#mckinleyi
Text

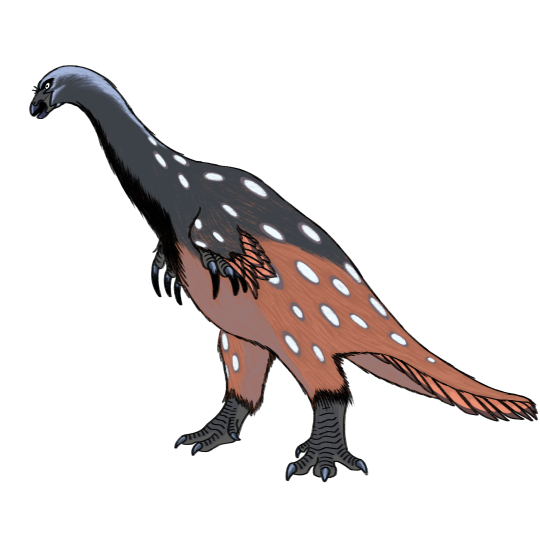
nothronychus mckinleyi - therizinosaurid - late cretaceous
a Very tall lady with some Quite impressive talons- i dont doubt the upkeep is a hassle! a study in this specific species of nothronychus (one of two, the other being n. graffami) and other therizinosaurs showed the family had very well developed senses useful for foraging! another future re-examination of n. mckinleyi's braincase in particular suggested an inclination to hearing low frequency sounds, meaning nothronychus likely had complex social behaviors- possibly even comparable to today's elephants!
higher resolution version under the cut!

#paleoart#paleoblr#therizinosaurid#nothronychus#she gets a cool outline to make up for lack of sparkles/accents <3#potentially unrealistic design but whatever. shes pretty and thats what matters <3#also i learned about hyperlinks. r u proud of me#hehe#5/20/23#dinosaur
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nothronychus mckinleyi, discovered in a part of the U.S. that was once thought to be part of the Western Interior Seaway. However, Nothronychus is obviously a terrestrial animal, and its bones were probably around 100 kilometers from what would’ve been the shoreline back then.

With Hatsune Miku for scale:

12 notes
·
View notes
Text
June Book Reviews: The Outlaws of Sherwood by Robin McKinley

I was reminded of the existence of this book by the wonderful @oldshrewsburyian and I thought it was time for a reread. This is the Robin Hood retelling about a man who really doesn’t want to be a protagonist but gets dragged into it kicking and screaming. This Robin is a competent, sensible man who is actually mildly terrible at archery, which is why all his stunts are done by Maid Marian. Robin has the feel of a character who’s been imported from a much grittier genre, especially compared to everyone else happily swashbuckling.
McKinley writes this book lighter on the romance than her usual-- Marian and Robin are essentially presented as an established couple with some minor communication issues to conquer. There’s a romance arc with secondary characters Little John and [redacted], but that’s more of a sideplot. In order to introduce the romance sideplot, McKinley switches halfway through to different character POVs, which in my opinion does the book’s structure no favors.
In the end, Robin’s genre wins out, and the book ends with the swashbuckling antics over and Richard the Lionheart home again. Ultimately, this is a book that stands out from the horde of Robin Hood books by virtue of its protagonist. If you don’t like the sensible Robin AU concept, you may not like the book.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nothronychus: Garra Perezosa
Es un género representado por dos especies de dinosaurios terópodos tericinosáuridos, que vivieron a finales del período Cretácico, hace aproximadamente entre 92 a 91 millones de años, en el Turoniense, en lo que hoy es Norteamérica. Nothronychus mckinleyi fue encontrado por James Ian Kirkland y Douglas G. Wolfe en 2001 en Nuevo México, Estados Unidos, cerca de la frontera con Arizona, en un área conocida como cuenca Zuni.
Nothronychus vivió hace 90 millones de años, durante finales del período cretáceo en la era mesozoica, en los bosques cenagosos similares a los pantanos modernos en Luisiana. La Era Mesozoica era un período de calentamiento extremo del planeta, con los niveles del océano más altos que los actuales en unos 300 metros, dejando una cantidad perceptiblemente menor de tierra firme. Se han encontrado muy pocos fósiles de dinosaurio en los sedimentos de este tiempo, particularmente en Norteamérica, haciendo este y los descubrimientos asociados muy importantes. El Nothronychus convivió con otros dinosaurios, el ceratopsio Zuniceratops y algunos terópodos pequeños, así lo indican algunos fragmentos y esqueletos parciales
1 note
·
View note
Text
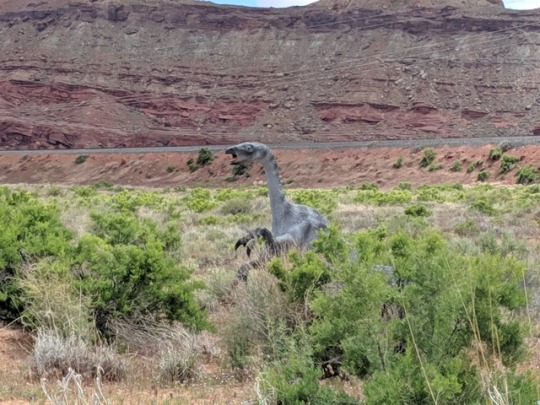

