#reproductivemedicine
Text



Greetings from ReproRevolution 🧚♀️✨
We are a non-profit organization advocating for comprehensive sex education, with the goal to de-stigmatize the taboos that continue to surround it.
We aim to build a safe space for you to learn and discuss all things body-related. 🥰
What are you waiting for? Follow us to be a part of our revolution 💖
#divorce#filipino#reproduction#philippines#reproductive choice#reproductive freedom#reproductive health#reproductive justice#reproductive rights#advocacy#education#empowerment#sex education#sex ed#reproductivemedicine#safe space#revolution
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Examining Reproductive Medicine in India: Progress, Difficulties, and Prospects
India has made great strides in reproductive medicine, positioning it as a global center for assisted reproductive technology (ART). India has emerged as a popular destination for people seeking fertility treatments thanks to its combination of cutting-edge technology, highly qualified medical staff, and reasonably priced therapies.

Advancements in Reproductive Medicine
India has achieved significant advancements in reproductive medicine, providing a broad spectrum of treatments to address a variety of infertility-related problems. In vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), and egg donation are examples of assisted reproductive technologies that are now widely used.
There are even more sophisticated methods available, like surrogacy, preimplantation genetic testing, and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Numerous couples have been able to achieve their desire of motherhood with the use of these approaches.
Modern fertility facilities and knowledgeable fertility doctors who are abreast of industry developments are features of India’s medical infrastructure. Reproductive medicine practices continue to evolve as a result of the nation’s emphasis on medical education and research.
Challenges Faced
In spite of the advancements, the area of reproductive medicine in India faces certain obstacles. The societal stigma and lack of understanding regarding infertility provide a major obstacle.
Because of social pressure and false beliefs, many couples are reluctant to seek medical attention. By addressing these problems through counseling and public education initiatives, the stigma attached to infertility might be lessened.
Strict laws that guarantee moral behavior and safeguard the rights of intended parents, surrogates, and donors present another difficulty.
Although India has taken steps to control assisted reproduction, more changes and regulations are needed to create a thorough legal system.
Hopeful Prospects
For infertile couples, the state of reproductive medicine in India gives optimism. For both domestic and foreign patients, the mix of cutting-edge technology, highly qualified medical staff, and reasonably priced treatment charges makes it a desirable option.
In addition, the Indian government is aggressively pushing medical tourism due to its recognition of its potential, which has resulted in higher investments and the construction of infrastructure.
Significant progress in reproductive medicine has been made in India, offering hope to many infertile couples. The advancement of assisted reproductive technology in India, along with the commitment of highly qualified medical experts, has made the country a top fertility treatment destination.
Ethical standards and the advancement of the sector will be further ensured by addressing issues with awareness, stigma, and regulation. Reproductive medicine in India has a bright future filled with hope and fulfillment for those wishing to become parents, provided there are ongoing improvements and a supportive atmosphere. If you are planning build a career in reproductive medicine StudyREPRO is the best option to learn reproductive medicine.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
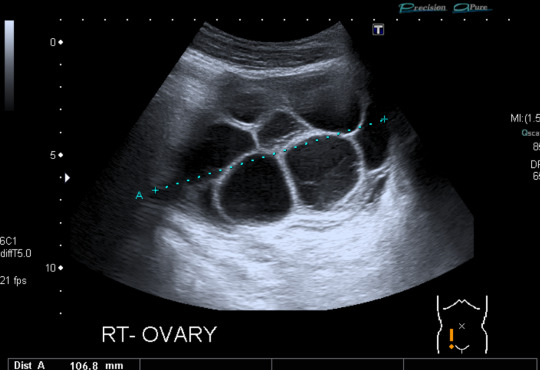
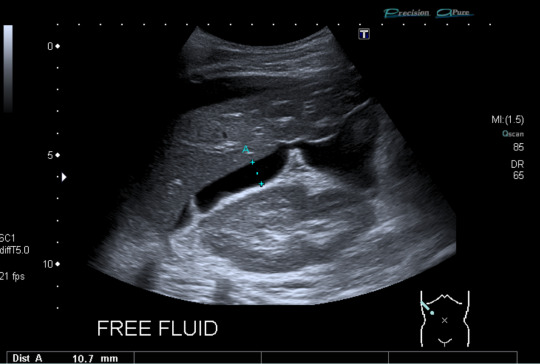
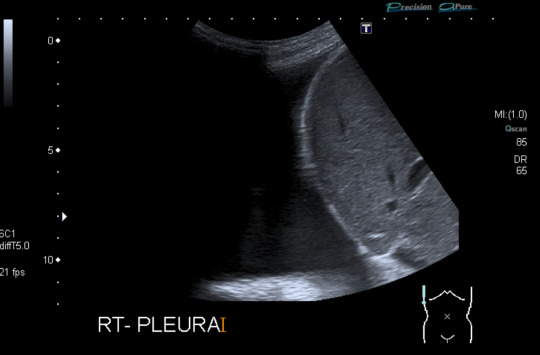
