#diabetes cure
Text
The insulin news is a great way to check to see how many people look for more information and how many people just say things online
(The patient treated was Type 1, however it was a singular patient so it needs much more testing and peer review before it can be considered a cure, and I have no idea if the treatment required use of immunosuppressants, basically it’s ‘promising’)
People really shouldn’t get their medical news from headlines; lest anyone forgot, that’s how we got anti-vaxxers
#off topic#not fiber arts#medical news#diabetes#diabetes cure#why does everyone assume all the resources go to type 2 all the time?#it’s getting weird…
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is diabetes, Symptom, causes, and cure?

I. Introduction
A. Definition of Diabetes
B. Significance of Understanding its Causes and Cure
II. Types of Diabetes
A. Type 1 Diabetes
1. Autoimmune Process
2. Insulin Dependency
B. Type 2 Diabetes
1. Insulin Resistance
2. Lifestyle Factors
III. Genetic Factors
A. Familial Predisposition
B. Genetic Mutations
IV. Environmental Influences
A. Diet
B. Sedentary Lifestyle
C. Stress
V. Hormonal Factors
A. Insulin Production
B. Glucagon Regulation
VI. Immunological Factors
A. Autoimmune Response
B. Inflammatory Processes
VII. Cellular Dysfunction
A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
B. Oxidative Stress
VIII. Microbiome and Gut Health
A. Gut Microflora Composition
B. Gut-Brain Axis
IX. Metabolic Syndrome
A. Insulin Resistance
B. Dyslipidemia
X. Pharmacological Treatments
A. Insulin Therapy
B. Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
XI. Lifestyle Interventions
A. Diet Modification
B. Exercise Regimens
XII. Stem Cell Therapy
A. Regenerative Potential
B. Clinical Applications
XIII. Immunotherapy
A. Targeting Autoimmune Response
B. Immune Modulation
XIV. Gene Therapy
A. CRISPR Technology
B. Genetic Engineering
XV. Conclusion
A. Holistic Approach to Diabetes Management
B. Future Directions in Research and Treatment
Diabetes, Causes, Cure
Introduction
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder, affects millions worldwide. Understanding its causes and potential cures is paramount in addressing its increasing prevalence and the associated health complications.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes results from an autoimmune process where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This leads to insulin deficiency and dependence on external insulin sources for survival.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes primarily stems from insulin resistance, where cells fail to respond effectively to insulin. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor dietary choices contribute significantly to its development.
Genetic Factors
Familial Predisposition
A family history of diabetes increases the risk of developing the condition due to shared genetic factors among relatives.
Genetic Mutations
Specific genetic mutations can predispose individuals to diabetes by affecting insulin production, glucose metabolism, or other related processes.
Environmental Influences
Diet

A diet high in refined sugars, saturated fats, and processed foods can contribute to insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction, increasing the risk of diabetes.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Physical inactivity disrupts glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, promoting the onset and progression of diabetes.
Stress
Chronic stress triggers hormonal imbalances and inflammation, adversely affecting insulin function and contributing to diabetes development.
Hormonal Factors
Insulin Production
Disruption in insulin production by pancreatic beta cells or inadequate insulin secretion in response to glucose levels contributes to diabetes pathogenesis.
Glucagon Regulation
Imbalances in glucagon, a hormone that opposes insulin's actions, can disrupt blood glucose control and contribute to diabetes progression.
Immunological Factors
Autoimmune Response
In type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune reaction against beta cells destroys insulin-producing cells, leading to insulin deficiency and dependence on exogenous insulin.
Inflammatory Processes
Chronic inflammation plays a role in insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction, contributing to the development and progression of diabetes.
Cellular Dysfunction
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Impaired mitochondrial function within cells can disrupt energy metabolism and insulin signaling pathways, contributing to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Oxidative Stress
Increased oxidative stress damages cells and tissues, impairing insulin sensitivity and exacerbating diabetes-related complications.
Microbiome and Gut Health
Gut Microflora Composition
Alterations in gut microbiota composition can influence glucose metabolism and inflammation, impacting diabetes risk and progression.
Gut-Brain Axis
The bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain influences metabolic processes, including glucose regulation, and may play a role in diabetes development.
Metabolic Syndrome
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a hallmark of metabolic syndrome, characterized by impaired insulin action in target tissues, contributing to diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk.
Dyslipidemia
Abnormal lipid metabolism, including elevated triglycerides and decreased HDL cholesterol, is common in metabolic syndrome and exacerbates diabetes complications.
Pharmacological Treatments
Insulin Therapy
Insulin replacement therapy is essential for managing type 1 diabetes and may be necessary for type 2 diabetes patients with advanced disease or beta cell failure.
Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
Various oral medications target different aspects of glucose metabolism, including enhancing insulin sensitivity, stimulating insulin secretion, or inhibiting glucose production in the liver.
Lifestyle Interventions
Diet Modification
Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can improve blood glucose control and reduce diabetes risk.
Exercise Regimens

Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, promotes weight loss, and helps control blood sugar levels, making it a cornerstone of diabetes management.
Stem Cell Therapy
Regenerative Potential
Stem cell-based therapies hold promise for regenerating pancreatic beta cells and restoring normal insulin production in diabetes patients.
Clinical Applications
Ongoing research explores the use of stem cells in diabetes treatment, including transplantation approaches and cell-based therapies to replace damaged or dysfunctional cells.
Immunotherapy
Targeting Autoimmune Response
Immunotherapy aims to modulate the immune system to halt the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells in type 1 diabetes.
Immune Modulation
Various immunomodulatory strategies, such as antigen-specific tolerance induction and regulatory T cell therapy, show potential for preserving beta cell function and delaying disease progression.
Gene Therapy

CRISPR Technology
Advancements in gene editing technologies like CRISPR offer the possibility of correcting genetic mutations associated with diabetes and restoring normal cellular function.
Genetic Engineering
Gene therapy approaches aim to deliver functional genes or modify existing ones to enhance insulin production, improve glucose metabolism, and potentially cure diabetes.
Click here
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted causes of diabetes and the development of innovative treatments offer hope for effectively managing and ultimately curing this pervasive disease. Embracing a holistic approach that addresses genetic, environmental, hormonal, immunological, and metabolic factors is essential for improving diabetes outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for affected individuals. As research continues to uncover new insights and therapeutic strategies, the pursuit of a cure for diabetes remains a top priority, guiding the future of healthcare and ushering in a new era of personalized medicine.
Click here to get link
DISCLAIMER :- This article contains affiliate link, which may beneficial for me.
#health & fitness#diabetes#healthcare#insulin#type 2 diabetes#sugarcontrol#diabetes care#diabetes causes#diabetes products#diabetes symptoms#diabetes treatment#diabetes control#diabetes medicine#diabetes cure
0 notes
Video
youtube
Grandma's Bizarre 14-Day Diabetes Reversal Formula is Saving Lives and Leaving Doctors Speechless! After Being Diagnosed With Severe Diabetes, This 82-Year-Old Stumbled Upon a Weirdly Effective Natural Remedy That Reversed Her Condition in Just 2 Weeks. Click Here to Learn Her Secret!Here is the link 🤩🤩==>> https://bit.ly/49VQSnf
#diabetes#how to reverse diabetes#type 2 diabetes#diabetes cure#natural treatment for diabetes#high blood sugar#how to lower blood sugar levels
0 notes
Text
Managing Diabetes and Finding Type-1 Diabetes Cure

Introduction
Living with type 1 diabetes can be challenging. Because of this autoimmune disease, the pancreas makes little to no insulin, which raises blood sugar levels. Are you looking for a Type 1 diabetes cure? It is difficult to get permanent relief from type 1 diabetes, but here we come with some therapies that can help control the illness enhance the lives of individuals who have it, and help you in your diabetes care journey.
Best Ayurveda for Type 1 Diabetes Cure
Type 1 diabetes is one of the many medical disorders that may be managed holistically by the ancient Indian medical system known as Ayurveda. Ayurveda helps you in your diabetes care, which includes diabetes therapy, herbal medications, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes, is among the most promising. Ayurvedic doctors frequently advise a customized strategy to treat diabetes's underlying causes and restore the body's equilibrium.
Herbal Products for Type 1 Diabetes Cure
Several herbal products are renowned in Ayurveda for their potential to assist in managing type 1 diabetes. These include Madhuant Tablets, formulated with natural ingredients like bitter gourd, neem, and giloy, known for their blood sugar-regulating properties; Safed Musli Powder, a medicinal herb recognized for its anti-diabetic properties that may improve insulin sensitivity; Gurmar Powder, also known as "sugar destroyer," traditionally used to lower blood sugar levels and reduce sugar cravings; Chandraprabha Vati Tablets, containing a blend of herbs like guggul, haritaki, and Amalaki, which may aid in managing diabetes by improving digestion and metabolism; and Trikatu Tablets, a combination of ginger, black pepper, and long pepper believed to enhance digestion, metabolism, and insulin sensitivity, thus supporting diabetes management.
Conclusion
Sevayucuba is the greatest place to find a type 1 diabetes cure. The diabetes care program is designed to manage diabetes through blood sugar monitoring, stress management, yoga and pranayama practices, herbal supplements, and dietary adjustments.
0 notes
Text

