#lewisuchus
Text

Last week I mentioned the one oddball dinosauriform that had crocodilian-like osteoderm armor, so let's take a look at that one too.
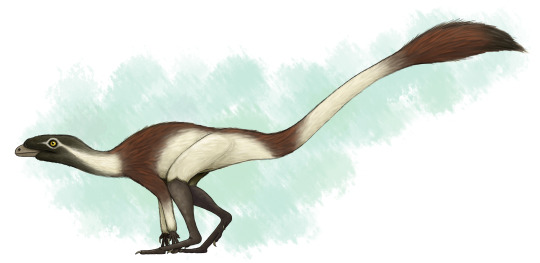
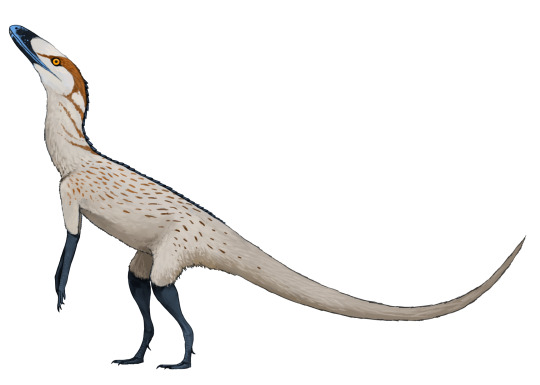
Lewisuchus admixtus lived in what is now northwest Argentina during the late Triassic, around 236-234 million years ago. About 1m long (3'3"), it was an early member of the silesaurids – a group of dinosauriforms that weren't quite dinosaurs themselves, but were very closely related to the earliest true dinosaurs.
(They've also been proposed as instead being early ornithisichians, but we're not getting into that today.)
Much like its later silesaurid relatives Lewisuchus had a long neck and slender limbs, and was probably mainly quadrupedal, possibly with the ability to briefly run bipedally to escape from threats. Its serrated teeth suggest it was carnivorous, likely feeding on both smaller vertebrates and the abundant insects found in the same fossil beds.
Uniquely for an early dinosauriform it also had a single row of bony osteoderms running along its spine. Although it lived at close to the same time as the similarly-armored Mambachiton their last common ancestor was at least 10 million years earlier, and no other early dinosaur precursors with osteoderms are currently known – so this was probably a case of Lewisuchus independently re-evolving the same sort of feature.
—
NixIllustration.com | Tumblr | Patreon
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#lewisuchus#silesauridae#dinosauriformes#avemetatarsalia#archosaur#reptile#art#the early ornithischian idea is intriguing BUT it's also being pushed by the ornithoscelida gang#so that's a thing#(...i should probably also talk about the state of ornithoscelida at some point; it's been what almost seven years?)#(short version: we still dunno and early dinosaur relationships resolve in multiple equally-likely ways; More Data Is Needed)
522 notes
·
View notes
Text
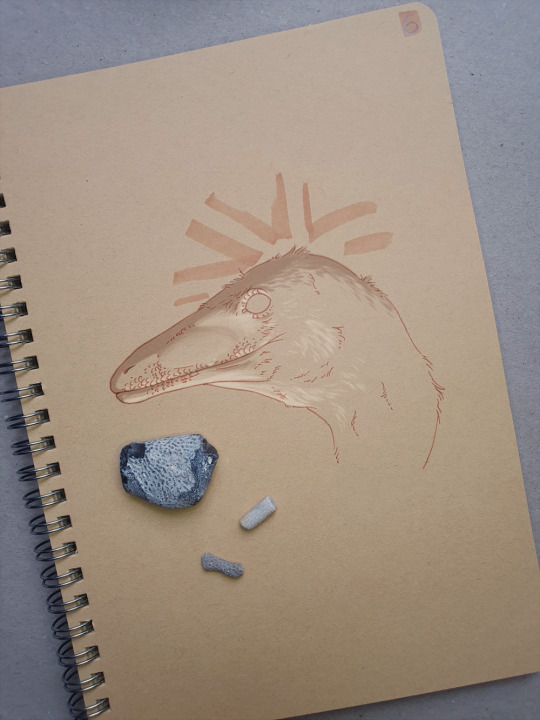

Day 6: Lewisuchus admixtus
#paleoart#art#dinosaur#prehistoric#paleontology#digitalart#traditionalart#Archovember2023#Archovember#Dinovember#Dinovember2023#DrawDinovember#DrawDinovember2023#Lewisuchus#Lewisuchusadmixtus
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
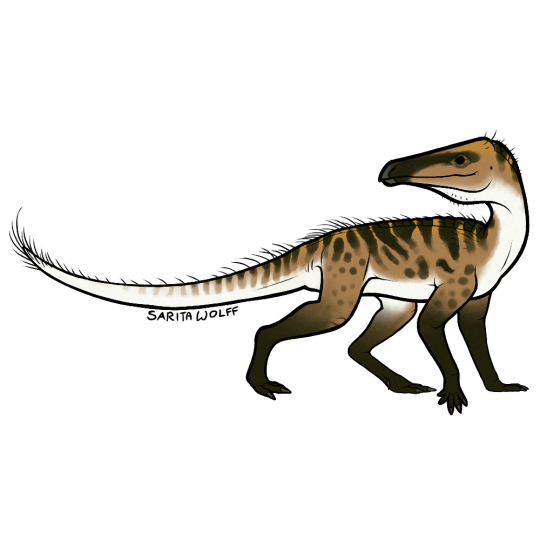