Today's case is a pelvic ultrasound of a 35-year-old woman who presented with abdominal pain and bloating 9 days after initiating controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in preparation for IVF. Ultrasound reveals enlarged ovaries with multiple large follicles, ascites, and pleural effusions. Findings are compatible with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) which occurs in approximately 5% of women undergoing ovarian stimulation. Fluid shift results in hemoconcentration and oliguria. Treatment is supportive and may include paracentesis or thoracentesis to relive discomfort from accumulated fluid. Severe cases can be fatal, so patient education, prompt recognition and timely intervention are key. Risk factors include PCOS and prior OHSS. Younger age and low body weight are not good predictors of risk, as was previously posited by some papers.
Case courtesy of René Pfleger, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 29070
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Reproductive Medicine Demo Class | Medical Courses for Doctors
Learn about Reproductive Medicine with DMHCA - PG Diploma Courses, Fellowship & Certificate Courses.
We have tailored course modules as per the latest updates in the healthcare industry. After completing courses, participants will get certification from the top university in India/Abroad & IBMP(USA).
We have 150+ Medical Courses for doctors, specialties like fetal medicine, obstetrics & Gynecology, infertility Management,etc.
We have tie-ups with different top medical hospitals for practical-training.
Join Now and Earn a discount upto 15%
Connect with our admission counsellor for more details at +91 971-141-4110
#certificate courses#fellowship courses#pg diploma courses#courses for doctors#courses after mbbs#clinical cardiology course#online diploma in obstetrics and gynaecology#reproductivemedicine#Youtube
0 notes
Text

Associate Professor Hassan Bakos, PhD, MBA, alongside Marcus Hedenskog, Rep Director & President of Vitrolife KK, and Vice President of Vitrolife JPAC & Igenomix APAC are attending the 68th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society for Reproductive Medicine in Kanazawa.
Their presence at this prestigious event highlights their joint commitment to rolling out the Felix technology across Japan and providing the best treatment options to patients.
#JSRM2023#ReproductiveMedicine#InnovationInHealthcare#GlobalLeadership#Vitrolife#Igenomix#ResearchAdvancements
0 notes
Text
How to Ace Your Embryology Training: Tips and Tricks from the Pros

Embarking on a journey in clinical embryology is both exciting and challenging. Whether you're just starting or looking to advance your career, the world of embryology is filled with possibilities.
In this article, we'll explore the essential tips and tricks that can help you excel in your embryology training and emerge as a professional in the field.
Choosing the Right Training Program
When it comes to mastering embryology, the first step is selecting the right training program. Here's what you need to consider:
Research the Best Programs
Start by researching the top clinical embryology courses in India. Look for programs that offer comprehensive curricula and hands-on experience. Keep an eye out for reviews and ratings to gauge their reputation.
Evaluate Course Modules
Each program may have a slightly different curriculum. Evaluate the course modules to ensure they cover the topics and skills you want to learn. A well-rounded program should include both theory and practical training.
Check Accreditation
Accreditation is crucial for the credibility of your training. Ensure that the program you choose is accredited by relevant authorities. This will open doors to better career opportunities.
Building a Strong Foundation
Once you've chosen your training program, it's time to build a solid foundation in embryology. Here's how:
Master the Basics
Start with the fundamentals. Understand the anatomy and physiology of the reproductive system. Familiarize yourself with the stages of embryonic development. These basics are your building blocks.
Hands-On Experience
Practical experience is invaluable in embryology. Work in a laboratory setting, handling embryos, and mastering techniques. The more hands-on experience you get, the more confident you'll become.
