had wanted to denounce Desmoulins and the other dantonists before arresting them, but been downvoted by their colleagues:
Why should I not say that [the dantonist purge] was a meditated assassination, prepared for a long time, when two days after this session where the crime was taking place, the representative Vadier told me that Saint-Just, through his stubbornness, had almost caused the downfall of the members of the two committees, because he had wanted that the accused to be present when he read the report at the National Convention; and such was his obstinacy that, seeing our formal opposition, he threw his hat into the fire in rage, and left us there. Robespierre was also of this opinion; he believed that by having these deputies arrested beforehand, this approach would sooner or later be reprehensible; but, as fear was an irresistible argument with him, I used this weapon to fight him: You can take the chance of being guillotined, if that is what you want; For my part, I want to avoid this danger by having them arrested immediately, because we must not have any illusions about the course we must take; everything is reduced to these bits: If we do not have them guillotined, we will be that ourselves.
Regardless of whether this be true or not, on March 30, Saint-Just was one of eighteen men to sign the by Amar drafted arrest warrant for Danton, Delacroix, Philippeaux and Desmoulins, who were all arrested in the night. The next day at the Convention, Robespierre shut down Legendre when he suggested the accused be allowed to come and defend themselves before the Convention, after which Saint-Just entered the hall, mounted the rostrum and read out the act of accusation the two of them had worked out.
Receiving a copy of Saint-Just’s report in his cell at the Luxembourg prison, Desmoulins got around to preparing a defence. In it, he claimed the author of the report had personal reasons for wanting him dead. He also referred to him as ”Monsieur le Chevalier de Saint-Just,” a nicknamed previously used by the girondin Salle:
If I had gotten the chance to print in turn, if one hadn’t put me in isolation, if one had lifted the seals and if I had the paper neccesary to establish my defense, if one gave me only two days to make a number seven, imagine how I would confront M. the chevalier Saint-Just! Imagiene how I would convince him of the most atrocious slander ! But Saint-Just writes leisurely in his bath, in his bathtub, he plots my murder during fifteen days, while I have no place to put my writing desk and only a few hours to defend my life. What is this if not the the duel of the Emperor Commodus, who, armed with an excellent blade, forced his enemy to fight with a simple foil garnished with cork? […] I arrive at the part of the report which concerns me. In living memory, there is no example of such atrocious slander as this piece. And yet there is not a single person in the Convention that doesn’t know that Monsieur the former chevalier Saint-Just holds for me an implacable hatred for a slight joke that I allowed myself five months ago in one of my numbers. Bourdaloue said: Molière puts me in his comedy, I will put him in my sermon. I put Saint-Just in a giggly number, and he puts me in a guillotine report where there isn’t a single true word in my regard. When Saint-Just accuses me of being an accomplice of Orléans and Dumouriez, he shows well that he is a patriot of yesterday. Who denounced Dumouriez first of all, and before Marat and more vigorously than anyone else? Certainly one cannot deny that it was me? My Tribune des Patriotes exists, let Saint-Just read the portrait I there painted of Dumouriez six months before his treason in Belgium, he will see that I have never since added anything to this portrait. And Orléans who he makes me the accomplice of, who doesn’t know that I was the first to denounce him? That the only writings on this faction that the Jacobins have printed and distributed were written by me? Does Saint-Just no longer remember my Histoire des Brissotins? […] There are witnesses to the fact that the great republican Saint-Just, at the beginning of the Convention, said: Oh! They want a republic, she shall cost them dearly! There are witnesses to the fact the ambitious Saint-Just said: I know where I go.
In an unfinished and unsent letter written to Robespierre around the same time, Lucile Desmoulins too held Saint-Just as the main culprit behind her husband’s fate, arguing that he had misled their friend:
…As far from the insensibility of your Saint-Just as from his base jealousies, [Camille] recoiled in front if the idea of accusing a college comrade, a companion in arms. […] Robespierre, can you really complete the fatal projects which the vile souls that surround you no doubt have inspired you to? […] Had I been Saint-Just’s wife I would tell him this: the sake of Camille is yours, it’s the sake of all the friends of Robespierre!
