#l'ami du people
Text

When I'm having a crappy day at work, I sometimes visit "L'Ami du Peuple" during my lunch break. It tends to put all the petty day-to-day stuff into perspective…
During the quieter moments, like today, when room 55 is nearly empty, I can't help but notice a pattern. Every single visitor, upon entering, pauses before the painting.
They do a double-take at the painting's name and give him another look. Some snap a photo they'll probably never look at again.
Then they move on.
Most of them likely have no clue who he is. They don't know he's holding a note from his assassin. If they even notice "L'An Deux" written at the bottom, they're probably confused by it.
But still, for those 30 seconds, David's brushstrokes exquisitely forming the face of this stricken man make them pause. What makes them linger? Is it the vaguely familiar name? The face they've seen on numerous posters and leaflets? The unsettling quiet brutality of the piece?
It doesn’t really matter why. Because, for that half-minute, through their eyes, he exists. He is present. He is contemporary.
#pseudo-philosophical ramblings#frev#french revolution#marat#jean paul marat#l'ami du people#jacques louis david#my happy place is a picture of a 18th century dead guy#personal opinion
88 notes
·
View notes
Text

@rex-and-regina
1) marat did not encourage "murder of innocent civilians" in l'ami du peuple. while he did sometimes use violent rhetoric (like in the "five hundred heads" quote that people love to throw around with no context), that was pretty much the norm for political journals at the time. they were sensational and emotional and dramatic and hyperbolic. that was pretty much the stylistic standard. if you compare marat's paper with, say, hebert's or even desmoulins's, you'll find he's actually pretty academic and straightforward for the era.
2) if you try to counter my first point with "but the september massacres", you need to know that marat was not directly responsible for those either. the narrative that he caused it stems from the fact that he put out an issue of his paper a little while before the massacres that said some stuff about taking up arms to defend the homeland from conspirators and traitors, etc. etc. except, y'know, a bunch of people were saying stuff like that in their papers (see above). it's true that he didn't explicitly condemn the massacres, but nobody in the government really wanted to talk about it because of how messy of a situation it was. someone else even said something like "we will draw the curtain over this event and leave its judgement to posterity".
3) robespierre.... did not cause the "reign of terror". in fact they did not even call it the reign of terror at the time (historians came up with that later). actually, if we want to get pedantic, the term terreur had a very different connotation in the 18th century than it does now, but I digress. robespierre was the subject of a massive smear campaign when his coworkers realized they couldn't make him shut up about various crimes that they were involved in and killed him to keep him from airing out their dirty laundry. they also killed a bunch of his political allies because they couldn't have them exonerating him, could they? look it up it's actually wild. so they blamed him for all the issues that the government had, even the ones he was trying to fix (he opposed the shitshow in lyons and nantes, cautioned against needless bloodshed, abhorred the practice of treating executions as a spectacle). also he didn't actually have nearly as much power as people seem to think now. he was a member of the national convention (the french republic's elected legislative body), and a member of the committee of public safety (a council elected from members of the convention to deal with the escalating war situation and some other stuff). he was not the leader of the CSP (which did not have a leader) or the convention (which had a presidency that was mostly ceremonial and worked on a rotating basis). he also never sentenced anyone to death because it was the tribunals that did that, not the convention or CSP.
4) the time period that is generally considered the "reign of terror" (as flawed a concept as that is) is usually placed after the assassination of marat. because a big reason for the paranoia that led to the escalation of security measures was the fact that marat was killed. marat was seen as kind of unkillable by the people of paris (won his own political show trial, etc.) so if you could kill marat, you could kill anyone. so it's kind of hard to say what marat would've supported or not supported after he died, especially since his death itself heavily influenced the next stage of the revolution.
5) charlotte corday wasn't even a monarchist. she was aligned with the girondins, who were moderate republicans in favor of the free market. she didn't like marat because marat was calling the girondins corrupt in his newspaper after a prominent girondin official turned traitor and deserted to the austrians (whom france was at war with). not entirely sure what she thought she would accomplish with this, because a great way to make your political faction seem really corrupt is to brutally murder a guy for criticizing it.
6) a bunch of people actually tried to stop marat through various means, legal and illegal. namely lafayette and brissot and capet and barbaroux and necker and... you get the picture. charlotte corday was just the one that succeeded.
a final point: why do you criticize marat for "encouraging" (but never committing) murder while you simultaneously praise corday for committing a literal actual murder? only one of the three people (marat, robespierre, corday) you mentioned actually killed anybody, and it wasn't marat or robespierre.
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
French Revolution Snapshots from Paris compilation: part II

Eugène Delacroix's Liberty Leading the People my beloved ->
I know it's the 1830 Revolution, but still. It felt surreal being able to see it in person!; Louvre

Marat's L'Ami du peuple!; Musée Carnavalet

The 1793 constitution, too good for this world, too pure (excuse the bad quality I tried my best); Musée Carnavalet
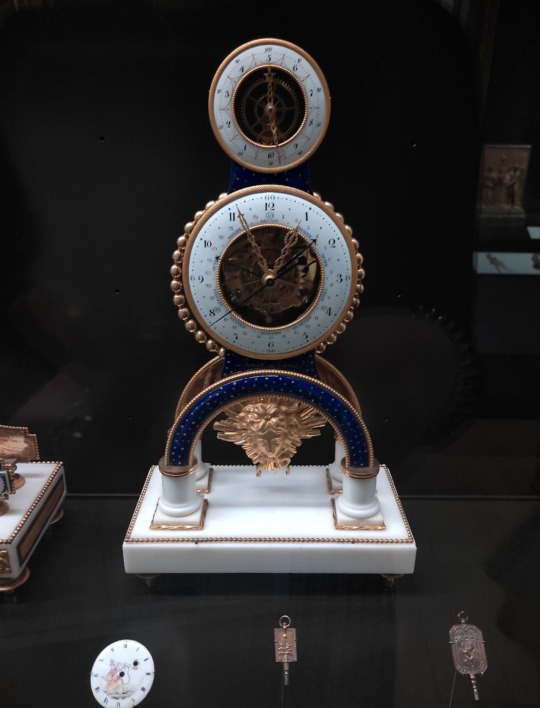

This beautiful French revolution era clock which includes the 10-hour dial; Musée Carnavalet
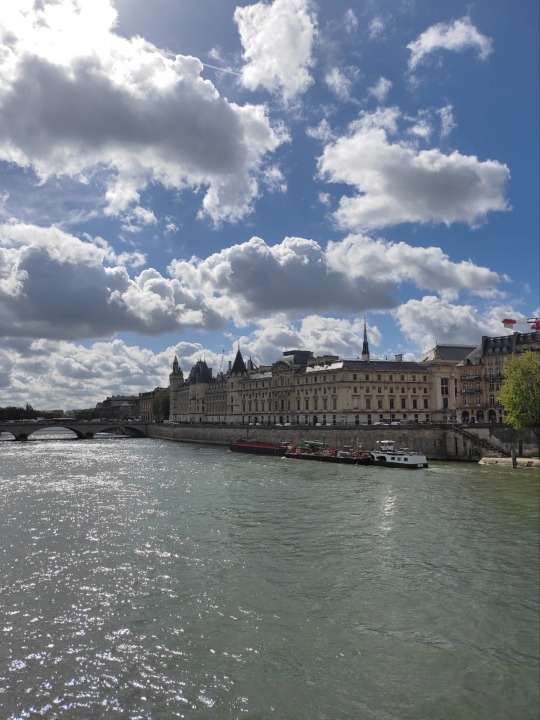