#Archovember Day 6 - Lewisuchus admixtus
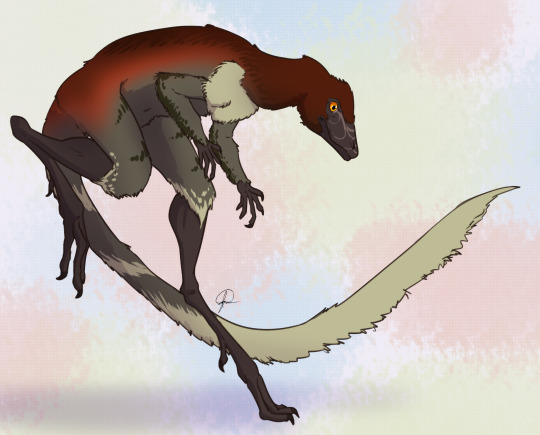
Lewisuchus admixtus was a silesaurid, a type of Triassic archosaur closely related to dinosaurs. Silesaurids all had the same general body plan: a long neck, long legs, and a mostly quadrupedal stance. However, they seem to have all filled a variety of niches. The white-tailed deer-sized Silesaurus was an insectivore. The collie-sized Kwanasaurus was an herbivore. But the smaller, earlier silesaur Lewisuchus was a carnivore, with teeth unique among silesaurids. In fact, its teeth and other anatomical features are so unique that some consider it to be a basal dinosauriform, coming before the silesaurids and dinosaurs split into two groups. It was also found with a single row of osteoderms down its back, something that other silesaurids don’t seem to have. Either way, it was a tiny, unique predator that paved the way for its strange, long-legged cousins.
Living in Late Triassic Argentina, Lewisuchus could have shared habitat with (and probably been hunted by) yesterday’s species, Herrerasaurus. But in the slightly older Chañares Formation, it was more likely to come across Proterochampsids such as Chanaresuchus, Tropidosuchus, and Gualosuchus, and probably competed with them for food. It would have also lived alongside other early dinosauriforms such as Marasuchus, early pterosauromorphs such as Lagerpeton, and the tiny pseudosuchian Gracilisuchus. Cynodonts were plentiful here, and Lewisuchus could have hunted small ones such as Probainognathus.

#my art#SaritaDrawsPalaeo#Lewisuchus#Lewisuchus admixtus#silesaurs#silesaurids#??#archosaurs#archosauromorphs#reptiles#Archovember#Archovember2023
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

Lewisuchus
Lewisuchus — рід архозаврів, що жили під час пізнього тріасу (ранній карній). Це представник групи силезавридів, це рептилії, які найчастіше вважаються найближчими родичами динозаврів (можливо, це вже були справжні динозаври). Скам’янілості тварини були знайдені в формації Чаньярес (Chañares) в Аргентині. Довжина Lewisuchus була приблизно 1 метр і в нього були остеодерми вздовж спини.
Повний текст на сайті "Вимерлий світ":
https://extinctworld.in.ua/lewisuchus/
#lewisuchus#triassic#archosaur#dinosaur#argentina#late triassic#south america#paleoart#silesaurus#reptiles#paleontology#animals#prehistoric#extinct#prehistory#illustration#daily#fossils#art#палеоарт#палеонтологія#динозавр#тварини#мова#україна#ukraine#ukrainian#animal art#українська мова#archosauria
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
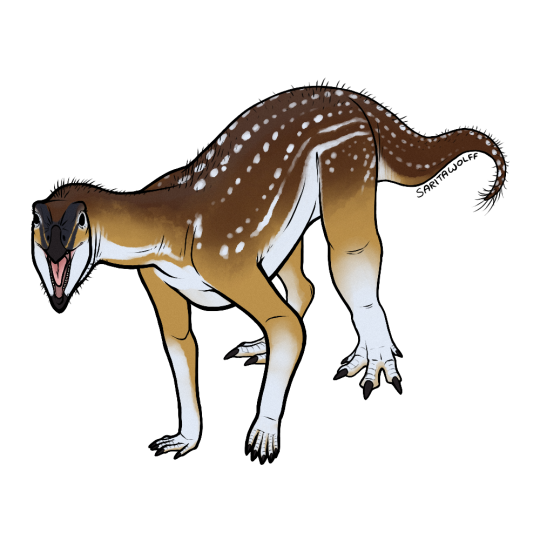

