#homoneanderthalensis
Text
Neandertaller Kimdi ve Onlara Ne Oldu?
Neandertaller, Homo neanderthalensis olarak bilinen ve günümüzden yaklaşık 250.000 ila 40.000 yıl önce yaşamış bir insan türüdür. İlk Neandertal fosili, Almanya'nın Düsseldorf kenti yakınlarındaki Neander Vadisi'nde 1856 yılında keşfedilmiştir. Bu keşif, Neandertallerin adını aldığı Neander Vadisi'nin Almanca'daki eski yazım biçiminden gelmektedir (thal: vadi). Fosilleri muhafaza etmeye uygun kireç taşı mağaralarda yaşadıkları için haklarında oldukça fazla bilgiye sahibiz ve bu bilgi modern kültürde “mağara adamı” imajını yaratmıştır (Vikipedi: Özgür Ansiklopedi) (Eksiseyler).
Neandertallerin Kökeni ve Özellikleri
Neandertaller, modern insanlardan (Homo sapiens) daha kısa ve daha güçlü yapılarıyla bilinirlerdi. Daha kalın kemik yapıları, geniş burunları ve çıkıntılı kaş kemerleriyle tanınan Neandertaller, soğuk iklimlere uyum sağlamışlardı. Beyin hacimleri modern insanlara yakın olmakla birlikte, yüz yapıları ve vücut oranları farklıydı. Soğuk iklimlere uyum sağlamak için geniş burun delikleri ve daha büyük akciğer kapasiteleri bulunuyordu (Brain Center İstanbul) (Vikipedi: Özgür Ansiklopedi).
Neandertallerin Yaşam Alanları ve Kültürleri
Neandertaller, Avrupa'nın geniş bir alanında ve Batı Asya'da yaşamışlardır. Fosil kalıntıları İspanya'dan Sibirya'ya kadar geniş bir coğrafyaya yayılmıştır. Neandertallerin en yoğun yaşadığı bölgeler, modern Fransa, Almanya, İspanya ve Hırvatistan'da bulunan mağaralar olmuştur. Bu bölgelerde keşfedilen fosiller ve arkeolojik kalıntılar, Neandertallerin yaşam tarzı ve kültürü hakkında değerli bilgiler sunmaktadır (Evren Atlası).
Neandertaller, taş aletler yapmada ustaydılar ve Musteryen kültürü olarak bilinen bir alet kültürü geliştirmişlerdi. Musteryen alet kültürü, genellikle bıçağın yalnızca bir tarafının yontulduğu temel mızrak uçları ve baltalardan oluşuyordu. Bu kültür, Neandertallerin avlanma ve günlük yaşam aktivitelerinde oldukça etkili olduklarını göstermektedir. Ayrıca Neandertaller, ateşi kullanmayı biliyor ve avladıkları hayvanları pişirerek tüketiyorlardı (Evren Atlası) (Vikipedi: Özgür Ansiklopedi).
Neandertaller sosyal varlıklardı ve karmaşık bir sosyal yapıya sahiptiler. Aralarındaki yaralı ve sakat bireylerle ilgilendiklerine dair kanıtlar bulunmuştur. Bu, Neandertallerin empati yeteneği ve topluluk içinde işbirliği yaptığını göstermektedir. Ayrıca mağara resimleri yapmışlar ve sembolik amaçlarla pigmentler kullanmışlardır. Hatta müzik aletleri olarak flütler bile yapmış olabilecekleri düşünülmektedir (Brain Center İstanbul) (Evren Atlası).
Neandertaller ve Modern İnsanlar
Genetik çalışmalar, modern insanın DNA'sının %1-2'sinin Neandertallerden geldiğini göstermektedir. Bu durum, Neandertaller ve Homo sapiens'in çiftleştiğini ve gen alışverişinde bulunduğunu ortaya koymaktadır. Özellikle Afrikalı olmayan modern insanların DNA'sında bu genetik izler daha belirgindir. Bu genler, bazı hastalıklara karşı bağışıklık kazanmamıza bile yardımcı olmuştur. Örneğin, Neandertallerden gelen bazı genlerin, Epstein-Barr virüsü gibi hastalıklara karşı modern insanları daha dirençli hale getirdiği bilinmektedir (Evrim Ağacı) (Evrim Ağacı).
Neandertaller ve modern insanlar arasındaki etkileşimler, hem kültürel hem de genetik alışverişi içermektedir. Neandertallerin bazı teknolojik yenilikleri modern insanlardan öğrenmiş olabileceği gibi, modern insanlar da Neandertallerden avlanma ve barınma teknikleri öğrenmiş olabilirler. Bu etkileşimler, iki türün birbirine karşı düşmanca değil, aksine işbirlikçi bir şekilde yaşadığını düşündürmektedir (Brain Center İstanbul) (Evren Atlası).
