#virtual power plants
Text
New Poem on Virtual Power Plants
1 note
·
View note
Text
EVs as Virtual Power Plants (VPP)
Electric Vehicles (EVs) have become a popular mode of transportation around the world as they offer a sustainable solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, these vehicles can do much more than just transport people and goods. They can also be used as virtual power plants (VPPs) that can help balance the electrical grid and provide ancillary services.
What is a VPP?
A VPP is a…
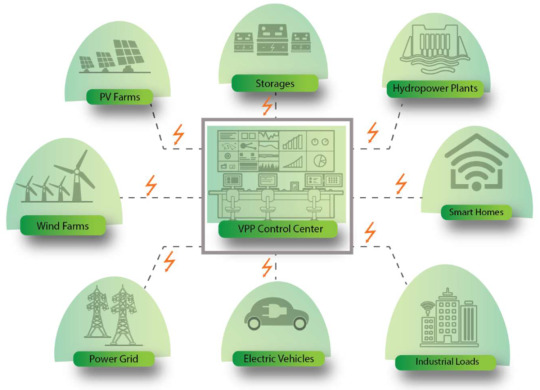
View On WordPress
#AI#Artificial Intelligence#digital transformation#Electric Vehicle#Electric Vehicles#Energy saving#EV#Solar Power#virtual power plants#virtual power plants (VPPs)#VPP
0 notes
Text
Croatian start-up to build largest battery system in South-eastern Europe

Croatia got the green light from Brussels to give a EUR 19.8 million grant to a domestic start-up for a massive energy storage project. IE-Energy is planning to build a battery system of 50 MW, which means it would be the biggest in South-eastern Europe.
The European Commission has approved, under the European Union’s aid rules, a EUR 19.8 million Croatian aid measure in favour of energy storage operator IE-Energy[1].
The package is aimed at helping the firm partially finance the procurement and installation of grid-scale batteries to provide transmission system operators (TSOs)[2] with balancing services. TSOs use grid-scale batteries to maintain a continuous balance between electricity supply from power stations and demand from consumers and to store electricity when needed.
The aid is necessary and appropriate to address an existing market failure, the EU’s top regulator concluded
The aid will take the form of a direct grant and will cover approximately 30% of capital expenditures. The commission concluded that the aid is necessary and appropriate to address an existing market failure, as there is a lack of incentives to provide balancing services to TSOs through grid-scale energy storage facilities[3].
Furthermore, the measure contributes to the modernisation of Croatia’s energy network, as well as increases in the country’s and the EU’s energy security of supply, the 27-member bloc’s executive arm said. In addition, it will accelerate the decarbonisation of the Croatian energy sector, according to the announcement.
Batteries are for balancing services for HOPS
IE-Energy is based in Rijeka, Croatia’s fourth-largest city. It joined the intraday and day-ahead markets at the Croatian Power Exchange (CROPEX) last year. Documents reveal the project is scheduled to start on December 1.
The firm intends to build the battery system near Šibenik in Dalmatia. It would have 10 MW in operating power and the capacity of 22 MWh in the first phase, scheduled to be completed in the first quarter of next year.
Moreover, IE-Energy said it would boost the system to 50 MW and 110 MWh by 2024. There is no storage facility in South-eastern Europe yet with such a capacity. Of note, a 250 MW project is under development in Turkey, with an envisaged capacity of 1 GWh.
The batteries would be used for balancing services for the independent Transmission System Operator in Croatia (HOPS)[4], domestic media reported.
The European Union’s documentation shows the project is scheduled to start at the beginning of December.
IE-Energy is developing virtual power plant
The start-up’s core activity is the development of a flexible and decentralised power provider – virtual power plant[5] or aggregator[6] – to allow small and medium-sized power producers (prosumers)[7] and consumers to participate directly in the energy market.
Aggregators have an important role in the integration of renewable energy sources, as power supply from wind and solar parks is unstable due to changes in the weather
Operators of such cloud-based systems unify available electricity sources so they can jointly increase output when the transmission system lacks power. Aggregators have an important role in the integration of renewable energy sources, as power supply from wind and solar parks is unstable due to changes in the weather.
