#modernity
Text
Reject modernity.
Embrace tradition.

#groosthetic#weirdcore#scenecore#nostalgiacore#aesthetic#early 2000s#2000s#2000s nostalgia#religion#modernity#rejection
447 notes
·
View notes
Text
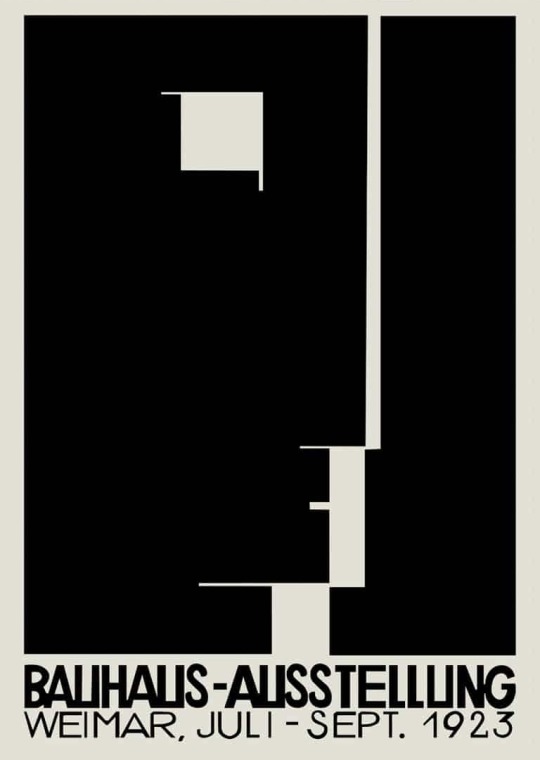
Herbert Bayer Poster Bauhaus Exhibition Weimar July - Sept 1923
#bauhaus poster#bauhaus#bauhaus movement#design#architecture#art#bauhaus masters#le corbusier#ludwig mies van der rohe#wassily kandinsky#walter gropius#bauhaus women#style#modernart#modernity
171 notes
·
View notes
Text
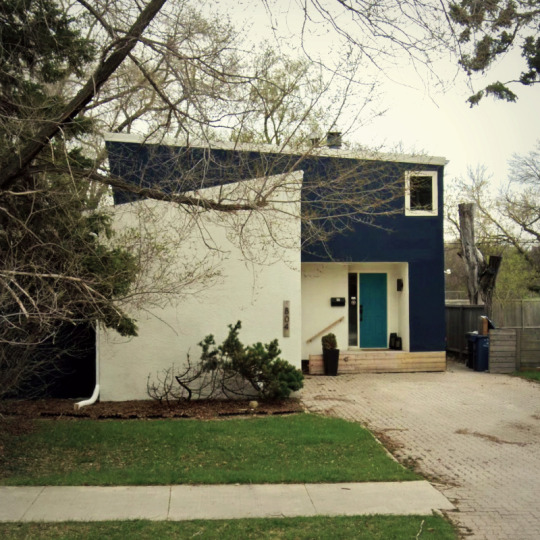

Walls / Holly Avenue, Winnipeg, Manitoba.
228 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lately, I've been reading about Sumer, Egypt, Assyria, Asia, Greece, and various early human civilizations. In the past, the general notion of 'religion' once entwined art, science, and ethics. That is to say that religion has, by and large, been a quasi-unifying way of viewing nature as one dynamic, connected thing.
Modernity seems to have abstractly tried to separate these ideas and isolate them into their own realms, as if they exist independently of one another.
This is kind of ironic. Because today we know from both physics and plain observation that ideas and things are interconnected. Denying this is absurd.
Knowledge itself, like great art and science, is often forged through great adversity. This is counter-intuitively good. One can get an understanding of a culture from how its inhabitants view both its ancestors and the hard-earned knowledge that's been passed down from generation to generation. Or, failing that, inquiring about where, exactly, it gets its knowledge from.
And physical and spiritual traits tend to be entwined, too (medical issues aside). One tends to accompany the other. For example, traits at a spiritual and metaphysical level get reflected at the object level. Thus, we can observe that the morals or values of a culture are sometimes reflected in the outward appearances, behaviors, and artistic creations of the people. Many of these principles are surprisingly generalizable.