Networking and Mentorship
In the world of embryology, connections matter. Establish a network and seek mentorship.
Join Professional Associations
Become a member of professional associations related to embryology. Attend conferences and seminars. These events offer opportunities to connect with experts and peers.
Find a Mentor
A mentor can provide guidance and share their practical wisdom. Seek out experienced embryologists willing to mentor you. Their insights can be priceless.
Staying Updated
The field of embryology is constantly evolving. To stay at the top of your game, you must keep up with the latest developments.
Continuous Learning
Consider enrolling in advanced courses or workshops even after completing your initial training. This will help you stay updated and enhance your skills.
Final Thoughts
Embarking on a career in M.sc in clinical clinical embryology is a rewarding journey. By choosing the right training program, mastering the basics, building a network, and staying updated, you'll be well on your way to becoming a successful embryologist.
Embryology is a field of great promise, and as you gain knowledge and experience, you'll contribute to the exciting world of reproductive medicine in India and beyond. So, take these tips and tricks from the pros and soar in your embryology training with confidence.
In conclusion, achieving excellence in your embryology training is a path filled with discovery and opportunity. By following the right training program, building a strong foundation, networking, and staying updated, you can excel in this dynamic field. With the constant evolution of clinical embryology, you have the chance to make a meaningful impact and contribute to the advancements in reproductive medicine. As you continue your journey, remember that the key to success lies in dedication, continuous learning, and a passion for the science of life.
#EmbryologyTraining#ClinicalEmbryology#EmbryologyCourses#MedicalEducation#ReproductiveMedicine#PGDiploma#MastersInEmbryology#CareerInEmbryology
0 notes
Text
Whitefield's Top IVF Specialist: Pioneering Fertility Solutions
Introduction
In the bustling city of Whitefield, hopeful couples and individuals seeking to start a family are turning to the expertise of top IVF specialists. In recent years, Whitefield has emerged as a hub for cutting-edge fertility treatments, attracting patients from various parts of the country and beyond. Among these specialists, one stands out for pioneering fertility solutions and transforming the lives of countless individuals and families – the Top IVF Specialist in Whitefield.
The Rise of IVF Specialists in Whitefield
As advancements in medical science continue to break barriers, assisted reproductive technologies have witnessed a remarkable revolution. In Whitefield, the demand for IVF specialists has grown significantly, and it's no surprise why. IVF, or In Vitro Fertilization, has offered a ray of hope to couples struggling with infertility issues, single individuals desiring parenthood, and same-sex couples wanting to start a family.
The Expertise of Whitefield's Top IVF Specialist
The Top IVF Specialist in Whitefield is a beacon of hope for those facing challenges in conceiving naturally. Their journey began with a strong dedication to reproductive medicine and an unwavering commitment to their patients' well-being. Years of rigorous education, specialized training, and hands-on experience have equipped these specialists with the expertise required to handle complex fertility cases.
Their clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art technology, creating an optimal environment for successful IVF procedures. The team of experienced embryologists, nurses, and support staff work cohesively to ensure personalized care and emotional support throughout the process.
Pioneering Fertility Solutions
What sets Whitefield's Top IVF Specialist apart is their relentless pursuit of pioneering fertility solutions. They stay abreast of the latest advancements in the field and adopt innovative techniques to maximize success rates. The specialist's approach is personalized, understanding that each patient's journey is unique and requires tailored solutions.
Their expertise encompasses various assisted reproductive techniques, such as Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT), and Egg Freezing, among others. This comprehensive range of fertility solutions enables them to cater to diverse cases and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Compassionate Patient Care
Navigating the world of fertility treatments can be emotionally challenging for patients. Recognizing this, Whitefield's Top IVF Specialist emphasizes compassionate patient care and open communication. They listen attentively to their patients' concerns, addressing doubts and fears with empathy. This approach not only fosters trust but also ensures that patients are actively involved in decision-making throughout the treatment process.
High Success Rates and Positive Outcomes
Whitefield's Top IVF Specialist boasts a track record of high success rates and numerous heartwarming success stories. The specialist's dedication to excellence, coupled with the employment of the latest technologies, has resulted in positive outcomes for many patients. Their success is a testament to their commitment to helping individuals and couples achieve their dream of parenthood.