Virtual power plants can also coordinate a decrease in consumption, for example in factories and shopping malls, or facilitate a boost in consumption in the case of a jump in electricity production, mostly when an unexpected burst of wind or sunshine boosts the level of renewable energy in the grid.
Source
Igor Todorović, Croatian start-up to build largest battery system in South-eastern Europe, in: Balkan Green Energy News, 15-09-2022, https://balkangreenenergynews.com/croatian-startup-to-build-largest-battery-system-in-southeastern-europe/?fbclid=IwAR3mRDg8V0xHuVwWKcDjgMRaXSaDBDx3KLXYBu5cyY_iecPkqYW4TL0ifx0
[1] IE-ENERGY Ltd. is a start-up company based in Rijeka, Croatia with sole purpose of creating new type of energy company focused on creating flexible smart grid. The company was set-up in March of 2020 and has been licensed in August of 2020 by Croatian Energy Agency (HERA) as Energy Trader in accordance with the Act on the Regulation of Energy Activities and has received international EIC code (EIC: 31X-0138-T-000-2) by HOPS (TSO) in September of 2020. https://ie-energy.hr/
[2] A transmission system operator (TSO) is an entity entrusted with transporting energy in the form of natural gas or electrical power on a national or regional level, using fixed infrastructure. The term is defined by the European Commission. The certification procedure for transmission system operators is listed in Article 10 of the Electricity and Gas Directives of 2009. Due to the cost of establishing a transmission infrastructure, such as main power lines or gas main lines and associated connection points, a TSO is usually a natural monopoly, and as such is often subjected to regulations. In electrical power business, a TSO is an operator that transmits electrical power from generation plants over the electrical grid to regional or local electricity distribution operators. In natural gas business, a TSO receives gas from producers, transports it via pipeline through an area and delivers to gas distribution companies. The United States has similar organizational categories: independent system operator (ISO) and regional transmission organization (RTO).
[3] Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when electricity is plentiful and inexpensive (especially from intermittent power sources such as renewable electricity from wind power, tidal power and solar power) or when demand is low, and later returned to the grid when demand is high, and electricity prices tend to be higher.
[4] HOPS is the Croatian Transmission System Operator and its mission is electric power system operation and maintenance, electricity transmission, as well as construction and development of the electricity transmission network in order to maintain security of supply with minimal costs and environmental protection. HOPS is the sole electricity transmission system operator in the Republic of Croatia, and the owner of the entire Croatian transmission network. https://www.hops.hr/en/Home/Index
[5] A virtual power plant (VPP) is a cloud-based distributed power plant that aggregates the capacities of heterogeneous distributed energy resources (DER) for the purposes of enhancing power generation, as well as trading or selling power on the electricity market. Examples of virtual power plants exist in the United States, Europe, and Australia.
[6] An aggregator ensures better coordination between supply and demand of electricity. Especially with an increase in solar and wind energy (on summer days) there will be an oversupply on the electricity market. The problem of oversupply or shortage is that there is an imbalance on the grid. The grid operators have a statutory duty to safeguard the grid balance. This can be done, for example, by asking customers to (temporarily) postpone their energy consumption during off-peak times or to purchase extra electricity from the grid during peak times. The Aggregator can respond to this by bundling their demand or supply flexibility on behalf of a group of households and companies and offering them in an aggregated form on a flexibility market. The aggregator can control smart devices in the home or business processes, thus shifting the energy consumption of the parties it represents to 'off-peak times'. In fact, the Aggregator acts as an intermediary between consumers, network operators and suppliers. This makes 'demand response' a (cheaper) alternative for, for example, extra investments in upgrading the electricity grid. For example, greenhouses or cold stores may be able to postpone their energy consumption for some time, without this having major consequences for the temperature present (which can drop/rise a few degrees without spoiling production).
[7] A prosumer is an individual who both consumes and produces. The term is a portmanteau of the words producer and consumer. Research has identified six types of prosumers: DIY prosumers, self-service prosumers, customizing prosumers, collaborative prosumers, monetised prosumers, and economic prosumers. The terms prosumer and prosumption were coined in 1980 by American futurist Alvin Toffler, and were widely used by many technology writers of the time. Technological breakthrough and a rise in user participation blurs the line between production and consumption activities, with the consumer becoming a prosumer.