A culture is the sum of this and more. Categories of things like these can reveal how a culture organizes itself. How it reproduces itself—not just sexually but memetically. It's customs and practices. How it records itself, thinks of itself, and artistically expresses itself. And what it permits and forbids.
Religion is like culture. And culture is almost indistinguishable from religion.
The main difference, I think, is that religion is encompassing in the sense that it has functionally served as a container for science, art, and itself for much of history.
In this way, religion is like an overarching organic structure that has served various functions in structuring ideas as well as social order.
Furthermore, every culture and subculture is a sort of quasi-religion, even if it doesn't explicitly identify as one.
Some claim that we have transcended religion, that we have eclipsed the past, and that we have left even our primitive shadows behind. But I don't think this is true at all.
It's religion all the way down. We still worship; we still play primal games; and we still play with fire and blood, albeit in different ways. It's just today that we're a primitive culture of Simians with computers. Some might say we are savage robots.
Others assert we are more highly evolved and know more today than ever before. And maybe, in some ways, we do know more. But in some other ways, it seems we have forgotten many of the obvious things that we once knew.
*This post is not a claim that religion is intrinsically good. It's an observation that religion is organic—and that in the spirit of functionalism, it served a purpose—that it was once (and still is, to some extent) a container for many things. But knowledge, science, ethics, and so on are collectively dynamic and evolving things. And we can all agree that nobody would want to live in a universe where people are put to death for wearing the wrong clothes or some other frivolous triviality. To say that humanity was completely better off at some point in the ancient past is blasphemy against human progress.
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Adulthood is just trying to find the correct balance of legal and illegal substances to be productive while dulling the senses enough you that don’t have to think about the monotony and isolation of daily life.
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's a big mess of hubris; the manipulative use of scientific language to legitimate/validate the status quo; Victorian/Gilded Age notions of resource extraction; the "rightness" of "land improvement"; and the inevitability of empire.

This was published in the United States one year before the massacre at Wounded Knee.
This was the final year-ish of the so-called "Indian Wars" when the US was "completing" its colonization of western North America; at the beginning of the Gilded Age and the zenith of power for industrial/corporate monopolies; when Britain, France, and the US were pursuing ambitious mega-projects across the planet like giant canals and dams; just as the US was about to begin its imperial occupations in Central America and Pacific islands; during the height of the "Scramble for Africa" when European powers were carving up that continent; with the British Empire at the ultimate peak of its power, after the Crown had taken direct control of India; in the years leading up to mass labor organizing and the industrialization of war precipitating the mass death of the two world wars.
This was also the time when new academic disciplines were formally professionalized (geology; anthropology; archaeology; ecology).
Classic example of Victorian-era (and emerging modernist and twentieth-century) imperial hubris which implies justification for its social hierarchies built on resource extraction and dispossession by invoking both emerging technical engineering prowess (trains, telegraphs, electricity) and the in-vogue scientific theories widely popularized at the time (Lyell's work, dinosaurs, and the geology discipline granting new understanding of the grand scale of deep time; Darwin's work and ideas of biological evolution; birth of anthropology as an academic discipline promoting the idea of "natural" linear progression from "savagery" to imperial civilization; the technical "efficiency" of monoculture/plantations; emerging systems ecology and new ideas of biogeographical regions).
While also simultaneously doing the work to, by implication, absolve them of ethical complicity/responsibility for the cruelty of their institutions by naturalizing those institutions (excusing the violence of wealth disparities, poverty, crowded factory laboring conditions, mass imprisonment, copper mines, South Asian famine, the industrialization of war eventually manifesting in the Great War, etc.) by claiming that "commerce is a science"; "pursuit of profit is Natural"; "empire is inevitable".
This tendency to invoke science as justification for imperial hegemony, whether in Britain in the 1880s or the United States in the 1920s and such, might be a continuation of earlier European ventures from the sixteenth to eighteenth centuries which included the use of cartography, surveying/geography, Linnaean taxonomy, botany, and natural history to map colonies/botanical resources and build/justify plantations and commercial empires in the Portuguese slave ports, Dutch East Indies, or the Spanish Americas.