Conclusion
Whitefield's Top IVF Specialist has emerged as a beacon of hope and a leading figure in the field of reproductive medicine. Their pioneering fertility solutions, combined with compassionate patient care and unwavering dedication, have made them a trusted partner for individuals and couples seeking fertility treatments. For those in search of an experienced IVF specialist in Whitefield, their clinic stands as a symbol of hope, providing innovative solutions and nurturing the dreams of parenthood for many.
#IVFWhitefield#WhitefieldIVFSpecialist#FertilitySolutions#ParenthoodDreams#IVFTreatment#IVFSuccess#TopIVFSpecialist#PioneeringFertility#ReproductiveMedicine#IVFClinic#WhitefieldFertility#HopefulParents
0 notes
Text

Journal of Reproductive Medicine, Gynaecology and Obstetrics (ISSN: 2574-2574) Issue released with "6" articles. Online now!
Impact factor - 1.44*.
Read, Follow & Share:
#heraldopenaccess#openaccess#reproductivemedicine#reproducción#gynaecology#obstetrics#journal#viral trends#top trends#tumblr trends#trending#trendingnow#viral online#viral on social media
0 notes
Text
Cylinders and Assemblage- Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumour -Ovary
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour is an exceptionally discerned, ovarian neoplasm composed of sex cord or Sertoli cells admixed with stromal component expounded by Leydig cells. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour may occur in association with DICER1 syndrome or emerge as a sporadic phenomenon. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour manifests as well differentiated, moderately differentiated or intermediate grade and poorly differentiated neoplasms. Additionally, categories such as Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour with heterologous elements or retiform variant of Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour may be expounded. Majority of paediatric Sertoli- Leydig cell tumours are moderately differentiated or poorly differentiated, concur with DICER1 syndrome and frequently display heterologous elements or retiform tumour configuration. Histological categorization of neoplasms with enhanced tumour grade appears challenging [1,2].
Well differentiated tumefaction exhibits distinctive Sertoli cell and Leydig cell components. Moderately differentiated or minimally differentiated neoplasms appear devoid of well-formed Sertoli cell tubules with scant Leydig cells [1,2].
The infrequent, paediatric, preponderantly unilateral ovarian neoplasm is commonly delineated within young females with mean age of tumour emergence at 25 years although postmenopausal women may be implicated. Retiform tumour configuration or germline DICER1 mutations occur in neoplasms occurring in younger females [1,2].
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour is associated with DICER 1 syndrome which is an exceptional, tumour predisposition syndrome engendered by germline mutations within DICER1, a gene which encodes RNase III enzyme confined to microRNA maturation pathway.
Germline mutation expounds as a truncating mutation which may comprehensively incriminate the gene. Second hit somatic mutation occurs as focused, hotspot missense mutation implicating RNase IIIb domain of DICER [1,2].
Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumour Exhibits Distinctive Molecular Subtypes as
• DICER1 mutant wherein moderately differentiated or poorly differentiated tumour exemplifies heterologous elements or retiform configuration and incriminates young subjects [1,2].
• FOXL2 c.402C>G (p.Cys134Trp) mutant wherein moderately differentiated or poorly differentiated tumefaction is devoid of retiform component or heterologous elements and incriminates postmenopausal women [1,2].
• DICER1 / FOXL2 wildtype wherein well differentiated neoplasm appears devoid of retiform component or heterologous elements and implicates middle aged women.
• somatic hotspot DICER1 mutations are frequently associated with germline DICER1 mutations [1,2].
• DICER1 mutations commonly appear within moderately differentiated or poorly differentiated neoplasms. In contrast, well differentiated tumours are devoid of DICER1 mutations [1,2].
• Sporadic, moderately differentiated or poorly differentiated Sertoli-Leydig cell tumours harbour somatic mutations within hotspot of DICER1 gene. FOXL2 mutation may concur with DICER1 mutations [1,2]. Clinical symptoms of hormonal or androgenic activity are discerned. However, certain representative features may concur or recede, as denominated with characteristic androgenic symptoms or tumour emergence within elderly, peri-menopausal or postmenopausal women. Clinical manifestations as pelvic pain or pelvic tumefaction may be discerned. Ascites or tumour rupture is exceptional [1,2]. Androgenic hormonal symptoms or virilisation is commonly represented as hirsutism, clitoromegaly, breast atrophy, menstrual irregularities or amenorrhea [1,2]. Oestrogenic hormonal manifestations are infrequently observed. Histological subtype and tumour grade are concordant to clinical behaviour [1,2]. Upon gross examination, predominantly unilateral tumefaction may demonstrate a cystic component, foci of heterologous elements or retiform configuration. Poorly differentiated neoplasms exhibit foci of tumour necrosis. Tumour magnitude varies from < 1 centimetre to ~ 35 centimetres with mean diameter of 12 centimetres to 14 centimetres. Characteristically, cut surface is solid and tan to yellow [1,2). Frozen section exemplifies an admixture of Sertoli cell tubules or compressed cellular cords variably intermingled with Leydig cell clusters. Intracytoplasmic Reinke crystals may be delineated [1,2].