Patreon request for @/rome.and.stuff (Instagram) - Asilisaurus kongwe
Asilisaurus kongwe means “Ancient Ancestor.” As one of the first silesaurs, Asilisaurus is one of the oldest-known Avemetatarsalians (the clade which includes dinosaurs, silesaurs, and pterosaurs.) Found in the Manda Formation of Tanzania, it lived during the earliest portion of the Late Triassic. It appears to have been very common (or at least very prone to fossilization) as it is known from a relatively large amount of fossils.
Based on the length of its limbs, Asilisaurus was likely quadrupedal, but probably could have also reared up on its hind legs. It had no teeth in the tip of its snout, indicating the presence of a small beak, and also had fewer teeth than other silesaurs. Because of this, it is hypothesized that Asilisaurus was an omnivore or even a herbivore. The peglike shape of its teeth may have also lended to piscivory. As silesaurs seemed to have diets which were just as varied as dinosaurs (the Argentinian Lewisuchus was a specialized carnivore, the North American Kwanasaurus was an obligate herbivore, and the Polish Silesaurus was an insectivore and herbivore), Asilisaurus’ diet can’t be based on phylogenetic bracketing.
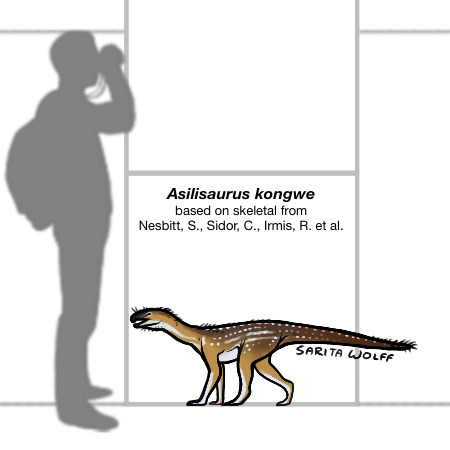
There seem to be two different adult morphologies of Asilisaurus: a “slender” form and a “robust” form. While traditionally regarded as a sign of sexual dimorphism, newer studies show that this could have simply been individual variation and a difference of growth in plentiful vs depleted environments (ie epigenetics), similar to differences seen in Plateosaurus and the modern Alligator.
In the Early Carnian of Tanzania, Asilisaurus kongwe would have lived alongside a variety of pseudosuchians such as Nundasuchus and Mambawakale, as well as the possible early dinosaur, Nyasasaurus. The environment was rich in synapsids as well, including dicynodonts like Angonisaurus, Kannemeyeria, and Tetragonias, and cynodonts like Cynognathus and Diademodon. Asilisaurus would have been preyed on by the aphanosaur Teleocrater and possibly some of the larger, carnivorous cynodonts, which is why I have given it spots for camouflage!
#Asilisaurus kongwe#Asilisaurus#silesaurs#silesaurids#archosaurs#archosauromorphs#reptiles#Manda Formation#Tanzania#Middle Triassic#Late Triassic
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
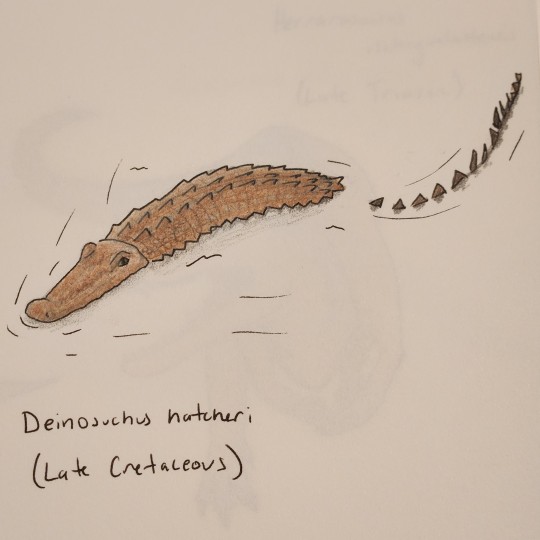
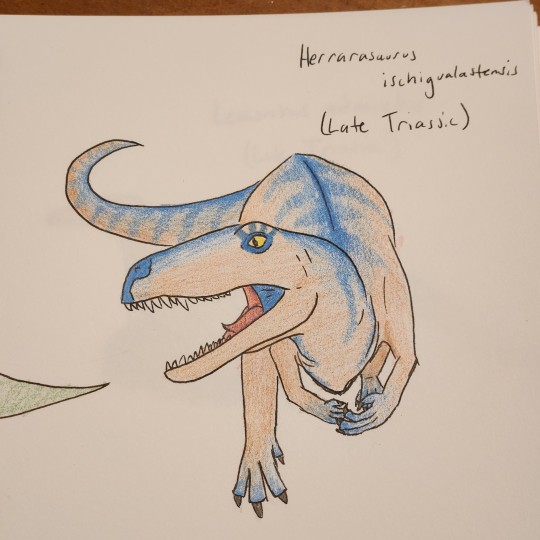



Days 4-6: Deinosuchus, Herrarasaurus, and Lewisuchus. I'm actually happy with how all 3 came out. I might do this for weekends because my schedule gets all screwed up then lol
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lewisuchus admixtus

By Scott Reid on @drawingwithdinosaurs
PLEASE SUPPORT US ON PATREON. EACH and EVERY DONATION helps to keep this blog running! Any amount, even ONE DOLLAR is APPRECIATED! IF YOU ENJOY THIS CONTENT, please CONSIDER DONATING!
Name: Lewisuchus admixtus
Name Meaning: Lewi Crocodile
First Described: 1972
Described By: Romer
Classification: Avemetatarsalia, Ornithodira, Dinosauromorpha, Dinosauriformes, Silesauridae
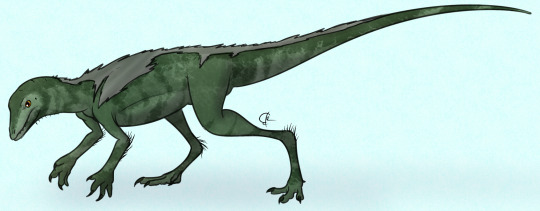
Lewisuchus is a Silesaurid that is probably synonymous with Pseudolagosuchus, having been treated as synonymous in much of the literature, but never fully confirmed as synonymous in studies (i.e., one study indicated they are probably synonymous, other studies since have just treated it as such without rigorously testing it). To be fair, of course, it cannot be rigorously tested, as they don’t have very much overlapping material! It was found in the Chañares Formation of Argentina, living about 236 to 234 million years ago, in the Ladinian age of the Middle Triassic. It was about one meter long, and would have been a lithe, quadrupedal animal, like other Silesaurids.
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lewisuchus
Shout out goes to @mandasaurodon!
#lewisuchus#lewisuchus admixtus#silesaurid#dinosauriform#dinosauromorph#palaeoblr#mandasaurodon#dinosaur#paleontology#prehistory#prehistoric life#dinosaurs#biology#a dinosaur a day#a-dinosaur-a-day#dinosaur of the day#dinosaur-of-the-day#science#nature#factfile#Dìneasar#דינוזאור#डायनासोर#ديناصور#ডাইনোসর#risaeðla#ڈایناسور#deinosor#恐龍#恐龙
79 notes
·
View notes
Photo
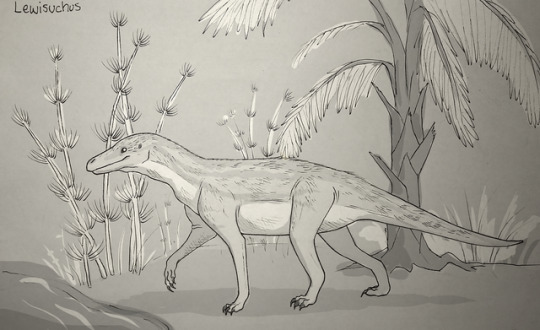
Well, it looks like an old timey movie still, but here’s my first Dinovember: Lewisuchus, an early Dinosauriform which was about a meter long and lived about 235 million years ago.
Realizing that my drawings are going to take quite a bit of research and conjecture! I went for quadrupedal from a skeleton I saw (which i’m realizing now could be very wrong lol) with a light layer of protofeathers and an attempt to not shrinkwrap too much haha.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