Some of the issues at play:
-- Commerce is "A Science". Commerce is shown to be both an ecological system (by illustrating it as if it were a landscape, which is kinda technically true) and a physiological system (by equating infrastructure/extraction networks with veins) suggesting wealth accumulation is Natural.
-- If commerce/capitalism are Natural, then evolutionary theory and linear histories suggest it is also Inevitable (it was not mass violence of a privileged few humans who spent centuries beating the Earth into submission to impose the Victorian/Gilded Age state of things, it was in fact simply a natural evolutionary progression). And if wealth accumulation is Natural, then it is only Right to pursue "land improvement".
-- US/European hubris. They can claim to perceive the planet in its apparent totality (as a globe, within the bounds of extraterrestrial space as if it were a laboratory or plantation). The planet and all its lifeforms are an extension of their body, implying a justified dominion.
-- However, their anxiety and suspicions about the stability of empire are belied by their fear of collapse and the simultaneous US/European obsession at the time with ancient civilizations, the "fall of Rome", classical ruins, etc. At this time, the professionalization of the field of archaeology had helped popularize images and stories of Sumer, Egypt, the Bronze Age, the Aegean, Rome, etc. And there was what Ann Stoler has called an "imperialist nostalgia" and a fascination with ancient ruins, as if Britain/US were heirs to the legacy of Athens and Rome. You can see elements of this in the turn of the century popularity of Theosophy/spiritualism, or the 1920s revival of "classical" fashions. This historicism also popularized a sort of "linear narrative" of history/empires, reinforced by simultaneous professionalization of anthropology, which insinuated that humans advance from a "primitive" state towards modernity's empires.
-- Meanwhile, from the first decades of the nineteenth century when Megalosaurus and Iguanodon helped to popularize fascination with dinosaurs, Georgian and later Victorian Britain became familiar with deep time and extinction, which probably contributed to British anxiety about extinction, imperial collapse, lastness, and death.
-- Simultaneously, the massive expansion of printed periodicals allowed for sensationalist narrativizing of science.
-- The masking of the cruelty in a euphemism like "land improvement". Like sentencing someone to a de facto slow death and deprivation in a prison but calling it a "sanatorium" or "reformatory". Or calling the mass amounts of poor, disabled, women, etc. underclasses of London "unfortunates". Whether it's Victorian Britain or early twentieth century United States: "Our empire is doing this for the betterment and advancement of all mankind."
-- If an ecosystem is conceived as a machine, "land improvement" actually means monoculture, high-density production, resource extraction, concentration.
-- The image depicts the body is itself is also a mere machine (dehumanization, etc.). And if human bodies are shown to be also systems, networks, machines like an ecosystem, then human bodies can also be concentrated for efficiency and productivity (literal concentration camps, prisons, factories, company towns, slums, dosshouses, etc.). This is the thinking that reduces humans and other creatures to objects, resources, to be concentrated and converted into wealth.
And so after the rise of railroads and coal-power and industrial factories in the earlier nineteenth century, the fin de siecle and Edwardian era then saw the expansion of domestic electricity, easier photography, telephones, radio, and automobiles. But you also witness the spread of mass imprisonment, warplanes, and machine guns, etc. And in the midst of this, the Victorian/Gilded Age also saw the rise of magazines, newspapers, mass media, pop-sci stuff, etc. So this wider array of published material, including visual stuff like maps and infographics could "win over" popular perception. This is nearly a century after the Haitian Revolution, so more and more people would have been able to witness and call out the contradictions and hypocrisies of these "civilized" nations, so scientific validation was important to empire's public image. (Think: 100 years prior, everyone witnessed widespread revolutions and slave rebellions, but now the European empires are still using indentured labor, expanding prisons, and growing even more powerful in Africa, etc. An outrage.)
Illustrations like this ...
It's people with power (or people with a vested interest in these institutions, people who aspire to climbing the social ladder, people who defend the status quo) looking around at the general state of things, observing all of the cruelty and precarity, and then using scientific discourses to concede and say "this was inevitable, this was natural" and not only that, but also "and this is good".