• Well differentiated Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour expounds open or compressed Sertoli cell tubules admixed with clusters of Leydig cells accumulated within intervening stroma. Cellular and nuclear atypia or mitotic activity is absent [1,2]. Sertoli cells appear as low, columnar to cuboidal cells with spherical to elliptical nuclei, nuclear grooves and miniature nucleoli. Leydig cells demonstrate abundant, eosinophilic cytoplasm with characteristic Reinke crystals, lipofuscin pigment and spherical nuclei [1,2].
• Moderately differentiated Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour characteristically depicts diffuse or lobulated architecture with alternating hypo-cellular and hyper-cellular areas. Sertoli cells configure compressed tubules, cords or diffuse sheets wherein cells are imbued with hyperchromatic, elliptical or spindle-shaped nuclei. Mild to moderate nuclear atypia and mitotic figures ~ 5 per 10 high power fields are discerned. Exceptionally, miniature clusters of Leydig cells appear commingled with Sertoli cell component. Discernible follicular differentiation may simulate juvenile granulosa cell tumour [1,2].
• Poorly differentiated Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour is constituted of diffuse sheets of immature, sarcomatoid Sertoli cells with configuration of infrequent, indistinct cords. Nuclear atypia is moderate to marked. Mitotic activity is significant with ~ 20 mitoses per 10 high power fields. Undiscernible Leydig cells are represented by few, miniature clusters, characteristically accumulated upon periphery of tumour nodules [1,2].
• Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour with heterologous elements is constituted of epithelial or mesenchymal elements represented within moderately differentiated, poorly differentiated or retiform Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour. Benign, borderline or malignant intestinal or gastric type mucinous epithelium is a common heterologous element. Trabecular or goblet cell carcinoid tumour may arise from heterologous mucinous epithelium. Heterologous mesenchymal elements as cartilage or skeletal muscle are uncommon. Focal differentiation into hepatic parenchyma and elevated serum α-fetoprotein (AFP) levels is infrequent [1,2].
• Retiform variant of Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour demonstrates focal or diffuse retiform pattern with configuration of anastomosing, slit-like, irregular spaces or multi-cystic, sievelike or papillary architecture [1,2].
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour is immune reactive to general sex cord proteins as inhibin, calretinin, SF1, FOXL2, CD56, WT1, CD99, vimentin, pancytokeratin, Melan A/MART1, CK20, CDX2, AFP, arginase or HepPar1 [3,4]. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour is immune non-reactive to CK7 or EMA.
Neoplasm is devoid of histochemical staining with reticulin.
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour requires segregation from neoplasms such as endometrioid adenocarcinoma, adult granulosa cell tumour, fibroma or tubular Krukenberg tumour emerging from metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma. Retiform variant of Sertoli- Leydig cell tumour necessitates distinction from yolk sac tumour or low grade, borderline serous carcinoma ovary. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour with heterologous elements mandates distinction from carcinosarcoma, teratoma and primary or metastatic ovarian mucinous neoplasms [3,4].
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour can be assessed with pertinent clinical examination of young women manifesting features such as virilisation with elevated testosterone levels. An ovarian or pelvic tumefaction can be detected upon imaging. Intraoperative frozen section is optimal for cogent tumour evaluation and adoption of relevant surgical procedures. Incriminated subjects depict elevated serum testosterone levels. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour can be appropriately investigated with imaging of pelvic cavity with techniques as ultrasonography, computerized tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Upon imaging, a preponderantly solid or solid and cystic adnexal tumefaction is denominated [3,4].
Genetic counselling and assessment of germline DICER1 mutation is recommended [3,4].
