#scientific equipment
Text



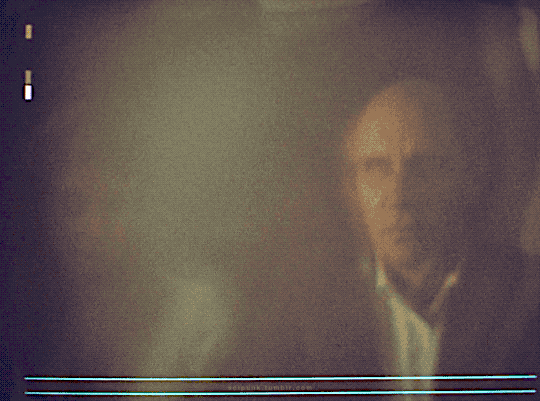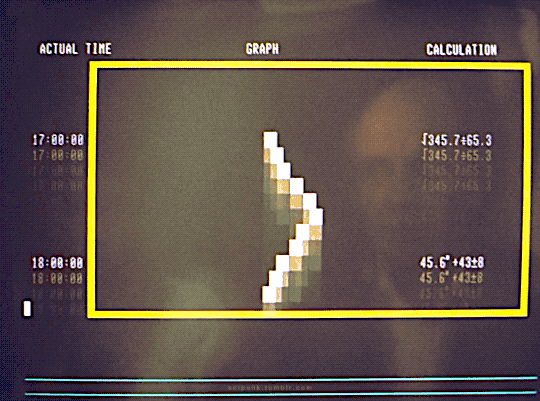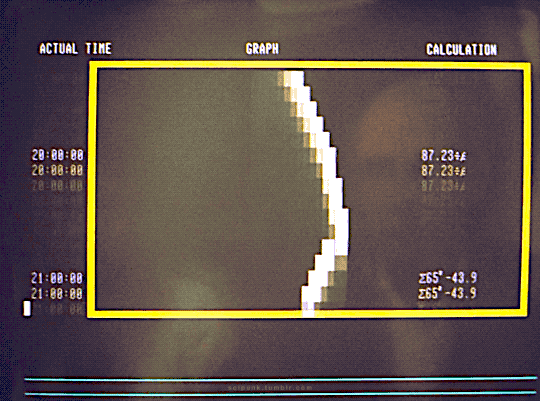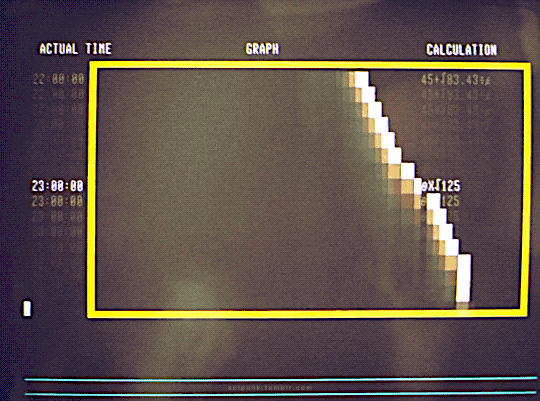
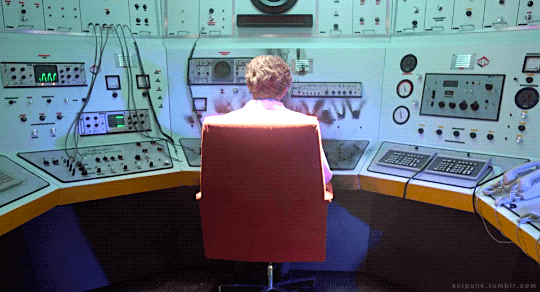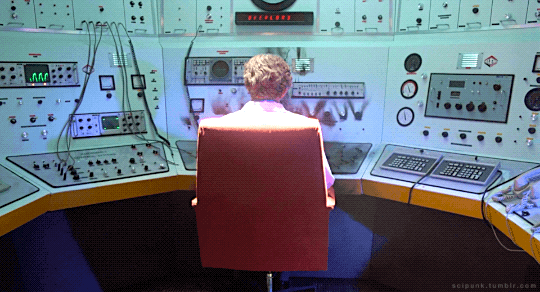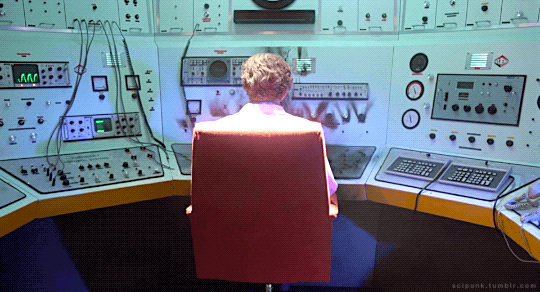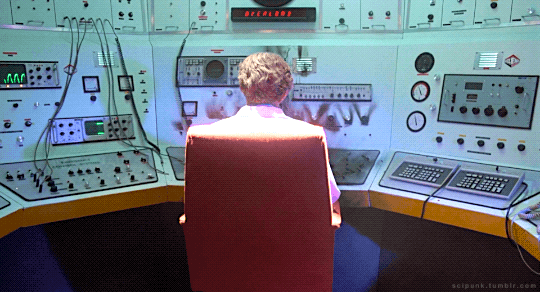

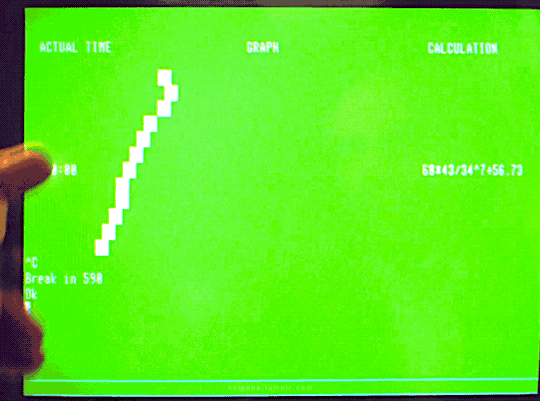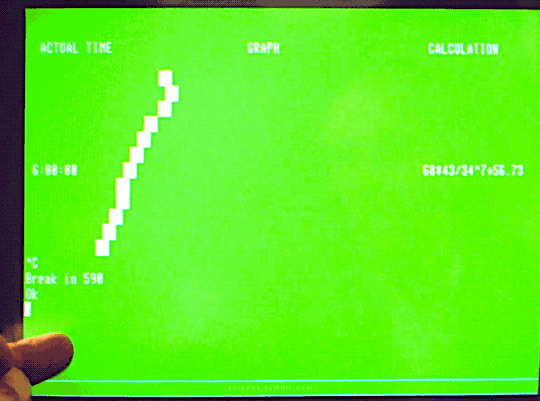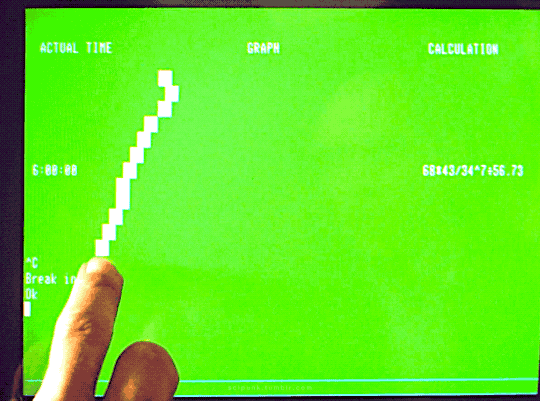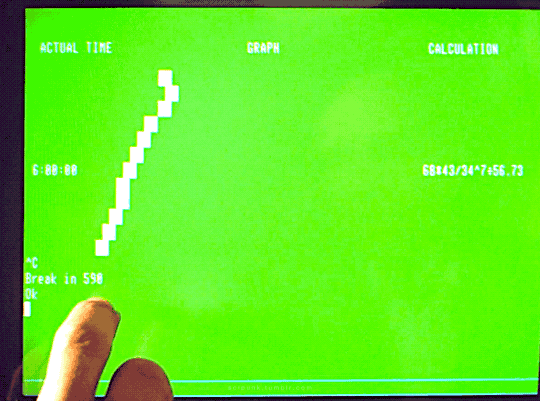
The Quiet Earth (1985)
#the quiet earth#80s#scifi movies#post apocalyptic#retro aesthetic#1980s#vintage#computers#eighties#scientific equipment#80s aesthetic#scifi aesthetic#80s movies#retro scifi#indie movie#indie film#cult classic#hidden gems#gif#gifset
112 notes
·
View notes
Text


19th century microscope plates
#historical artifacts#ephemera#vintage#victorian era#scientific equipment#collection#19th century#arsenic green#scheele's green#specimen#dark academia#academia#antique#⭒* ·˚ ☾ ⊹.