Whelp we’ve got about a week and a half til November (aaaaaah), so I guess I’ll post this year’s Archovember list now!
It’s a bit dinosaur-heavy this time, but there are a lot of species I’d really like to try my hand at! Also, we have two leptoceratopsians and two Araripesuchus species. I thought it would be interesting to compare and contrast these species within the same month, so I hope it doesn’t get /too/ repetitive!
For new folks: this is my “Draw Dinovember” list that I expanded out to include other archosauriforms. I started doing this a few years ago to challenge myself to draw species I’ve never drawn before and/or ones that don’t get a lot of attention. Feel free to join in! You can do the whole list, just the dinosaurs, just the pterosaurs, just the pseudosuchians, just your favorites, just ones you’ve never drawn before, roll a D20 and a D10 and draw the sum of whichever numbers you get, etc. Just make sure they’re posted on or after their specific day so I remember to share them on my blog! You can use #Archovember or #Archovember2023, as those are the tags I follow. (Note that I and the whole Archovember event are usually a lot more active on Instagram so if you have an IG I encourage you to join in there!)
Anyway, here is the list in case the graphic is hard to read:
1. Your Choice!
2. Furcatoceratops elucidans
3. Tupandactylus navigans
4. Deinosuchus hatcheri
5. Herrerasaurus ischigualastensis
6. Lewisuchus admixtus
7. Supersaurus vivianae
8. Zhejiangopterus linhaiensis
9. Dynamosuchus collisensis
10. Megalosaurus bucklandii
11. Macrospondylus bollensis
12. Miragaia longicollum
13. Dorygnathus banthensis
14. Leptoceratops gracilis
15. Stagonolepis robertsoni
16. Shantungosaurus giganteus
17. Paleorhinus bransoni
18. Cascocauda rong
19. Kelenken guillermoi
20. Prestosuchus chiniquensis
21. Yangchuanosaurus shangyouensis
22. Istiodactylus latidens
23. Kunbarrasaurus ieversi
24. Araripesuchus wegeneri
25. Tylocephale gilmorei
26. Ixalerpeton polesinensis
27. Udanoceratops tschizhovi
28. Tapejara wellnhoferi
29. Araripesuchus rattoides
30. Scutellosaurus lawleri
One last note, and a warning I usually issue to new paleoartists: while looking for references for these species you’ll come across David Peters. His references tend to dominate search results when looking for less well-known species. They are also highly inaccurate, even the skeletals. So make sure you omit “The Pterosaur Heresies” and “Reptile Evolution” from your google search. If you have issues finding references, let me know and I can share what I’m using!
#my art#Archovember#Archovember2023#SaritaDrawsPalaeo#dinosaurs#pterosaurs#pseudosuchians#archosaurs#archosauriforms
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
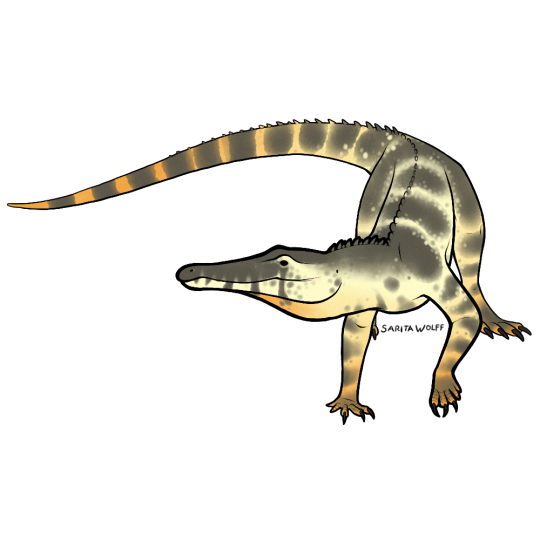

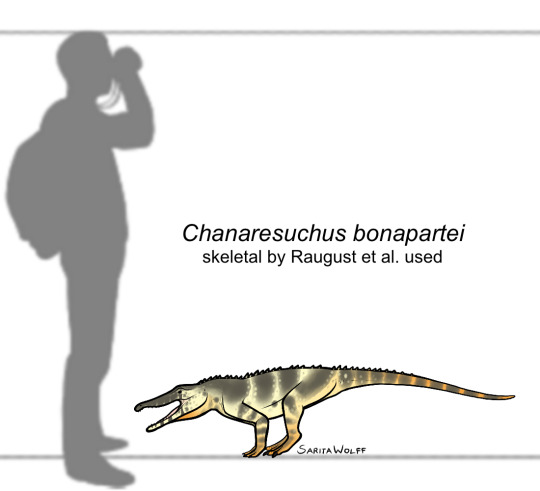
#Archovember Day 26 - Chanaresuchus bonapartei
The proterochampsians were early archosauriforms from the Triassic period. Of them, Chanaresuchus bonapartei was fairly large, living in Late Triassic Brazil. It had a long, narrow snout. Unlike many other early archosauriforms, it had very little body armour, and just a single row of small osteoderms down the back. It is hypothesized that Chanaresuchus lived a similar lifestyle to pseudosuchians and phytosaurs due to its upward facing nostrils and eyes. However, there is a distinct lack of aquatic animal fossils in the Chañares Formation, suggesting that the area was dry and arid.
Chanaresuchus would have lived alongside dicynodonts like Dinodontosaurus, cynodonts like Probainognathus and Massetognathus, silesaurs like Lewisuchus, the lagerpetid Lagerpeton, the basal dinosauriform Marasuchus, the pseudosuchians Gracilisuchus and Luperosuchus, and fellow proterochampsian Gualosuchus.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lagerpeton