Optimally, Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour occurring in young women is treated with fertility sparing surgical techniques. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour can be appropriately managed with conservative, fertility sparing surgical procedures as unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. Cogent tumour staging along with or devoid of regional lymph node dissection can be performed in young women exemplifying stage I tumours. Incriminated elderly females, where fertility preservation is unnecessary, can classically be subjected to bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, total abdominal hysterectomy and comprehensive surgical staging of tumefaction. Platinum based adjuvant chemotherapy is beneficial in treating moderately differentiated or poorly differentiated tumours and neoplasms with heterologous mesenchymal elements, advanced tumour stage or tumour rupture [3,4].
Biological behaviour is contingent to histological subtype and tumour grade. Well differentiated Sertoli-Leydig cell tumours are essentially benign neoplasms whereas ~ 10% of moderately differentiated and ~59% of poorly differentiated tumours demonstrate malignant biological behaviour. Occurrence of heterologous elements, retiform tumour configuration, tumour rupture, tumour dissemination beyond ovary, stage II or advanced stage neoplasms delineate an adverse prognostic outcome. Neoplasms demonstrating germline DICER1 mutations exhibit favourable prognosis, in contrast to tumours with singular somatic DICER1 mutation [3,4].
To Know More About Global Journal of Reproductive Medicine https://juniperpublishers.com/gjorm/index.php
0 notes
Video
youtube
WORLD WAR II, EXPERIMENTS ON ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION
During the Second World War, experiments on artificial insemination were carried out to dispel concerns about the declining birth rate in several countries and the need to maintain a strong population, including a sufficient number of potential soldiers. These experiments focused primarily on the development of artificial insemination techniques with the aim of increasing the birth rate of healthy, physically fit individuals.
An important aspect of these experiments was the preservation of sperm. The researchers worked on methods for obtaining, storing, and transporting sperm to ensure their viability and efficacy for artificial insemination. This research contributed to the development of sperm bank techniques, which became an important tool in fertility treatment and reproductive medicine after the war.
Donor selection was another important component of these experiments. Scientists and doctors carefully selected donors who were considered physically fit, intelligent, and free of hereditary diseases. The idea was to improve the genetic quality of the offspring, and this selection process laid the foundation for later advances in sperm donor screening and selection in the field of assisted reproduction.
In addition, these experiments led to the development of fertility treatments and assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs), which are still used today. The researchers looked at various methods to improve fertility in both men and women, including hormone treatments and artificial insemination procedures. These discoveries paved the way for modern infertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI).
However, it is important to acknowledge the ethical concerns surrounding these experiments. In many cases, the participants were not sufficiently informed about the nature of the experiments or gave their consent under duress. This raises significant ethical questions about how to deal with those affected.
To sum up, the experiments on artificial insemination during World War II were a complex and multifaceted aspect of war research. Not only did they contribute to advances in reproductive medicine and fertility treatments, but they also underscore the ethical dilemmas associated with scientific research in wartime. These experiments played an important role in shaping the landscape of reproductive medicine, but their ethical implications remain the subject of debate and reflection.
#PLB_ATROCITIESWW2, ATROCITIES OF WORLD WAR II IS A CHRONICLE OF HUMAN SUFFERING
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLlGY5JKyfHGwk6uQI7wlHz4A-JxRTVtie
#WorldWarII #Artificialinsemination #ReproductiveMedicine #Fertilityresearch #Spermpreservation #DonorSelection #EthicalDilemmas #Assistedreproduction #ScientificExperiments #PLB_ATROCITIESWW2
0 notes
Text
Kate Clancy explains why reproductive justice should include the right to stop contraception. Read more here and join the conversation.
#ReproductiveMedicine #ReproductiveHealth #ReproductiveJustice #health #books
0 notes
Text
An Understanding of the Different Causes of Infertility
A disorder known as infertility occurs when a person cannot conceive despite trying for a year. Many different factors can lead to this. These include endometriosis, low testosterone, low sperm count, and ovulatory problems. Age raises the chance of infertility. Patients with infertility have access to a range of therapy alternatives.
Know Infertility In-depth
One disorder of the reproductive system is infertility. It makes it difficult for people to become pregnant. It can happen for a variety of causes and impact anyone.
Getting pregnant involves the following steps.
The reproductive hormones that regulate ovarian function are produced by your brain.