A rumor claiming that Lucile had been sent money from the imprisoned Arthur Dillon conveniently arrived around the same time the trial against the indulgents started getting off the rails. In the afternoon of April 4, after the proceedings had been closed for the day, Saint-Just again mounted the rostrum at the Convention and revealed the discovery of this new conspiracy:
The public prosecutor of the revolutionary tribunal reported that the revolt of the guilty had caused the court proceedings to be suspended until the Convention had taken measures. You have escaped the greatest danger that ever threatened freedom: now all the accomplices are discovered, and the revolt of the criminals at the foot of justice itself. Intimidated by the law, the secret of their conscience; their despair, their fury, everything announces that the good nature they presented was the most hypocritical trap that had been set for the revolution. What innocent person has ever rebelled before the law? There is no need for any other proof of their attacks than their audacity. What! those whom we accused of having been the accomplices of Dumouriez and Orléans, those who only made a revolution in favor of a new dynasty, those who conspired for the misfortune and slavery of the people are at the height of their infamy! If there are men here who are truly friends of liberty, if the energy that suits those who have undertaken to liberate their country is in their hearts, you will see that there are no longer any conspirators on the front line, who, counting on the aristocracy with whom they have marched for several years, call upon the people the vengeance of the crime. No, liberty shall not recoil in front of her enemies; their coalition has been revealed. Dillon, who ordered his army to march upon Paris, has declared that the wife of Desmoulins had received money in order to promote a movement to assassinate the patriots and the Revolutionary Tribunal. We thank you for placing us in the position of honor; like you, we will cover the fatherland with our bodies. Dying is nothing, provided that the revolution triumphs; here is the day of glory; this is the day when the Roman senate fought against Catiline; This is the day to consolidate public liberty forever. Your committees respond to you with heroic surveillance. Who can refuse you his veneration in this terrible moment when you fight for the last time against the faction which was lenient towards your enemies, and which today finds fury to fight liberty?
After having heard Saint-Just’s report, the Convention used this new discovery to order ”that the Revolutionary Tribunal shall proceed with the instruction relating to the conspiracy of Lacroix, Danton, Chabot and others. The President shall make use of every means which the law permits to cause his authority and that of the Revolutionary Tribunal to be respected, and to repress every attempt on the part of the accused to trouble public tranquillity and to hinder the course of justice. It is decreed that all persons accused of conspiracy who shall resist or insult the national justice shall be outlawed and receive judgment on the spot.” This order became essential for getting the dantonists condemned to death the following day.
Saint-Just had however nothing to do with the actual arrest warrant for Lucile, signed the same day by Robespierre, Billaud-Varennes, C-A Prieur, Carnot, Couthon, Barère, Du Barran and Voulland, which would lead to her ending up on the scaffold as well nine days later.
I’m currently blanking when it comes to contemporaries who had anything to say regarding the relationship between Saint-Just and Desmoulins.
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
"And what shall be the reward of spilling so much blood, one drop of which has more worth than all the crowned heads of the world?"
L’Ami du Peuple, No 634, from Thursday 19th April 1792.
[The very next day, on the 20th April 1792, war was declared against Austria]
If it was still impossible to doubt the traitorous dispositions of the court, after all the plots that it has formed to this day, in order to crush the people, to ruin the nation, and to re-establish despotism, the scene of high scandal that the ministerial cabinet has just been playing out should have sufficed to open the eyes of all.
On the 14th of this month, the ministers presented themselves in the Assembly. The Minister of Foreign affairs [Dumouriez; he took this post on 15th March 1792] took the floor to communicate to them, after the orders of the king, of the dispatches that, he said, were delivered by an extraordinary courier who arrived during the night. He first read out the letter written [by Louis XVI] to sieur [Louis Marie Antoine, Vicomte de] Noailles, ambassador at the court of Vienna, demanding the new king of Hungary [Franz II of the Holy Roman Empire, nephew of Antoinette] to give a categorical response on his attitudes towards France. He then read out the response of sieur Noailles, containing a formal refusal to continue a negotiation that he [Noailles] said was impracticable and an announcement of his [Noailles’s] resignation. He [Dumouriez] proceeded to give a reading of a very pressing dispatch [from Louis XVI] addressed to sieur Noailles. Finally, he [Dumouriez] announced that Louis XVI had just written in his own hand a letter to the king of Hungary, and sieur Molle the field marshal was to deliver it. The response to this letter would arrive on the 10th of next month at the latest and would decide whether peace or war would be. In this epistle, one can clearly sense that Louis XVI is repeating his crude joke of professing his love for the Constitution.
Scarcely had these readings been finished than sieur Briche and sieur Guadet demanded a decree of indictment against sieur Noailles for having disobeyed the orders of the king; they must say so, for he had betrayed the interests of the nation and compromised public safety. After several light debates, this decree was given a near-unanimous pass. Already the ones that did not follow the thread of the story were singing to their victory, for they saw that he was declared a nation-harming (lèse-nation) criminal, he who is an ambassador of France, a close relative (cousin-germain) to sieur Motier [Noailles and Lafayette had the same father-in-law], a member of the Tuileries committee, and a pillar of the Feuillant club; that is to say, one of the main conspirators, bolstered by all the forces of his accomplices, and sure of the support of the vast majority of counter-revolutionary conscript fathers. But their joy was short-lived. Several hours after the decree of indictment, the veil was ripped to lay bare the juggleries of the ministerial cabinet. Sieur Dumouriez appeared on stage to announce to the president a letter that he had allegedly just received from sieur Noailles, who had finally obeyed the orders of Louis XVI and had given news that the king of Hungary refused all negotiations, declaring war on the French nation.
