Note
frok=frokost?
i received the frokussy anon on september 23rd 2022 and frokussy has been haunting me ever since. tonight i can finally sleep peacefully.
1 note
·
View note
Text
im reading (listening to) the odyssey, but im taking frequent breaks, and frankly i'd like to exercise my brain during those breaks, so yea
my ask box is like extra open these days. it's open for basically anything you want, as long as it's language related (e.g., chatting about language or linguistics, requests for Danish contents, questions about linguistics or Danish, basically whatever).
#if youre that one anon who asked about scandinavian women and their frokussy:#it is not open to you unless you wish to finally explain to me what the FUCK you meant when you wrote frokussy#what is frok? i yearn to know#langblr#language#linguistics#danish#danish language#personal for ts
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
apparently this smiley is an exclusive for those who use the big internet (computer) as opposed to the small internet (mobile). but i consider myself the generous sort, so here you go

everyone wake up, new smiley just dropped
̆͗̈
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
everyone wake up, new smiley just dropped
̆͗̈
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to articulate your emotions in Danish
WARNING: LONG POST AHEAD
Literal years ago, I got an ask about how to talk about emotions in Danish. I was never really entirely sure, what the person was asking about, but I recently had the idea to just flat out translate one of those "how to identify which emotion you're experiencing" charts. So here goes nothing
Please note: all of these are approximations, and a lot of the words that are used to describe the same general feeling are in fact more or less interchangeable, as is the case with the emotion chart.
This is the chart I used:

[ID in alt text]
bange - fearful
noun: frygt - fear
bange, frygtsom, ræd - scared
hjælpeløs - helpless
skræmt, rædselsslagen - frightened
nervøs, ængstelig - anxious
overvældet - overwhelmed
bekymret - worried
usikker - insecure
utilstrækkelig - inadequate
underlegen, mindreværdig - inferior
svag - weak
værdiløs - worthless
ubetydelig, betydningsløs - insignificant
afvist - rejected
holdt udenfor, ekskluderet - excluded
forfulgt - persecuted
truet - threatened
nervøs - nervous
udsat - exposed
sur - angry
noun: vrede - anger
skuffet, svigtet - let down
forrådt - betrayed
forurettet - resentful
ydmyget - humiliated
ikke føle sig respekteret - feel disrespected
gjort nar ad, latterliggjort - ridiculed
bitter - bitter
forarget - indignant
krænket - violated
vred - mad
rasende - furious
jaloux - jealous
aggressiv - aggressive
provokeret - provoked
hostile - fjendtlig
frustreret - frustrated
arrig - infuriated
irriteret - annoyed
fjern - distant
tilbagetrukken/tilbagetrukket - withdrawn
følelsesløs, følelsesforladt - numb
kritisk - critical
skeptisk - sceptical
affejende, afvisende - dismissive
frastødt - disgusted
noun: afsky - disgust
misbilligende - disapproving
fordømmende - judgemental
pinligt berørt - embarrassed
skuffet - disappointed
forfærdet - appalled
væmmes (verb, reflexive) - to be revolted
e.g. jeg væmmes ved lugten af fisk 'I am revolted by the smell of fish'
frygtelig - awful
kvalm - nauseated
foragtelig - detestable
frastødt - repelled
forfærdet - horrified
tøvende - hesitant
ked af det - sad
noun: bedrøvelse, sorg - sadness, sorrow
såret - hurt
flov - embarrassed
skuffet - disappointed
deprimeret*, nedtryk - depressed
mindreværdig - inferior
tom, følelsesforladt - empty
*while deprimeret like English depressed primarily should be used in relation to a medical diagnosis of depression, it is also used as a synonym of nedtrykt (literally ned 'down, de' + trykt 'pressed') in the vernacular
skyldig - guilty
fortrydende, skyldbetynget, angerfuld - remorseful
skamfuld - ashamed
fortvivlelse - despair
adj: fortvivlet - despairing
sorg - grief
adj: sorgfuld, sorgramt, sørgende - grief-stricken, grieving
magtesløs - powerless
sårbar - vulnerable
gjort til offer, offergjort - victimised
skrøbelig - fragile
ensom - lonely
isoleret - isolated
efterladt - abandoned
glad - happy
noun: glæde, lykke - happiness
legesyg, legende - playful
ophidset - aroused
fræk - cheeky
tilfreds - content
fri - free
lykkelig, glad - joyful
interesseret - interested
nysgerrig - curious
videbegærlig - inquisitive
stolt - proud
succesfuld, succesrig - succesful
selvsikker - confident
accepteret - accepted
respekteret - respected
værdsat - valued