La Conciergerie which served as a prison during the revolution (didn't have enough time to go inside, sadly)

This detailed map of Paris just before the revolution broke out!; Musée Carnavalet
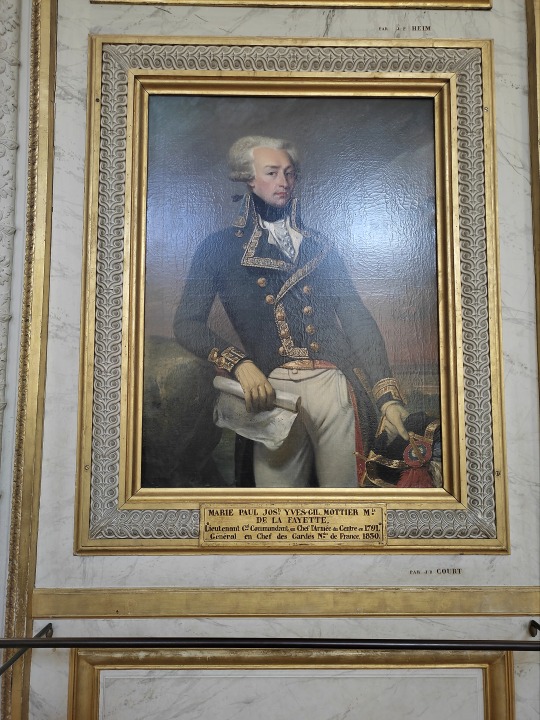

Marquis de Lafayette, looking like he's judging you severly; Versailles
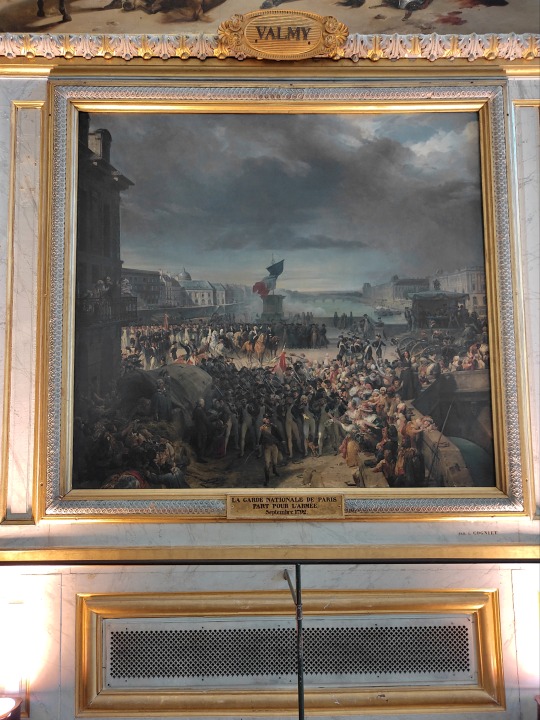
A painting of the National Guard in Paris, 1792 (there's a painting of Valmy just above it which I have as well); Versailles
#frev#french revolution#frevblr#art#frev art#1700s#history#18th century#paris#louvre#versailles#marat#jean paul marat#marquis de lafayette#lafayette#amrev#paris trip#musée carnavalet#historical artifacts#eugene delacroix#frev community#french history
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Masterlist of Resources
Very much a work in progress, please be patient <3
table of contents for my own resources (posts, translations, etc.) and suggested readings from experts and people in the frevblr community.
Saint-Just:
Convention Speeches: (with partial English translations)
First Speech: 13 November 1792 on the debate of putting the King to trial.
19 vendémiaire an II (10 October 1793)
9 Thermidor an II (28 July 1794)
"Praise the Victories and Forget Ourselves" Excerpt
"Tarpeian Rock" Analogy from 9 Thermidor Speech draft
Misc:
Why I study SJ
My Thoughts on SJ's Thoughts on the Terror
SJ's Paris Apartment ( w/ @/ vieillesmaisons)
SJ's various lodgings
Speech to Army of the Rhine excerpt
Alsace Mission Map
Linton on SJ as the face of "the Terror"
Saint-Just on Marat
SJ Handwriting example deciphered
Arlequin-Diogene (SJ's play) [working on a translation]
What inspired the nature elements of Organt
Saint-Just: Apostle of the Terror by Geoffrey Bruun (my personal favorite English SJ bio)
Bio Recs
Marat:
general resources
L' Ami du Peuple Archive (all issues presumed)
PS- Head over to @dailymaratmail for daily L'Ami du Peuple and other Marat writing excerpts (in collaboration with @/viellesmaisons and @/lamarseillasie
Robespierre:
Bio recs
Robespierre's silly snot poem
Why are there Anti-Robespierrests?
Misc.:
My Carnavalet photos, SJ Bust , Marat Bathtub, Cordeliers monastary, Marat Printer, Panthèon National Convention Sculpture, Robespierre Bust.
On Brissot
On Lafayette
School of Mars, (see Barère, Le Bas)
Camille Desmoulins' letter to his father (1789)
Frevolutionaries' symbols on rural calendar
Anecdotes
Most important basic info [coming soon]
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
it's easy to say "let's not ignore the negatives" about the french revolution. it's not as easy to see just what the "negatives" were.
the french revolution did not bring about a "power vacuum". the legislative assembly was formed as soon as the constituent assembly completed a new constitution and dissolved itself. in the constituent, the legislative, and the national convention, at any time, a president would be elected every 15 days. the word "anarchy" carried with it very derogatory notions, and even marat and robespierre condemned it.
the "if violent, then don't" type of criticism to the frev is reductive, and risky of using double standards.
a)
it is reductive because "the frev" is a long period across a vast geographical area (if we say the frev spanned 1789-1799, then haiti was not independent during this time).
are we talking the potential violence of the louis xvi's german and swiss guards, or the parisian urban poor running to seize arms in the bastille to protect themselves?
are we talking the national guard shooting the peaceful petitioners calling to put louis xvi on trial for his fleeing to varennes on 17th july 1791, or are we talking about marat's strongly-worded condemnation of the national guard in response (l'ami du peuple no.524, 20th july, 1791)?
are we talking the declaration of pillnitz was on 27th august 1791, where prussian and austrian armies vague-posted about forming a military coalition against the constituent assembly, or are we talking brissot and his friends' eagerness to declare war and even potentially to extend the revolution beyond metropolitan france, or are we talking the consequence of brissot's decision of rushing into war with an army so untrained, so underpaid, so unarmed?
you get the idea. to vaguely condemn violence would obfuscate everybody's position, and nullify any discussion of just what course of action to take in order to build a republic from scratch.
b)
it is risky of double standards, because violence was not an exception, especially not in the late 18th century. before this was the seven years' war. after this was the empire. i strongly recommend reading about the united irish rebellion of 1798 and the british response to that, and see what violent injustice "some of the most famous names" of ireland in the same time period had to face.
as for the "original goal" of the french revolution, more well-read mutuals can brief you on just how many goals the jacobins had alone. the goals of the gironde were a very different set of goals from the very beginning, the goals of the monarchiens more different still.
but in any case, the "original goal" was not "independence". france was (and is) an economically strong part of the imperial core. one of the goals of the haitian revolution was independence from france.
that the bourbons restoration happened at all says everything about bonaparte's failure to withstand the coalition wars that came back to him again and again and again, like waves on a shore (see my point on brissot above). it says very little about the Spirit of revolution, which in the end shall save us all.
They say revolutions turn out badly. But they're constantly confusing two different things, the way revolutions turn out historically and people's revolutionary becoming. These relate to two different sets of people. Men's only hope lies in a revolutionary becoming: the only way of casting off their shame or responding to what is intolerable.
(Gilles Deleuze, Negotiations, New York: Columbia University Press 1995,p. 171, which can be read here, in its entirety.)
just what name should be given to the period of july 1793 - july 1794 is a matter that is still not settled among historians themselves. the word "terror" got its negative notions from tallien, who was very biased, so biased in fact he tried to assassinate his opponents in the convention. tallien did not succeed despite the execution, without a trial, of his opponents (maximilien robespierre, augustin robespierre, aristide couthon, antoine saint-just, françois hanriot, and some one hundred others). he did not seize more power himself. he himself was denounced by his colleagues as complicit in violent excesses. he shifted blames onto his colleagues in turn. his career was more or less ended by the moderates he sought to please.
and then the "reign" part was only added when this term entered the english-speaking parts of the world. so this name was both biased and non-universal. it is still biased and non-universal.
i genuinely do not wish to tell anybody what to do, but if you say "reign of terror" uncritically, people are going to tell you that you are using a reactionary term, because you are.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
September 16th, 1789: 234 years ago, Jean-Paul Marat published the first issue of L'Ami Du Peuple