Immediately Thuriot, Goupilleau, Vaublanc, Gentil, Dumas *and the other gangrenous ministers demanded that the decree of indictment be revoked. Sieur Kersaint and Sieur Delacroix ⁑ proposed that the letter of the minister [Dumouriez] and the dispatch of the ambassador be sent back to the diplomatic committee, so that the report would be done on time.
The report done, under the name of the committee, by sieur Lasource, the decree of indictment was adjourned. Such was the conclusion of the ministerial and senatorial farce against sieur Noailles. Thus, by the method of a double correspondence, the perfidious agents of the prince will always get away with their deeds, just like how pirates escape by the method of using false flags. Always the artifices of the court will render the laws illusory; always the apparent acts of justice from the legislator will be none but lures to deceive the people; and no matter how things turn out, always the public enemies at the helm of the vessel of the State will manage to throw it at the reefs, and to direct it in such a way as that shall see it broken by the storm and engulfed by the waves in the end.
So finally here is war declared on the French by the powers plotted against freedom. However, who does not see that all these pretend ministerial negotiations with foreign courts had no other goal than to amuse the nation and to buy time, until all these powers have their batteries loaded, and they are ready to shoot us? Who does not see that all these bellicose preparations, arranged by the Assembly, had no other goal than to lure the nation to sleep in deep dreams of security? Who does not see that all these sending-back to the executive power, the denunciations, the prevaricating ministers, and these complaints of citizen soldiers crammed onto the frontiers and left without munitions, without weapons, without clothes, without pay, had no other goal than to leave the patrie with no means of defence, to leave the State in the grip of the machinations of the court, of the undertakings of the fugitive plotters, of the attacks of the foreign lackeys.
Will there be war? Everybody is saying yes. It is certain that this opinion has finally prevailed in the cabinet, after the representations of sieur Motier who, without doubt, has made it the only way in order to distract the nation from the concerns within to occupy with concerns without, in order to make the nation forget the internal dissensions in favour of news in gazettes, in order to dissipate the national property into military preparations, instead of employing it to liberate the State and to comfort the people, in order to crush the Nation under the feet of taxes, and in order to slit the throats of patriots of the infantry and of the citizen army, leading them to the butcher’s, under the pretext of defending the barriers of the empire.
It is always certain that he pressures the monarch to stop negotiating and to order the campaign to be started, which he regards as a means to honourably end his own career, if he runs out of ways to regain the nation’s confidence with new acts of seduction and of hypocritical devotion to the cause of liberty.
Lost in the heady rhetoric from Brissot, from Lemontey, from Girardin, from Delacroix, from Gouvion, from Dumas and from other scoundrels who have sold themselves to the court, seduced by a false image of national forces, intoxicated by the fumes of Gallic boastfulness, the people seem no less desiring for war than their implacable enemies do. For three years I have represented war as the last resort of counter-revolutionaries and I have not stopped working to thwart the various undertakings of the cabinet to set it aflame. Since then, my attitude has not changed, and in my eyes, war is always the cruellest curse that may be cast on the kingdom. Whatever new focus that war will draw public attention to, by only fixing it onto news in gazettes, war will leave an open field for the enemies within to machinate at their ease and to breathe the fire of civil dissensions into all parts of the kingdom, to instigate troubles, and to set traps for proponents of freedom; the war will completely squander the national property and accelerate public bankruptcy; the war will consummate the loss of everything that France has in good citizens and it will drain the State of all the patriotic youth, because it is the most zealous proponents of the revolution who have been rushing to the defence at the frontiers, and they will always do so.
However fearless they may be, they are without weapons ¹, without discipline, without tactics, without idea of grand manoeuvres ², without the smallest notion of the art of war, without experienced chiefs, without shrewd and faithful generals. How would the soldiers of the patrie resist the attacks from the disciplined armies of lackeys, they who are commanded by shrewd generals?
If war happens, I repeat, regardless of the bravery of the defenders of freedom, it does not take an eagle-eyed genius to foresee that our armies will be crushed in the first campaign.
I can conceive that the second campaign would be less disastrous and that the third could even be a glorious success, since it is impossible that we would not learn at our own expense, impossible that some great man would not be given a position. Yet, to wrest victory from our enemies, we will need to suffer a long and disastrous war. Now, it would fall short of the truth, to say that our losses, over three campaigns, shall round to a billion livres and five hundred thousand combatants.