Neandertallerin Yok Oluşu
Neandertallerin yok oluşuna dair çeşitli teoriler bulunmaktadır. Bunlar arasında modern insanlarla rekabet, hastalıklar, iklim değişiklikleri ve genetik faktörler yer almaktadır. İklim değişiklikleri, kaynakların azalmasına ve yaşam koşullarının zorlaşmasına neden olmuştur. Hastalıkların da önemli bir rol oynadığı düşünülmektedir; modern insanlar, daha geniş bir patojen havuzuna maruz kaldıkları için daha güçlü bağışıklık sistemlerine sahiptiler ve bu da Neandertallerin savunmasız kalmasına neden olmuş olabilir (Brain Center İstanbul) (Evren Atlası) (Evrim Ağacı).
Bazı teorilere göre, modern insanlarla Neandertaller arasındaki rekabet de Neandertallerin yok olmasına katkıda bulunmuştur. Daha gelişmiş aletler ve sosyal organizasyonlar, modern insanların Neandertaller karşısında avantaj sağlamasına neden olmuş olabilir. Örneğin, modern insanlar, daha keskin ve etkili av silahları geliştirmişler ve bu da Neandertallerin avlanma ve hayatta kalma becerilerini gölgede bırakmıştır (Evren Atlası) (Evrim Ağacı).
Neandertaller, insan evriminde önemli bir yere sahiptir ve onların incelenmesi, modern insanın evrimini ve adaptasyonlarını daha iyi anlamamıza yardımcı olmaktadır. Hem genetik hem de kültürel mirasları, günümüzde bile insan biyolojisi ve kültürü üzerinde etkili olmaya devam etmektedir. Neandertallerin yok oluşu, büyük olasılıkla birçok faktörün birleşimi sonucu gerçekleşmiştir ve bu olay, insanlığın evrimsel tarihinde önemli bir dönüm noktasıdır (Vikipedi: Özgür Ansiklopedi) (Evrim Ağacı).
Kaynaklar ve İleri Okuma
Kaynaklar ve İleri Okuma
- R. D. Escarcega, et al. (2023). The Tardigrade Damage Suppressor Protein Dsup Promotes DNA Damage In Neurons. Elsevier BV, sf: 103826. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2023.103826
- Military Medical Sciences. (2023). Biological Effects Of Damage Suppressor Gene (Dsup) Expression On Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Military Medical Sciences, sf: 326-333. doi: 10.7644/j.issn.1674-9960.2023.05.002
- GIGAZINE. A Chinese Military Research Team Carries Out A Genetic Experiment To Insert The Gene Of The Strongest Organism Tardigrade" Into Human Stem Cells, To Develop A Super Soldier" Resistant To Nuclear Attack Radiation. (5 Nisan 2023). Alındığı Tarih: 15 Mayıs 2024
- S. Chen. Team Behind Extreme Animal Gene Experiment Eyes Human Nuclear Resistance. (29 Mart 2023). Alındığı Tarih: 15 Mayıs 2024. Alındığı Yer: South China Morning Post
- R. D. Escarcega, et al. (2023). The Tardigrade Damage Suppressor Protein Dsup Promotes DNA Damage In Neurons. Elsevier BV, sf: 103826. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2023.103826
- Evrim Ağacı. Çinli Araştırmacılar Tardigrad Genlerini Kullanarak Süper Askerler Üretmenin Peşinde Olabilir.
İlginizi Çekebilir
İlginizi Çekebilir
- Neandertaller Kimdi ve Onlara Ne Oldu?
- Çinli Araştırmacılar Tardigrad Genlerini Kullanarak Süper Askerler Üretmeye Çalışıyor
- Ölübotlar: Ölümden Sonra (Yapay) Yaşam Olabilir mi?