L'Ami du Peuple, or, as it was called at the time it was founded, L'Ami Du Peuple ou Le Publiciste Parisien, was an active revolutionary newspaper and also one of the most absolutely fascinating and interesting pieces of the entire French Revolution, created and edited by Marat from September 1789.
The year 1789 was a relatively turbulent period for both Marat's career and the history of the Revolution. This can be seen simply by the number of projects that Marat began in a short space of time. In February, just two months after publishing his Offrande à la Patrie (1788), he published the Supplément à l'Offrande (1789). In March, he began to attend the sessions of the electoral assembly of his district, Carmes-Déchaussés, with great assiduity and was soon elected to the electoral committee. In August, he began publishing Le Moniteur Patriote and also published the Projet de déclaration des droits de l'homme et du citoyen suivi d'un Plan de constitution juste, sage et libre. Finally, in September, he published No. 1 of Le Publiciste Parisien, and consequently No. 5 of the then L'Ami Du Peuple ou Le Publiciste Parisien, which marked the birth of the famous Friend of the People, a character Marat would identify with until the last day of his life. It can be said that this newspaper came about when Marat found himself in a situation where he would have to produce and publish newspapers and pamphlets independently and without the approval of his colleagues. He proposed to the committee that it should have a press, which was apparently not accepted by the district.
More than just one of the many periodicals that existed during the course of the revolution, L'Ami du Peuple is a precious historical source of information and there is no doubt that it was important for the unfolding of revolutionary events. Not even Delisle de Sales, in his Essai sur le journalisme depuis 1735 jusqu'à l'an 1800 (1811), a work that expressed the author's deep aversion to the revolutionary process and especially to Marat, denies that L'Ami Du Peuple left a mark on the philosophical memory of the history of French journalism.
Albert Mathiez, in a summary of Gottschalk's Marat in the 1927 AHRF (pp. 599-602), makes an interesting comment on Marat's analysis in the context of revolutionary journalism:
"In my opinion, what makes Marat original among the journalists and statesmen of the Revolution has not been sufficiently appreciated by M. Gottschalk. (...) He was never naïve about the revolution that was taking place. From the first moment, he proclaimed that the proletarians - an expression he had already used in its current sense - would gain nothing. (...) No other revolutionary had the same degree of feeling that the proletariat was a class distinct from the bourgeoisie. (...) What always distinguished Marat, presented as an enlightened man, was the correctness of his vision, the total absence of candor, the profound and even pessimistic realism. Marat was not only one of the most determined and precocious republicans. He also did not conceive of the Republic except in the form of direct rule."
In addition to the abundant and impressive number of issues that were written (L'Ami du Peuple had almost 700 issues in total, not counting the pamphlets and later works), it is even more astonishing when we stop to consider that a large part of all the work produced by Marat during the five years of revolution was almost entirely uninterrupted, but mainly clandestine. He managed not to be prevented even by laws (such as the decree of March 9, 1793, which obliged members of the Convention who were newspaper editors to choose between legislation and journalism) from continuing to produce and publish his writings.
Today's date is important and significant for history - the history of journalism and the revolution, but especially and undoubtedly the history of Marat. L'Ami du Peuple was, above all, a character. He is a truly dedicated patriot, brave and fearless, who cares about his fellow citizens and the people. He is an important character for Marat because the two, at a certain point, become one. L'Ami du Peuple, who initially appears as the construction of a publicity strategy, quickly becomes a kind of romantic hero of the revolution, with whom Marat identifies and whom he also uses to continue ceaselessly defending what was right for him, what fit in with his very well-founded and observed political and social principles. The previous Marat, the Marat Man of the Enlightenment, physicist, doctor and experimenter, had a passion that managed to outshine all his other interests: politics, and of that there is no doubt. Marat found himself moved by this political passion a few times before the Revolution - Chains Of Slavery (1774), for example, which was written incessantly over just three months, with mainly political aims, is living proof of Marat's burning passion in this area - but none of the times he expressed his interest was as strong and as significant for him as the creation of L'Ami du Peuple, which signified Marat's definitive entry into the revolution. L'Ami du Peuple was important to Marat because it was through it that he was able to express and make his politics heard; because L'Ami du Peuple made Marat so passionately committed to a revolution that it gave him, definitively, a homeland: the France.
#l'ami du peuple day!!! 🦦#this is very personal to me sorry for the longmaratposting#marat#l'ami du peuple#jean paul marat#french revolution#my posts
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
1793 – Jean-Paul Marat
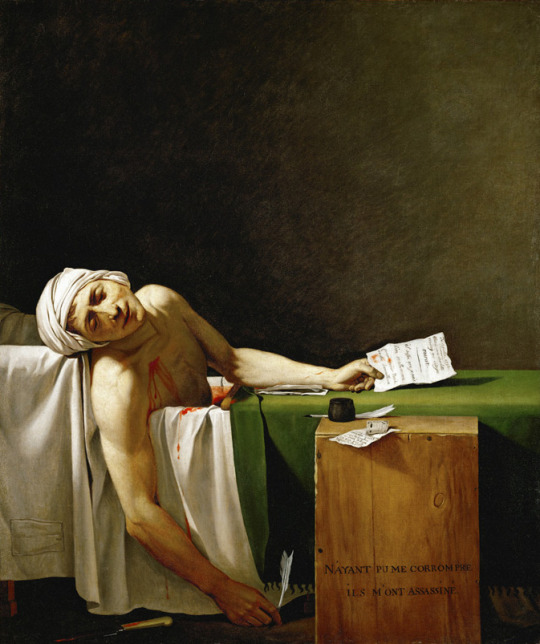