Related reading:
Peoples on Parade: Exhibitions, Empire, and Anthropology in Nineteenth-Century Britain (Sadiah Qureshi, 2011); The Earth on Show: Fossils and the Poetics of Popular Science, 1802-1856 (Ralph O’Connor); "Science in the Nursery: the popularisation of science in Britain and France, 1761-1901" (Laurence Talairach-Vielmas, 2011); Citizens and Rulers of the World: The American Child and the Cartographic Pedagogies of Empire (Mashid Mayar); "Viewing Plantations at the Intersection of Political Ecologies and Multiple Space-Times" (Irene Peano, Marta Macedo, and Collette Le Petitcrops); “Paradise Discourse, Imperialism, and Globalization: Exploiting Eden" (Sharae Deckard); "Forgotten Paths of Empire: Ecology, Disease, and Commerce in the Making of Liberia's Plantation Economy" (Gregg Mitman, 2017); Imperial Debris: On Ruins and Ruination (Ann Laura Stoler, 2013)
Fairy Tales, Natural History and Victorian Culture (Laurence Talairach-Vielmas, 2014); Mining the Borderlands: Industry, Capital, and the Emergence of Engineers in the Southwest Territories, 1855-1910 (Sarah E.M. Grossman, 2018); Pasteur’s Empire: Bacteriology and Politics in France, Its Colonies, and the World (Aro Velmet, 2022); "Shaping the beast: the nineteenth-century poetics of palaeontology" (Talairach-Vielmas, 2013); In the Museum of Man: Race, Anthropology, and Empire in France, 1850-1960 (Alice Conklin, 2013); Inscriptions of Nature: Geology and the Naturalization of Antiquity (Pratik Chakrabarti, 2020)
90 notes
·
View notes
Photo






Pink, or Pink? ¤·♀️ A Soft Symphony of Contemporary Fashion
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
What I am proposing, essentially, is that we engage in a kind of thought experiment. What if, as a recent title put it, “we have never been modern”? What if there never was any fundamental break, and therefore, we are not living in a fundamentally different moral, social, or political universe than the Piaroa or Tiv or rural Malagasy?
There are a million different ways to define “modernity.” According to some it mainly has to do with science and technology, for others it’s a matter of individualism; others, capitalism, or bureaucratic rationality, or alienation, or an ideal of freedom of one sort or another. However they define it, almost everyone agrees that at somewhere in the sixteenth, or seventeenth, or eighteenth centuries, a Great Transformation occurred, that it occurred in Western Europe and its settler colonies, and that because of it, we became “modern.” And that once we did, we became a fundamentally different sort of creature than anything that had come before.
But what if we kicked this whole apparatus away? What if we blew up the wall? What if we accepted that the people who Columbus or Vasco da Gama “discovered” on their expeditions were just us? Or certainly, just as much “us” as Columbus and Vasco da Gama ever were?
I’m not arguing that nothing important has changed over the last five hundred years, any more than I’m arguing that cultural differences are unimportant. In one sense everyone, every community, every individual for that matter, lives in their own unique universe. By “blowing up walls,” I mean most of all, blowing up the arrogant, unreflecting assumptions which tell us we have nothing in common with 98% of people who ever lived, so we don’t really have to think about them. Since, after all, if you assume the fundamental break, the only theoretical question you can ask is some variation on “what makes us so special?” Once we get rid of those assumptions, decide to at least entertain the notion we aren’t quite so special as we might like to think, we can also begin to think about what really has changed and what hasn’t.