I swear, I left the car right here!
0 notes
Text
Erlikosaurus andrewsi

By Ripley Cook
Etymology: Demon-King Reptile
First Described By: Perle, 1980
Classification: Dinosauromorpha, Dinosauriformes, Dracohors, Dinosauria, Saurischia, Eusaurischia, Theropoda, Neotheropoda, Averostra, Tetanurae, Orionides, Avetheropoda, Coelurosauria, Tyrannoraptora, Maniraptoromorpha, Maniraptoriformes, Maniraptora, Therizinosauria, THerizinosauridea, Therizinosauridae
Status: Extinct
Time and Place: About 90 million years ago, in the Turonian of the Late Cretaceous
Erlikosaurus is found in the Bayan Shireh Formation in Dornogovi, Mongolia

Physical Description: Erlikosaurus was a kind of Therizinosaur, the very bulky feathered dinosaurs with long, pointed claws extending from their hands. They’re weird in other ways, too - they have backward-facing hip bones like those of birds and Ornithischians, and giant pot-bellies to let them digest large amounts of plant material. As such, they stood up almost as vertical as people do - rather than horizontally like… all other dinosaurs. Erlikosaurus had a long neck, a squat body, short legs and a short tail; while its arms were normal length, it also had very long curved claws, like other therizinosaurs. It had very large and long nostrils for a therizinosaur, and a very high number of teeth compared to its relatives. Interestingly enough, therizinosaurs like Erlikosaurus also had swollen, pneumatized braincases, which allowed them to be lighter weight and potentially cool off quicker. Erlikosaurus also, unlike other Therizinosaurs, ahd long and slender claws on its feet. It may have been around six meters long. Like other therizinosaurs, it would have been covered with feathers all over its body, and potentially had very primitive long feathers on its arms like wings.
Diet: Erlikosaurus, like other therizinosaurs, was an herbivore.
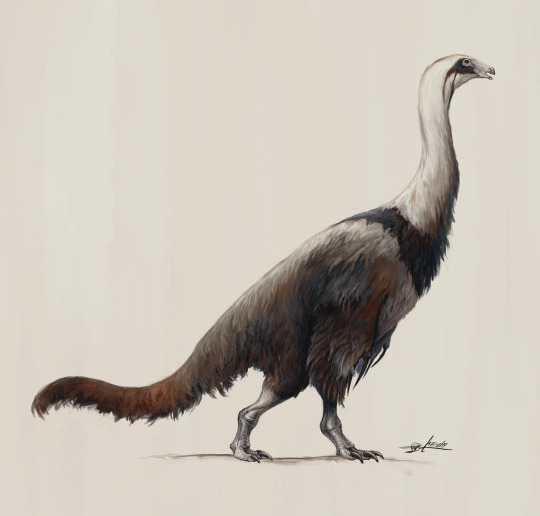