- Evrim Teorisi ve Genetik Analizler: Bilimsel Bir Bakış
- Miskin Süngerler Bizim İlk Atalarımızdı
Sıkça Sorulan Sorular (SSS)
Neandertaller kimdi ve neden önemliydiler?Neandertaller, yaklaşık 250.000 ila 40.000 yıl önce yaşamış bir insan türüdür. Onlar, modern insanın evrimsel tarihinde önemli bir yere sahiptir ve genetik ve kültürel mirasları günümüzde bile insan biyolojisi ve kültürü üzerinde etkili olmaya devam etmektedir.Neandertallerin modern insanlardan farkı nedir?Neandertaller, modern insanlardan daha kısa ve güçlü yapılarıyla bilinirlerdi. Soğuk iklimlere uyum sağlamışlardı ve geniş burun delikleri ve daha büyük akciğer kapasiteleri vardı. Ayrıca, modern insanlarla kıyaslandığında daha kalın kemik yapısına sahiptiler.Neandertaller nasıl yok oldu?Neandertallerin yok oluşuna dair çeşitli teoriler bulunmaktadır. Modern insanlarla rekabet, hastalıklar, iklim değişiklikleri ve genetik faktörler bu yok oluşta rol oynamış olabilir. Özellikle iklim değişiklikleri ve modern insanlarla rekabetin etkili olduğu düşünülmektedir.Neandertallerin genetik mirası nedir?Genetik çalışmalar, modern insanın DNA'sının %1-2'sinin Neandertallerden geldiğini göstermektedir. Bu genetik miras, bazı hastalıklara karşı bağışıklık kazanmamıza yardımcı olmuştur ve modern insanın evriminde önemli bir rol oynamıştır.
Read the full article
#Antropoloji#Evrim#Fosilkeşifleri#GenetikAraştırmalar#Homoneanderthalensis#İnsanEvrimi#ModerninsanveNeandertalilişkisi#Musteryenkültürü#Neandertalfosilleri#Neandertaller#Neandertalleringenetiği#Neandertallerinyokoluşu#Paleoantropoloji#Tarihöncesiinsanlar#Taşaletler
0 notes
Text
Línea del tiempo sobre la Evolución del Hombre

Esta línea del tiempo proporciona un resumen general de la evolución del hombre, pero es importante tener en cuenta que los descubrimientos y la comprensión científica continúan evolucionando, por lo que los detalles y las fechas exactas pueden estar sujetos a cambios en futuras investigaciones.
- Hace aproximadamente 7 millones de años: Los primeros homínidos aparecieron en África. El más conocido de ellos es el Ardipithecus ramidus.
- Hace aproximadamente 4 millones de años: Los Australopithecus, como el famoso "Lucy", vivieron en África. Estos homínidos eran bípedos y caminaban erguidos.
- Hace aproximadamente 2.5 millones de años: Apareció el género Homo, representado por especies como Homo habilis, que fue el primer homínido en fabricar herramientas de piedra.
- Hace aproximadamente 1.8 millones de años: El Homo erectus se expandió desde África hacia otras partes del mundo, como Europa y Asia. Esta especie fue la primera en abandonar África y utilizar el fuego.
- Hace aproximadamente 300,000 años: Apareció el Homo neanderthalensis en Europa y partes de Asia. Esta especie desarrolló herramientas más avanzadas y mostraba evidencia de comportamiento simbólico.
- Hace aproximadamente 200,000 años: Surgió el Homo sapiens en África. Esta especie es la única superviviente de todos los homínidos y es la que representa a los humanos modernos.
- Hace aproximadamente 70,000 años: Los humanos modernos comenzaron a migrar fuera de África y se dispersaron por todo el mundo.
- Hace aproximadamente 12,000 años: Se produjo el surgimiento de la agricultura y la domesticación de animales, lo que llevó al establecimiento de asentamientos permanentes y al desarrollo de las primeras civilizaciones.
- Hace aproximadamente 5,000 años: Surgieron las primeras civilizaciones antiguas en Mesopotamia, Egipto, India y China, lo que marcó el comienzo de la historia registrada.
- Desde la antigüedad hasta la actualidad: La historia de la humanidad se ha caracterizado por importantes desarrollos científicos, tecnológicos, culturales y sociales, incluyendo el surgimiento de imperios, el Renacimiento, la Ilustración, las revoluciones industriales, las guerras mundiales y la era de la información.
Read the full article
#agricultura#asentamientos#Australopithecus#China#civilizaciones#culturales#desarrolloscientíficos#domesticación#Egipto#evolución#guerrasmundiales#historiaregistrada#hombre#homínidos#Homoerectus#Homohabilis#Homoneanderthalensis#Homosapiens#ilustración#India#Mesopotamia#migración#Renacimiento#revolucionesindustriales#tecnológicos
0 notes
Text
La fluidità cognitiva mantiene giovane il cervello umano
Nel cervello umano si nasconde il segreto dell'eterna giovinezza: lo studio. Pubblicati su Nature Ecology & Evolution i risultati di una ricerca a cui ha partecipato anche il paleoantropologo Antonio Profico dell’Università di Pisa.