stærk, magtfuld - powerful
modig - courageous
kreativ - creative
fredfyldt - peaceful
kærlig - loving
taknemmelig - thankful
tillidsfuld - trusting
følsom, sensitiv - sensitiv
intim, tæt - intimate
optimistisk - optimistic
håbefuld - hopeful
inspireret - inspired
overrasket - surprised
noun: overraskelse - surprise
forskrækket - startled
chokeret - shocked
forfærdet - dismayed
forvirret - confused
desillusioneret - disillusioned
perpleks - perplexed
forbløffet - amazed
forbavset - astonished
ærefrygt - awe
begejstret, spændt - excited
ivrig - eager
energisk - energetic
dårligt - bad
kede sig (verb, reflexive) - to be bored
e.g. jeg keder mig 'I am bored'
ligeglad - indifferent
apatisk - apathetic
travl - busy
presset - pressured
forhastet - rushed
stresset - stressed
overvældet - overwhelmed
ude af kontrol - out of control
træt - tired
søvnig - sleepy
ufokuseret - unfocussed
#danish#danish language#danish langblr#emotions#langblr#tongueblr#vocab list#vocabulary list#danish vocabulary#original#this is a little rushed (hæhæ) because i saw this chart and then blacked out and spent two hours on this#and am posting it without proof reading#but fuck it amirite lads
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Let’s face it - English is a crazy language. There is no egg in eggplant nor ham in hamburger; neither apple nor pine in pineapple. English muffins weren’t invented in England or French fries in France. Sweetmeats are candies while sweetbreads, which aren’t sweet, are meat. We take English for granted. But if we explore its paradoxes, we find that quicksand can work slowly, boxing rings are square and a guinea pig is neither from Guinea nor is it a pig. And why is it that writers write but fingers don’t fing, grocers don’t groce and hammers don’t ham? If the plural of tooth is teeth, why isn’t the plural of booth beeth? One goose, 2 geese. So one moose, 2 meese? One index, 2 indices? Doesn’t it seem crazy that you can make amends but not one amend? If you have a bunch of odds and ends and get rid of all but one of them, what do you call it? If teachers taught, why didn’t preachers praught? If a vegetarian eats vegetables, what does a humanitarian eat? In what language do people recite at a play and play at a recital? Ship by truck and send cargo by ship? Have noses that run and feet that smell? How can a slim chance and a fat chance be the same, while a wise man and a wise guy are opposites? You have to marvel at the unique lunacy of a language in which your house can burn up as it burns down, in which you fill in a form by filling it out and in which an alarm goes off by going on. English was invented by people, not computers, and it reflects the creativity of the human race (which, of course, isn’t a race at all). That is why, when the stars are out, they are visible, but when the lights are out, they are invisible.”
— (via be-killed)
#etymology and semantics my beloveds <3#though i do kinda hate semantics like lowkey#not as much as pragmatics but like.... meaning bad :/#grammar good!! etymology good!! :)#english#semantics#etymology#meaning
336K notes
·
View notes
Text
Danish numbers - A defense, as referenced above
9 number things you might not know as a foreign speaker of Danish
This is a mishmash of both cultural things and linguistic things. The idea for this post appeared in my head at 3 am so bear with me. As for the lack of links, I am adding them in a reblog to try to avoid tumblr nerfing my post.
1) Quarters – how to measure time
In Denmark, we love measuring time in quarters of an hour. We love it so much we don't care about specifying the kind of quarter, it's just kvarter (itk.). Generally, we tend to use kvarter mostly just when speaking about 15 or 45 minutes, but it does go further than that. So here's a quick guide on how to tell time other than just doing as you would in English:
15 minutes – et kvarter
30 minutes – en halv time
45 minutes – tre kvarter
75 minutes/1h 15m – en time og et kvarter · fem kvarter
90 minutes/1h 30m – halvanden time (see 2)
105 minutes/1h 45m – en time og tre kvarter
and so forth, if you care to. Using fem kvarter is uncommon but acceptable, but never go further than that using just quarters of an hour. I would say that once you pass 2 hrs, I most commonly hear people starting to just count hours and minutes as you would in English.
2) Halvanden – half second
An archaic way of saying 'one and a half' that just stuck for some reason. This is the preferred way to say 'one and a half ' for most people. No, this is not a joke.