0 notes
Text

#SOMA#soma game#pathos-ii#site upsilon#upsilon power plant#sci-fi horror#horror game#survival horror#frictional games#game screenshots#virtual photography#soma:red
31 notes
·
View notes
Link
Excerpt from this story from Inside Climate News:
Vicken Kasarjian is giddy as he describes a project that aims to address two of Richmond, California’s greatest problems: a lack of affordable housing and unreliable electricity.
Kasarjian is the chief operating officer of MCE, a nonprofit electricity provider that serves parts of four Bay Area counties. MCE’s plan is to retrofit about 100 houses and 20 businesses with rooftop solar, batteries and smart appliances, and then sell excess electricity from the solar and batteries into the grid.
He’s talking about a “virtual power plant,” which is when a company uses software to coordinate a series of energy systems—usually batteries—to export power to the grid at the same time. The result is a power plant that can participate in the state power market, selling its electricity at times of high demand and high prices.
There are dozens of virtual power plants in development across the country, with thousands of households and businesses involved. What’s different about the MCE project is it has a housing component, with plans to renovate abandoned properties and then sell them at subsidized prices to first-time homebuyers with qualifying incomes.
Richmond, with a population of about 110,000, has suffered for decades from air pollution from a giant Chevron oil refinery. The city has low incomes for the region, but high housing prices due to a lack of supply and proximity to some of the most affluent parts of the country, like Berkeley, which is 10 miles away.
“A virtual power plant is decentralized, decarbonized and democratized,” said Alexandra McGee, MCE’s manager of strategic initiatives.
The “decentralized” part is pretty self-explanatory, as is “decarbonized,” considering that the electricity is coming from solar and batteries. But how is this “democratized”?
She said the process is democratic because MCE’s board is made up of local elected officials from the communities served, and because the project would make residents more active participants in the energy system. MCE would come up with a system to compensate people for the electricity that gets exported.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The global Virtual Power Plant Market is expected to grow from an estimated USD 1.9 billion in 2024 to USD 5.5 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 23.4% during the forecast period. Virtual power plants are essential because they provide enhanced grid stability by optimizing and integrating diverse energy sources, contributing to increased energy efficiency and the seamless incorporation of renewable energy into power systems. This results in a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure. Growth in the smart grid directly influences the virtual power plant market. Additionally, factors such as an increasing share of renewable energy, declining costs of solar generation and energy storage, and a shift from centralized to distributed generation drive the virtual power plant market expansion.
#Virtual Power Plant#Power Plant#power plants#energy#energia#power generation#utilities#power#utility#electricity#renewable power#renewableenergy#renewable resources#ren#renewables#distribu#distri#distributed power generation#distributed energy#distributed generation#clean power generation#clean energy#sustainable energy#sustainability
0 notes
Text
Virtual Power Plant Market: Global Industry Analysis and Forecast 2023 – 2030

The Global Virtual Power Plant Market size was valued at USD 556.1 Million in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 2.27 Billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 26.5 % from 2022 to 2028.
A virtual power plant is a cloud-based distributed power plant that aggregates the capacities of heterogeneous distributed energy resources for the purposes of enhancing power generation, trading or selling power on the electricity market, and demand side options for load reduction. Depending on the particular market environment, a virtual power plant (VPP) can accomplish a whole range of tasks. In general, the objective is to network distributed energy resources such as wind farms, solar parks, and Combined Heat and Power (CHP) units, in order to monitor, forecast, optimize, and trade their power.
Get Full PDF Sample Copy of Report: (Including Full TOC, List of Tables & Figures, Chart) @
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/request/16599
Updated Version 2024 is available our Sample Report May Includes the:
Scope For 2024
Brief Introduction to the research report.
Table of Contents (Scope covered as a part of the study)
Top players in the market
Research framework (structure of the report)
Research methodology adopted by Worldwide Market Reports
Moreover, the report includes significant chapters such as Patent Analysis, Regulatory Framework, Technology Roadmap, BCG Matrix, Heat Map Analysis, Price Trend Analysis, and Investment Analysis which help to understand the market direction and movement in the current and upcoming years.