By Jack Wood
Behavior: Erlikosaurus is a fascinating dinosaur behavior-wise because we actually have a decent number of scans of its brain, which may teach us aspects of its behavior. Erlikosaurus had a very well developed sense of smell, hearing, and balanced, which means that it retained a lot of the traits of carnivorous theropods - and probably used them to its advantage as an herbivore. It also probably was able to sense oncoming predators well and have complex social behavior. The range of its mouth, however, was narrower than that of its close carnivorous relatives - indicating that herbivorous dinosaurs, much like herbivorous mammals, had smaller mouth gapes than carnivores. With complicated social behavior, long claws, and good senses, Erlikosaurus would have been incredibly paranoid - and dangerous - ready to fend off anyone that would have threatened their family groups with those long scythe claws. As a social dinosaur, Erlikosaurus would have probably taken care of its young, and been warm blooded. The scythe claws, when not used in defense, would have been helpful in gathering plants down from the trees, much like with sloths today.
Ecosystem: The Bayan Shireh Environment was one of many such ecosystems found in the mid to late Cretaceous, showcasing a wide variety of animals that were almost - but not quite - like their latest Cretaceous counterparts. Here was a braided river environment, going through season wet and dry seasons as the mud and sand interchanged from one another leading to a variety of rock types and depositional environments. There were many water plants and flowering plants lining the shores, giving it a lush and green feel for at least part of the year - and giving Erlikosaurus something to eat! There were also fish, molluscs, the mammal Tsagandelta, and turtles making frequent appearances in the environment. Unnamed crocodylian relatives and Azhdarchid pterosaurs were present, but most of the charismatic animals present were other dinosaurs. Erlikosaurus wasn’t the only Therizinosaur, and also lived with Segnosaurus and Enigmosaurus. The very large, weird, and lopsided sauropod Erketu graced the treetops, slowly foraging on food, while the much smaller Ornithomimosaur Garudimimus scurried about between them all. Ankylosaurs went absolutely wild here, represented by Talarurus, Maleevus, and Tsagantegia. There were two small bipedal Ceratopsians, Graciliceratops and Microceratus, and the early hadrosauroid Gobihadros. There was also a mystery dinosaur, Amtosaurus, which has no affinity beyond “Ornithischian” at this point in time. As for predators, there was the very large raptor Achillobator and the small tyrannosaur Alectrosaurus - both similar in size to one another, and both giant dangers to the roaming herds of Erlikosaurus!
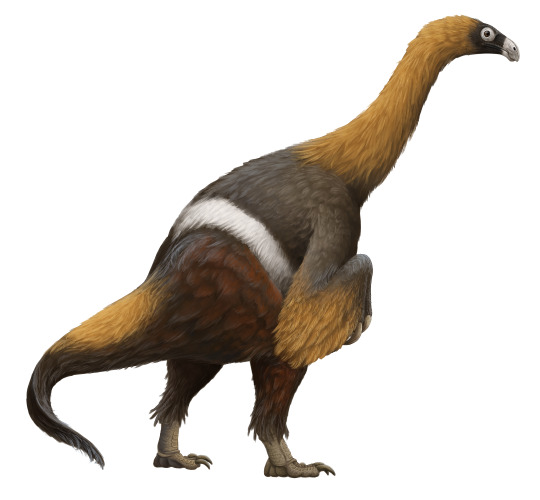