By Tas
Etymology: Rabbit Reptile
First Described By: Romer, 1971
Classification: Biota, Archaea, Proteoarchaeota, Asgardarchaeota, Eukaryota, Neokaryota, Scotokaryota Opimoda, Podiata, Amorphea, Obazoa, Opisthokonta, Holozoa, Filozoa, Choanozoa, Animalia, Eumetazoa, Parahoxozoa, Bilateria, Nephrozoa, Deuterostomia, Chordata, Olfactores, Vertebrata, Craniata, Gnathostomata, Eugnathostomata, Osteichthyes, Sarcopterygii, Rhipidistia, Tetrapodomorpha, Eotetrapodiformes, Elpistostegalia, Stegocephalia, Tetrapoda, Reptiliomorpha, Amniota, Sauropsida, Eureptilia, Romeriida, Diapsida, Neodiapsida, Sauria, Archosauromorpha, Crocopoda, Archosauriformes, Eucrocopoda, Crurotarsi, Archosauria, Avemetarsalia, Ornithodira, Dinosauromorpha, Lagerpetidae
Referred Species: L. chanarensis
Status: Extinct
Time and Place: About 235 to 234 million years ago, in the Carnian of the Late Triassic
Lagerpeton is known from the Chañares Formation in La Rioja, Argentina

Physical Description: Lagerpeton was named as the Rabbit Reptile, and for good reason - in a lot of ways, it represents a decent attempt by reptiles in trying to do the whole hoppy-hop thing. You might think that it resembles Scleromochlus in that way, and you’d be right! Scleromochlus and Lagerpeton are close cousins, but one is on the line towards Pterosaurs - Scleromochlus - and the other is on the line towards dinosaurs - Lagerpeton. So, hopping around was an early feature that all Ornithodirans (Dinosaurs, Pterosaurs, and those closest to them) shared. Lagerpeton itself was about 70 centimeters in length, with most of that length represented as tail; it was slender and lithe, built for moving quickly through its environment. It had a small head, a long neck, and a thin body. While it had long legs, it also had somewhat long arms, and while it may have been able to walk on all fours it also would have been able to walk on two legs alone. It was digitigrade, walking only on its toes, making it an even faster animal. Its back was angled to help it in hopping and running through its environment, and its small pelvis gave it more force during hip extension while jumping. In addition to all of this, it basically only really rested its weight on two toes - giving it even more hopping ability! As a small early bird-line reptile, it would have been covered in primitive feathers all over its body (protofeathers), though what form they took we do not know.
By Scott Reid
Diet: As an early dinosaur relative, it’s more likely than not that Lagerpeton was an omnivore, though this is uncertain as its head and teeth are not known at this time.
Behavior: Lagerpeton would have been a very skittish animal, being so small in an environment of so many kinds of animals - and as such, that hopping and fast movement ability would have aided it in escaping and moving around its environment, avoiding predators and reaching new sources of food (and, potentially, chasing after smaller food itself). Lagerpeton may have also been somewhat social, moving in small groups, potentially families, to escape the predators and chase after prey together, given its common nature in its environment. As an archosaur, Lagerpeton was more likely than not to take care of its young, though we don’t know how or to what extent. The feathers it had would have been primarily thermoregulatory, and as such, they would have helped it maintain a constant body temperature - making it a very active, lithe animal.
By José Carlos Cortés
Ecosystem: Lagerpeton lived in the Chañares environment, a diverse and fascinating environment coming right after the transition from the Middle to Late Triassic epochs. Given that the first true dinosaurs are probably from the start of the Late Triassic, this makes it a hotbed for understanding the environments that the earliest dinosaurs evolved in. Since Lagerpeton is a close dinosaur relative, this helps contextualize its place within its evolutionary history. This environment was a floodplain, filled with lakes that would regularly flood depending on the season. There were many seed ferns, ferns, conifers, and horsetails. Many different animals lived here with Lagerpeton, including other Dinosauromorphs like the Silesaurid Lewisuchus/Pseudolagosuchus and the Dinosauriform Marasuchus/Lagosuchus. There were crocodilian relatives as well, such as the early suchian Gracilisuchus and the Rauisuchid Luperosuchus. There were also quite a few Proterochampsids, such as Tarjadia, Tropidosuchus, Gualosuchus, and Chanaresuchus. Synapsids also put in a good show, with the Dicynodonts Jachaleria and Dinodontosaurus, as well as Cynodonts like Probainognathus and Chiniquodon, and the herbivorous Massetognathus. Luperosuchus would have definitely been a predator Lagerpeton would have wanted to get away from - fast!