Your ovary must mature an egg.
Your ovary needs to discharge an egg.
The fallopian tube needs to take the egg.
To reach your fallopian tube, sperm must pass via your uterus and up your vagina.
An embryo is created when the sperm fertilises the egg.
The embryo enters your uterus through your fallopian tube and implants there.
Pregnancy won’t occur if any of these procedures doesn’t occur.
If you are under 35, your doctor may diagnose infertility after a year of infertility treatment. Having regular, unprotected intercourse is the definition of trying to get pregnant. If you are 35 years of age or older and have frequent, unprotected sex for six months, your provider may diagnose infertility.
Contrary to popular belief, infertility is more common. Those who want to start or grow a family have access to a wide range of treatment alternatives.
Types Of Infertility
Types Of infertility include:
Primary infertility:This is what happens after a year of consistent, unprotected sexual activity if you have never given birth and are unable to conceive.
Secondary infertility:After at least one successful pregnancy, this is the point at which you are unable to conceive.
Unexplained infertility:This is what happens when an individual or couple’s infertility test results reveal no medical cause for their infertility.
Is Infertility Common?
Men and those assigned male at birth (AMAB) and women and those assigned female at birth (AFAB) are equally affected by infertility. Infertility is a prevalent issue. In the US, 1 in 5 women between the ages of 15 and 49 experience problems with primary infertility, and 1 in 20 experience problems with secondary infertility. Worldwide, almost 48 million couples struggle with infertility.
Symptoms Of Infertility
Being unable to conceive after six months or a year of regular, unprotected intercourse is the primary indicator of infertility. It’s possible that you’re symptom-free. However, some people could exhibit physical signs.
They could consist of:
Pelvic or abdominal pain
irregular menstruation, irregular vaginal bleeding, or none at all
Penile diseases or problems ejaculating
Causes Of Infertility
The reasons behind infertility are numerous. The reason you are not conceiving is not easily explained. The optimum Reproductive medicine course of action and cause identification are only possible by a healthcare professional.
Treatment for fertility depends mostly on the cause and your goals. Your age and the duration that you have been trying are factors while deciding the treatment.
Hope you found this information helpful. Wishing you a blissful parenthood!
0 notes
Photo

#cardiology #Cardiologist #genmed #generalmedicine #emergencymedicine #Obg #obgjobs #obstetrics #ortho #orthopedics #reproductivemedicine #fellowshipinreproductivemedicine (at Pondicherry) https://www.instagram.com/p/CXxhXlDlSK7/?utm_medium=tumblr
#cardiology#cardiologist#genmed#generalmedicine#emergencymedicine#obg#obgjobs#obstetrics#ortho#orthopedics#reproductivemedicine#fellowshipinreproductivemedicine
0 notes
Text

Some women with low ovarian reserve, ovarian failure, thin endometrium, or women approaching menopause prefer to use their own eggs for pregnancy rather than opting for egg donation. PRP treatment has promising results in such cases by increasing the number of eggs and improving the endometrium thickness leading to a successful pregnancy.
In this procedure, the patient's blood is taken, and platelets are separated. These platelet-rich plasma are injected directly into the patient's ovaries or uterine endometrium, depending on the treatment objective under anesthesia.
To know if you are an ideal candidate for PRP and more details on PRP procedure, meet our fertility specialists today!
📷: www.hegdefertility.com/ovarian-prp/
📷: 8880 747474
#hegdefertility#prptreatment#prp#ovarianreserve#lowovarianreserve#femaleinfertility#ovarianhealth#infertilitysupport#infertilityproblems#infertilitycauses#reproductivemedicine#ttc#womenshealth#infertilityawareness
0 notes
Text
The Basics of Clinical Embryology: What You Need to Know to Get Started
Clinical embryology is a fascinating field that plays a vital role in reproductive medicine. It involves the study of human embryos and the various processes that occur from fertilization to the formation of a healthy baby. If you're considering a career in embryology or are simply curious about the subject, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the basics of clinical embryology.
What is Clinical Embryology?
Clinical embryology is a branch of reproductive medicine that focuses on the study of human embryos. It involves techniques and procedures used to aid in fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and genetic testing. Clinical embryologists play a crucial role in assisting couples struggling with infertility to achieve their dream of having a child.