Fragments of an Anarchist Anthropology, by David Graeber
#david graeber#anarchism#social science#anthropology#history#world history#politics#quote#quotes#books#book quotes#colonialism#capitalism#modernity
68 notes
·
View notes
Photo
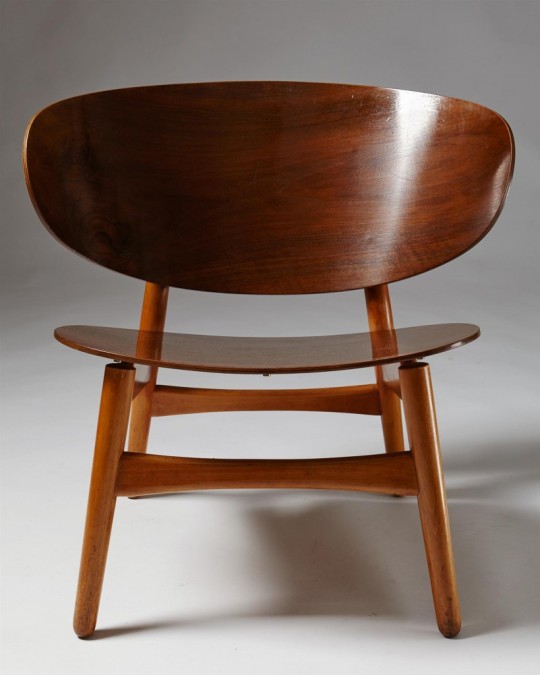




Shell chairs model FH-1936, Denmark. 1948,
Designed by Hans Wegner for Fritz Hansen,
Walnut veneered plywood and beech legs.
H: 70 cm/ 27 1/2''
W: 70 cm/ 27 1/2''
D: 64 cm/ 25 1/4''
Courtesy: Modernity
#art#design#furniture#seat#chair#shell#denmark#1948#hans wegner#fritz hansen#walnut#mid century modern#modernity#plywood#beech
170 notes
·
View notes
Note
What are your thoughts on how many anarcho-primitivist/luddite/anticiv spaces have been taken over by right-wing types? It seems less people are actually engaging in primitivist thought and more so thinking it's "based" and "trad."
I saw how you got downvoted for insulting whatalthist, and this is what led me to ask this question.
I'm assuming you're referring to online spaces. There's a strong effort by the right to co-opt primitivism. There are some forums that are frequented by right-wingers, though they're in the minority; most problematic spaces are the ones about Kaczynski and things directly related to him. There are also many social media accounts that express primitivistic ideas in combination with authoritarian and rightist politics (e.g. individuals who adore both Ted Kaczynski and Pentti Linkola). Most concerning to me are actually the offline examples that get press coverage.
I see this as being both due to deliberate efforts to co-opt primitivism, much in the manner Nazis co-opted socialism, and due to ignorance on the part of many right-wingers. It isn't too hard to misinterpret Kaczynski's remarks about leftism if you read him inattentively, and conclude that he must be some sort of right-winger. Ted's mistake was focusing on attacking the left too much and worrying too little about the right, but at the time he wrote his manifesto this choice made sense.
Ted was a fan of Earth First! and when he wrote Industrial Society and its Future the wounds of an ideological split within it were still fresh. EF! started out as a truly ecocentric movement with extremely narrow goals of protecting the wilderness from the ravages of industrialism and other harm caused by civilized humans. After gaining a lot of momentum, EF! attracted thousands of newcomers, many of whom leaned more to the side of leftist humanism than deep ecology, causing conflict — the newcomers were trying to transform the movement into one about ecology-related social justice issues, while the original Earth First!ers preferred to only focus on wilderness conservation. (For more on this check out Earth First!: Environmental Apocalypse by Martha F. Lee). The right-wing in America at the time was comprised mostly of people who were staunch prometheans, warmongers, etc., and Ted rightly assumed they weren't going to take over his movement. However as the political climate changed they became one.
The US and the rest of the "West" seems to be experiencing a rise in right-wing back-to-nature ideas, similar in many ways to the so-called "right-wing hippies" of the Weimar republic. I'm talking about doomsday preppers, christian nationalist communes, etc. Kaczynski did not anticipate this, and by the time news about who was adopting (some of) his ideas — not just anarchists and former Earth First!ers, but people including the Greek fascist Golden Dawn party, and Andreas Breivik — reached Kaczynski in his supermax prison it was a bit late. He penned a short note titled Ecofascism: An Aberrant Branch of Leftism in 2020, arguing against their ideas and saying he's their enemy. However, more people read and will read ISAIF in the future than this obscure note and the few other scattered critiques of the right that can be found throughout his work.