How shall we compensate for the loss of so many brave soldiers, the flower of the French citizens? And what shall be the reward of spilling so much blood, one drop of which has more worth than all the crowned heads of the world? To prevent this precious blood from being shed, I have proposed for a hundred times an infallible method, which is to take hostage among us Louis XVI, along with his wife, his son, his daughter, his sisters ⁂, and hold them accountable to what happens. A senate faithful to the patrie will speak to him thus: “King of the French, it is in vain that you (vous) hide in the detours of a tortuous policy to see us ensnared in the disasters of war; you have no escape from the avenging power of the people. We declare to you, in the name of the nation, who is your august sovereign, that we do not wish to deal with your fellowmen, the princes of Europe, that we wish to make no preparations at all for war. Whether or not you compromise with them is your choice. The duty to remind your rebellious brothers and cousins is upon you, and so is the duty to divert your fellowmen from all hostile undertakings. The barriers of the State will stay open, yet rest assured that upon certain news that the first corps of enemies shall have crossed them, your culpable head will roll at your feet, and your entire dynasty shall be extinguished in its own blood.”
But a senate faithful to the patrie is even rarer than a patriotic king. How insensible the people is, that they do not sense the necessity to finally choose a supreme dictator, to give him powers that would be circumscribed, so that he would have no authority to dominate, but unlimited authority to cut down the chief conspirators that the public voice has identified, to force the corrupt legislator to put at a price the heads of kings, of princes and of the generals who will come with weapons against us, to offer sums of gold to their troops who will deliver these kings, princes, and generals to us, living or dead, and to receive these troops among children of the State. Soon we shall see their numerous legions, running with weapons and equipment under the flags of freedom, and France shall be delivered from her enemies forever.
The fate that awaits her is less consoling for the friends of the patrie, but the fate that awaits her enemies will be terrible.
At the first shot of the canon fired on the frontier, the departments agree on a plan to reduce the castles and the gardens to ashes and to slit the throats of all public enemies who can be found in cities and in the countryside. As the army will massacre its own perfidious chiefs and conspiratorial generals, and as the entire nation will rise up against its own worthless representatives to seize back the powers that they have stripped from her, the mysterious veil long hung over the intrigues of the cabinets will be torn: however impatient the cabinets are to put the French back into chains, I strongly doubt that Louis XVI shall have the humour to do nothing if he even takes a look at this terrible picture. Let some good man have the courage to put it before his eyes.
---------------------------
Notes in the original:
[1] It is an unchanging fact that sieur de Grave, despite all his civic affectations, has not given a single order to prompt the ministry to arm the national guards of the frontiers since he arrived at the ministry. It is upon their actions, and not upon their talk, that the royal agents must be judged.
[2] It was to prevent the citizen battalions from training for grand manoeuvres that the generals have kept them divided and dispersed into different posts.
Translator's notes:
*This would be Mathieu Dumas (1753 - 1837), a colonel of the general staff of Paris, long lambasted by Marat for refusing to fight, and whose name had come from his father, and not to be confused with Thomas-Alexandre Dumas (1762 - 1806) the Haitian general, whose name had come from his mother, an enslaved and nigh-erased woman.
⁑ This would be Jean-François Delacroix (1753 - 1794) the Dantonist, not to be confused with Charles-François Delacroix (1741 - 1805) the Thermidorian, and father to the painter Eugène Delacroix (1798 - 1863).
⁂ Marat notably did not mention either of the brothers of Louis XVI, because the comte de Provence (future Louis XVIII) emigrated in June 1791 to the Austrian Netherlands, and the comte d’Artois (future Charles X) emigrated even earlier, on 17th July 1789 to Savoy.
I am indebted to @citizen-card for helping me with finding out about the relation between Motier and Noailles, and to @lamarseillasie for making me interested on "just what was Marat's view on dictatorship" in the first place.
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
#richard armitage#trevor belmont#alejandra reynoso#sypha belnades#richter belmont#james callis#alucard#adrien fahrenheit tepes#graham mctavish#vlad dracula tepes#dracula#wallachia#castlevania#castlevania nocturne#netflix#castlevania spin off#spin off#france#french revolution#1792#kevin kolde#clive bradley#samuel deats#adam deats#powerhouse animation#frederator studios#animation studio#september 2023#official trailer#news
231 notes
·
View notes
Text
Toss a coin for John Paul Jones
John Paul Jones has been lauded as the father of the US Navy since 1775. His influence and leadership were fundamental to the founding of our Navy and in many ways to the success of the American War of Independence.

The tomb of John Paul Jones in the U.S. Naval Academy Chapel's crypt, Annapolis, Maryland
The remains of John Paul Jones were interred in 1906 in a ceremony presided over by President Theodore Roosevelt in the crypt beneath the Naval Academy crypt. Since his death in 1792, John Paul Jones' remains had lain in a grave in France, where he also died.