Embryologist Training
To become a clinical embryologist, extensive training is required. A strong foundation in the biological sciences, particularly in human anatomy, physiology, and genetics, is essential. Most embryologists hold advanced degrees in reproductive biology or embryology.
Embryologist training typically involves a combination of academic coursework, laboratory experience, and hands-on clinical training. Many universities and institutions offer specialized programs in reproductive medicine and embryology. These programs cover topics such as reproductive endocrinology, assisted reproductive technologies, and laboratory techniques for embryo culture, cryopreservation, and genetic screening.
SEART: Empowering Embryologist Training
SEART, a renowned brand in the field of reproductive medicine, has emerged as a leader in providing comprehensive training programs for aspiring embryologists. With a focus on practical skills and cutting-edge techniques, SEART offers a unique learning experience that prepares students for the challenges of the field.
The Importance of Clinical Embryology
Clinical embryology is crucial for the success of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as IVF. Embryologists are responsible for ensuring the quality and viability of embryos before transfer into the uterus. They play a significant role in the selection and culture of embryos, as well as the implementation of techniques like intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and preimplantation genetic testing (PGT).
Embryologists work closely with reproductive endocrinologists, urologists, and other healthcare professionals to provide personalized care to patients. Their expertise in embryo assessment, cryopreservation, and genetic screening helps maximize the chances of a successful pregnancy while minimizing the risk of genetic disorders.
Key Techniques in Clinical Embryology
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a widely used technique in assisted reproduction. It involves the retrieval of eggs from the ovaries, fertilization with sperm in a laboratory, and subsequent culture of the resulting embryos before transfer into the uterus.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): ICSI is used when male infertility issues are present. It involves the injection of a single sperm directly into the egg, increasing the chances of fertilization.
Embryo Culture: Embryo culture involves creating an optimal environment for embryo development in the laboratory. Embryologists monitor and nurture the embryos, ensuring they reach the appropriate developmental stages before transfer.
Cryopreservation: Cryopreservation allows the long-term storage of embryos, eggs, or sperm for future use. This technique is particularly beneficial for patients who produce excess embryos during IVF or wish to preserve their fertility for medical reasons.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT): PGT involves the genetic screening of embryos for inherited genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities. This technique helps identify healthy embryos for transfer, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy and reducing the risk of genetic diseases.
Career Opportunities in Clinical Embryology
The field of clinical embryology offers exciting career opportunities for individuals passionate about reproductive medicine and genetics. Graduates of embryology programs can pursue various paths, including:
Clinical Embryologist: Working in fertility clinics, embryologists perform procedures such as IVF, ICSI, and embryo culture. They are responsible for assessing and selecting the best embryos for transfer.
Research Scientist: Embryologists can contribute to scientific advancements in reproductive biology by conducting research studies on embryo development, genetic manipulation, and stem cell research.
Laboratory Director: With experience and additional training, embryologists can become laboratory directors, overseeing the daily operations of reproductive medicine laboratories.
Educator: Experienced embryologists can choose to teach at universities, training the next generation of embryologists and researchers.
Conclusion
Clinical embryology is a captivating field that combines reproductive medicine, genetics, and laboratory techniques to help couples overcome infertility and achieve their dream of parenthood. Embryologist training, such as the programs offered by SEART, equips aspiring professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in this specialized field. With continuous advancements in reproductive technologies, the demand for skilled clinical embryologists is likely to grow, offering rewarding career opportunities and the chance to make a meaningful impact on people's lives.
#clinical embryology#embryologist training#SEART#reproductivemedicine#fertilitytreatment#IVF#genetictesting#embryoculture#cryopreservation#PGT#assistedreproduction#infertility#reproductivebiology#researchscientist#laboratorydirector#stemcellresearch#parenthood#careeropportunities#reproductivehealth
0 notes
Photo

Join in to Hear - Dr. Durga Vytla ( MBBS, DGO, Fellowship in #ReproductiveMedicine ) Live Discussion on Diagnosis & Various Treatments available for #Infertility.
Date: 06-August-2019
Only on #TNews @ 3:30 PM
For more details Visit: https://hegdefertility.com/
Or Cal us on 8880 74 74 74
#HegdeFertility Fertility HegdeHospital InfertilityproblemsInfertilityTreatment IUI IVF Pregnancy#Tnews#Infertility#reproductivemedicine
0 notes