C’è una caratteristica che accomuna il cervello di Homo sapiens e Homo neanderthalensis e cioè che entrambi hanno mantenuto un alto livello di interazione tra le aree cerebrali sia nella fase giovanile che nella fase matura e, come in una sorta di sindrome di Peter Pan, non sono mai diventati veramente adulti. Lo dimostra uno studio internazionale pubblicato sulla rivista Nature Ecology & Evolution a cui ha partecipato il paleoantropologo Antonio Profico, ricercatore del Dipartimento di Biologia dell’Università di Pisa, e coordinato dal professor Pasquale Raia dell'Università di Napoli Federico II.

Il ricercatore Antonio Profico
Per studiare l’evoluzione del cervello, un team di ricercatori di università italiane e internazionali ha ricostruito la superficie interna del cranio tramite tecniche di antropologia virtuale. In questo modo gli autori hanno analizzato la forma del cervello in 148 specie di primati viventi e diverse specie di Hominina (Homo neanderthalensis compreso). Oltre alla forma del cervello i ricercatori hanno studiato le interazioni tra le aree cerebrali (integrazione morfologica) utilizzando un nuovo metodo sviluppato a questo scopo e applicato per la prima volta in questo studio.
Gli autori dello studio hanno dimostrato che non sono solo le grandi dimensioni del nostro cervello a renderci differenti dagli altri primati. I ricercatori hanno dimostrato che nelle scimmie antropomorfe (i nostri parenti più prossimi) e nella nostra specie le diverse aree cerebrali presentano alti livelli di integrazione dalla nascita fino allo stadio di sviluppo immediatamente precedente la maturità sessuale. Tuttavia, quando entra nella fase adulta, il cervello delle scimmie antropomorfe perde improvvisamente la coordinazione tra i lobi, probabilmente a favore della specializzazione delle diverse aree cerebrali. Homo sapiens invece mantiene un’alta coordinazione tipica dei cervelli delle antropomorfe giovanili per tutta la vita, non mostrando nessun cambiamento da 'adulto'. Solo un'altra specie vicina a noi, Homo neanderthalensis, mostra segni di questo stesso fenomeno.
"I cervelli dei neandertaliani e degli umani moderni sono molto simili in termini di volume, ma nei Neanderthal il cervello ha una forma diversa, molto più primitiva - spiega Profico - Il fatto che Homo neanderthalensis e Homo sapiens mantengano alti livelli di integrazione cerebrale durante l'età adulta è sorprendente, perché fino ad ora pensavamo che la comparsa del comportamento umano moderno fosse legato quasi esclusivamente alla presenza di un cervello globulare". Homo sapiens è infatti caratterizzato dalla presenza di un cervello molto voluminoso ed è di circa tre volte più grande di quello dello scimpanzè. Nella nostra specie la dimensione del cervello è analoga a quella dei neandertaliani, quello che cambia è la forma: il nostro cervello è globulare mentre in Homo neanderthalensis è allungato antero-posteriormente a 'palla da rugby'. Questa differenza tra le due specie umane più encefalizzate viene spesso correlata a differenze funzionali e cognitive evidenti dall’analisi del record paleoantropologico.
"La mente umana è particolarmente creativa, capace di mescolare pensieri astratti in nuove combinazioni che forniscono possibilità sempre nuove e spesso impreviste - commenta Pasquale Raia - I nostri risultati suggeriscono che l'elevata coordinazione tra le diverse aree cerebrali possa essere stato il meccanismo alla base della 'fluidità cognitiva' teorizzata da Steven Mithen: la capacità di combinare moduli del pensiero originariamente progettati per compiti specifici".
Read the full article
#cervelloumano#eternagiovinezza#evoluzione#fluiditàcognitiva#Hominina#homoneanderthalensis#HomoSapiens#neandertaliani#paleoantropologia
0 notes
Text
i hate the uncanny valley sometimes because people will be like “oooooo if we’re afraid of this there means there must be an evolutionary reason 😱 if we’re so afraid of things that look human but aren’t then there must mean there was once something out there 😧” like yeah there fucking was actually. 1. homosapiens weren’t the only humanoid species. all kinds of other archaic humans existed alongside our species for some time, such as homoneanderthalensis. 2. dead bodies exist. they decay. they appear human but have distinct warping to features as they rot. same goes for point 3. which is diseases often warp the human form!! especially extreme ones that are oftentimes more fatal than not. we aren’t evolutionary scared of the “uncanny valley” because slenderman terrorized our ancestor some hundreds of thousands of years ago, but because coming into contact with a human that looks off often led to death. yknow. just like why we’re evolutionarily afraid of everything else. because it could kill us. diseases and other species could kill us. stop inciting paranoia in people goddamn.