Journalist and French revolutionary Jean-Paul Marat is assassinated in his bathtub by Charlotte Corday, a member of the opposing political faction.


Jean-Paul Marat (UK: /ˈmærɑː/, US: /məˈrɑː/,[1][2]French: [ʒɑ̃pɔl maʁa]; born Mara; 24 May 1743 – 13 July 1793) was a French political theorist, physician, and scientist.[3] A journalist and politician during the French Revolution, he was a vigorous defender of the sans-culottes, a radical voice, and published his views in pamphlets, placards and newspapers. His periodical L'Ami du peuple (Friend of the People) made him an unofficial link with the radical Jacobin group that came to power after June 1793.

His journalism was known for its fierce tone and uncompromising stance toward the new leaders and institutions of the revolution. Responsibility for the September massacres has been attributed to him, given his position of renown at the time, and a paper trail of decisions leading up to the massacres.[4] Others posit the collective mentality that made them possible resulted from circumstances and not from the will of any particular individual.[5] Marat was assassinated by Charlotte Corday, a Girondin sympathizer, while taking a medicinal bath for his debilitating skin condition. Corday was executed four days later for his assassination, on 17 July 1793.
#Jul.13.1793#date of death#Jean-Paul Marat#Swiss-French physician#scientist#theorist#assassination#Charlotte Corday#history today
1 note
·
View note
Photo

13th July 1793, murder of French political theorist, physician and journalist Jean-Paul Marat. A radical voice during the early years of the French Revolution, Marat championed the voice of the poor through his periodical ‘L'Ami du peuple’ (Friend of the People), aligning himself with the radical Jacobins. Upon the ascension of the Jacobins to power this same year, they sought to eradicate their moderate rivals known as the Girondins. One Girondin sympathiser and royalist named Charlotte Corday, one this day gained access to Marat’s house, while he was taking a medicinal bath to aid the debilitating skin condition he suffered from. After claiming that she had vital information on a group of escaped Girondins, she withdrew a five-inch kitchen knife out from her corset, and brought it down hard into Marat's chest. For the murder Charlotte Corday was guillotened four days later, claiming "I killed one man to save 100,000." Marat was later immortalised the same year by the French painter Jacques-Louis David in his painting, ‘The Death of Marat’. 14th July 1789, pre revolutionary tensions in Paris culminate at the site of the Mediaeval prison known as the Bastille. Although only housing seven prisoners on this day, the fortress was seen as representing the pinnacle of monarchical abuse of power. With rioting already occurring across Paris, hostilities began at the Bastille by impassioned speeches by French journalist and revolutionary Camille Desmoulins, and one of the Bastille’s own residents, the Marquis De Sade, who was removed at the beginning of the month, for shouting from the window of his cell, that the prison authorities planned to massacre the inmates, (continued in the comments). #gothichorrorart #romanticismart #romanticism #gothichorror #gothicacademia #frenchrevolution #bastille #bastilleday #bastilleday🇫🇷 #guillotine #gothicillustration #darkacademiaaesthetic #frenchhistory #tarotart #gothicprint #gothicprints #darkromance #darkromantic #gothicliterature #darkarts #darkillustration #tarothistory #darkartwork #darkartandcraft #darkaesthetic #darkartistssubmission #headlessportrait #18thcenturyhistory #19thcenturyhistory #gothichistory https://www.instagram.com/p/Cf_pVaROUHe/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#gothichorrorart#romanticismart#romanticism#gothichorror#gothicacademia#frenchrevolution#bastille#bastilleday#bastilleday🇫🇷#guillotine#gothicillustration#darkacademiaaesthetic#frenchhistory#tarotart#gothicprint#gothicprints#darkromance#darkromantic#gothicliterature#darkarts#darkillustration#tarothistory#darkartwork#darkartandcraft#darkaesthetic#darkartistssubmission#headlessportrait#18thcenturyhistory#19thcenturyhistory#gothichistory
1 note
·
View note
Text
why are we, as a society, so morbid
#i was wondering if anyone ever fully translated all of l'ami du peuple...#do people really think about cirque du soleil that much?
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Marat: YOU THINK I HAVE TIME TO BE NORMAL??!!?
Robespierre: *frightened*
#latest l'ami du peuple headline:#'normal people scare me uwu'#french revolution#frev#incorrect quotes#marat#robespierre
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ekphrasis in The Danton Case, Thermidor, and their adaptations
Ekphrasis is invoking a piece of visual media into a literary piece. It can be done for a variety of reasons, from entirely pragmatic (mostly grounding the literature in reality - if the invoked piece is a real piece of art, one you could find in a museum, for example) or more poetic (drawing some symbolic meaning between the piece of art and the idea behind the text).
In Przybyszewska's plays ekphrasis is nonexistent, at least on the foreground. I don't recall any clearly established visual, given to the readers by the original author. It's not weird in any way - how many pieces of medai do you recall which refrain from its sophisticated and additional piece of subtext and iformation? Hundreds, probably. The only other artistic thing that she has weaved into her plays is La Marseillaise, which is invoked twice in The Danton Case. There are also three book references to Othello, Orlando furioso and this one book Robespierre summarizes to Saint-Just when he's talking about hatred (but of which I have no idea if it's a real one - it probably is - or not). Other than that - nothing, plus the books count only a little, forekpfrasis should be, as I said, visual in nature.
Of course, the historical aspect of her works is what grounds them in our reality, and so cleverly, too (seeing as they're not really historical plays in any way or form, but manage to fool most anybody). And thanks to her extensive stage directions, we have no need of any additional element helping us visualize the scenes, for she does it perfectly enough on her own.
However, seein as these are plays calls for a mirror ekpfrastic effect and thus theatrical and cinematographical adapations are born. And they, on the other hand, have a potential to be filled to the brim with visual refernces. Here I would like to have a look at a few, which are taken from one of the most well known staging and the famous Wajda movie (plus some). In no particular order, there goes:

This is the very first scene of a controversial theatre adaptation of The Danton Case. Instead on portraying Robespierre as a firm leader, who only in the very end collapsed temporarily under the huge responsibility he now had to bear, the director decided to portray him as someone physically weak, not in the sense Danton meant when he called him a weakling, but in the sense of somebody who already bears so much responsibility, pain, physical ailments, doubts and whatnot. Just: everything, everythin a human could possible deal with, he deals with, and has to do so in a way that doesn't make people suspiscious about his "shortcomings". There is a interesting parallel between him and Saint-Just, whose upright and unbreakeable character is symbolised by a neck braces, something which people wear after a spine endangering accidents - and incidentally, wasn't it Saint-Just who accused Robespierre of "breaking his spine"? But not in this adaptation, oh no - here their very last scene is cut extremely short and they recite the last few sentences along with some Thermidor lines as two floating heads, a vision into the future which awaits them.
Enough about Saint-Just, though, let's focus on Robespierre and Marat. I must admit I know next to nothing about him, only what some passage here and there in this or that historical study might tell me, but I know, as does everybody, that he was known as L'ami du Peuple, which is why of the reasons, I think, why the director took this image and transposed it onto Robespierre: to make him even more likeable, to show for the umpteenth time that it is Robespierre whom we should cheer on and whom we should feel sorry for. This might also be a parallel between their both's tarnished health, their premature deaths and - last but not least - the role of an icon of the Rvolution both of them play in nowadays' audience's minds. You don't have to study history to knowwho Robespierre was, you don't have to study art to know this painting. Even if you don't agree with some more in-depth explanation of linking this person to this painting, it is a good opening image. It captures our attention in a good way.

I had mention Saint-Just and there he is, in the background of the picture, symbolically assisting Danton and his clique in their last moments. Instead of shwoign them in torn shirts, the director went into another direction altogether and enshrouded them in white sheets from heads to toes, making them all look like very stereotypical ghosts, whom they will all become in just a couple of moments.
In Polish culture, the first thing that comes to mind when talking about ghosts is Dziady, an old slavic tradition that is now replaced with the Catholic All Souls Eve. Dziady is no longer, apart from perhaps some small minorities who still practice old pagan faiths, but as a ritual, they are immortalised in a play by Adam Mickiewicz, undoubtedly the greatest Polish poet ever. Everybody know this play, some scens - by heart, and they were and are being staged pretty much constantly from one point on. Needless to say, they inspire a lot of art, and I decided to show this very fmous poster by the most famous Polish poster designer, Franciszek Starowieyski…

…who is important in this case, because he played David in Wajda's movie.
Not many people know - because his other carreer overshadowed by a lot his first one - that Wajda was a painter. Who actually hated his art, some of his pieces are in the national museum of contemporary art in Łódź alongside stars such as Władysław Strzemiński (the hero of Wajda's very last movie), which is a fact he absolutely detested. I dont know, nor do I care, why was that, because what matters is his previous education as an artist at the very least helped him not only to envision the visuals of the movie, but also acquainted him with great works of art. On which he could model this or that setup. I think it's a nice little detail he catsed Starowieyski as David, a real painter acting as another real painter, it adds a layer of reality onto the movie, and presumably makes for a more natural acting in the few scenes he was in his studio (I also think they look alike).
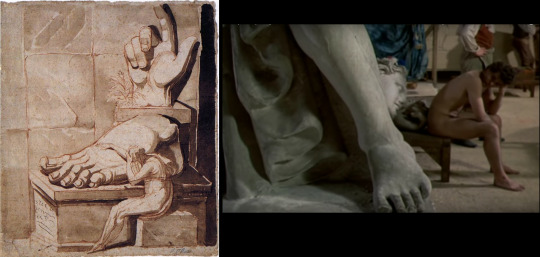
Speaking of David's studio, I once stumbled upon a lecture which drew parallels between some scenes in the movie and some paitings, which was mostly focused on character and costume design, and truth be told didn't contribute much to the overall watching experience of Danton. However, I must admit the lecturer had a very good eye in this one particular case, in which he pointed out that this quick shot in David's studio pretty obviously invokes the Fussli's The Artist's Despair Before The Grandeur Of Ancient Ruins. I don't think it's a coincidence (or at the very least, would be funny if it were) this shot is shown during the scene where Robespierre starts to grasp at desperate measures to save the country/save his own face in the trial. It is an artist's despair, only artist of a different kind. And it is a despair when being faced with a (possible) ruin of something great, even if its greatness is not yet formed, as opposed to the greatness passed.

The very last example I was able to think of was this photo I found of The Danton Case from 1975. It is one of those old, very classical (I presume) adaptations, which are mostly filled to the brim with riddiculosly attractive people and very often deliberately drew from other sources of artistry, like the one pictured above. No matter what the real relationship between Louise Danton and her husband was, in the play it is portrayed as something atrocious, and I cringe whenever directors try to make it something else without good reasons for doing so, so I am very glad in the past at least they stuck with classicaly depicted acts of violation against women, not because it is a violation, but because in the classical stories (like the myth of Persephone shown in the sculpture above) the woman will usually get her revenge. Just like Przybyszewska's Louison did.
Thank you for bearing with me until the end, and if you have any other examples of this come to your mind, I compel you to share them with me!
List of pieces of art in the order of their appearance:
Jacques-Louis David, The Death of Marat
Franciszek Starowieyski, Dziady
Jacques-Louis David, Self-portrait
Heinrich Fussli, The Artist's Despair Before The Grandeur Of Ancient Ruins
Gianlorenzo Bernini, The Rape Of Persephone
#Stanisława Przybyszewska#stanislawa przybyszewska#andrzej wajda#the danton case#sprawa dantona#thermidor#jan klata#jerzy krassowski#jacques louis david#heinrich fussli#gianlorenzo bernini#art#ekphrasis#franciszek starowieyski#painting#sculpture#ekfraza#rzeźba#sztuka#Ekphrasis is my current hobby so I had to pull this together
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Red Palace by June Hur (April 2022)