What we need to do is to aggressively shun these types until we successfully repel them. This applies to real life and online interactions. There will always be some who'll try to co-opt primitivism, but this big wave needs to be halted. There are also some who are genuinely willing to learn and adjust their beliefs, but they're few in between. It's necessary to distinguish between the two, keep the latter and reject the former.
#anarcho primitivism#anti civ#anarchy#green anarchy#anprim#anticiv#anprimgang#luddism#deep ecology#luddite#theodore kaczynski#ted kaczynski#anti state#modernity#unabomber#environment and nature#environment#earth liberation#earth first!#earth love#primal anarchy#anarcho primitivist#primitivism#ecocentrism#eco anarchism#anti tech
51 notes
·
View notes
Quote
It is a mistake to think that because some aspects of modern technology are useful, we therefore need or should prefer all aspects of modernity. Development need not and should not be universally high-tech; if a given modern complex technology is worth keeping, that does not mean all other modern high technologies are (especially on a mass scale). In other words, MRI machines and wind turbines do not require ICBMs and F-350s. Agriculture can mix low-tech agroecological methods with electric tools. Architecture can mix low-tech, energy-efficient design with solar panels. Transportation can mix walking and biking with high-speed rail and electric buses.
Matthew J. Haugen, What Is to Be Grown?
470 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bauhaus Masters' Houses. The semi-detached house, built by Walter Gropius in Dessau in 1926, has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1996. The ensemble of the Masters' Houses is an outstanding architectural achievement of the Bauhaus.
3D modelling, texturing, illumination, postproduction and editing by Sarah Möllenbrok | lichtecht. Music "Serenity" by Dreamsfall.
#bauhaus#bauhaus movement#bauhaus masters#le corbusier#ludwig mies van der rohe#wassily kandinsky#design#modernity#less is more#walter gropius
182 notes
·
View notes
Text
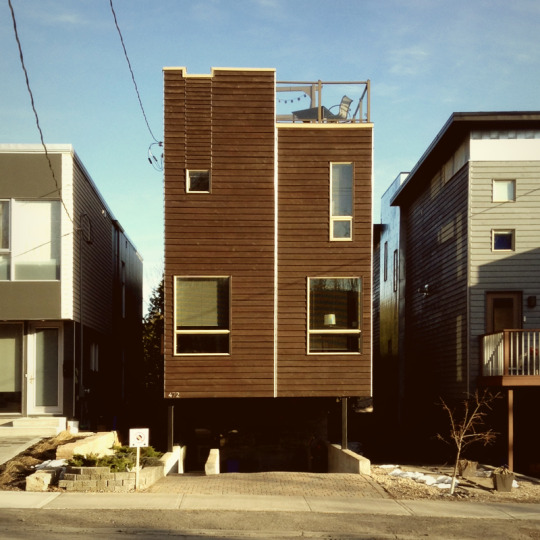

Walls / Sunnyside Avenue, Ottawa, Ontario.