Halvanden, 'half second' means halfway between one and two. Until quite recently (we're talking less than a century) halvtredje (2.5), halvfjerde (3.5), etc. were also in common use, but they have disappeared so rapidly that most current speakers will have absolutely no idea what the hell you're talking about. However, the ghosts of this way of counting live on in the numbers halvtreds (50), halvfjerds (70), and halvfems (90). You can read more about that in my old post about Danish numbers (see reblogs).
3) Week 42
We use week numbers! Week 1 is the first week in the new year to contain a Thursday, as we count weeks as Monday through Sunday. You don't necessarily need to know what week it is all the time, but a lot of adults use weeks in place of specific dates. I am forever thankful to ugenr.dk (you just type in a date and it tells you what week it is in or vice versa).
Important weeks are:
Week 7/8 – winter break for kids in primary and secondary school (not to be confused with Christmas break). It varies depending on municipality whether it's week 7 or 8. Lots of people go skiing these weeks.
Week 26 through 31 – summer break is usually during these weeks. All students in primary and secondary school, as well as university students and students doing professional bachelor's degrees and the like have these weeks off from school.
Week 42 – arguably the most important week. All students mentioned above have this week off from school. It's autumn break and it's ALWAYS week 42 and JUST week 42. Originally, it was to allow students in rural areas help their parents harvest potatoes (a nickname for autumn break is kartoffelferien 'the potato break'), and we just kept it.
4) DD-MM-(YY)YY
If you write dates as MM-DD people will think you're a lunatic. Don't, unless you're specifically talking about 9/11, colloquially referred to as just 9/11 (nine-eleven, as you would say it in English).
5) 00:00
Denmark, like a lot of other European countries, uses 24hr clocks. Obviously, analogue clocks and watches are common, and it's perfectly ok to say stuff like klokken fire om eftermiddagen 'four o'clock in the afternoon' or klokken otte om aftenen 'eight o'clock in the evening', but you are expected to just know that 21:00 is the same as 9 PM. You can also say klokken toogtyve 'twenty-two o'clock', and it's quite normal to ask for clarification of whether people are talking AM or PM by saying stuff like klokken elleve eller klokken treogtyve? 'eleven o'clock or twenty-three o'clock?'. You cannot use AM and PM when speaking or writing Danish. The day begins at midnight; 00:00.
Don't worry yourself too much over this. Everyone occasionally forgets that 19:00 is in fact 7 o'clock and not 9 o'clock.
6) Halv to – half one
When you're measuring half hours in Danish, you're always measuring towards the next whole number. It's never half past, it's always half to. As such, half (past) one is halv to 'half two' in Danish.
7) Grades (years)
This is an ultra quick rundown of the Danish school system. School is mandatory for 10 years and homeschooling is allowed. This covers primary and lower secondary school.
Most people start school the year they turn 6. My birthday is in April, so I was 6 when I stated school, my sister's birthday is in September, so she was 5.
The mandatory grades are as follows. The ages are all possibly ages of a child attending that grade (not accounting for starting school early or late):
Indskolingen, grades 0-3
0. klasse/børnehaveklasse - 5-7 yo
1. klasse – 6-8 yo
2. klasse – 7-9 yo
3. klasse – 8-10 yo
Mellemtrinnet, grades 4-6
4. klasse – 9-11 yo
5. klasse – 10-12 yo
6. klasse – 11-13 yo
Overbygningen/udskolingen, grades 7-9
7. klasse – 12-14 yo
8. klasse - 13-15 yo
9. klasse - 14-16 yo
Some may choose to do 10. klasse, if they feel like they need more schooling or maybe if they're attending an efterskole.
Once they've finished their mandatory schooling, a lot of Danes choose to attend upper secondary school. You can do it in 3 years (stx, hhx, htx, and eux) or 2 years (hf, 2-årigt studenterkursus). Special circumstances like being an elite level athlete or attending MGK (preparation for attending a music conservatoire) may lead to people spending 4 years in upper secondary. Hf often sees a lot of adult students.
Gymnasium/HF, the grades are said as [ordinal number, letter(s)]
1.g (15-17 yo)/1.hf
2.g (16-18 yo)/2.hf
3.g (17-19 yo)
8) Grades (performance)
Danish schools have a 7-grade system. It's called 7-trinskalaen, and each grade corresponds to an ECTS grade (in fact, it's specifically designed for compatibility, and a lot of people above the age of 30 miss the old scale). Generally, students don't get grades until 7th grade. The grades are:
12 – A
10 – B
7 – C
4 – D
02 – E
00 – Fx
-3 – F
If you are not familiar with the ECTS system, E, Danish 02, is the lowest passing grade. The intention behind the 0's in 02 and 00 is to make it impossible for the students to "change" their grade by just adding 1 in front of the grade, but the 0's are in fact also said out loud.