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
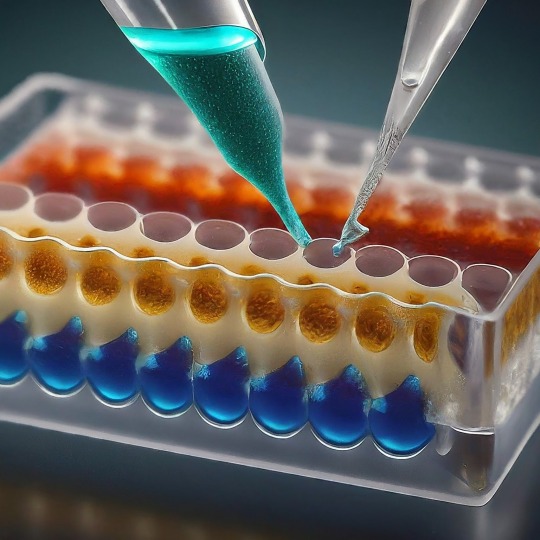
ELISA: A Powerful Tool for Detecting the Invisible
ELISA, or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, has become a cornerstone of medical diagnostics and biological research. This versatile technique allows scientists to detect and quantify minute amounts of target molecules, such as proteins, antibodies, and even viruses, with remarkable accuracy. In this blog, we'll delve into the world of ELISA, exploring its various types, its applications, and the exciting future directions this technology holds.
At its core, ELISA relies on the exquisite specificity of antibodies. Antibodies are highly specialized proteins produced by the immune system in response to foreign invaders. Each antibody can bind to a unique structure, called an antigen, on a specific molecule. In an ELISA, scientists leverage this binding property to create a sensitive detection system.
The 1960s witnessed a surge in interest in immunoassays, techniques that utilize the specificity of antibodies to detect target molecules. One such technique, radioimmunoassay (RIA), developed by Rosalyn Yalow and Solomon Berson, revolutionized medical diagnostics. RIA used radioactively labeled antibodies to detect antigens, offering high sensitivity. However, concerns regarding the safety of radioactive materials fueled the search for a safer alternative. The year 1971 marked a turning point. Independently, Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann published their work on a novel technique – the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). ELISA replaced radioactive labels with enzymes, eliminating the safety concerns associated with RIA. Like RIA, ELISA harnessed the specific binding between antibodies and antigens. However, it employed enzymes that could generate a detectable signal, such as a color change, upon interacting with a substrate. This innovation paved the way for a safer and more user-friendly diagnostic tool.
The basic ELISA protocol involves immobilizing the target antigen on a solid surface like a plate well. Then, a sample containing the molecule of interest (e.g., a suspected virus) is introduced. If the target molecule is present, it will bind to the immobilized antigen. Next, an antibody specific to the target molecule, linked to an enzyme, is introduced. This "detection antibody" binds to the target molecule already attached to the antigen. Finally, a substrate specific to the enzyme is added. This antigen-antibody binding is visualized using an enzyme linked to a reporter molecule. When the enzyme encounters its substrate, a detectable signal is produced, such as a color change or luminescence. The intensity of this signal is directly proportional to the amount of antigen present in the sample, allowing for quantification.