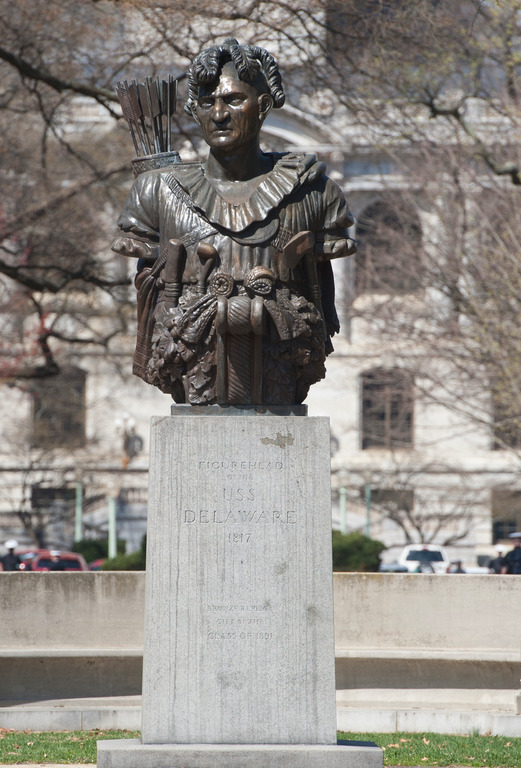

The Tamanend Figurehead of the USS Delaware, 1817
Now, since 1906, it has been the custom of the Midshipmen of the Academy to deposit coins at his grave to ask and thank him for help in examinations and a successful graduation as well as a successful career. Another helper on campus is the statue of Tamanend, a peaceful Delaware chief of the Lenape Nation, to whom coins are also offered to request his help in examinations.
#naval history#sailors superstition#american midshipmen#midshipman monday#age of steam#early 20th century
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
In defense for Marie Antoinette
A long time ago following a passionate debate and good reblogs that you can easily find on Tumblr (if everyone agrees I will put the link), I had fun defending Marie Antoinette (although a fervent sympathizer about the Montagnards).As in two weeks it will be the defense of Manon Roland, I will put this ability to defend to the test by publishing what I had already written about the former queen of France. Here we go:
The problem with Marie Antoinette is that her education was often neglected, and her mother, the Great Marie Thérèse, an excellent politician, instilled in her very conservative ideas, not to mention the fact that she wanted her daughter to become a spy but without the great talent political of her mother. This will be one of the reasons why it will be a great problem when she arrives at the Court.
She won't have the necessary mental strength to face the heaviness of the protocol, and although she caused major problems initially in terms of expenditure, her frankness, unsuitable for a dauphine then a queen, and her frivolity don't help. In addition to the expenses she incurs to please her friends (notably Polignac), wanting to forget the pressure her mother puts on her, despite Louis being a good husband to her, with no children, which is a source of gossip, she decides to increasingly take refuge in Trianon, which again leads to excessive spending, not to mention new clothes. But it's important to note that once she had children, she behaved much less frivolously, more reasonably, less extravagantly, but refused to reintegrate Versailles, which she deemed as heavy and hypocritical (rightly so, but as her mother said, with privileges come duties; if she had made a concession on this side, perhaps she could have obtained less absurd protocol).
Once she had children with her husband Louis XVI, they did everything to ensure that their offspring did not have a high opinion of themselves. Just look at the fact that she wanted her children to dress equally to some of the household children and in her letters indicates that she does not want her daughter to be as arrogant as her aunts. She even tells them that since there are more and more poor people in France, they won't have gifts at a certain period. So she's not a snobbish woman.
Contrary to popular belief, Louis XVI is never influenced by his wife; in fact, she herself knows how to stay in her place as a queen consort and simply prefers to organize certain festivities. But her excessive frankness, rejection of her duties, frivolity in expenditure, and the fact that she sometimes openly shows disdain, for example, for Turgot (one of the few good financial controllers of Louis XVI) will make her the object of all vices in France and a scapegoat for all the decisions of the old Regime.
Do you know who agrees on this point? The revolutionary Saint Just himself in his writings in 1792, who immediately grasped the personality of the Queen in these terms: "Rather deceived than deceitful, rather light than perjured, entirely devoted to pleasure, she seemed to reign not in France but at Trianon."
Moreover, Joséphine de Beauharnais, who was a hundred times more spendthrift and frivolous than her, was much more loved because she took care of her image unlike Marie Antoinette. Perhaps because Marie Antoinette was more frank than her .
In the end, Marie Antoinette stole less from the coffers, so to speak, because her husband wouldn't have let her, and she herself wouldn't have wanted to. Theresia Cabarrus, who profited well from Tallien's scam, was seen as wonderful because she took care of her image. Furthermore, Marie Antoinette clearly displayed her allegiance and stuck to it until the end (although this allegiance was outdated, her mother's conservative ideas about absolute monarchy), faithful to the people she loved (she insisted on sheltering her friends, but Lamballe returned despite the queen's pleas not to do so to support her, faithful to her husband, despite the arranged marriage, because even though she insisted they leave, she didn't want to leave him alone), isn't a friend of the good day only, compared to Cabarrus, who claimed to be imbued with Enlightenment ideas, said she didn't like bloodshed, but in the end, went from one bloody person to another not out of survival (as she liked to say) but out of wealth before marrying a royalist. Yet Theresia and Beauharnais (who took part in the serious scandal during the creation of the Bank of France as a shareholder) did not receive as much criticism.