By Scott Reid
Other: Erlikosaurus was a very advanced therizinosaur, similar to later members of the group like Therizinosaurus rather than Early Cretaceous varieties. As such, it shows that the more classic therizinosaur body shape was around by the “mid” Cretaceous. In addition, it may or may not be the same animal as the other therizinosaurs found in its home - more research is needed to determine as such.
~ By Meig Dickson
Sources Under the Cut
Averianov, A. O. 2007. Theropod dinosaurs from Late Cretaceous deposits in the northeastern Aral Sea region, Kazakhstan. Cretaceous Research 28:532-544
Barsbold, R., and A. Perle. 1980. Segnosauria, a new infraorder of carnivorous dinosaurs. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 25(2):187-195
Barsbold, R. 1981. Bezzubyye khishchnyye dinozavry Mongolii [Toothless carnivorous dinosaurs of Mongolia]. Sovmestnaia Sovetsko-Mongol’skaia Paleontologicheskaia Ekspeditsiia Trudy 15:28-39
Barsbold, R. 1983. Khishchnye dinosavry mela Mongoliy [Carnivorous dinosaurs from the Cretaceous of Mongolia]. Transactions of the Joint Soviet-Mongolian Paleontological Expedition 19:1-117
Barsbold, R. 1997. Mongolian dinosaurs. In P. J. Currie & K. Padian (ed.), Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs 447-450
Carroll, R. L. 1988. Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution 1-698
Clark, J. M., T. Maryanska, and R. Barsbold. 2004. Therizinosauroidea. In D. B. Weishampel, P. Dodson, and H. Osmolska (eds.), The Dinosauria (second edition). University of California Press, Berkeley 151-164
Clark, J. M., M. A. Norell, L. M. Chiappe and A. Perle. 1995. The phylogenetic relationships of "segnosaurs" (Theropoda, Therizinosauridae). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 15(3, supl.):24A
Clark, J. M., A. Perle, and M. A. Norell. 1993. The skull of the segnosaurian dinosaur Erlikosaurus. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 13(3, suppl.):30A-31A
Clark, J. M., A. Perle, and M. A. Norell. 1994. The skull of Erlicosaurus andrewsi, a Late Cretaceous "segnosaur" (Theropoda: Therizinosauridae) from Mongolia. American Museum Novitates 3115:1-39
Currie, P. J. 1992. Saurischian dinosaurs of the Late Cretaceous of Asia and North America. In N. J. Mateer, P.-j. Chen (eds.), Aspects of Nonmarine Cretaceous Geology. China Ocean Press, Beijing 237-249
Currie, P. J., and D. A. Eberth. 1993. Palaeontology, sedimentology and palaeoecology of the Iren Dabasu Formation (Upper Cretaceous), Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. Cretaceous Research 14:127-144
Currie, P. J. 2000. Theropods from the Cretaceous of Mongolia. In M. J. Benton, M. A. Shishkin, D. M. Unwin, & E N. Kurichkin (eds.), The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia 434-455
Danilov, I. G. 1999. A new linholmemydid genus (Testudines: Lindholmemydidae) from the mid-Cretaceous of Uzbekistan. Russian Journal of Herpetology 6(1):63-71
Eberth, D. A., P. J. Currie, D. B. Brinkman, M. J. Ryan, D. R. Braman, J. D. Gardner, V. D. Lam, D. N. Spivak, and A. G. Neuman. 2001. Alberta's dinosaurs and other fossil vertebrates: Judith River and Edmonton groups (Campanian-Maastrichtian). In C. L. Hill (ed), Society of Vertebrate Paleontology, 61st Annual Meeting, Bozeman. Guidebook for the Field Trips: Mesozoic and Cenozoic Paleontology in the Western Plains and Rocky Mountains, Museum of the Rockies Occasional Paper 3:49-75
"Erlikosaurus." In: Dodson, Peter & Britt, Brooks & Carpenter, Kenneth & Forster, Catherine A. & Gillette, David D. & Norell, Mark A. & Olshevsky, George & Parrish, J. Michael & Weishampel, David B. The Age of Dinosaurs. Publications International, LTD. p. 142.