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
Watkins: design and domesticity
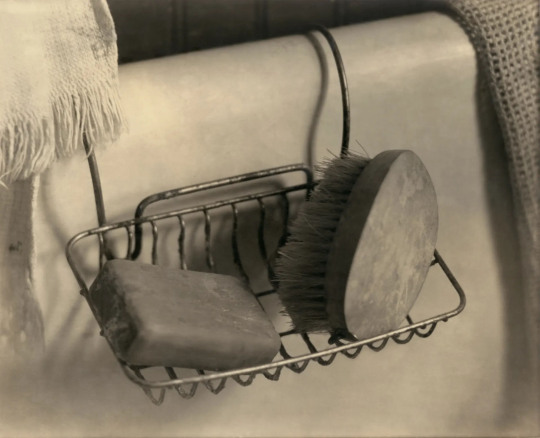

Margaret Watkins (1884-1969) ~ Still Life – Bathtub, New York, 1919 | src The Revolutionary Gaze at The Guardian
View more on WordPress
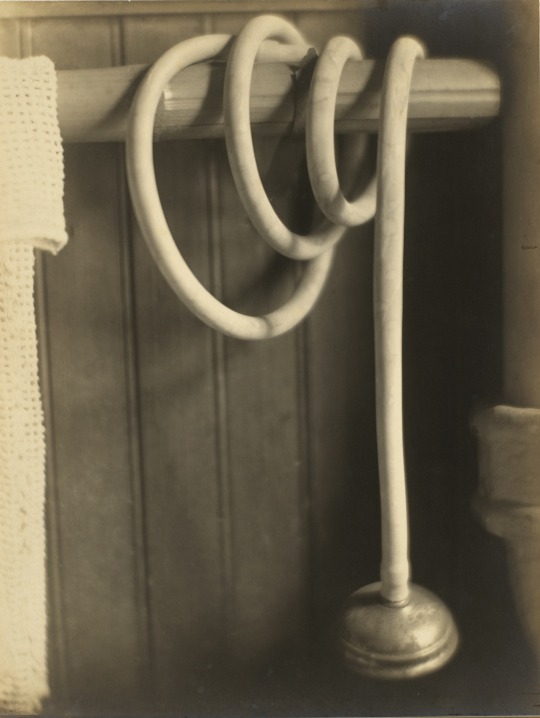

Margaret Watkins (1884-1969) ~ Still Life – Shower Hose (1919); gelatin silver print. | src National Gallery of Canada
also, view this post on wordPress
#Margaret Watkins#design#domestic scene#domestic scenes#Domestic Symphonies#modernism#modernity#still life#Stillleben#nature morte#naturaleza muerta#natura morta#1920s#1910s#tradition#women artists#women photographers#bathtub#bathroom
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
Whitewash is extremely moral. Suppose there were a decree requiring all rooms in Paris to be given a coat of whitewash. I maintain that that would be a police task of real stature and a manifestation of high morality, the sign of a great people. -- Le Corbusier
A shocking call for compulsory whitening is made at the end of a key modernist manifesto. The pronouncement is associated with the signature whiteness of modern architecture -- an aesthetic regime that was presented as a complete revolution of the built environment in the 1920s and became the unconscious default setting of everyday life. Just look at the predominantly white background of most of the kitchens, offices, living rooms, bedrooms and bathrooms around the world [...]. Le Corbusier didn’t simply call for whitewash to be imposed by the police in the name of health. It was meant to act as a form of policing in its own right, a technology of surveillance that would put in motion an ever-expanding culture of self-policing. Whitewash exposes every dimension of life in front of it to judgement. It acts like “a court of assize in permanent session” that will “give a power of judgement to the individual,” and thereby “make each one of us a prudent judge.” [...] A “Law of Ripolin” -- the brand name of the hard impermeable and washable enamel “sanitary paint” invented at the end of the nineteenth century [...] is needed to ensure that all interiors are painted white to target any form of dirt or darkness:
Imagine the results of the Law of Ripolin. Every citizen is required to replace his hangings, his damasks, his wall-papers, his stencils, with a plain coat of white ripolin. His home is made clean. There are no more dirty, dark corners. Everything is shown as it is. Then comes inner cleanness [...]. When you are surrounded with shadows and dark corners you are at home only as far as the hazy edges of the darkness your eyes cannot penetrate. You are not master in your own house. Once you have put ripolin on your walls you will be master of yourself. [...]
---
Whiteness manufactures health, morality, and intelligence. [...] The office of a modern factory that is “clear and rectilinear and painted with white ripolin” is a place of “healthy activity” and “industrious optimism.” [...] Le Corbusier’s routinely authoritarian and often explicitly eugenic and fascist impulses, associations, and actions make him an easy target. But there are endless, quieter, ultimately more controlling and insidious celebrations of whiteness in other hands. Le Corbusier is but a tip of the vast iceberg of whiteness. [...]
The very idea of an interior is the effect of this everyday violence. Architecture is never simply complicit with authority. Authority without architecture might not even be thinkable. [...]
There is no apolitical concept of health; no natural body or brain waiting to be cared for or abandoned by medicine and architecture that is not already an effect of those biopolitical regimes.
