Photo
Solve it.... #diagnosis #neetpreparation #medicine #doctor #respiratorytherapist #aiims https://www.instagram.com/p/CEpMhcXjjwYmToP7rDEpgOFZdvniXecdFB7fpg0/?igshid=zu82fzqvmpp1
0 notes
Photo

#neetpreparation #medicine #cardio #diagnosis #doctor https://www.instagram.com/p/CEpJwn3jW60Gmhkkbw2fgnwYsUNHOWLOG2xr5Y0/?igshid=15kzj0ib8zu8y
0 notes
Text
Pseudomonas aeruginosa

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Aerobic, non-lactose fermenting, oxidase-positive, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, P. aeruginosa is a multidrug-resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes.
Pathogenesis:
•phospholipase C – produced to degrade cell membranes
•endotoxin, which leads to – fever, hypotension, disseminated intravascular coagulation
•exotoxin A – this inactivates elongation factor 2 (EF-2), which stops protein synthesis via ADP ribosylation
•pyoverdine and pyocyanin pigment – leads to a blue-green pigment
Bacteria are constantly finding new ways to avoid the effects of antibiotics. For example, some Pseudomonas can produce enzymes called carbapenemases that break down antibiotics including carbapenems, making the drugs ineffective. Carbapenem antibiotics are typically reserved to treat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, so when bacteria develop resistance to them, treatment options can be extremely limited.
youtube
P. aeruginosa is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of P. aeruginosa infections as mentioned earlier can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse effects may result.
Pseudomonal infections can involve the following parts of the body, with corresponding symptoms and signs:
- Respiratory tract (eg, pneumonia)
- Bloodstream (bacteremia)
- Heart (endocarditis)
- CNS (eg, meningitis, brain abscess)
- Ear (eg, otitis externa and media)
- Eye (eg, bacterial keratitis, endophthalmitis)
- Bones and joints (eg, osteomyelitis)
- GI tract (eg, diarrhea, enteritis, enterocolitis)
- Urinary tract
- Skin (eg, ecthyma gangrenosum)
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Playing with pharmacology.... Sunday ~funday
0 notes
Text
# chemotherapy 2
Antimicrobial Agents - Inhibition of DNA and Protein Synthesis
Bacterial chromosome replication
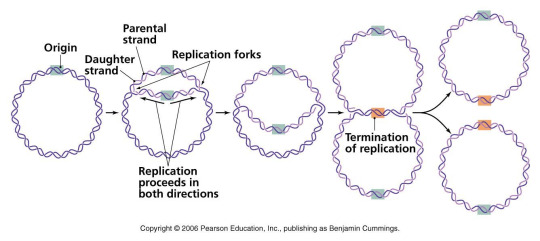
DNA replication
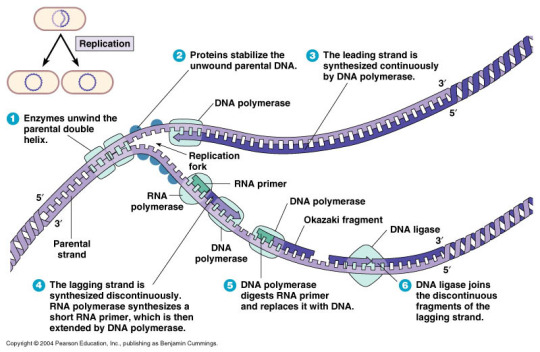
Bacterial Topoisomerases
maintain DNA in appropriate state of supercoiling
cut and reseal DNA
DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) introduces negative supercoils
Topoisomerase IV decatenates circular chromosomes
these are the targets of the quinolone antibacterial agents
Quinolones
bind to bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV after DNA strand breakage
prevent resealing of DNA
disrupt DNA replication and repair
bactericidal (kill bacteria)
Fluoroquinolone is particularly useful against
Gram +ves: Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci
Gram -ves: Enterobacteriacea; Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Anaerobes: e.g. Bacteroides fragilis
many applications e.g. UTIs, prostatitis, gastroenteritis, STIs
Adverse effects
Relatively well tolerated
GI upset in ~ 5% of patients
allergic reactions (rash, photosensitivity) in 1 - 2% of patients
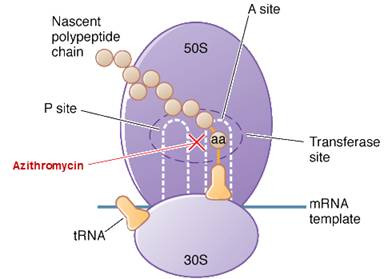
Inhibition of Bacterial Protein Synthesis
Macrolides
in 1952: Erythromycin was isolated as the first macrolide (Streptomyces erythreus)
Newer macrolides: clarithromycin, azithromycin
Structurally they consist of a lactone ring (14- to 16-membered) + two attached deoxy sugars
Mode of action
bind reversibly to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit
causes growing peptide chain to dissociate from ribosome → inhibiting protein synthesis
bacteriostatic (stops reproduction)
Macrolides’ spectrum of activity
good antistaphylococcal and antistreptococcal activity
treatment of respiratory & soft tissue infections and sensitive intracellular pathogens • e.g. Chlamydia, Legionella
Adverse effects
Generally well tolerated
nausea
vomiting
diarrhoea
rash
Aminoglycosides
large family of antibiotics produced by various species of Streptomyces (“mycin”) and Micromonospora (“micin”)
include: streptomycin, neomycin, kanamycin, gentamicins, tobramycin
Structure = linked ring system composed of aminosugars and an aminosubstituted cyclic polyalcohol
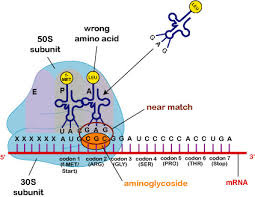
Mode of action of aminoglycosides
Bind irreversibly to 30S ribosomal subunit
disrupt elongation of nascent peptide chain
translational inaccuracy → defective proteins
bactericidal
Spectrum of activity
broad spectrum; mainly aerobic G-ve bacilli (e.g. P. aeruginosa)
used to treat serious nosocomial infections (hospital acquired infections)
First TB antibiotic
Used for cystic fibrosis
Adverse effects
all aminoglycosides have low Therapeutic Index (only a small amount needed to become toxic)
renal damage, ototoxicity, loss of balance, nausea
799 notes
·
View notes
Text
# chemotherapy
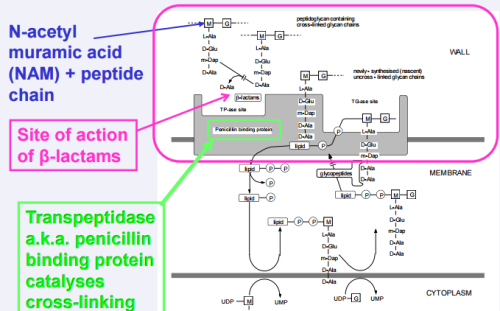
Penicillin