Of course, we can also understand Marie Antoinette's criticism of Necker, a proud man who is content to borrow and pretend to be more competent than he really is and stabs people in the back (he criticized Turgot but if Turgot hadn't played the "villain," Necker wouldn't have been able to borrow a penny to cover his good reputation not to mention his weather vane attitude and his false attitude as a friend of the people that Marat denounced ), although I don't understand the contempt she had for Turgot.
For her betrayal towards France, I agree with all of you , it's inexcusable, I won't go back on that. What Louis XVI did (primarily him because he was never influenced by his wife, but she also has some responsibility in this regard) is involuntary mass homicide against the French people for the return of absolute monarchy. The problem is that at that time we didn't have the necessary evidence to condemn her (although there was legitim suspicion of the truth), it was a parody and even Saint Just seemed to oppose this execution by telling Robespierre that "this act (the execution) would not benefit national sovereignty." Unfortunately, the person who said this in one of the forums, however, very educated, lost the citation from this book, so let's go cautiously, especially since if the letters had been found, I think Saint Just would have been in favor of the execution of Marie Antoinette. But as mentioned above, at least Antoinette did not betray any ideals, she was clear about that unlike Cabbarus who claimed that she rejected Tallien because of the blood in his hand but then go to Barras, said that she is attired by « les idées lumières » and go to wedding a monarchist, etc., who do not receive as much criticism. But I also understand the hatred she received from Jacques Roux, from a Momoro, and from so many others who never had luxury and found her expenses and behavior legitimately scandalous. But like everyone else outraged and shocked by the behavior of Hébert (and Pache, Chaumette, and Jacques Louis David should not be forgotten even though I like Pache and I find Chaumette unfairly maligned by their best moments it’s was not their best moments and should have died of shame for using such a method, as for Hébert and even to a lesser extent Jacques Louis David, let's not even talk about them).
At least Marie Antoinette unlike other didn’t betrayals the ideas of the revolution unlike some who claimed themself child of the revolution and then betray the revolutionnaries.
If we want to fight against the dishonest people who have blamed everything on people like Saint Just, Robespierre, Couthon, Billaud Varennes (isn't Fouché and Turreau?) we must also do the same thing even for people who are against the revolution even if I agree that the martyrdom of the upper class is tiring and that making Marie Antoinette a pure feminist and innocent icon is just as wrong (but I am here to defend her in this post).
P.S.: I know that Theresia and Joséphine did not harm people unlike their husbands and lovers at least not as much; I do not want to absolve Napoleon, Barras, Tallien; they did not need these women to do what they are reproached for, but to better situate them in relation to Marie Antoinette.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

Oil Painting, 1792, French.
By Jean-Baptiste Claude Robin.
Portraying François Devienne, a flutist, in an olive green coat and buff waistcoat.
Musées royaux des Beaux-Arts de Belgique.
#Musées royaux des Beaux-Arts de Belgique#jean Baptiste Claude Robin#François devienne#painting#1792#1790s#1790s france#1790s painting#1790s menswear
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Saint-Just Resources
A culmination of the many articles and other resources I use in my own research as someone studying to be a historian on the revolution. Will be added to as I progress in my research; please let me know if any links don't work!
Historians on Saint-Just:
Biography from Association pour la sauvegarde de la Maison de Saint-Just
Histoire de Saint-Just député à la Convention nationale (Hamel, 1860)
Lenôtre on SJ's 1791-early 1792 life in rural France
Saint-Just (Cioti, 1991)
Saint-Just: Sohn, Denker und Protagonist der Revolution (Monar, 1993)
Saint-Just (Gignoux, 1947)
Saint-Just en mission la naissance d'un myth (J.P. Gross, 1967)
Saint-Just et les femmes (Quennedey, 2016)
Saint-Just: Apostle of the Terror by Geoffrey Bruun (my personal favorite English SJ bio)
The Man of Virtue: The Role of Antiquity in the Political Trajectory of L.A. Saint-Just (Linton, 2010)
Saint-Just: The French Revolution's "Angel of Death" (Linton, 2015)
Three Letters of Saint-Just (Bruun, 1934)
Saint-Just in modern Annales historiography (Vinot, Linton, Quennedey, etc., 2017)
Saint-Just : Une Constitution pour la République (on his role in the drafting of the 1793 Constitution) (Crucifix and Quennedey, 2018)
Saint-Just's Pre-Convention Life:
Monograph on the Château de Coucy (first believed to have been written in the 1780s as a school assignment, debunked by Vinot) - see this blog post by Anne Quennedey for more info.