The beauty of ELISA lies in its adaptability. Several variations exist, each tailored for specific detection needs.
The Four Main ELISA Formats are:
Direct ELISA: Simplicity at its finest. In this format, the antigen is directly coated onto the ELISA plate. A labeled antibody specific to the antigen is then introduced, binding directly to its target. After washing away unbound molecules, the enzyme linked to the antibody generates a signal upon addition of the substrate. Direct ELISA offers a rapid and straightforward approach, but sensitivity can be lower compared to other formats due to the lack of amplification.
Indirect ELISA: Unveiling the Power of Amplification. Similar to the direct ELISA, the antigen is first coated onto the plate. However, instead of a labeled primary antibody, an unlabeled one specific to the antigen is used. This is followed by the introduction of a labeled secondary antibody that recognizes the species (e.g., mouse, rabbit) of the primary antibody. This two-step approach acts as an amplification strategy, significantly enhancing the signal compared to the direct ELISA. However, the presence of an extra incubation step and the potential for cross-reactivity with the secondary antibody add complexity.
Sandwich ELISA: Capturing the Antigen Between Two Antibodies. Here, the capture antibody, specific for one region of the antigen, is pre-coated onto the ELISA plate. The sample containing the antigen is then introduced, allowing it to be "sandwiched" between the capture antibody and a detection antibody specific for a different region of the same antigen. A labeled secondary antibody or a labeled detection antibody itself can then be used to generate the signal. Sandwich ELISA boasts high sensitivity due to the double-antibody recognition and is often the preferred format for quantifying analytes.
Competitive ELISA: A Race for Binding Sites. In this format, the antigen competes with a labeled antigen (usually a known amount) for binding sites on a capture antibody pre-coated onto the plate. The more antigen present in the sample, the less labeled antigen can bind to the capture antibody. Following a washing step, the amount of bound labeled antigen is measured, providing an inverse relationship between the signal and the concentration of antigen in the sample. Competitive ELISA is particularly useful for studying small molecules that may be difficult to directly conjugate to an enzyme.
ELISA's Reach: From Diagnostics to Research. The applications of ELISA are as vast as they are impressive. Let's delve into some key areas where ELISA plays a vital role:
Unveiling the Mysteries of Disease:
Diagnostics: ELISA is a cornerstone of diagnosing infectious diseases like HIV, Hepatitis, and Lyme disease. It detects antibodies produced by the body in response to the invading pathogen, providing valuable information for early detection and treatment.
Monitoring Autoimmune Diseases: ELISA helps monitor autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus by measuring specific antibodies associated with these conditions.
Cancer Screening: Certain cancers can be detected by identifying tumor markers, proteins elevated in the blood of cancer patients. ELISA assays are being developed to detect these markers for early cancer screening.
Safeguarding Food Quality:
Allergen Detection: Food allergies can be life-threatening. ELISA ensures food safety by enabling the detection of allergens like peanuts, gluten, and milk in food products, protecting consumers with allergies.
Monitoring Foodborne Pathogens: ELISA can identify harmful bacteria, viruses, and toxins in food, preventing outbreaks of foodborne illnesses.
Environmental Monitoring:
Pollutant Detection: ELISA can detect pollutants like pesticides and herbicides in water and soil samples, contributing to environmental protection efforts.
Microbial Analysis: This technique can be used to identify and quantify specific microbes in environmental samples, providing insights into ecosystem health.
Research and Development:
ELISA plays a crucial role in various research fields:
Drug Discovery: It helps researchers assess the effectiveness of new drugs by measuring drug-target interactions and monitoring drug levels in the body.
Vaccine Development: ELISA is instrumental in developing vaccines by evaluating immune responses to vaccine candidates.