Penicillin is a widely used antibiotic prescribed to treat staphylococci and streptococci bacterial infections.
beta-lactam family
Gram-positive bacteria = thick cell walls containing high levels of peptidoglycan
gram-negative bacteria = thinner cell walls with low levels of peptidoglycan and surrounded by a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer that prevents antibiotic entry
penicillin is most effective against gram-positive bacteria where DD-transpeptidase activity is highest.
Examples of penicillins include:
amoxicillin
ampicillin
bacampicillin
oxacillin
penicillin
Mechanism(s)
Penicillin inhibits the bacterial enzyme transpeptidase, responsible for catalysing the final peptidoglycan crosslinking stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Cells wall is weakened and cells swell as water enters and then burst (lysis)
Becomes permanently covalently bonded to the enzymes’s active site (irreversible)
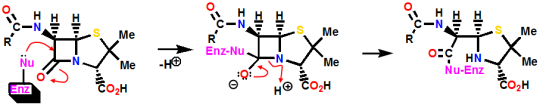
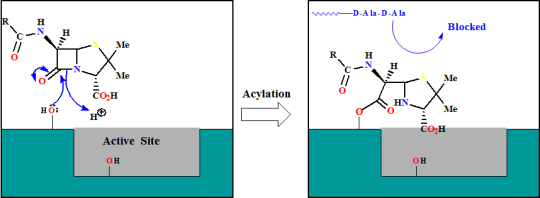
Alternative theory: penicillin mimics D-Ala D-Ala
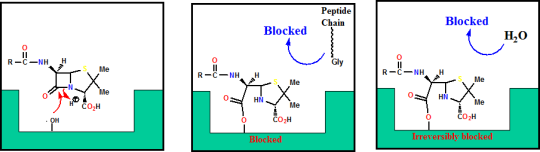
Or may act as an umbrella inhibitor
Resistance
production of beta-lactamase - destroys the beta-lactam ring of penicillin and makes it ineffective (eg Staphylococcus aureus - most are now resistant)
In response, synthetic penicillin that is resistant to beta-lactamase is in use including egdicloxacillin, oxacillin, nafcillin, and methicillin.
Some is resistant to methicillin - methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Demonstrating blanket resistance to all beta-lactam antibiotics -extremely serious health risk.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
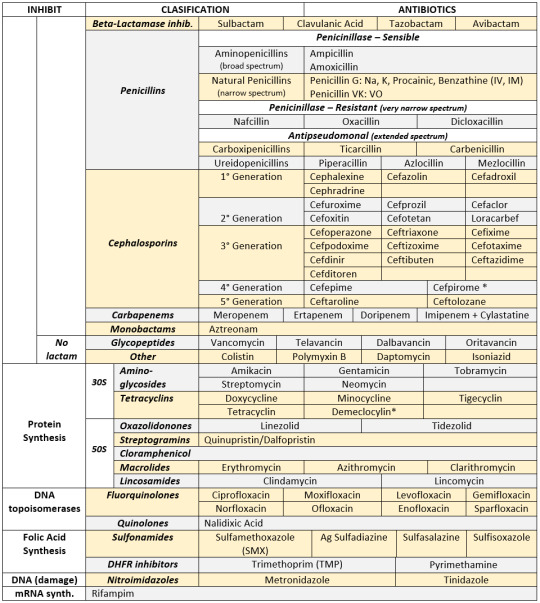
Classification of chemotherapy in nutshell
1 note
·
View note