Arlequin-Diogene (SJ's play) -> I did an English translation
L’esprit de la révolution et de la constitution de la France (1791)
Convention Speeches:
All Convention Speeches Summarized (Anne Quennedey, 2020)
First Speech: 13 November 1792 on the debate of putting the King to trial.
19 vendémiaire an II (10 October 1793)
Ventôse Decrees Proposal Convention Speech (my complete English translation)
9 Thermidor an II (28 July 1794) Speech/Draft
My full English translation
"Praise the Victories and Forget Ourselves" Excerpt
"Tarpeian Rock" Analogy from 9 Thermidor Speech draft
Miscellaneous:
Why I study SJ
My Thoughts on SJ's Thoughts on the Terror
SJ's Last Paris Apartment ( w/ @/ vieillesmaisons)
SJ's various lodgings in Paris
Speech to Army of the Rhine excerpt
Alsace Mission Map
Saint-Just on Marat
#saint just#french rev#french revolution#antoine saint just#frev resources#saint just resources#queue
145 notes
·
View notes
Note
bro they literally killed the king to abolish monarchy. drastic much?
Who, the English? Why yes, I believe it became a republic with the execution of Charles I.
Not France though. French National Convention abolished the monarchy on 21st September 1792. Louis XVI stopped being the king, but he was alive at that point. France did NOT become a Republic with the death of the king. That was England actually.
849 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Metternichs about Junot
Metternich to Mme Metternich, 14 February 1810
It is with true sorrow that I take up my quill today. Your letter of 26 January contains one of the scenes that show us the people of 1792 and 1793 exposed and naked. Place a being like J[unot] in a very high position, he will drink blood without letting any misgivings stop him.
That’s Metternich reacting to the news of the scandal Junot had caused after having discovered the correspondence between his wife Laure and Metternich, proving they had had an affair. Metternich himself was not in Paris at the time but had left some time after the war of 1809 between France and Austria had begun, and in the meantime had taken over the ministry of foreign affairs in Austria. However, Lorel Metternich with the kids had stayed in Paris, and Junot had dragged her right in the middle of a scene of severe domestic violence that she immediately informed her husband of, with the help of a secret agent Metternich had in Paris, Benoit des Androuins.
Interestingly, Lorel Metternich at first does not mention any involvement of Caroline Murat in this event, she only lists her as one of the people gossipping about it.
Other than that, Lorel apparently behaved as prudently as she could once she had entered Junot’s house. According to the letter by Androuins, Junot had forced Laure to write a message to Lorel, urgently inviting her over. On entering, Lorel found Laure Junot crying on the sofa, hiding her face in both hands. - According to Laure’s own journal intime, the last hours had been a nightmare for her, including attempted rape and attempted murder. - Once Lorel Metternich was in the room, Junot locked the door behind both women and started to rage against Metternich, demanding Lorel take revenge upon him etc. The only thing Lorel answered was: "But you are mistaken, Monsieur le Duc. This is not my husband’s handwriting." - Despite the fact she had obviously recognized it. Again, according to Laure’s journal intime, she at some point managed to silently ask Laure if she could do something for her.
Despite Lorel’s calm reaction, the scene must have scared her a lot. At least she seems rather relieved to learn that the Junots were to leave the capital, when she writes to her husband:
Bluebeard has finally left with his amazon and, as I am assured, probably never to return.
"Bluebeard" obviously referring to Junot.
Edit: Forgot to add the source for the two letters: Conti, "Metternich und die Frauen", Vol. 1 - The description of what may (or not) have happened during the night when Laure was alone with Junot are a brief summary of the excerpts from Laure's "journal intime" quoted in Toussaint du Wast, "Laure Junot". It is to be noted that this "journal intime" may have been written years after the event for Balzac, and that it is per se unverifiable.
However, Lorel Metternich calling Junot "Bluebeard" at least strongly hints at her, too, being convinced that Junot had physically abused and possibly tried to murder Laure.
Edit II: On second reading, I added an "attempted" to the accusation of rape. Of course, by the reasoning of the law at the time, rape in the judicial sense would not even have been possible between spouses. Obeying to the husband's needs was the wife's job. - As to Laure's "journal intime", she describes that Junot tried to force himself on her, but claims that she managed to make him stop. (I am not sure I fully believe her.) Junot then at some point attacked her with a pair of scissors, wounding her, before trying to strangle her. He only stopped when Laure was close to loosing consciousness and when he literally saw her blood on his hands. That's how Madame Metternich found Laure on entering.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some of my favourite terminology for sex, sexuality, and gender that have mostly fell out of use:
Sapphist: Similar to the term Sapphic which is still in use, derived from the woman loving Greek poet Sappho. The -ist has implications of doing rather than being. A Sapphist is a woman who has romantic and sexual relationships with other women. It was commonly used in the 19th and early 20th century, eventually replaced by lesbian in common usage. Some famous historical figures who used this term include Vita Sackville-West, who also used the terms lesbian and homosexual.