9) Ordinal numbers
Ordinal numbers are written as a number followed by a full stop. You do not capitalise the first letter of any word following the full stop (see 7) even though MS Word will try to convince you it's the right thing to do.
You can read a lot more about numbers on the Danish numbers post (again, in a reblog), but the basics that might not be covered by formal learning materials are:
nulte zeroth. This literally only exists for 0. klasse and for numbers to the zeroth power.
fyrretyvende/fyrrende* – fortieth
halvtredsindstyvende/halvtredsende* – fiftieth
tresindstyvende/tressende* – sixtieth
halvfjerdsindstyvende/halvfjerdsende* – seventieth
firsindstyvende/firsende* – eightieth
halvfemsindstyvende/halvfemsende* – ninetieth
The forms marked with an asterisk are largely informal spoken language to the degree that they are even considered wrong by some. Generally, they are accepted as the standard forms among the younger generations, but be careful when talking to people above the age of ~45.
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
9 number things you might not know as a foreign speaker of Danish
This is a mishmash of both cultural things and linguistic things. The idea for this post appeared in my head at 3 am so bear with me. As for the lack of links, I am adding them in a reblog to try to avoid tumblr nerfing my post.
1) Quarters – how to measure time
In Denmark, we love measuring time in quarters of an hour. We love it so much we don't care about specifying the kind of quarter, it's just kvarter (itk.). Generally, we tend to use kvarter mostly just when speaking about 15 or 45 minutes, but it does go further than that. So here's a quick guide on how to tell time other than just doing as you would in English:
15 minutes – et kvarter
30 minutes – en halv time
45 minutes – tre kvarter
75 minutes/1h 15m – en time og et kvarter · fem kvarter
90 minutes/1h 30m – halvanden time (see 2)
105 minutes/1h 45m – en time og tre kvarter
and so forth, if you care to. Using fem kvarter is uncommon but acceptable, but never go further than that using just quarters of an hour. I would say that once you pass 2 hrs, I most commonly hear people starting to just count hours and minutes as you would in English.
2) Halvanden – half second
An archaic way of saying 'one and a half' that just stuck for some reason. This is the preferred way to say 'one and a half ' for most people. No, this is not a joke.
Halvanden, 'half second' means halfway between one and two. Until quite recently (we're talking less than a century) halvtredje (2.5), halvfjerde (3.5), etc. were also in common use, but they have disappeared so rapidly that most current speakers will have absolutely no idea what the hell you're talking about. However, the ghosts of this way of counting live on in the numbers halvtreds (50), halvfjerds (70), and halvfems (90). You can read more about that in my old post about Danish numbers (see reblogs).
3) Week 42
We use week numbers! Week 1 is the first week in the new year to contain a Thursday, as we count weeks as Monday through Sunday. You don't necessarily need to know what week it is all the time, but a lot of adults use weeks in place of specific dates. I am forever thankful to ugenr.dk (you just type in a date and it tells you what week it is in or vice versa).
Important weeks are:
Week 7/8 – winter break for kids in primary and secondary school (not to be confused with Christmas break). It varies depending on municipality whether it's week 7 or 8. Lots of people go skiing these weeks.
Week 26 through 31 – summer break is usually during these weeks. All students in primary and secondary school, as well as university students and students doing professional bachelor's degrees and the like have these weeks off from school.
Week 42 – arguably the most important week. All students mentioned above have this week off from school. It's autumn break and it's ALWAYS week 42 and JUST week 42. Originally, it was to allow students in rural areas help their parents harvest potatoes (a nickname for autumn break is kartoffelferien 'the potato break'), and we just kept it.
4) DD-MM-(YY)YY
If you write dates as MM-DD people will think you're a lunatic. Don't, unless you're specifically talking about 9/11, colloquially referred to as just 9/11 (nine-eleven, as you would say it in English).
5) 00:00
Denmark, like a lot of other European countries, uses 24hr clocks. Obviously, analogue clocks and watches are common, and it's perfectly ok to say stuff like klokken fire om eftermiddagen 'four o'clock in the afternoon' or klokken otte om aftenen 'eight o'clock in the evening', but you are expected to just know that 21:00 is the same as 9 PM. You can also say klokken toogtyve 'twenty-two o'clock', and it's quite normal to ask for clarification of whether people are talking AM or PM by saying stuff like klokken elleve eller klokken treogtyve? 'eleven o'clock or twenty-three o'clock?'. You cannot use AM and PM when speaking or writing Danish. The day begins at midnight; 00:00.