Why your Morning fasting sugar level is high
Despite normal readings of less than 140 points post meals and no dependence on tablets! If this sounds like you, read on to find out what causes this phenomenon and what you can do to address it.
Read more: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/why-your-morning-fasting-sugar-level-is-high/1509
#why my blood sugar is high in the morning#high sugar level#High Sugar level range#High sugar level symptoms#Diabetes#Diabetes reversal#diabetes treatment#Diabetes cure
0 notes
Text
Amiclear for Diabetes Solution - Best Blood Glucose Normalizing Formula.
Introducing The Amiclear, an innovative product designed to support effective diabetes management. With its proven track record and positive user testimonials, The Amiclear offers a promising solution for older adults seeking to stabilize their blood sugar levels. Watch a detailed video presentation of Amiclear using the link below:
www.elderstechemporium.com/recommends/amiclear-for-diabetes-video-presentation
0 notes
Text
Diabetes Management: The Art of Navigating Life with Diabetes
Living with diabetes can be an intricate and multifaceted journey, necessitating profound insights and comprehensive tools to forge a gratifying existence despite its challenges. In this informative discourse, we shall delve into the intricacies of diabetes medicine, exploring its dynamic management strategies and embracing transformative lifestyle alterations that can genuinely wield a…
View On WordPress
#A1C Test#Aerobic Exercises#Balanced Diet#blood sugar levels#Blood Sugar Monitoring#Blood Tests#carbohydrates#cardiovascular complications#causes of diabetes#children and diabetes#conclusion#Diabetes#Diabetes complications#diabetes cure#Diabetes Management#diabetes management tips#diabetes medicine#Diabetes Prevention#Diabetes symptoms#Diagnosing Diabetes#dietary recommendations#exercise for diabetes#eye problems#flexibility exercises#foot care#foot complications#genetic factors in diabetes#gestational diabetes#gestational diabetes explanation#glucose tolerance test
0 notes
Text
The types of diets for Diabetes
In this article, we will explore some of the most popular diets that are recommended for and followed by diabetic patients.
First, let us understand the meaning of diet.
The term diet usually refers to the consumption of nutritious food with a focus on either managing health or weight.
The diet for Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease linked to the regulation of blood glucose levels. So, it becomes crucial to consume a diet that does not cause an immediate spike in blood sugar or that does not override the blood glucose levels.
Hence, patients suffering from Diabetes, mainly focus on controlling their blood glucose levels and devise a diet regime knowing that it will directly influence the amount of insulin administered.
When composing a diet, factors to be kept in mind –
It is balanced and supplies the body with all essential nutrients.
It is sustainable and can be followed long-term
Is not a “crash diet” that puts the body in a state of rapid weight loss due to extreme deficiency in calories or nutrition
In order to structure our diet, let us know the minimum caloric requirements recommended by the Department of Health and Human ServicesPersonCalorie requirementsSedentary children: 2–8 years1,000–1,400Active children: 2–8 years1,000–2,000Females: 9–13 years1,400–2,200Males: 9–13 years1,600–2,600Active females: 14–30 years2,400Sedentary females: 14–30 years1,800–2,000Active males: 14–30 years2,800–3,200Sedentary males: 14–30 years2,000–2,600Active people: 30 years and over2,000–3,000Sedentary people: 30 years and over1,600–2,400
The 6 essential nutrients to incorporate in your diet include –
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Fats
Vitamins
Minerals
Water
Some of the most popular diets followed to manage diabetes are –
The low-carb diet
Keto-diet
Vegetarian diet
Whole-food plant-based diet
The low-carb diet
This is the most common diet followed by diabetic patients since a low-carb diet helps in keeping the blood glucose levels under control. Before insulin was discovered for the treatment of diabetes, people were kept on strict diet controls and recommended a low-carb diet to keep their blood glucose levels in check. However, consuming a diet that is deficient in carbohydrates may not be a replacement for insulin administration but it will surely decrease the dosage.
The Keto diet
In a ketogenic diet or a low-carb high-fat diet, nutritional ketone production is the goal through decreased carbohydrate or protein intake. A keto diet mainly consists of fats from plant or animal sources. A person following a keto-diet, essentially keeps himself supplemented only with dietary sources rich in fat. It is important to remember that although a keto diet is low in carbohydrates, it is not the same as a low-carb diet since fat-rich foods are a prerequisite to fall under the keto criteria.
A vegetarian diet
Vegetarian diets prevent insulin resistance and reduce the sharp rise in blood sugar through foods that release glucose slowly into the blood or foods that have a low glycemic index. Studies have shown that people following a vegetarian diet stand a 35-53% lower chance of developing type 2 diabetes. This diet not only helps in maintaining weight but also helps in improving heart, gut and brain health.
Whole food plant-based diet
This diet is particularly followed in the modern age where the benefits of a diet rich in fresh and natural nutrients are given importance. In a whole food plant-based diet, dairy and processed foods are eliminated with the consumption of only food that is obtained directly from nature with no preservatives or additives. The requirement of a whole food plant-based diet is that the food needs to be complete or whole in itself and not refined or processed.
The philosophy behind this diet is that food from nature is complete by itself with all the essential nutrients and man separated it into carbohydrates, proteins and fats while trying to again put together a balanced diet consisting of all essential nutrients. This diet is known to not only prevent lifestyle-related diseases like thyroid and diabetes but also known to reverse them.
know more about diabetes diet plan and how you can reverse your diabetes naturally
Conclusion