Mukhannathun: Translates roughly to "effeminate ones" or "ones who resemble women", typically refers to a feminine male, an intersex person, or one whose sex is indistinct. Modern scholars place the term Mukhannath in correlation with trans feminine. Mukhannathun traditionally took on the social roles of women in Saudi Arabia and feature in Ḥadīth Islamic literature. They were often musicians and entertainers, Abū ʿAbd al-Munʿim ʿĪsā ibn ʿAbd Allāh al-Dhāʾib (or Tuwais) being perhaps the first famous Mukhannath musician. I could not find any depictions of Mukannathun.
Invert: Sexology in the early 20th century believed that same sex desire and cross gender identification were natural in some people. It was coined in German by Karl Friedrich Otto Westphal (1833-1890) and translated across Europe and eventually into English as sexual inversion by John Addington Symonds Jr. (1840-1893) in 1883. Inverts were people whose natural sex instinct (heterosexual, cisgender) were "inverted", causing a natural desire for the same sex or to live as the other sex. It was thought that most inverts desired a relationship with a "normal" member of their own sex, for example a masculine presenting woman would desire a feminine presenting "normal" woman, a feminine presenting man would desire a masculine or "normal" man. While most sexologists thought sexual inversion was natural, they worried about corruption of "normal" people by inverts. The writer 'John' Radclyffe Hall (1880-1943) identified as an invert and explored the life of inverts in her 1928 novel The Well of Loneliness.

Uranism: A Uranian was a man who was romantically or sexually interested in other men. One of the earliest records of the term comes from Friedrich Schiller's 'Sixth Letter' in the Aesthetic Education of Man in 1795. It is derived from the ancient Greek goddess Aphrodite Urania, a manifestation of Aphrodite who was free of physical desire and instead was attracted by mind and soul. Ancient Greek literature was very important in the early formations of queer identity and self-recognition. Oscar Wilde (1854-1900) was known to use the term Uranian.

Tribadism: Derived from the Greek "tribas" which means "to rub", tribadism denotes both a sexual position (now known as tribbing or scissoring) and a woman who seeks to sexual dominate and/or penetrate another woman. This term could also be used to describe an intersex person who lives as female and is the penetrating partner during sex with women. It became the most common word to describe any kind of sexual intimacy between women in English literature from the 16th to 19th centuries. Marie Antoinette, queen of France from 1773 to 1792 was "defamed" in many anti-monarchist newspapers as being a tribade.

Eonism: Eonism was coined by English sexologist Havelock Ellis (1859-1939) to describe cross gender identification and presentation. "Eon" after the French diplomat Charlotte-Geneviève-Louise-Augusta-Andréa-Timothéa d'Éon de Beaumont, who was assigned male at birth but lived as a woman from 1777 until her death in 1810. Eonism was later replaced by transvestism in popular usage in the early to mid 20th century, coined by Magnus Hirschfeld (1868-1935) in 1910.

Eunuch: the term Eunuch has many connotations but the one common factor that almost all definitions share is that a eunuch is an intentionally castrated male. Eunuchs can also be uncastrated, but put into the social role as eunuch due to their 1) feminine presentation 2) inability to procreate 3) attraction to men. Eunuchs were not seen as men in most cultures, they were specifically chosen and castrated in order to fill a specific, separate social role from men and women. It was sometimes punitive, for example under Assyrian law men who were caught in sexual acts with other men were castrated. Eunuchs often had positions in royal households in the Ancient Middle East, their sexlessness was seen to enhance their loyalty to the crown as they were less likely to be distracted by sex or marriage, and it also allowed for jobs to be given on merit, and not inherited since Eunuchs could not reproduce. In Ancient Greece certain sects of male priests were eunuchs. China had Eunuchs who were fully castrated (penis and testicles) and high ranking in imperial service. In Vietnam, many eunuchs were self castrated in order to gain employment in the royal households.

Homophile: coined in 1924 by Karl-Günther Heimsoth (1899-1933) in his dissertation Hetero- und Homophilie. The term was in common use in the 50s and 60s in gay activism groups. It was an alternative to homosexual coined in 1868 by Károly Mária Kertbeny (1824-1882) which was thought to have pathological and sexual implications, whereas homophile prioritised love and appreciation over the sex act or pathology. It is still in use in some parts of northern Europe. The Homophile Action League was founded by lesbian couple Ada Bello (1933-2023) and Carole Friedmann (1944-?) in Pennsylvania, U.S.A. in 1968, a year before the Stonewall Riots.

111 notes
·
View notes