Joseon (Korea), 1758. There are few options available to illegitimate daughters in the capital city, but through hard work and study, eighteen-year-old Hyeon has earned a position as a palace nurse. All she wants is to keep her head down, do a good job, and perhaps finally win her estranged father's approval.
But Hyeon is suddenly thrust into the dark and dangerous world of court politics when someone murders four women in a single night, and the prime suspect is Hyeon's closest friend and mentor. Determined to prove her beloved teacher's innocence, Hyeon launches her own secret investigation.
In her hunt for the truth, she encounters Eojin, a young police inspector also searching for the killer. When evidence begins to point to the Crown Prince himself as the murderer, Hyeon and Eojin must work together to search the darkest corners of the palace to uncover the deadly secrets behind the bloodshed.
Would I recommend it to anyone? Yes, I really liked this book and I'd recommend it to people who like historical mysteries. Especially if you like Korea or are curious about it.
Level of (dis)satisfaction based on the summary and my expectations? Honestly, I was just very curious and I wanted the mystery to stay a mystery for as long as possible. I hate guessing correctly half of the plot by page 10 and this story delivered. So I was agreeably surprised.
My thoughts on it? The plot was very nicely executed, I was still trying to guess who the culprit was almost until the end. Everything that happened around the investigation (Hyeon's relationship with her parents and Eojin, the secondary characters...) everything was so well done, I loved this book.
I have to add that, as someone who knows nothing about Korean culture or history outside of the 3 k-dramas I've watched in my life, I had no troubles keeping up. Even when there were Korean words or expressions it wasn't a problem because they were always followed by a little translation or explanation, or I could understand through context. I really appreciated that because it shows that June Hur wrote her book with the plebs who don't know a thing about Korea in mind. Plus, it didn't cut into the flow of the story or the sentences, it was very smooth.
French version under the cut
Joseon (Corée), 1758. A la capitale, peut d'options s'offrent aux filles illégitimes, mais en travaillant dur et en étudiant, Hyeon, 18 ans, a obtenu une position en tant qu'infirmière du palais. Tout ce qu'elle désire est garder la tête basse, faire du bon travail, et peut-être enfin gagner l'approbation de son père.
Mais Hyeon est soudain plongée dans le monde obscur et dangereux de la politique de cour lorsque quatre femmes sont assassinées dans la même nuit et que le principal suspect est l'amie la plus proche et mentore de Hyeon. Déterminée à prouver l'innocence de la professeure qu'elle aime tant, Hyeon se lance dans sa propre enquête secrète.
Dans sa quête de la vérité, elle rencontre Eojin, un jeune inspecteur de police également à la recherche du tueur. Lorsque les indices commencent à pointer dans la diction du Prince Héritier, Hyeon et Eojin doivent travailler ensemble pour chercher les recoins les plus sombres du palais pour découvrir les secrets mortels cachés derrière le carnage.
Est-ce que tu le conseillerais à quelqu’un ? Oui, j’ai vraiment beaucoup aimé ce livre et je le conseille à ceux qui aiment les mystères historiques. Surtout si vous aimez la Corée ou que vous êtes curieux.
Niveau de déception/satisfaction par rapport au résumé et tes attentes ? Honnêtement, j’étais juste très curieuse et je voulais que le mystère reste un mystère le plus longtemps possible. Je déteste deviner la moitié de l’histoire d’un livre au bout de 10 pages et cette histoire-là a fait son taff. Donc j’ai été agréablement surprise.
Avis sans spoiler ? L’intrigue était vraiment bien menée, j’essayais de deviner qui était le coupable quasiment jusqu’à la fin. Tout ce qui se passait autour de la résolution du meurtre (la relation entre Hyeon et ses parents, sa relation avec Eojin, les personnages secondaires…) tout était tellement bien fait, j’ai adoré ce livre.
Je dois ajouter qu’en tant que personne qui ne connaît rien à la culture ou l’histoire coréenne à part pour les 3 k-drama que j’ai regardé dans ma vie, je n’ai eu aucun problème à suivre. Même lorsqu’il y avait des termes ou des expressions coréennes ce n’était pas un problème parce qu’il y avait toujours une petite traduction ou explication derrière ou alors je comprenais grâce au contexte. J’ai beaucoup apprécié parce que ça montre que June Hur a écrit son livre en pensant aux gueux qui n’y connaîtraient rien, puis le tout restait très fluide, ça n’impactait pas le rythme des phrases ou de l’histoire.
#the red palace#books#booklr#book recommendations#book recs#book review#book reviews#mystery books#mysteries#ya books#historical fiction#asian literature#june hur
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
#13JULY1793
Today, Jean Paul Marat had died.

Jean Paul Marat was killed by Charlotte Corday, on his flat in rue de Cordeliers, while he was in his bathtub.
Marat was born in Switzerland on 24 May 1743, first son of a priest from Sardinia (My country 🤩) and a swiss mom.
He was a doctor and a journalist. He was called "l'Ami du peuple" (Friend of the people).
He never had children.
Today I want to remember him❤
(And of course, because HE IS MY EROTIC DREAM. And I don't know why)

#french revolution#jean paul marat#charlotte corday#marat#frev history#french history#history#frev#france#revolution francaise
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
I know about anthropology but how would it be possible to study frev through this discipline?
Ok, first of all, it’s important to know that when I say “anthropology”, I mean it in the European sense (socio-cultural anthropology, which studies culture). In North American sense, it can include anything from archaeology and biological anthropology to socio-cultural anthropology and linguistic anthropology.
Since socio-cultural anthropology mainly focuses on the present, existing cultures, any study of frev would be inter-disciplinary. There are generally two ways to go:
1) Study specific aspects of culture from the late 18th century France/Frev (for example, how they understand concepts such as virtue, masculinity and femininity, sexuality; tensions between centre and periphery, the role of religion, etc.)
2) Study how we, today, perceive frev and what it tells about us (for example, how today’s political situation makes frev ideas more appealing to young people, or changing attitudes towards Robespierre, SJ, etc. and what those can tell us about today’s understanding of politics, sexuality, masculinity, etc.)
Both are very exciting to me, although #2 is more accessible to me atm because my French is too weak to tackle primary sources (and you can’t study frev properly without primary sources or sources in French).
If we take anthropology in the North American sense, frev can be (and is) studied in different ways: analysis of material culture from the revolutionary period (archaeology), or studying human remains and DNA (biological anthropology), such as that study on Marat’s blood from l'Ami du Peuple copy he was holding when he got stabbed.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
In honor of Marat's birthday I found a complete (?) collection of L'Ami du Peuple ! Happy reading frev pals and happiest of birthdays to Jean-Paul, wherever he may be. In memory of our forever favorite sewer-dwelling doctor, scientist, and revolutionary friend of the people.