Don't worry yourself too much over this. Everyone occasionally forgets that 19:00 is in fact 7 o'clock and not 9 o'clock.
6) Halv to – half one
When you're measuring half hours in Danish, you're always measuring towards the next whole number. It's never half past, it's always half to. As such, half (past) one is halv to 'half two' in Danish.
7) Grades (years)
This is an ultra quick rundown of the Danish school system. School is mandatory for 10 years and homeschooling is allowed. This covers primary and lower secondary school.
Most people start school the year they turn 6. My birthday is in April, so I was 6 when I stated school, my sister's birthday is in September, so she was 5.
The mandatory grades are as follows. The ages are all possibly ages of a child attending that grade (not accounting for starting school early or late):
Indskolingen, grades 0-3
0. klasse/børnehaveklasse - 5-7 yo
1. klasse – 6-8 yo
2. klasse – 7-9 yo
3. klasse – 8-10 yo
Mellemtrinnet, grades 4-6
4. klasse – 9-11 yo
5. klasse – 10-12 yo
6. klasse – 11-13 yo
Overbygningen/udskolingen, grades 7-9
7. klasse – 12-14 yo
8. klasse - 13-15 yo
9. klasse - 14-16 yo
Some may choose to do 10. klasse, if they feel like they need more schooling or maybe if they're attending an efterskole.
Once they've finished their mandatory schooling, a lot of Danes choose to attend upper secondary school. You can do it in 3 years (stx, hhx, htx, and eux) or 2 years (hf, 2-årigt studenterkursus). Special circumstances like being an elite level athlete or attending MGK (preparation for attending a music conservatoire) may lead to people spending 4 years in upper secondary. Hf often sees a lot of adult students.
Gymnasium/HF, the grades are said as [ordinal number, letter(s)]
1.g (15-17 yo)/1.hf
2.g (16-18 yo)/2.hf
3.g (17-19 yo)
8) Grades (performance)
Danish schools have a 7-grade system. It's called 7-trinskalaen, and each grade corresponds to an ECTS grade (in fact, it's specifically designed for compatibility, and a lot of people above the age of 30 miss the old scale). Generally, students don't get grades until 7th grade. The grades are:
12 – A
10 – B
7 – C
4 – D
02 – E
00 – Fx
-3 – F
If you are not familiar with the ECTS system, E, Danish 02, is the lowest passing grade. The intention behind the 0's in 02 and 00 is to make it impossible for the students to "change" their grade by just adding 1 in front of the grade, but the 0's are in fact also said out loud.
9) Ordinal numbers
Ordinal numbers are written as a number followed by a full stop. You do not capitalise the first letter of any word following the full stop (see 7) even though MS Word will try to convince you it's the right thing to do.
You can read a lot more about numbers on the Danish numbers post (again, in a reblog), but the basics that might not be covered by formal learning materials are:
nulte zeroth. This literally only exists for 0. klasse and for numbers to the zeroth power.
fyrretyvende/fyrrende* – fortieth
halvtredsindstyvende/halvtredsende* – fiftieth
tresindstyvende/tressende* – sixtieth
halvfjerdsindstyvende/halvfjerdsende* – seventieth
firsindstyvende/firsende* – eightieth
halvfemsindstyvende/halvfemsende* – ninetieth
The forms marked with an asterisk are largely informal spoken language to the degree that they are even considered wrong by some. Generally, they are accepted as the standard forms among the younger generations, but be careful when talking to people above the age of ~45.
#original#danish#danish language#danish langblr#langblr#tongueblr#danish numbers#school#time#dates#numbers#uhhh i think thats it
56 notes
·
View notes
Link
Newcomer is a fantasy video game where players are immersed in the second language they want to learn. 100+ characters to communicate with, eight language learning mechanics, and RPG features make second language acquisition an adventure. Designed for beginner - intermediate learners, players progress and learn a second language at their own pace.
Thought langblr might be interested in this. Current languages are French, Italian, English, and Spanish, with Japanese as a stretch goal!