#icarus speaks#vent#<- just in case???#i fucking hate these people#and i LOVE uncanny valley stuff sometimes!!!#i love slenderman mythos. the rake was GENUINELY terrifying to me as a child#both of those things are humanoid but not enough. i wasn’t afraid of them because they were actually out there#but because of VERY LOGICAL EXPLANATIONS
86 notes
·
View notes
Photo
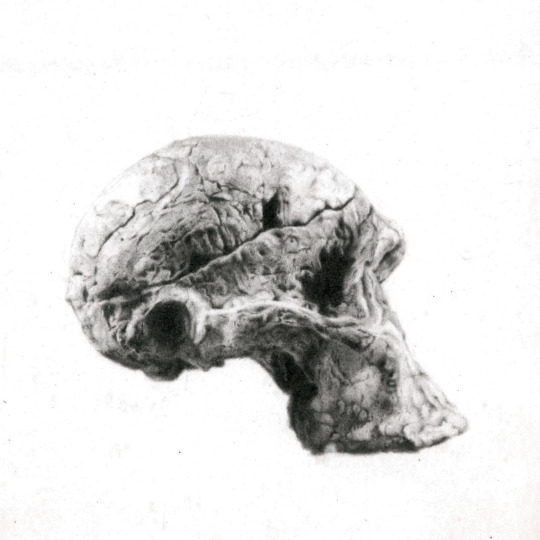
Eduardo Kickhöfel. Skull of Australopithecus africanus. The graphite drawing shows the famous “Mrs Ples”, a skull discovered at Sterkfontein cave in South Africa in 1947.
1 note
·
View note
Photo
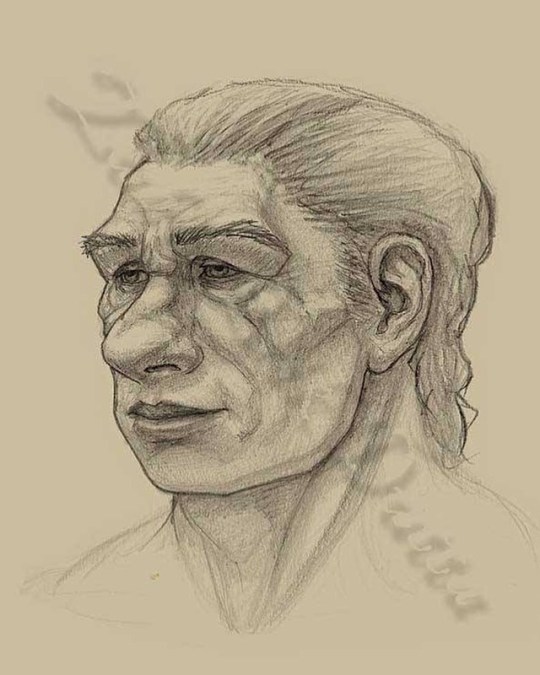

“Tommy” An old sketch I did of a Neanderthal man, without a beard so I could show off more of his facial anatomy. #neanderthal #homoneanderthalensis #neanderthalman #iceagehunter #caveman #paleoart #paleontology #paleobiology #paleoanthropology #physicalanthropology #biologicalanthropology #art #sketch #doodle #portrait #drawing #portraiture #archaichuman #anatomy #humananatomy #naturalhistory #naturalhistoryillustration #naturalhistoryart https://www.instagram.com/p/B1qQXhAFAcd/?igshid=1p9koe9xu0pde
#neanderthal#homoneanderthalensis#neanderthalman#iceagehunter#caveman#paleoart#paleontology#paleobiology#paleoanthropology#physicalanthropology#biologicalanthropology#art#sketch#doodle#portrait#drawing#portraiture#archaichuman#anatomy#humananatomy#naturalhistory#naturalhistoryillustration#naturalhistoryart
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo
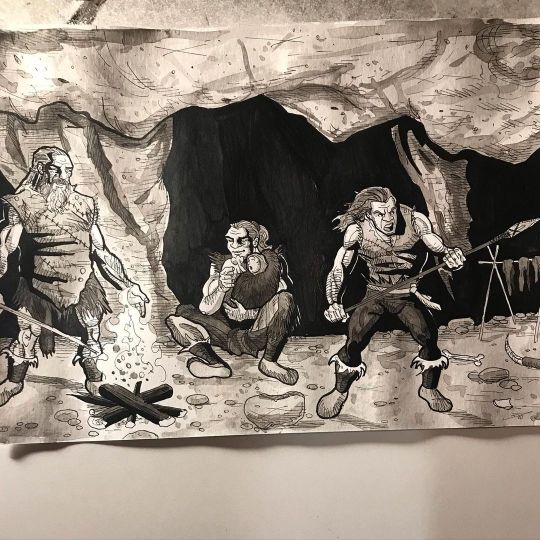

Illustration 20 for Bob Gymlan YouTube video titled el pombero #dredfunn #freddunn #wip #wipart #youtube #youtubechannel #youtuber #art #artistsoninstagram #artoftheday #artwork #comic #comicart #comics #comicbook #neanderthal #bobgymlan #homofloresiensis #homoneanderthalensis #cavemen https://www.instagram.com/p/CWzZtG7gXG9/?utm_medium=tumblr
#dredfunn#freddunn#wip#wipart#youtube#youtubechannel#youtuber#art#artistsoninstagram#artoftheday#artwork#comic#comicart#comics#comicbook#neanderthal#bobgymlan#homofloresiensis#homoneanderthalensis#cavemen
0 notes
Text
Denisovans: New clue to human evolution's biggest mystery emerges in Philippines | CNN
Denisovans: New clue to human evolution’s biggest mystery emerges in Philippines | CNN
Researchers explain their work at a community assembly in the Philippines. The Filipino and Swedish researchers studied the DNA of 118 ethnic groups. Image: CNN (photographer not credited)
Source: Denisovans – DNA from Fossils in the Philippines Reveal New Clues to Humans’ Evolution
In above linked article by Katie Hunt for CNN paleontologists present new findings that might alter our…

View On WordPress
#archeology#denisovans#DNA#homoneanderthalensis#homosapiens#humanevolution#moderndayhumans#paleontology#philippines
0 notes
Photo

Mother of All Humanity • 𓋹 . . . . . . . . . . . ✉️ DM for credit #homosapiens #homosapienssapiens #homo #sapiens #africa #black #genetics #neanderthal #art #pictureoftheday #instagram #humanity #homoneanderthalensis #maroc #kenya #human #cromagron #woman #man #science #history #paleontology #digitalart #homoerectus #australopithecus #lucy #mitochondrialeve #meresoriginelles #originalsmother https://www.instagram.com/p/COEkhzijKHB/?igshid=1kx90jaivv33t