Basic Research: Scientists use ELISA to study various biological processes by detecting and quantifying specific molecules involved in these processes.
Despite its established role, ELISA is evolving alongside technological advancements. New multiplex platforms allow for the simultaneous detection of various targets in a single sample, boosting efficiency in biomarker discovery and disease analysis. Automation streamlines workflows minimizes errors, and increases throughput, making high-throughput screening feasible in drug development and clinical settings. Miniaturization and portable devices enable rapid on-site diagnostics, providing healthcare professionals with real-time data for quicker interventions. Additionally, ongoing research is improving assay sensitivity, reducing background noise, and expanding detection limits, allowing for the identification of trace analytes and early disease biomarkers with greater accuracy than ever before. Integration of ELISA with emerging technologies such as microfluidics, nanotechnology, and artificial intelligence holds promise for enhancing assay performance, scalability, and data analysis capabilities.
These advancements hold promise for even wider applications of ELISA in the future. ELISA has revolutionized our ability to detect and quantify biological molecules. Its versatility, accuracy, and adaptability make it an invaluable tool across various scientific disciplines. As research continues to refine and innovate ELISA techniques, we can expect even more exciting possibilities to emerge in the years to come. ELISA's future is bright, promising to play a pivotal role in unraveling the mysteries of the biological world and improving human health.
#science sculpt#life science#molecular biology#science#biology#artists on tumblr#ELISA#immunology#immunotherapy#diagnostic management software#diagnosticimaging#history of immunology#scientific advancements#biotechnology#scientific research#scientific equipment#scientific instruments#techniques in biotechnology#scientific illustration#lab equipment#sciencenature#laboratory#lab skills#molecular diagnostics market
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blood Bag Tube Sealer
Blood Bag Tube Sealer NBTS-100 is a compact, lightweight tube sealer that uses a high frequency sealing technology to seal the blood bags, infusion bags, and urine bags without causing hemolysis or blood leakage. It is suitable for blood bags with a diameter of 2 to 6 mm and a sealing time of 2 to 4 seconds. Designed with a single chip and automatic sealing voltage. Equipped with an electronic tube with a lifespan of approximately 1000 hours

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pocket Dissolved Oxygen Tester

The Pocket Dissolved Oxygen Tester has a polarographic sensor for measuring dissolved oxygen levels. The dissolved oxygen meter's system menu allows you to configure six settings such as the number of calibration points, temperature units, and so on. It can determine the amount of dissolved oxygen in water, wastewater, and other liquids and solutions.
#pocketdissolvedoxygentester#laboratory equipment#scientific equipment#analytical equipment#water testing equipment
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Vacuum concentrator centrifuge comes with exquisite design, LCD touch screen monitor with micro-computer controlled system and direct operation interface. It uses centrifugal force to carry out the concentration of samples, vacuum conditions for evaporating solvents from the sample. It comes with 1350 rpm and temperature range of room temperature to 55 ℃ for different applications.
#Vacuum Concentrator Centrifuge#Laboratory Centrifuge#Laboratory Equipment#Scientific Equipment#Laboratory Instrument#Scientific Instrument
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anesthesia Machine

Anesthesia machine consists of a 7-inch TFT LCD screen and four tube mechanical flowmeters. The system is equipped with the oxygen flush technique with ventilation modes such as IPPV, A/C, SIGH, MANUAL, and SIMV. It has multiple working modes such as volume control and pressure control, which also change according to the patient. The device is incorporated with a power and voltage failure alarm.
https://href.li/?https://www.zimed.com/anesthesia-machines/
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
At specific light wavelengths, a spectrophotometer accurately measures electromagnetic energy. It is the cause of the high demand for this equipment in all different kinds of enterprises and laboratories. Without prior knowledge, selecting the appropriate equipment can be challenging. Learn more about spectrophotometers and how to find the right spectrophotometer manufacturers.