#NEWCOMER IS OUT#i was scrolling my own blog and pondering my original content issues#and then I SAW THIS AND IT IS OUT NOW
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
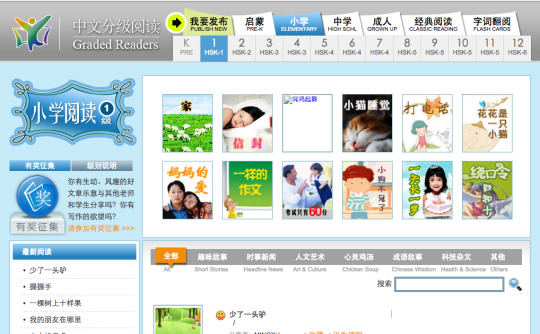
Yes! Chinese Graded Readers
Recently, I found a really useful Chinese reading resource for learners of all levels. As the name states, it contains a bunch of graded readers split up based on grade level and HSK level. I’ve selected Elementary School Grade 1 (HSK-1), and here’s what it looks like:
I’ve selected the story 少了一头驴. As you can see, the vocabulary and grammar should be tailored to the grade level, so it’s really useful, especially if you’re studying for the HSK. All the stories include audio, and some of the lower grade levels even have nice background music and sound effects. Some of the higher levels only have Google Translate audio though (even though Google Translate for Mandarin still pretty decent). Here’s the layout of the stories:
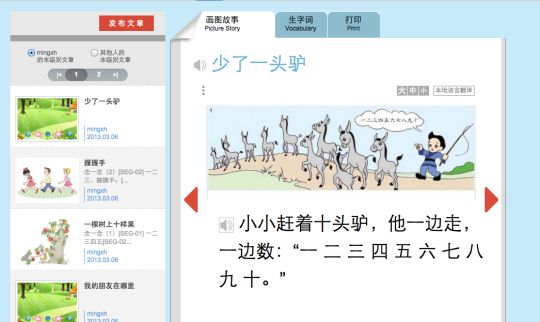
There are 3 tabs: Picture Story, Vocabulary and Print. “Picture Story” is just the story itself, and “Vocabulary” is exactly what it sounds like, although not every story has a vocabulary list ready to go. Here’s a snippet of a vocabulary list from another story:

Going back to the story itself: if you hover over the words, you’ll highlight a vocabulary word/phrase and two things will pop up:

If you click on the audio button, the highlighted words will be pronounced, and if you click on the screen looking button, the following will pop up:

This is a really thorough one-on-one analysis of each character. It gives you some common usages of the character (there are several panels of common words; just click on the numbers in the top left), the Pinyin, and the stroke order.
Pressing the “P” will show the breakdown of the Pinyin and how it’s pronounced:

Pressing the play button will play the stroke order gif, and the rewind button is to restart the gif:

Definitely check out this site for reading practice, I can’t believe I just found out about it. Keep this bookmarked if you’re planning on doing the HSK anytime soon!
Yes! Chinese Website: (link)
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
大草原不可避 : Keyboard smashing in Japanese