Leading players involved in the Virtual Power Plant Market include:
ABB (Switzerland), Siemens (Germany), General Electric (U.S.), AGL Energy (Australia), Schneider Electric (France), Cisco Systems Inc. (U.S.), Bosch (Germany), Autogrid Systems Inc. (U.S.), Enel X Inc. (U.S.), Next Kraftwerke (Germany), and Other Major Players
If You Have Any Query Virtual Power Plant Market Report, Visit:
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/inquiry/16599
Segmentation of Virtual Power Plant Market:
By Technology Type
Demand Response
Distributed Generation
Mixed Asset
By Source
Solar
Wind
Small Hydro
Batteries
Others
By End Users
Commercial
Industrial
Residential
Market Segment by Regions: -
North America (US, Canada, Mexico)
Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Rest of Eastern Europe)
Western Europe (Germany, UK, France, Netherlands, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Western Europe)
Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, The Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, Rest of APAC)
Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, Israel, South Africa)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA)
Importance of the Report :
• Qualitative and quantitative analysis of current trends, dynamics and estimates;
• Provides additional highlights and key points on various Virtual Power Plant market segments and their impact in the coming years.
• The sample report includes the latest drivers and trends in the Virtual Power Plant market.
• The report analyzes the market competitive environment and provides information about several market vendors.
• The report provides forecasts of future trends and changes in consumer behavior.
• Comprehensive fragmentation by product type, end use and geography.
• The study identifies many growth opportunities in the global Virtual Power Plant market.
• The market study also highlights the expected revenue growth of the Virtual Power Plant market.
Our study encompasses major growth determinants and drivers, along with extensive segmentation areas. Through in-depth analysis of supply and sales channels, including upstream and downstream fundamentals, we present a complete market ecosystem.
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
Acquire This Reports: -
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/checkout/?user=1&_sid=16599
About us:
Introspective Market Research (introspectivemarketresearch.com) is a visionary research consulting firm dedicated to assisting our clients to grow and have a successful impact on the market. Our team at IMR is ready to assist our clients to flourish their business by offering strategies to gain success and monopoly in their respective fields. We are a global market research company, that specializes in using big data and advanced analytics to show the bigger picture of the market trends. We help our clients to think differently and build better tomorrow for all of us. We are a technology-driven research company, we analyse extremely large sets of data to discover deeper insights and provide conclusive consulting. We not only provide intelligence solutions, but we help our clients in how they can achieve their goals.
Contact us:
Introspective Market Research
3001 S King Drive,
Chicago, Illinois
60616 USA
Ph no: +1-773-382-1047
Email: [email protected]
#Virtual Power Plant#Virtual Power Plant Market#Virtual Power Plant Market Size#Virtual Power Plant Market Share#Virtual Power Plant Market Growth#Virtual Power Plant Market Trend#Virtual Power Plant Market segment#Virtual Power Plant Market Opportunity#Virtual Power Plant Market Analysis 2023
0 notes
Text
Virtual Power Plant Market, Market Size, Market Share | BIS Research

Market Overview:
The increasing demand for power generation from renewable sources of energy across the globe has propelled the need for virtual power plants. Moreover, there is an increased concern for decentralized power generators in the electricity distribution supply chain to reduce the electricity demand. High growth in the coming future is expected to be driven by rising awareness among governments of various countries about the need to mitigate power outages while also making attempts to preserve the environment.
Renewable Energy Integration:
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, has fueled the demand for VPPs. These systems help address the intermittency and unpredictability associated with renewable energy generation by aggregating diverse energy assets.
Grid Stability and Resilience:
VPPs play a pivotal role in enhancing grid stability and resilience. The ability to balance supply and demand in real-time, coupled with the incorporation of energy storage solutions, contributes to a more reliable and robust energy infrastructure.
Technological Advancements:
Advances in smart grid technologies, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence have empowered the development of sophisticated VPP platforms. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated control, optimizing the performance of the virtual power plants.