Gianechini, F. A., P. J. Makovicky, and S. Apesteguía. 2011. The teeth of the unenlagiine theropod Buitreraptor from the Cretaceous of Patagonia, Argentina, and the unusual dentition of the Gondwanan dromaeosaurids. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 56(2):279-290
Hendrickx, C., and O. Mateus. 2014. Abelisauridae (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Late Jurassic of Portugal and dentition-based phylogeny as a contribution for the indentification of isolated theropod teeth. Zootaxa 3759(1):1-74
Hicks, J.F., Brinkman, D.L., Nichols, D.J., and Watabe, M. (1999). "Paleomagnetic and palynological analyses of Albian to Santonian strata at Bayn Shireh, Burkhant, and Khuren Dukh, eastern Gobi Desert, Mongolia." Cretaceous Research, 20(6): 829-850.
Jerzykiewicz, T. and Russell, D.A. (1991). "Late Mesozoic stratigraphy and vertebrates of the Gobi Basin." Cretaceous Research, 12(4): 345-377.
Kirkland, J. I., D. K. Smith, and D. G. Wolfe. 2005. Holotype braincase of Nothronychus mckinleyi Kirkland and Wolfe 2001 (Theropoda; Therizinosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous (Turonian) of west-central New Mexico. In K. Carpenter (ed.), The Carnivorous Dinosaurs. Indiana University Press, Bloomington 87-96
Lautenschlager, Stephan; Rayfield, Emily J.; Altangerel Perle; Zanno, Lindsay E.; Witmer, Lawrence M. (2012). "The Endocranial Anatomy of Therizinosauria and Its Implications for Sensory and Cognitive Function". PLoS ONE. 7 (12): e52289.
Lautenschlager, Stephan (November 4, 2015). "Estimating cranial musculoskeletal constraints in theropod dinosaurs". Royal Society Open Science. 2 (11): 150495.
Li, D., C. Peng, H. You, M. C. Lamanna, J. D. Harris, K. J. Lacovara, and J. Zhang. 2007. A large therizinosauroid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Early Cretaceous of northwestern China. Acta Geologica Sinica 81(4):539-549
Mader, B. J., and R. L. Bradley. 1989. A redescription and revised diagnosis of the syntypes of the Mongolian tyrannosaur Alectrosaurus olseni. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 9(1):41-55
Makovicky, P. J., and M. A. Norell. 1998. A partial ornithomimid braincase from Ukhaa Tolgod (Upper Cretaceous, Mongolia). American Museum Novitates 3247:1-16
Nessov, L. A. 1995. Dinozavri severnoi Yevrazii: Novye dannye o sostave kompleksov, ekologii i paleobiogeografii [Dinosaurs of northern Eurasia: new data about assemblages, ecology, and paleobiogeography]. Institute for Scientific Research on the Earth's Crust, St. Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg 1-156
Paul, G. S. 1984. The segnosaurian dinosaurs: relics of the prosauropod-ornithischian transition?. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 4(4):507-515
Perle, A. 1977. O pervoy nakhodke Alektrozavra (Tyrannosauridae, Theropoda) iz pozdnego Mela Mongolii [On the first discovery of Alectrosaurus (Tyrannosauridae, Theropoda) in the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia]. Shinzhlekh Ukhaany Akademi Geologiin Khureelen 3(3):104-113
Perle, A. 1981. Noviy segnozavrid iz verchnego mela Mongolii [A new segnosaurid from Mongolia]. Trudy - Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol'skaya Paleontologicheskaya Ekspeditsiya 15:50-59
Pu, H., Y. Kobayashi, J. Lu, Y. Wu, H. Chang, J. Zhang, and S. Jia. 2013. An unusual basal therizinosaur with an ornithischian dental arrangement from northeastern China. PLoS ONE 8(5):e63423
Qian, M.-p., Z.-y. Zhang, Y. Jiang, Y.-g. Jiang, Y.-j. Zhang, R. Chen, and G.-f. Xing. 2012. [Cretaceous therizinosaurs in Zhejiang of eastern China]. Journal of Geology 36(4):337-348
Rauhut, O. W. M. 2003. The interrelationships and evolution of basal theropod dinosaurs. Special Papers in Palaeontology 69:1-213