Read more :
#spectrophotometer#spectrophotometer manufacturer#spectrophotometer supplier#scientific equipment#Top laboratory equipment manufacturer#Spectrophotometer exporters
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Blues n greeny
0 notes
Text
Dissolution Samplers
Dissolution samplers are crucial instruments used in pharmaceutical quality control to collect samples during dissolution testing. They are designed to withdraw aliquots of the dissolution medium at specific time intervals from dissolution vessels containing solid dosage forms, such as tablets or capsules. These samples are then analyzed to assess the release rate of the active pharmaceutical ingredient(s) from the dosage form. Dissolution samplers help ensure accurate and reproducible results in dissolution testing, which is essential for assessing the performance and quality of pharmaceutical formulations.

0 notes
Text
Buy Task Medical Examination Couch - Ama Products
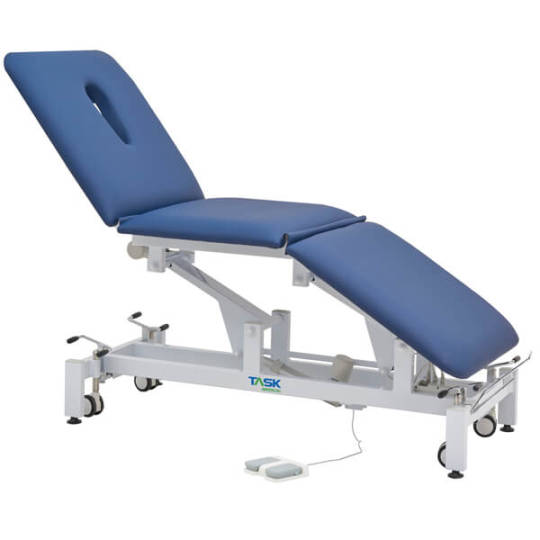
Introducing our Task Medical Hi-Lo Examination Couch - a premium choice for medical professionals. This 3-section, 3-motor couch in Navy Blue offers optimal comfort and functionality. With electric controls and included towel roll holder, it's designed for efficiency.
Explore our competitive Task Medical Examination Couch prices and elevate your practice today!
0 notes
Text
External Threaded Cryo Vials
External threaded cryo vials are specialized containers designed for the safe storage and preservation of biological specimens at ultra-low temperatures, typically ranging from -80°C to -196°C (-112°F to -321°F). These vials are crucial in various fields such as biomedical research, clinical diagnostics, and pharmaceutical development.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Tools, Testers, and DIY: Empowering Your Projects with Precision and Creativity
Welcome to our comprehensive collection of Tools, Testers, and DIY essentials! Whether you’re a professional tradesperson, a hobbyist, or a DIY enthusiast, we’ve got everything you need to tackle projects with confidence and creativity. From top-quality hand tools and power tools to precision testers and measurement equipment, we offer a diverse range of products to suit every need and budget. Dive into our selection of DIY kits and project materials, perfect for unleashing your creativity and bringing your ideas to life. With our tools and testers at your disposal, there’s no project too big or too small. Empower your projects today and discover the satisfaction of craftsmanship with Tools, Testers, and DIY essentials from our store!
Click to Know More

0 notes
Text
Recirculating Water Chiller Bath
Recirculating Water Chiller Bath NRWC-100 is an enclosed laboratory chiller with an all steel construction for durability for routine laboratory cooling applications. Equipped with powerful pump, it provides constant flow rates whereas the microprocessor PID controller maintains precise temperature control or cooling below ambient temperature. These chillers are ideal for laboratory applications for daily operation like cooling rotary evaporators, analytical instrumentation, vacuum systems, etc., assisted with a simple interface for quick setup.

0 notes
Text
#heavy equipment#roll out cantilever rack#scientific equipment#equipment#Roll Out Pallet#Roll Out Sheet Rack#Roll Out Racks
0 notes
Text
The Disintegration Tester is a precision instrument used to assess the disintegration time of tablets, capsules, and other pharmaceutical products in compliance with industry standards.

0 notes