Government Initiatives and Incentives:
Governments worldwide are actively promoting the adoption of clean energy solutions. Subsidies, incentives, and regulatory support for virtual power plants encourage businesses and utilities to invest in sustainable energy infrastructure.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the Virtual Power Plant market is on a growth trajectory, it faces several challenges:
Interoperability and Standardization:
The integration of diverse energy assets poses challenges related to interoperability and standardization. Establishing common protocols and communication standards is crucial for seamless operation and scalability.
Download the free sample and understand better @ Virtual Power Plant Market
Cybersecurity Concerns:
As VPPs rely heavily on digital technologies, they become susceptible to cybersecurity threats. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is imperative to safeguard the integrity of the virtual power plant infrastructure.
Regulatory Hurdles:
Evolving regulatory frameworks and policies need to adapt to the dynamic nature of virtual power plants. Clear guidelines and standardized regulations will facilitate the widespread adoption of VPPs.
The Future Outlook:
The future of the Virtual Power Plant market looks promising, with several trends and developments shaping its trajectory:
Energy Communities:
The rise of energy communities, where individuals and businesses actively participate in energy sharing and trading through VPPs, is expected to gain momentum. This decentralized approach empowers local communities and promotes energy democratization.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms will further enhance the capabilities of VPPs. Predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and autonomous decision-making will optimize energy resource allocation and increase overall efficiency.
Global Expansion:
As awareness and acceptance of VPPs grow, their implementation is likely to expand globally. Developing regions, in particular, stand to benefit from the flexibility and scalability offered by virtual power plants in addressing energy access challenges.
To understand better have a look at our vertical page @ Energy and Power
Conclusion:
The Virtual Power Plant market represents a pivotal shift towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future. As technology continues to evolve and stakeholders collaborate to overcome challenges, virtual power plants are poised to play a central role in reshaping the global energy landscape. With a commitment to innovation, collaboration, and sustainable practices, the journey towards a cleaner, more efficient energy ecosystem is well underway.
#Virtual Power Plant Market#Virtual Power Plant Market Report#Virtual Power Plant Market Industry#Virtual Power Plant Key Players
0 notes
Link
#Puerto Rico#Science and Environment#battery#Contextomy#Grist#Luma Energy#Puerto Rico Solar and Energy Storage Association#Solar Energy#United States Department of Energy#Virtual power plant
0 notes
Text
Tesla Expands Virtual Power Plant to 244 San Diego Homes
Tesla’s Virtual Power Plant (VPP) program in San Diego is zooming towards significant milestones, as it inches closer to enrolling 250 homes. Launched with the aim to make renewable energy more accessible and grid power more sustainable, the program is gaining rapid traction. Homeowners equipped with Tesla Powerwalls and solar panels are getting an opportunity to serve the greater good, all while…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The Global Virtual Power Plant Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 27.68% during the forecast period, i.e., 2023-28. The market is driven primarily by the mounting demand for power generation from renewable energy sources, coupled with an essential concern for decentralized power generators in the electricity distribution supply chain to balance energy production & consumption levels.
#Global Virtual Power Plant Market#Global Virtual Power Plant Market size#Global Virtual Power Plant Market Share
0 notes
Text
The global Virtual Power Plant Market is expected to grow from an estimated USD 1.9 billion in 2024 to USD 5.5 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 23.4% during the forecast period. Virtual power plants are essential because they provide enhanced grid stability by optimizing and integrating diverse energy sources, contributing to increased energy efficiency and the seamless incorporation of renewable energy into power systems. This results in a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure. Growth in the smart grid directly influences the virtual power plant market. Additionally, factors such as an increasing share of renewable energy, declining costs of solar generation and energy storage, and a shift from centralized to distributed generation drive the virtual power plant market expansion.
#virtual power plant#energy#energia#power generation#utilities#power#utility#electricity#renewable power#renewableenergy#renewable resources#distributed power generation#distributed energy#distributed generation#renewables#clean power generation#sustainable development#sustainable energy#sustainable#sustainability#carbon reduction#reduce carbon emission
0 notes
Text
How Homeowners Benefit from SunPower’s California Virtual Power Plant with OhmConnect
Over the past century, our energy needs have changed drastically, and with it, how we power our world has shifted too. As more homes transition to more sustainable, all-electric solutions, demand for electricity continues to soar. Affordable renewable energy sources like solar power are meeting the demand head-on to help foster a better, cleaner planet.