#french rev#frev#french revolution#frev resources#marat#jean paul marat#resources#history#maratposting#queue
136 notes
·
View notes
Text
L'Ami du Peuple No 214, Tuesday 7th September 1790, my translation
L’Ami du Peuple au sieur Necker
From the Friend of the People to Sire Necker
Si votre démission, Monsieur, n’était pas feinte, si votre retraite était sans retour, si vous aviez rendu fidèlement vos comptes, si vous étiez puni de vos malversations, la justice satisfaite m’imposerait silence. La haine que j’ai portée à un administrateur infidèle, à un ministre dangereux, à un suppôt redoutable du despotisme, expirerait avec votre pouvoir et je ne verrais plus en vous qu’un particulier dont je dédaignerais de m’occuper un moment.
If your resignation, Sir, were not a pretence, if you were to retire with no return, if you had given your explanation faithfully, if you were punished for your malversations, I would be made silent by justice well-served. The hatred that I have held for an unfaithful administrator, for a dangerous minister, for a dreadful supporter of despotism, would expire along with your power and I would no longer see you as anyone other than a private individual whom I would loathe to dwell on for one moment more.
Mais je crois assez connaître votre caractère ambitieux, pour me défier du parti que vous venez de prendre, pour regarder votre départ comme l’effet d’un orage que vous prévoyez et dont vous voulez éviter l’éclat, ou comme le dernier des pièges que vous voulez tendre aux Français. Vous le couvrez du prétexte de l’altération de votre santé, du retour de ces maux qui vous ont mis l’hiver dernier sur le bord de la tombe et qui n’empêchèrent pas le mort ou le mourant de figurer à l’Assemblée nationale pour séduire le peuple. Vous alléguez aussi les inquiétudes mortelles de votre compagne chérie qui vous presse d’aller retrouver l’asile dont vous a tiré l’Assemblée nationale. Mais en dépit de vous, la vérité vient se placer au bout de votre plume.
But I believe I understand your ambitious character well enough to distrust your recent course of action, and see your departure as the effect of a storm that you anticipate and whose thunder you wish to avoid, or as the last of the pitfalls that you wish to set for the French. You mask it with the excuse of the deterioration of your health, of the return of those illnesses that put you at death’s door last winter and did not prevent the dead or dying from standing in the National Assembly to seduce the people. You also put forward the deadly worry of your beloved companion who is pressing you to return to the asylum from which the National Assembly has taken you. Yet regardless of you, the truth appears on the tip of your pen.
En achevant sa phrase, l’ex-ministre donne aux pères de la patrie la clef de l’énigme.
“A l’époque de mon arrivée, Messieurs, leur dites-vous, vous approchez du terme de votre session et je suis hors d’état d’entreprendre une nouvelle carrière.” Ce qui signifie : Il faut, Messieurs, que je prenne enfin mon parti ; il n’y a que des gens de votre espèce qui puissent maintenir en place un agent de la mienne ; vous approchez de la fin de votre bail et je suis hors d’état de lutter contre vos successeurs qui, probablement, s’aviseront d’abord de vouloir faire leur devoir, qui m’éplucheront des pieds à la tête et qui me forceront de changer de marche, si plutôt ils ne me livrent à la vindicte publique.
As he finishes his statement, the ex-minister gives the fathers of the patria the key to the enigma.
“At the time of my arrival, Gentlemen,” you say to them, “you are approaching the close of your session and I am not in no fit state to undertake a new career.” Which means: I must, Gentlemen, take my side at last; only those of your type can keep an agent of my type in place of power; you are approaching the end of your lease and I am in no fit state to fight your successors who, probably, will dare to do their duty first, will examine me from head to foot and will force me to change my course, if not expose me to the public vengeance.
Permettez-moi de jeter un coup d’œil rapide sur la manière dont vous justifiez votre administration. Voici vos propres expressions :
“Vous m’avez demandé, Messieurs, un compte de la recette et de la dépense, à[1] commencer du premier mai 1790. Je vous l’ai remis. Vous avez chargé votre comité des Finances de l’examiner. Je crois qu’il aurait déjà pu reconnaître s’il existe quelque dépense ou quelque autre disposition digne de reproches. Cette recherche est la seule qui concerne essentiellement le ministère, car l’inspection des titres, la révision des quittances sont particulièrement applicables à la gestion des payeurs, des receveurs et des différents particuliers comptables.”
[1] On dira sans doute que le comité des Finances s’entendait avec le fripon, pour n’avoir fixé qu’à cette époque la reddition des comptes.
Let me take a glance at the way you justify your administration. Here are your own expressions:
“You have asked me, Gentlemen, for an account of the revenue and expenditure, starting [1] from the 1st of May 1790. I have given it to you. You have tasked your Finance committee to examine it. I believe that they would have already recognised if there exists any expenditure or other arrangement worthy of reproach. This investigation is the only one that the ministry is essentially of concern to the ministry, since the inspection of the securities, and the reviewing of the receipts are particularly applicable to the management of the payers, the receivers and the various private individuals taking accounts.”
[1] Marat’s note: It will be said doubtlessly that the Finance committee went along with the rascal, having only secured accountability at that time.
Ce qui veut dire que sans s’amuser à vérifier les pièces, vraies ou fausses, le comité des Finances doit se borner à examiner si vous avez bien additionné et soustrait. Or, soyez-en sûr, Monsieur, personne ne s’avisera de douter de votre savoir-faire.
This means that without wasting time checking the documents, be they true or false, the Finance committee must be limited to examining if you have correctly added and subtracted. Yet, you may rest assured, Sir, nobody will dare to doubt your know-how.
La fin de votre lettre est digne d’observation. La voici :
“Les inimitiés, les injustices dont j’ai fait l’épreuve m’ont donné l’idée de la garantie que je viens d’offrir. Mais quand je rapproche cette pensée de ma conduite dans l’administration des Finances, il m’est permis de la réunir aux singularités qui ont accompagné ma vie !”
The end of your letter is worth noting. Here it is:
“The enmities, the injustices that I have stood the test of have prompted me to think of the guarantee that I have now offered. But when I bring this thought together with my conduct through the administration of Finances, I am entitled to see it as one of the singularities that have characterised my life!”
Ce n’est pas là, Monsieur, soit dit en passant, le langage d’un administrateur intact, qui s’est empressé de mettre sous les yeux du public, le fidèle tableau de sa gestion, ce n’est pas là le ton d’un cœur pur, oppressé de douleur, qui s’enveloppe dans le manteau de son innocence, moins encore celui d’une âme fière au-dessus de la calomnie, mais le ton d’un homme sans honneur, qui ne s’était jamais offensé des soupçons injurieux tant de fois élevés sur son administration, au milieu même du sénat, mais celui d’un petit intrigant éconduit. Vous accusiez l’injustice du sort. Eh ! qu’y a-t-il donc de si étrange dans ce qui vous arrive aujourd’hui ? Depuis dix ans, vous receviez nos adorations en vous moquant de notre simplicité, et vous nous accabliez d’emprunts. Vous avez affecté de rendre compte de votre gestion dans un temps où rien ne vous y obligeait; vous avez imposé ce devoir à vos successeurs; vous avez refusé dès lors de vous y soumettre vous-même, malgré les instances du public; vous vous êtes joué des ordres des représentants de la nation; enfin vous avez remis un compte où l’on ne comprend rien; vous nous avez donné mille raisons puissantes de vous regarder comme le chef des accapareurs du grain et du numéraire, le père du projet de famine qui a fait notre désespoir une année entière; vous nous avez épuisés par un impôt vexatoire; vous avez opprimé les pauvres dont vous vous disiez le père; vous vous êtes opposé au plan de la liquidation des dettes de l’Etat. Vous fuyez au moment où l’on vous en demande un meilleur, et vous avez le courage de vous plaindre ?