#homosapiens#homosapienssapiens#homo#sapiens#africa#black#genetics#neanderthal#art#pictureoftheday#instagram#humanity#homoneanderthalensis#maroc#kenya#human#cromagron#woman#man#science#history#paleontology#digitalart#homoerectus#australopithecus#lucy#mitochondrialeve#meresoriginelles#originalsmother
0 notes
Photo

Me apasiona el paleolítico y la ilustración histórica... Mis ilustraciones de "Miguelón" y el homo edelbergensis aparecieron una publicación científica. #paleolitico #prehistoria #homoedelbergensis #edelbergensis #neanderthal #neanderthalensis #homoneanderthalensis #homosapiens #prehistory #paleolithic
#homoneanderthalensis#edelbergensis#homoedelbergensis#homosapiens#paleolithic#paleolitico#neanderthal#prehistoria#neanderthalensis#prehistory
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Neanderthal Parallax Trilogy by Robert J. Sawyer Just added! Link in bio. Tor Books (2003-2004) This is the moment I have been waiting for! If you've read my newsletter you know how much I enjoy reading Robert J. Sawyer and how these books are on my all-time favorite list. I searched for a long time trying to put together this trilogy in good condition and here it is. I'm excited to pass these on and that I have the opportunity to present Sawyer's work. I'm also not sure why the cover of Hybrids says 'Sequel to Hominids' because Humans is the sequel to Hominids. Could this be a misprint or am I missing something? . These books depict the effects of the opening of a connection between two versions of Earth in different parallel universes: the world familiar to the reader, and another where Neanderthals became the dominant intelligent hominid. It's a perfect mash of evolution, speculation, and science. The cover artist is Donato Giancola. . Overall Great Condition, Good Spines With Very Light Crease On Hominids, Binding Tight, Pages Look Great, Cover Tear As Shown On Hybrids . . #robertjsawyer #adikor #paperbacksciencefiction #sciencefiction #fiction #instabooks #bookstagram #instabookstagram #paperback #bookcollector #bookstore #science #scifi #instabook #bookaddict #bookishlove #bookish #library #homoneanderthalensis #donatogiancola #theneanderthalparallax #scifiart #syfy #scifibooks #torbooks #torsciencefiction https://www.instagram.com/p/CKwQ8trgvyo/?igshid=1wpjlsezeg85r
#robertjsawyer#adikor#paperbacksciencefiction#sciencefiction#fiction#instabooks#bookstagram#instabookstagram#paperback#bookcollector#bookstore#science#scifi#instabook#bookaddict#bookishlove#bookish#library#homoneanderthalensis#donatogiancola#theneanderthalparallax#scifiart#syfy#scifibooks#torbooks#torsciencefiction
0 notes
Photo

Something these anicent tribes wanted to convey, that "they were here". We are not certain though what kind of humans they were, were they Neanderthals or Sapiens or something else ? Acrylic painting on stretched canvas. Size 10x12 inches. Please, DM us for order. . . . #saadhiarts #saadhiartspainting #acrylicpainting #art #artistsoninstagram #tribepaint #tribalart #ancienttribes #homosapiens #humanart #ancienthumans #homoneanderthalensis #artislove❤️ #indianartists #artislife🎨 (at Bangalore) https://www.instagram.com/p/B4NF-zphpB9/?igshid=12suhc4o2jmkd
#saadhiarts#saadhiartspainting#acrylicpainting#art#artistsoninstagram#tribepaint#tribalart#ancienttribes#homosapiens#humanart#ancienthumans#homoneanderthalensis#artislove❤️#indianartists#artislife🎨
0 notes
Text
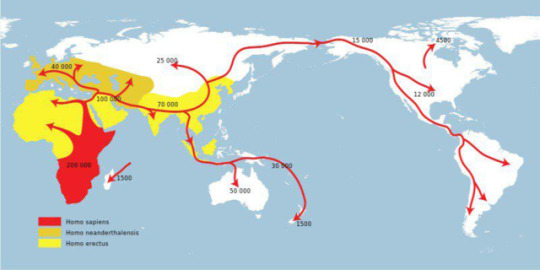