SunPower is working with OhmConnect to…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The way that I’m brainrotting over a DCxDP crossover with a Danny who’s a vengeful villain rn
Like, let’s just say that the GiW finally get into contact with the JL. They need help neutralizing a threat, you see, and they’re on their last limb trying to keep civilians safe.
They have video evidence! They have studies to back their claims! The JL have to help them!
Unfortunately, the JL believe them. They join a fight against Danny, and defeat him due to being far more experienced than he is. Danny is locked away and experimented on by the GiW.
That would CHANGE a person. Your heroes turning against you and seeing you as a monster, being experimented on for who knows how long, not knowing if your friends and family are safe.
Danny gets out due to a simple mistake on the GiW’s part; having Blüdhaven as part of their transport route.
Of course the trucks were attacked, they’re government property!
So now, whoever decided to raid the government transport trucks (the Penguin or something) has a ton of experimental weapons with no idea how they work, and a heavily traumatized teenager.
Danny knows how they work. Danny can be useful! They won’t throw him out if he’s useful! And so, now Danny is working for the Penguin, altering the ectoplasm weapons to make them work on humans.
It’s a good deal for both parties. Danny gets to neurotically imprint on the Penguin like a small baby animal, and the Penguin gets a brilliant mind who will stop at nothing to achieve his goals.
But eventually, Danny finds out what happened to his family in his absence.
Jazz is in Arkham. Not as a psychologist, but as a “patient.” Apparently, she snapped and completely destroyed the house, leveled a few blocks of Amity Park, and conducted organized attacks on government bases (mostly GiW) for months.
Sam and Tucker helped her, eventually splitting once Jazz was captured. Sam travels to areas of extreme pollution, completely overgrowing them with her plant powers. Currently she’s in the Amazon rainforest, engaging in an ongoing feud with logging companies. Sam is winning.
Tucker faked his death, and Danny has no idea where he is. He only knows that the death wasn’t real because of a code that the three of them made together, just in case.
Ellie’s trapped in the Infinite Realms. Danny had a failsafe in place so that if she was ever cornered by the GiW, she would be sent to her haunt in the GZ. However, with the portal destroyed, she can’t come back. Danny just hopes she’s okay.
His parents are now top GiW scientists. They’re traveling the country giving speeches. They’re working on a battery powered by ectoplasm, but apparently started “having difficulties” around the same time that Danny escaped.
None of it is fair. None of it is right.
The Justice League destroyed his life, the lives of his friends, and they’re doing as good as ever. The GiW is respected, and his parents are happily working away for them.
Danny takes up some of his more experimental weapons and breaks Jazz out of Arkham. She’s a little different now, colder and more quiet, but she still loves him all the same. It’s an unimaginable comfort to him to see his sister again.
He can’t use his powers anymore. He’s so used to associating them with pain that even transforming into his ghost form is enough to take him down for hours.
However, he understands ectoplasm more than anyone else in the world. He knows how to use it in virtually everything; how it can become a weapon, how it can be used as a supplemental ingredient in poisons and nerve agents, how it can twist and distort the mind if applied correctly.
He doesn’t care what happens to him. He’s going to take down the GiW, and destroy the lives of the JL members who helped lock him away, just as they did to him.
No matter the cost.
#dcxdp#dc x dp#dp x dc#dpxdc#dp x dc crossover#dc x dp prompt#let Danny be scary and unsettling and evil WITHOUT being Dan!! do it!!!!!#at first the JL just think they’re dealing with a normal villain who’s angry at the world#the more details they get on him the more dread they feel#eventually they realize that they locked a 16-year-old away to be experimented on by the government for YEARS#and not that same kid is determined to ruin their lives#the GUILT. the PAIN. the realization that they so completely and fully failed this child#they’re speedrunning the 5 stages of grief and Danny is just like ‘oh no! anyways’ *fakes killing Red Robin to fuck with the bat*
4K notes
·
View notes