By Ripley Cook
Other: Lagerpeton is one of our earliest derived Dinosauromorphs, showing some of the earliest distinctions the dinosaur-line had compared to other archosaurs. Lagerpeton was already digitigrade - an important feature of Dinosaurs - as shown by its tracks, called Prorotodactylus. These tracks also showcase that dinosaur relatives were around as early as the Early Triassic - and that their evolution, and the rapid diversification of archosauromorphs in general, was a direct result of the end-Permian extinction.
~ By Meig Dickson
Sources Under the Cut
Arcucci, A. 1986. New materials and reinterpretation of Lagerpeton chanarensis Romer (Thecodontia, Lagerpetonidae nov.) from the Middle Triassic of La Rioja, Argentina. Ameghiniana 23 (3-4): 233-242.
Arcucci, A. B. 1987. Un nuevo Lagosuchidae (Thecodontia-Pseudosuchia) de la fauna de los Chañares (Edad Reptil Chañarense, Triasico Medio), La Rioja, Argentina. Ameghiniana 24: 89 - 94.
Arcucci, A., C. A. Mariscano. 1999. A distinctive new archosaur from the Middle Triassic (Los Chañares Formation) of Argentina. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 19: 228 - 232.
Bittencourt, J. S., A. B. Arcucci, C. A. Marsicano, M. C. Langer. 2014. Osteology of the Middle Triassic archosaur Lewisuchus admixtus Romer (Chañares Formation, Argentina), its inclusivity, and relationships amongst early dinosauromorphs. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology: 1 - 31.
Brusatte, S. L., G. Niedzwiedzki, R. J. Butler. 2011. Footprints pull origin and diversification of dinosaur stem lineage deep into Early Triassic. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 278 (1708): 1107 - 1113.
Ezcurra, M. D. 2006. A review of the systematic position of the dinosauriform archosaur Eucoelophysis baldwini Sullivan & Lucas, 1999 from the Upper Triassic of New Mexico, USA. Geodiversitas 28(4):649-684.
Ezcurra, M. D. 2016. The phylogenetic relationships of basal archosauromorphs, with an emphasis on the systematics of proterosuchian archosauriformes. PeerJ 4: e1778.
Fechner, R. 2009. Morphofunctional evolution of the pelvic girdle and hindlimb of DInosauromorpha on the lineage to Sauropoda (Thesis). Ludwigs Maximillians Universita.
Fiorelli, L. E., S. Rocher, A. G. Martinelli, M. D. Ezcurra, E. Martin Hechenleitner, M. Ezpeleta. 2018. Tetrapod burrows from the Middle-Upper Triassic Chañares Formation (La Rioja, Argentina) and its palaeoecological implications. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 496: 85 - 102.
Kammerer, C. F., S. J. Nesbitt, N. H. Shubin. 2012. The first Silesaurid Dinosauriform from the Late Triassic of Morocco. Acta Palaeontological Polonica 57 (2): 277.
Kent, D. V., P. S. Malnis, C. E. Colombi, A. A. Alcober, R. N. Martinez. 2014. Age constraints on the dispersal of dinosaurs in the Late Triassic from magnetochronology of the Los Colorados Formation (Argentina). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111: 7958 - 7963.
Irmis, R. B., S. J. Nesbitt, K. Padian, N. D. Smith, A. H. Turner, D. T. Woody, and A. Downs. 2007. A Late Triassic dinosauromorph assemblage from New Mexico and the rise of dinosaurs. Science 317:358-361.
Jenkins, F. A. 1970. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. VII. The postcranial skeleton of the traversodontid Massetognathus pascuali (Therapsida, Cyondontia). Breviora 352: 1 - 28.
Langer, M. C., S. J. Nesbitt, J. S. Bittencourt, R. B. Irmis. 2013. Non-dinosaurian Dinosauromorphs. Geological Society London, Special Publications. 379 (1): 157 - 186.
Marsh, A. D. 2018. A new record of Dromomeron romeri Irmis et al., 2007 (Lagerpetidae) from the Chinle Formation of Arizona, U.S.A. PaleoBios 35:1-8.
Marsicano, C. A., R. B. Irmis, A. C. Mancuso, R. Mundil, F. Chemale. 2016. The precise temporal calibration of dinosaur origins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of AMerica 113 (3): 509 - 513.
Martz, J. W., and B. J. Small. 2019. Non-dinosaurian dinosauromorphs from the Chinle Formation (Upper Triassic) of the Eagle Basin, northern Colorado: Dromomeron romeri (Lagerpetidae) and a new taxon, Kwanasaurus williamparkeri (Silesauridae). PeerJ 7:e7551:1-71.
Nesbitt, S. J., R. B. Irmis, W. G. Parker, N. D. Smith, A. H. Turner and T. Rowe. 2009. Hindlimb osteology and distribution of basal dinosauromorphs from the Late Triassic of North America. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 29(2):498-516.
Nesbitt, S. J. 2011. The early evolution of archosaurs: relationships and the origin of major clades. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 353:1-292.
Perez Loinaze, V. S., E. I. Vera, L. E. Fiorelli, J. B. Desojo. 2018. Palaeobotany and palynology of coprolites from the Late Triassic Chañares Formation of Argentina: implications for vegetation provinces and the diet of dicynodonts. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 502: 31 - 51.
Rogers, R. R., A. B. Arcucci, F. Abdala, P. C. Sereno, C. A. Forster, C. L. May. 2001. Paleoenvironment and taphonomy of the Chañares Formation tetrapod assemblage (Middle Triassic), northwestern Argentina: spectacular preservation in volcanogenic concretions. Palaios 16: 461 - 481.
Romer, A. S. 1966. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. I. Introduction. Breviora 247: 1 - 14.
Romer, A. S. 1966. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. II. Sketch of the geology of the Rio-Chañares-Rio Gualo Region. Breviora 252: 1 - 20.
Romer, A. S. 1967. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. III. Two new gomphodonts, Massetognathus pascuali and M. teruggii. Breviora 264: 1 - 25.
Romer, A. S. 1968. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. IV. The dicynodont fauna. Breviora 295: 1 - 25.
Romer, A. S. 1969. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. V. A new chiniquodontid cynodont, Probelesodon lewisi - cynodont ancestry. Breviora 333: 1 - 24.
Romer, A. S. 1970. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. VI. A chiniquodont cynodont with an incipient squamosal-dentary jaw articulation. Breviora 344: 1 - 18.
Romer, A. S. 1971. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. VIII. A fragmentary skull of a large thecodont, Luperosuchus fractus. Breviora 373: 1 - 8.
Romer, A. S. 1971. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. IX: The Chanares Formation. Breviora 377: 1 - 8.
Romer, A. S. 1971. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. X. Two new but incompletely known long-limbed pseudosuchians. Breviora 378:1-10.
Romer, A. S. 1971. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XI. Two new long-snouted thecodonts, Chanaresuchus and Gualosuchus. Breviora 379: 1 - 22.
Romer, A. S. 1972. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XII. The post cranial skeleton of the thecodont Chanaresuchus. Breviora 385: 1 - 21.
Romer, A. S. 1972. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XIII. A fragmentary skull of a large thecodont, Luperosuchus fractus. Breviora 389: 1 - 8.
Romer, A. S. 1972. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. Lewisuchus admixtus, gen. et sp. Nov., a further thecodont from the Chañares beds. Breviora 390: 1 - 13.
Romer, A. S. 1972. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XV. Further remains of the thecodonts Lagerpeton and Lagosuchus. Breviora 394: 1 - 7.
Romer, A. S. 1972. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XVI. Thecodont classification. Breviora 395:1-24.
Romer, A. S. 1972. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XVII. The Chañares gomphodonts. Breviora 396: 1 - 9.
Romer, A. S. 1973. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XVIII. Probelesodon minor, a new species of carnivorous cynodont; family Probainognathidae nov. Breviora 401: 1 - 4.
Romer, A. S., and A. D. Lewis. 1973. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XIX. Postcranial materials of the cynodonts Probelesodon and Probainognathus. Breviora 407: 1 - 26.
Romer, A. S. 1973. The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XX. Summary. Breviora 413: 1 - 20.
Sereno, P. C., and A. B. Arcucci. 1994. Dinosaurian precursors from the Middle Triassic of Argentina: Marasuchus lilloensis, gen. nov. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 14(1):53-73.
#Lagerpeton#Dinosaurmorph#Lagerpetid#Triassic#Palaeoblr#Triassic Madness#Ornithodiran#Triassic March Madness#South America#Omnivore#Prehistoric Life#Prehistory#Palaeontology#Lagerpeton chanarensis#dinosaur#paleontology#dinosaurs#biology#a dinosaur a day#a-dinosaur-a-day#dinosaur of the day#dinosaur-of-the-day#science#nature#factfile
365 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lagosuchus talampayensis
By José Carlos Cortés
Etymology: Rabbit Crocodile
First Described By: Romer, 1971
Classification: Dinosauromorpha
Status: Extinct
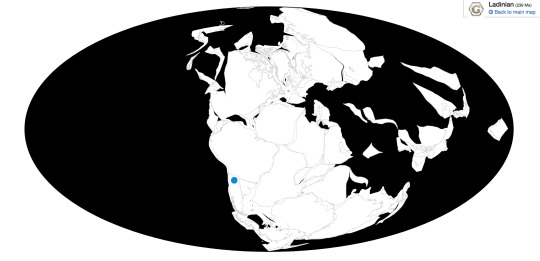
Time and Place: About 238 million years ago, in the Ladinian age of the Middle Triassic