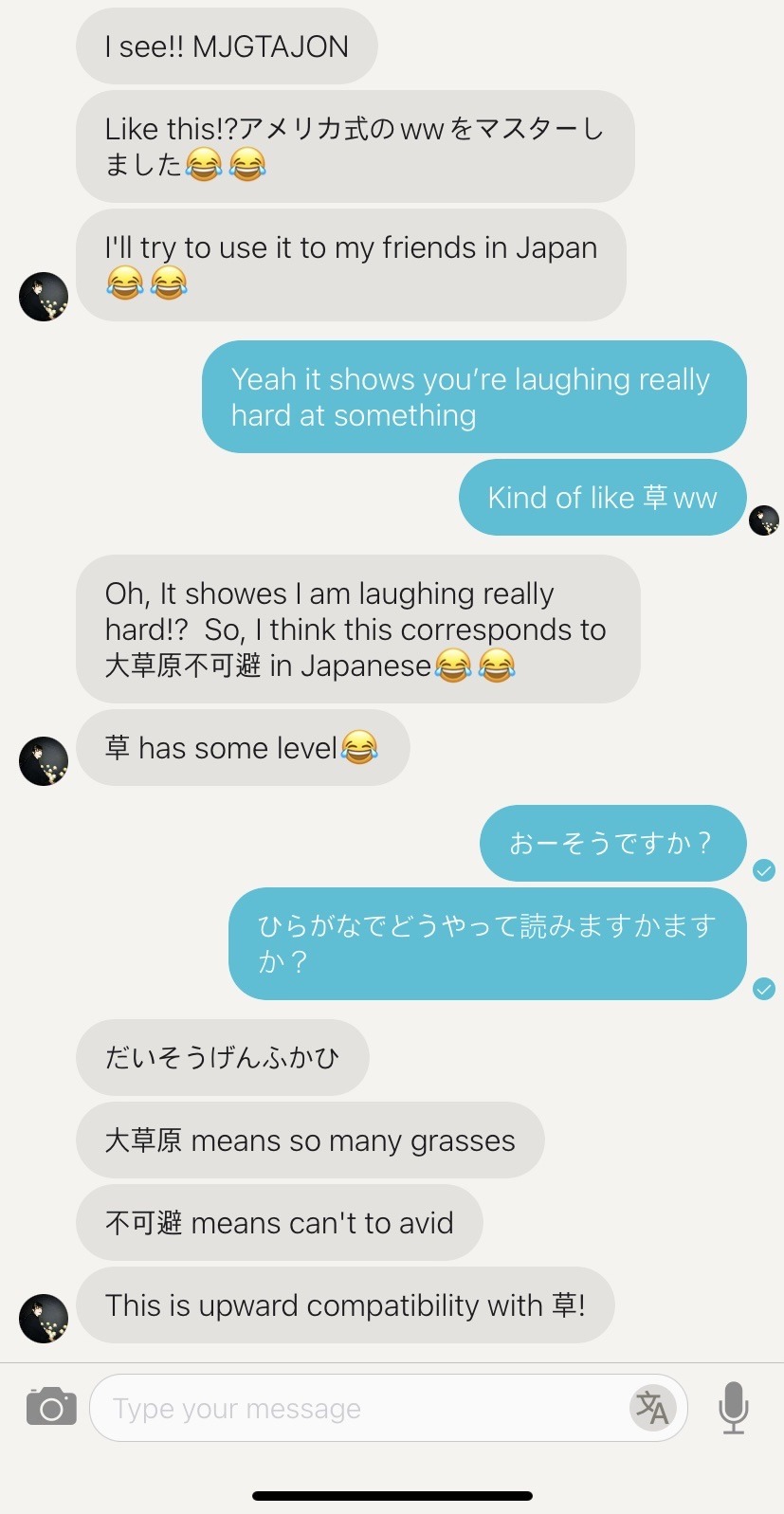
I explained how keyboard smashing in English expresses laughing really hard and she taught me the Japanese equivalent in return!!
As some of you might know, in Japanese, “w” from the word “to laugh” 笑う 「わらう」 is basically like “lol” in Japanese so when there’s a bunch of “w”’s together it looks like this wwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwww
and it looks like a bunch of grass so one slang word to show something is funny is 草 「くさ」 which is the word/kanji for grass so you don’t have to type out a bunch of w’s.
So the step up from 草 is 大草原 「だいそうげん」 which means prairie since there’s a lot more grass.
And if something leaves you laughing so much that you can’t hold it back you could say 大草原不可避 「だいそうげんふかひ」 which basically means “inevitable prairie”.
The “inevitable part”, 不可避 「ふかひ」 in this phrase means laughter is inevitable and you can’t help but laugh.
37K notes
·
View notes
Text










Norwegian Bokmål for Total Beginners (January 2024 Crash Course)
22. Hvor bor du? (Where do you live?)
Good morning/afternoon/evening to you! Today's post is a long one because we have some cultural insights at the end if you're interested. But if you're just here for the vocabulary, that's fine too.
by (m) - town, city
bygd (m/f) - village
vei (m) - road
gate (m/f) - street
bolig (m) - residence, housing
hus (n) - house
leilighet (m) - apartment/flat
boligblokk (m) - block of flats/apartments
hytte (m/f) - cottage, cabin
Sample Sentences
Bor du i et hus eller en leilighet? (Do you live in a house or a flat?)
Susanna bor i tredje etasje (Susanna lives on the third floor)
Den boligblokken har åtte etasjer (That block of flats has eight floors)
Bolige i Oslo er dyre (Housing in Oslo is expensive)
Husene på denne veien er veldig fine (The houses on this road are very nice)
Karl Johans gate er en lang gate i Oslo (Karl Johans street is a long street in Oslo)
False Friends in Norwegian
Lots of vocabulary in Norwegian is similar to English vocabulary. But there are some words that look like an English word, but actually have a different meaning! Today we learned that ei gate is NOT a gate, but a street!
Here are a few mor beginner-level false friends to watch out for!