This here, Sir, is incidentally not the language of an intact administrator, who quickly gave the faithful record of his management, to put it under the eyes of the public, this is not the tone of a pure heart, overwhelmed by sorrow, protecting itself in the cloak of its innocence, still less that of a proud spirit beyond the reach of slander, but it is the tone of a man without sense of honour, who has never been offended by the injurious suspicions levelled so many times against his administration, even among the Senate, it is the tone of a little scheming man spurned. You blamed the injustice of your lot. Eh! But what in your current situation is so surprising? For ten years, you have received our adorations while mocking our simplicity, and you have overloaded us with loans. You assigned yourself to account for your management at a time where you were under no obligation to do so; you imposed this duty on your successors; you refused thereupon to submit to it yourself, despite the insistence of the public; you toyed with the orders of the representative of the nation; finally you left us with an account that is incomprehensible; you have given us a thousand compelling reasons to regard you as the chief of the monopolisers of grain and of cash, the father of the famine project that has caused our despair for a whole year; you have depleted us with a vexatious tax; you have oppressed the poor whose father you claimed to be; you have opposed the plan of the liquidation of the debts of the State. You flee as soon as we ask for a better account, and now you have the nerve to complain?
Vous accusez le destin de la singularité des événements de votre vie. Que serait-ce si, comme l’Ami du Peuple, vous étiez le jouet des hommes et la victime de votre patriotisme ! Si, en proie à une maladie mortelle, vous aviez, comme lui, renoncé à la conservation de vos jours pour éclairer le peuple sur ses droits et sur les moyens de les recouvrer ! Si, dès l'instant de votre guérison, vous lui aviez sacrifié votre repos, vos veilles, votre liberté ! Si vous vous étiez réduit au pain et à l’eau pour consacrer à la chose publique tout ce que vous possédiez ! Si, pour défendre le peuple, vous aviez fait la guerre à tous ses ennemis ! Si, pour sauver la classe des infortunés, vous étiez brouillé avec tout l’univers, sans vous ménager un seul asile sous le soleil ! Si, accusé tour à tour d’être vendu aux ministres que vous démasquiez, au despote que vous combattiez, aux grands que vous accabliez, aux sangsues de l’Etat auxquelles vous vouliez faire rendre gorge, si, décrété tour à tour par les jugeurs iniques dont vous auriez dénoncé les prévarications, par le législateur dont vous auriez démasqué les erreurs, les iniquités, les desseins désastreux, les complots, la trahison, si, poursuivi par une foule d’assassins armés contre vos jours, si, courant d’asile en asile, vous vous étiez déterminé à vivre dans un souterrain pour sauver un peuple insensible, aveugle, ingrat! Sans cesse menacé d’être tôt ou tard la victime des hommes puissants auxquels j’ai fait la guerre, des ambitieux que j’ai traversés, des fripons que j’ai démasqués, ignorant le sort qui m’attend et destiné peut-être à périr de misère dans un hôpital, m’est-il arrivé de me plaindre ? Il faudrait être bien peu philosophe, Monsieur, pour ne pas sentir que c’est le cours ordinaire des choses de la vie. Et il faudrait avoir bien peu d’élévation dans l’âme pour ne pas se consoler par l’espoir d’arracher, à ce prix, 25 millions d’hommes à la tyrannie, à l’oppression, aux vexations, à la misère, pour les faire enfin arriver au bonheur.
You blame fate for the oddity of the events in your life. But what if, like the Friend of the People, you were toyed by men and victimised for your patriotism! What if, plagued by a life-threatening disease, you had, like him, renounced the preservation of your living days to clarify the rights and means to recovering rights to the people! What if, from the instant you were healed, you had sacrificed for them your repose, your waking hours, your freedom! What if you were reduced to bread and water to dedicate all your possessions to the res publica! What if, to defend the people, you had warred on all their enemies! What if, to save the class of the unfortunate, you fell out with the whole universe, without holding for yourself one single asylum under the sun! What if, you were alternately accused of being bought by the ministers you unmasked, by the despots you combatted, by the great ones you condemned, by the bloodsuckers of the State from whom you sought reparations, what if, you were in turn under the decrees of the iniquitous judges whose prevarication you would have denounced, by the legislator whose errors, iniquities, appalling purposes, schemes, and treason you would have unmasked, what if, you were pursued by a mob of assassins armed against your livelihood, what if, running from asylum to asylum, you were determined to live underground so that you might save an insensible, blind, and ungrateful people! Always under the threat of eventually falling victim to the powerful men I have fought against, to the ambitious men I have crossed, to the scoundrels I have unmasked, with no idea of the lot that awaits me and probably doomed to perish miserably in some hospital, have I ever complained? A quite unsound philosopher alone, Sir, would be able to deny that this is ordinarily the way things go. And quite undignified a soul alone would not find solace in the hope to wrest, at this price, five and twenty million men from tyranny, oppression, from vexation, and from misery, to see that they eventually find their own happiness.
Quant à vous, Monsieur, vos destinées sont un peu différentes. Vous avez sacrifié les adorations d’un peuple idolâtre aux sourires d’une cour perfide, dont peut-être vous avez encore la faveur. Mais il vous reste des trésors. Vous ne passez plus pour Aristide, mais vous êtes encore Luculle. Est-il un seul monarque qui ne s’empressât de vous offrir une retraite honorable, est-il un seul plaisir dans la vie que puisse donner la fortune et qui vous soit refusé ? Voluptés, honneurs, dignités, tout vous attend. Vous pouvez disposer de tout, excepté de l’estime des cœurs droits et des âmes élevées, ou de la gloire qui n’est pas non plus le prix de l’argent.
As for you, Sir, your destiny is a little different. You have sacrificed the adorations of an idolatrous people for the smiles of a perfidious court, whose favour you still will have. But you are left with treasures. As Aristides you can pass no more, but as Lucullus you remain no less. Is there a single monarch who would not be quick to offer you an honourable retirement, is there a single pleasure in life that fortune grants denied to you? Voluptuousness, honours, dignities, all await you. You can own everything, except the esteem of upright hearts and dignified souls, and except glory, which money still cannot buy.
Quoi qu’il en soit, Monsieur, si votre retraite n’est pas jouée, dès aujourd’hui, je m’impose à votre égard un éternel silence. J’ai travaillé à votre chute avec un zèle peu commun ; mais à l’instant que vous n’êtes plus un homme public dangereux, vous redevenez pour moi un particulier sans conséquence.
Be that as it may, Sir, as long as your retirement is not a prank, from today, I impose on you an eternal silence. To defeat you I have worked with quite uncommon zeal; but the moment you stop being a dangerous public figure, to me you revert to being a private individual of no importance.
11 notes
·
View notes