It is through the question of sickness that architecture reshapes the human. The idea of a healthy architecture is always about the health of a small group relative to multiple others [...]. Whiteness is coded as a fragility requiring protection through continual acts of preemptive violence. Whiteness is not a thing but a defense and deployment of power over others. [...]
---
Whiteness in Le Corbusier’s The Decorative Art of Today, for example, is simultaneously the most modern thing to do, the very symptom of modernity, and the most ancient of gestures. [...] Le Corbusier’s argument was first published in a late 1923 issue of L’Esprit Nouveau [...]. It was, after all, the extended “Voyage d’Orient” of 1911 (including the Balkans and Greece, but especially Turkey) where Charles-Édouard Jeanneret, the young architect from a small mountain town in Switzerland who would a decade later rename himself “Le Corbusier,” became “besotted with white” and convinced that the future of architecture was white. Whiteness is discovered in the lands of the non-white; of those seen to be closer to deeper human history and therefore to be admired and learned from. In fact, the very point of going to the East was to encounter its “great white walls” as an antidote to the self-absorbed decadence of architecture in the North, as Jeanneret explained [...]. Jeanneret expresses nostalgia for the more intact and mesmerizing whiteness of the great mosques and vernacular houses of Constantinople (Istanbul) [...] [and] “Algiers-the-white.” [...] This pervasive sense of contamination provoked the call for a second, more explicit law to impose whiteness not only onto industrial culture, but also onto its victims: the people of color and places seen as newly “unhealthy” -- requiring, as it were, a dose of “their” own medicine. [...]
---
The “white” architecture of the 1920s drew on countless experiments in whitening buildings in the name of health. This included, precisely, the use of Ripolin that had already become standard in clinics, hospital wards, and sanatoria rooms at the turn of the century.
In 1899, for example, the Touring-Club de France, inspired by one of its [...] cyclist members who was a doctor, started a campaign for an easily disinfected “hygienic room” in hotels that would be Ripolin-lined [...]. Hotel rooms were treated as hotspots for contagion [...]. Given the largely upper-middle-class membership of the club, this anxiety about disease was also class anxiety, fear of the unclean other. The tourist was to be mobile yet isolated by a prophylactic whiteness that would itself travel in advance.
The Touring-Club exhibited such a prototype “white room” with toilette and toilet spaces designed by Gustave Rives at the 1900 Exposition Universelle in Paris -- strategically placed just inside the entrance of the Palais de l’hygiène [...]. The Touring-Club installed a series of such model chambres hygiéniques in automobile shows, congresses on tuberculosis, and international fairs. It was successful in persuading thousands of hotels to install such spaces [...].
Ripolin was used “everywhere,” for example, on the walls of the “hygienic housing” project for workers in Paris by Henri Sauvage and Charles Sarazin in 1903–1904. [...] The project was originally intended to feature a radical all-glass street façade with every window surrounded by webs of floor-to-ceiling hexagonal glass blocks [...] which would have been the most polemical housing structure possible, the most therapeutic role of glass, more extreme even than any sanatorium. The design was produced in immediate response to the new public health law of 1902 and the associated new building regulations. [...]
---
It is always about control of the threatening other of epidemic disease and control of the laboring poor, itself coded as dark, migrant, and contagious, a disease in its own right. And throughout this discourse of control, there is a seemingly “modern” disdain for disease-incubating ornament in favor of smooth white surfaces. [...] What is remarkable in the end is this trans-historical resilience of whiteness [...]. It orchestrates life and death.
---
Text by: Mark Wigley. “Chronic Whiteness.” e-flux (Sick Architecture series). November 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me.]
230 notes
·
View notes
Text
me as a child: I was born in the wrong era 🙄
me now: I get to look at pictures of mushrooms and moss on the internet whenever I want
#Mushroom#Mushrooms#Cottagecore#Moss#Cozy#Cozycore#Comfort#Comfortcore#Nostalgia#Fairy#Fairycore#Far#Era#History#Eras#Time travel#Modernity#Text post#The internet
104 notes
·
View notes