Esta foto representa as liñas de expansión de tres especies diferentes ao longo dos anos: a cor vermella representa ao Homo sapiens que provén do sureste de África e expandiuse por todos os continentes.
A cor alaranxada representa ao homo Neanderthalensis que como ben sabemos e se representa na foto foi a primeira especie nacida en Europa.
A cor amarela representa ao Homo erectus que foi a primeira especie en salir de África.
Todas estas expansións fixeron que estas especies deran lugar a diferentes cruces expandindoos por diferentes continentes.
0 notes
Text
Neanderthal, Denisovan DNA Found Near Autism Genes in Modern Humans
Comparison of early Homo sapiens with Homoneanderthalensis. Credit: Wikipedia.
One of the most interesting questions of hominin evolution is exactly how much of our vanished cousins remains in us. Between 1-4 percent of the modern human genome is derived from Neanderthals everywhere but sub-Saharan Africa. In addition, between 4-6 percent of the modern Melanesian genome has been shown to be derived from a separate species of archaic hominin, Denisovans. Now, a new paper focused on comparing a specific type of genetic variance has found evidence suggesting that Denisovans and Neanderthals made large-scale, long-term positive contributions to the human genome. Our understanding of the impact of these changes is currently limited, but they occur in a rather interesting place.
Most of the studies that compare differences in human populations (or differences between archaic and modern hominins) focus on adaptive single-nucleotide variants (SNV). It was a single nucleotide variation that gave archaic northwest Europeans the ability to digest lactose, and the ability to do so is a textbook case of human natural selection. The image below shows the prevalence of adult lactase persistence as a percentage of the total population.
Image by Joe Roe, Wikipedia
Single nucleotide variations found in the genome of the Tibetan people are associated with greater acclimatization to high-altitude conditions. These originated in the Denisovan genome. While the Denisovan addition occurred much earlier than the adaptation for adult lactase digestion, both of them have been conserved (meaning they have persisted since initial evolution).
This new research isn’t focused on SNVs. Instead, it analyzed the modern Melanesian genome for signs of copy number variants (CNVs). Copy number variation is when the number of copies of an entire gene are different between individuals. Huntington’s disease, for example, is caused when a specific sub-section of the Huntington gene is repeated to the point that it causes altered protein production. CNVs are much larger than SNVs and they tend to exert very strong selective pressure. Any evidence of conserved CNVs in the Melanesian population that could be traced to the Denisovan or Neanderthal genomes would, therefore, be evidence that these variants conferred benefits.
One thing to know up front is that the impact of CNVs on the human genome is an active field of study. SNVs have historically received far more attention. The discovery of conserved CNVs in the Melanesian population from archaic Denisovan and Neanderthals is significant in its own right. It’s still not clear, however, exactly what either variation actually does. Part of the difficulty of analyzing CNVs is the fact that they’re much larger than SNVs with a much larger range of potential effects.