Lagosuchus is found in the Chañares Formation of Argentina
Physical Description: Lagosuchus was an early Dinosauromorph, aka the group that includes dinosaurs and all their closest relatives. Thus, Lagosuchus is one of many early archosaurs that showcase the origins of all dinosaurs! Lagosuchus isn’t known from particularly good remains, but it does show it was a lightly built, agile animal, which was probably bipedal and spent most of its times on its toes. At about 30 centimeters in length, it was around the size of a ferret. Its legs were amazingly long, and its toes were too, giving it good speed. It had an almost-erect posture - without the open hip sockets of dinosaurs proper, it couldn’t hold its legs directly underneath its body, but it almost could. Its forelimbs are a bit more murky, though it seems likely that Lagosuchus moved on all fours most of the time, switching to two legs when it needed to move quickly from place to place. Being an early dinosauromorph, it would have had some covering of protofeathers, though how much is a bit of question.
Diet: Lagosuchus was probably an omnivore, given the fact that early dinosaurs probably came from omnivorous origins
Behavior: Lagosuchus would have been a moderately active animal - close to a warm-blooded metabolism but not quite. As such, it probably would have spent most of its time on the move, hunting for food or searching for grubs and possibly plants it could have eaten. Lagosuchus could have used its speed to run away from predators, which were very common in its environment; and, of course, running after its own food!
It is uncertain if Lagosuchus was a social animal, or if it took care of its young; but it seems likely for the latter at least.