Russell, D. A. 1997. Therizinosauria. In P. J. Currie & K. Padian (ed.), Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs 729-730
Russell, D. A., and Z.-M. Dong. 1994. The affinities of a new theropod from the Alxa Desert, Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 30(10-11):2107-2127
Senter, P., J. I. Kirkland, and D. D. DeBlieux. 2012. Martharaptor greenriverensis, a new theropod dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah. PLoS ONE 7(8):e43911:1-12
Sereno, P. C. 1998. A rationale for phylogenetic definitions, with application to the higher-level taxonomy of Dinosauria. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen 210(1):41-83
Sues, H.-D. 1997. On Chirostenotes, a Late Cretaceous oviraptorosaur (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from western North America. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 17(4):698-716
Sukhanov, V. B., and P. Narmandakh. 1975. Cherepakhi gruppy Basilemys (Chelonia, Dermatemydidae) v Asiy [New turtles from the Basilemys group (Chelonia, Dermatemydidae) in Asia]. In N. Kramarenko, B. Luwsandansan, Yu. Voronin, R. Barsbold, A. Rozhdestvensky (eds.), Iskopaemaya Fauna I Flora Mongolii [Fossil Flora and Fauna of Mongolia]. Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol'skaya Paleontologicheskaya Ekspeditsiya, Trudy [The Joint Soviet-Mongolian Paleontological Expedition, Transactions] 2:94-101
Tsuihiji, T., M. Watabe, R. Barsbold and K. Tsogtbaatar. 2015. A gigantic caenagnathid oviraptorosaurian (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous of the Gobi Desert, Mongolia. Cretaceous Research 56(1):60-65
Turner, A. H., S. H. Hwang, and M. A. Norell. 2007. A small derived theropod from Öösh, Early Cretaceous, Baykhangor Mongolia. American Museum Novitates 3557:1-27
Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp.
Xu, X., Z.-H. Zhang, P. C. Sereno, X.-J. Zhao, X.-W. Kuang, J. Han, and L. Tan. 2002. A new therizinosauroid (Dinosauria, Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous Iren Dabasu Formation of Nei Mongol. Vertebrata PalAsiatica 40(3):228-240
Varricchio, D. J. 1997. Troodontidae. In P. J. Currie & K. Padian (ed.), Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs 749-754
Zanno, L. 2004. The pectoral girdle and forelimb of a primitive therizinosauroid (Theropoda: Maniraptora): new information on the phylogenetics and evolution of therizinosaurs. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 24(3, suppl.):134A
Zanno, L. E. 2006. The pectoral girdle and forelimb of the primitive therizinosauroid Falcarius utahensis (Theropoda, Maniraptora): analyzing evolutionary trends within Therizinosauroidea. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26(3):636-650
Zanno, Lindsay E. (2010). "A taxonomic and phylogenetic re-evaluation of Therizinosauria (Dinosauria: Maniraptora)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 8 (4): 503–543.
Zhang, X.-H., X. Xu, X.-J. Zhao, P. C. Sereno, X.-W. Kuang and L. Tan. 2001. A long-necked therizinosauroid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Iren Dabasu Formation of Nei Mongol, People's Republic of China. Vertebrata PalAsiatica 39(4):282-290
#erlikosaurus#erlikosaurus andrewsi#dinosaur#therizinosaur#feathered dinosaurs#factfile#palaeoblr#feathered dinosaur#maniraptoran#Cretaceous#Eurasia#Herbivore#Theropod Thursday#paleontology#prehistory#prehistoric life#dinosaurs#biology#a dinosaur a day#a-dinosaur-a-day#dinosaur of the day#dinosaur-of-the-day#science#nature
324 notes
·
View notes
Text
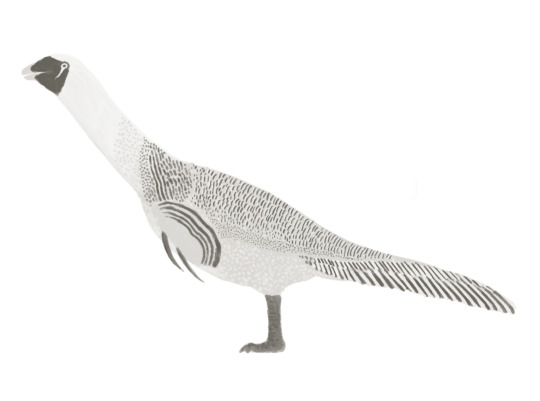
Impressions on Nothronychus mckinleyi and Nothronychus graffami


0 notes