🇳🇴en dress = 🇬🇧a suit
🇬🇧a dress = 🇳🇴en kjole
🇳🇴bra = 🇬🇧good, well
🇬🇧a bra = 🇳🇴en BH (brystholder = breast holder)
🇳🇴ei mappe = 🇬🇧a folder
🇬🇧a map = 🇳🇴et kart
🇳🇴en sky = 🇬🇧a cloud
🇬🇧sky = 🇳🇴himmel
🇳🇴å telle = 🇬🇧to count
🇬🇧to tell = 🇳🇴å fortelle
🇳🇴en advokat = 🇬🇧a lawyer
🇬🇧an advocate = 🇳🇴en forkjemper
🇳🇴akkurat = 🇬🇧exactly
🇬🇧accurate = 🇳🇴nøyaktig
Cultural Insight: Hytter i Norge
In Norway, it's common for families to own a cottage out in the countryside. They tar hyttetur (go on a cottage-trip) during the holidays, typically at Easter and often during the summer too. Some cottages are modern with all the comforts of home (wifi, kitchen gadgets etc), while some families are adamant that the true hytte-experience means being cut off from all that. Some cottages don't even have an inside toilet, and you'll have to use the utedo (outdoor toilet) instead!
Owning a cottage has become more popular over time, and in recent years (especially since covid and working from home) the industry has boomed. This is creating a lot of controversy in Norway: building more cottages to supply the demand means clearing large swathes of forests and marshlands. Norwegians are quite protective about nature (or, at least, they claim to be) and many are unhappy with this development. It's also a problem for the locals who can't buy houses in their hometowns simply because all the houses are being bought up by city folk. Additionally, it means that for large portions of the year these places are ghost towns and businesses may struggle to make ends meet.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
doing some absolutely thrilling wikipedia research

and while wikipedia is NOT a reliable source, I'm not sure Kasper is much better
#while this etymology is technically correct#its a very roundabout way to get to it#like husband is literally an anglification of husbond which yes does come of a norse compound of hus 'house' and bonde 'farmer; settled man#personal for ts#humour
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
re: hils
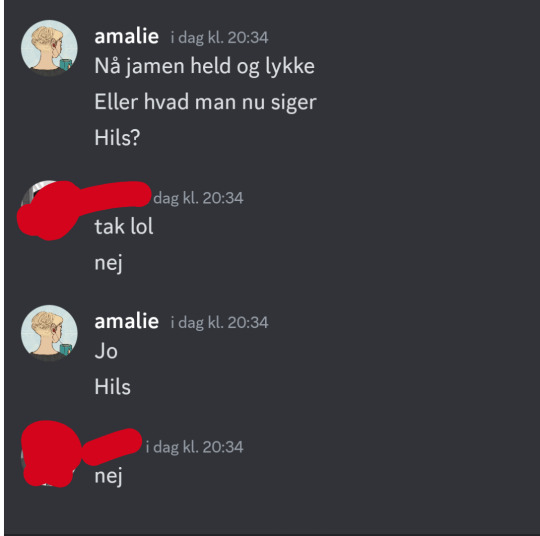
Translation:
amalie
oh well, good luck
or whatever
tell them I said hi?
red
thanks lol
no
amalie
yes
tell them i said hi
red
no
i am wildly underappreciated by my friends who don't want to tell healthcare professionals that neither of us knows that I said hi
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
it has come to my attention that i seem to have issues with adding the link for my top ten sayings to my original content masterpost (x), and it seems to be a general issue with adding any additional links to it.
based on this, i have reached the conclusion that tumblr does in fact not allow more than 50 links per post, and im not really sure how to solve this issue.
of course, i could choose to reblog it and add new links through the reblog, but first of all, im not even sure tumblr would allow that, and, second of all, it doesn't really work with the way i've chosen to categorise the posts.
i could also see if tumblr would finally show me mercy and allow me to use the page feature properly (it wouldn't before, which is why i even made the original content masterpost in the first place <3). however, this does come with the unfortunate downside that it won't be the first thing people see on my blog any longer
regardless, i don't really have a good solution for this rn, so im VERY open to suggestions
1 note
·
View note
Text

I decided to make some positive translation memes
[ID: a picture of kitten looking at a phone edited to be crying and surrounded by heart emoji with text reading 'when a translator worked hard for me to be able to access a piece of media']
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
one of those pop linguistic lists of untranslatable words except they don't tell you what they mean (because they are untranslatable)
19K notes
·
View notes