Denisovan and Neanderthal Contributions
The researchers found two specific CNVs — one associated with the Denisovan genome, and one associated with Neanderthals. 79 percent of Melanesians carry a duplication on chromosome 16p11.2 of >383,000 base pairs (kbp) that originated from Denisovans and was introduced into the native population 60,000-170,000 years ago.
Image from Science Mag
The second variation was introduced by Neanderthals and is carried by some 44 percent of modern Melanesians. It’s located on chromosome 8p21.3 and consists of a ~6-kbp deletion and a ~38-kbp duplication.
What’s particularly interesting about the Denisovan addition to the human genome is its location. According to the researchers, the specific area of 16p11.2 they identified as being Denisovan in origin is part of a locus which “exhibits an enrichment of complex recurrent structural rearrangements, which predisposes humans to the second most common genetic cause of autism, accounting for ~1% of patients.” To be more specific, the Denisovan CNV is directly adjacent to the area of the chromosome where genes known to be associated with autism are.
This specific section of the human genome is known to be unstable and prone to breakage errors. Previous research on 16p11.2 has found that an earlier duplicative transposition of the BOLA2 gene some 282,000 years ago “simultaneously increased copy number of a gene associated with iron homeostasis and predisposed our species to recurrent rearrangements associated with disease.”
The fact that the Denisovan contribution to the human genome is 1). Huge 2). Built in the metaphorical swamp of 16p11.2, and 3). Highly conserved suggests it was important to retain. The Neanderthal CNV encompasses TNFRSF10D (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 10D). According to the researchers, “TNFRSF10D has been reported as one of the primate-specific genes preferentially expressed in progenitor cells of the human fetal neocortex.”
What’s It All Mean?
Honest answer: Nobody is sure. The researchers theorize that these genes likely conveyed an evolutionary benefit to the Melanesians, probably one linked to their lives in an isolated tropical environment.
“Our results collectively suggest that large CNVs originating in archaic hominins and introgressed into modern humans have played an important role in local population adaptation and represent an insufficiently studied source of large-scale genetic variation,” the study authors wrote.
The problems with CNV analysis have made it difficult to apply until now. The application of these techniques suggests we may see them used more widely in the future, but the newness of the approach means we’ll be figuring out what these variances do for quite some time to come.
Written with assistance from Jessica Hall. Feature image is a comparison of early Homo sapiens with Homo neanderthalensis. Credit: Wikipedia.
Now Read:
Scientists Find Neanderthal Hybrid In a Siberian Cave
Researchers Claim Neanderthals Could Start Fires Using Stone Tools
Study: Humans Arrived in North America 100,000 Years Earlier Than Thought
from ExtremeTechExtremeTech https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/300458-neanderthal-denisovan-dna-found-near-autism-genes-in-modern-humans
from Blogger http://componentplanet.blogspot.com/2019/10/neanderthal-denisovan-dna-found-near.html
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Quanto di più aggiornato sull #homoneanderthalensis #uomodineanderthal #evoluzione #evolution #preistoria #neanderthal #buonalettura #consiglidilettura #bibliotecapersonale #antropologia #archeologia #archaeoporn
#antropologia#archeologia#preistoria#neanderthal#uomodineanderthal#evoluzione#bibliotecapersonale#archaeoporn#buonalettura#homoneanderthalensis#evolution#consiglidilettura
0 notes
Photo
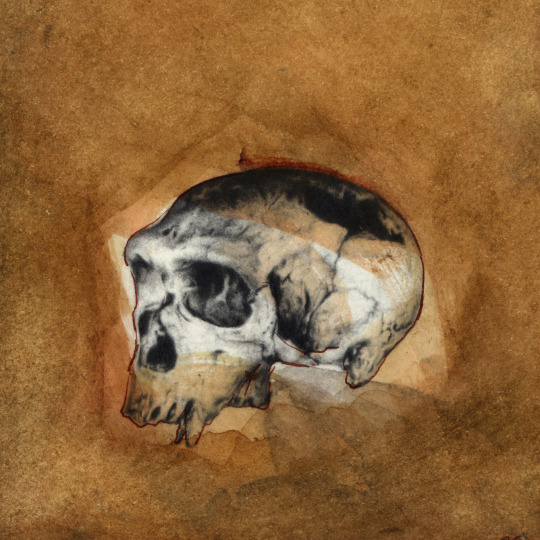
Eduardo Kickhöfel. Skull of Homo neanderthalensis. Skull of Homo neanderthalensis from La Chapelle-aux-Saints, discovered in 1908. This is another small graphite and watercolour drawing I made many years ago.
1 note
·
View note