By Ripley Cook
Ecosystem: The Chañares Formation was a middle triassic microcosm of the explosion of evolution occurring in the Triassic, showcasing a wide variety of animals evolving in the aftermath of the Permian mass extinction. This was a low lying lake system, filled with horsetails, ferns, and some nearby conifer trees. It was also very warm, though not as warm as locations closer to the equator. There were many kinds of animals - large predatory pseudosuchians that would have hunted Lagosuchus such as Gracilisuchus, Luperosuchus, and Tarjadia; other Avemetatarsalians such as Marasuchus, Pseudolagosuchus, Lewisuchus, and Lagerpeton; the carnivorous almost-mammals Probainoganthus and Chiniquodon; the herbivorous almost-mammal Massetognathus; giant Dicynodont herbivores like Dinodontosaurus and Jachaleria; and finally the vaguely-crocodile-like Proterochampsids Gualosuchus, Chanaresuchus, and Tropidosuchus. A fascinating community indeed!
Other: Lagosuchus isn’t a particularly well known dinosauromorph; fossils assigned to it at one point that are well known, Marasuchus, have been given their own genus. It is possible that Lagosuchus is, thus, closer to dinosaurs in relationship than we think just on its own without evidence from Marasuchus. More studying of these fossils is necessary to come to better conclusions.
~ By Meig Dickson
Sources under the Cut
Arcucci, A.B. 1987. Un nuevo Lagosuchidae (Thecodontia-Pseudosuchia) de la fauna de Los Chañares (Edad Reptil Chañarense, Triasico Medio), La Rioja, Argentina. Ameghiniana 24. 89–94.
Arcucci, A., and C.A. Marsicano. 1999. A distinctive new archosaur from the Middle Triassic (Los Chañares Formation) of Argentina. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 19. 228–232.
Bittencourt, Jonathas S.; Andrea B. Arcucci; Claudia A. Marsicano, and Max C. Langer. 2014. Osteology of the Middle Triassic archosaur Lewisuchus admixtus Romer (Chañares Formation, Argentina), its inclusivity, and relationships amongst early dinosauromorphs. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology _. 1–31.
Fiorelli, Lucas E.; Sebastián Rocher; Agustín G. Martinelli; Martín D. Ezcurra; E. Martín Hechenleitner, and Miguel Ezpeleta. 2018. Tetrapod burrows from the Middle–Upper Triassic Chañares Formation (La Rioja, Argentina) and its palaeoecological implications. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 496. 85–102.
Jose, B. 1975. "Nuevos materiales de Lagosuchus talampayensis Romer (Thecodontia-Pseudosuchia) y su significado en el origen de los Saurischia: Chañarense inferior, Triásico medio de Argentina." Acta Geológica Lilloana. 13 (1): 5–90.
Kent, Dennis V.; Paula Santi Malnis; Carina E. Colombi; Oscar A. Alcober, and Ricardo N. Martínez. 2014. Age constraints on the dispersal of dinosaurs in the Late Triassic from magnetochronology of the Los Colorados Formation (Argentina). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111. 7958–7963.
Marsicano, C. A., R. B. Irmis, A. C. Mancuso, R. Mundil, F. Chemale. 2016. "The precise temporal calibration of dinosaur origins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (3): 509–513.
Nesbitt, S.J. 2011. "The Early Evolution of Archosaurs: Relationships and the Origin of Major Clades" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 352: 189.
Romer, A. S. 1971. "The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. X. Two new but incompletely known long-limbed pseudosuchians". Breviora. 378: 1–10.
Romer, A. S. 1972. "The Chañares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XV. Further remains of the thecodonts Lagerpeton and Lagosuchus". Breviora. 394: 1–7.
Palmer, D., ed. 1999. The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 97.
Paul, G. 1988. Predatory Dinosaurs of the World. Simon & Schuster.
Perez Loinaze, V. S., E. I. Vera, L. E. Fiorelli, J. B. Desojo. 2018. Palaeobotany and palynology of coprolites from the Late Triassic Chañares Formation of Argentina: implications for vegetation provinces and the diet of dicynodonts. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 502: 31 - 51.
Pontzer, H., V. Allen, J. R. Hutchinson. 2009. "Biomechanics of Running Indicates Endothermy in Bipedal Dinosaurs". PLoS ONE. 4 (12): e7783.
Rogers, R.R.; A.B. Arcucci; F. Abdala; P.C. Sereno; C.A. Forster, and C.L. May. 2001. Paleoenvironment and taphonomy of the Chañares Formation tetrapod assemblage (Middle Triassic), northwestern Argentina: spectacular preservation in volcanogenic concretions. Palaios 16. 461–481.
Sereno, P. C., A. B. Arcucci. 1994. "Dinosaurian precursors from the Middle Triassic of Argentina: Marasuchus lilloensis, gen. nov". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 14 (1): 53–73.
#Lagosuchus#Lagosuchus talampayensis#Dinosauromorph#Prehistoric Life#Paleontology#prehistory#Outside Saurischia & Ornithischia#Triassic#South America#Omnivore#Mesozoic Monday
214 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pseudolagosuchus major
By Jack Wood on @thewoodparable
PLEASE SUPPORT US ON PATREON. EACH and EVERY DONATION helps to keep this blog running! Any amount, even ONE DOLLAR is APPRECIATED! IF YOU ENJOY THIS CONTENT, please CONSIDER DONATING!
Name: Pseudolagosuchus major
Name Meaning: False Lagosuchus
First Described: 1987
Described By: Arcucci
Classification: Avemetatarsalia, Ornithodira, Dinosauromorpha, Dinosauriformes, Silesauridae
Pseudolagosuchus was a Silesaurid that is probably synonymous with Lewisuchus, but due to the lack of major overlapping material, this has only been hypothesized, rather than fully confirmed. It is from the Chañares Formation of Argentina, living in the Ladinian age of the Middle Triassic, about 236 to 234 million years ago. It was about 1 meter long and was one of the more early derived Silesaurids.
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudolagosuchus
Shout out goes to @cat-acombes!
#pseudolagosuchus#pseudolagosuchus major#silesaurid#dinosauromorph#dinosauriform#cat-acombes#palaeoblr#dinosaur#paleontology#prehistory#prehistoric life#dinosaurs#biology#a dinosaur a day#a-dinosaur-a-day#dinosaur of the day#dinosaur-of-the-day#science#nature#factfile#Dìneasar#डायनासोर#דינוזאור#ديناصور#ডাইনোসর#risaeðla#ڈایناسور#deinosor#恐龍#恐龙
133 notes
·
View notes