#diabetes#diabetes reversal#ayurveda#diabetes diet#diabetes diet plan#diet for diabetes#diet plan#diabetes cure#type 2 diabetes
0 notes
Text
Is a Cure for Diabetes Possible? Exploring the Latest Research and Treatment Options
I. Introduction on Diabetes Cure
Diabetes Cure is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. The body requires insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, to convert glucose into energy. In people with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it properly, leading to a buildup of glucose in the blood.
Define diabetes and the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
I'm all for natural remedies and traditional medicine, but I think when your "natural remedy" is based on the idea that water can become medicinal by being in the presence of a teeny itty bit amount of something, then it's probably bullshit and you're getting scammed. Go buy some ibuprofen or see a doctor.
#this is a long way for me to say that homeopathy is a scam!!#and that ''homeopathic professionals'' deliberately prey on vulnerable and scared people#especially chronically and terminally ill women looking for help and answers to illnesses they don't understand#so then they end up paying absurd money for fucking PLACEBOS#literal bottles of water and sugar pills that can supposedly cure their diabetes or fibromyalgia or cancer#and it's fucking disgusting and shameful okay
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cure where there is no cure
It dawned on me like a revelation
This morning, we reviewed some previous specialist referrals in my chart at the doctor’s office. We talked about arthritis (osteoarthritis). I remarked that I was told there is no cure for arthritis but only some help to cope with the ailment. She in turn responded that if there was a cure she would not be seeing the patients she is now seeing.
I sheepishly…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
#diabetes#type 2 diabetes#diabetic#insulin#diabetes cure#health and fitness mantra#health and fitness tips
0 notes
Photo

Intermittent fasting is the best way to remain fit and active even at a growing age. if a diabetic patient is thinking of intermittent fasting. Then they must be in touch with the doctor. To know more, Visit https://nimba.in/intermittent-fasting-a-powerful-tool-to-treat-diabetes/
#intermittentfasting#intermittent diet#diabetes cure#Diabetes#diabetes naturally#treatment for diabetes#nathuropathy
1 note
·
View note
Text
Diabetes - Now common!
Diabetes is one of the most common health problems nowadays. It is mostly due to the increasing poor lifestyle and health habits of people. We hear a lot of stories on diabetes, how people survive with it, and read articles on the causes and treatments. Sometimes, all these may leave you confused and with even more questions in your mind.
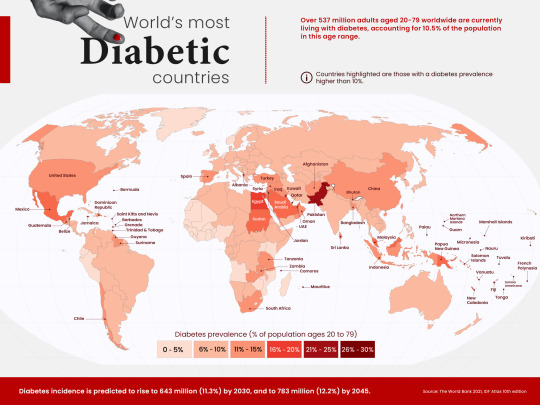
Diabetes is a life-long condition caused due to improper body metabolism. When you have food, sugar is converted to glucose and released into the blood. With the help of insulin produced from the pancreas, glucose is converted and transferred along the blood to the cells of the body to act as energy for carrying out various activities. But in case of a diabetic, insulin is not used properly. Hence the glucose levels remain elevated. This is harmful to the body.
In type 2 diabetes, though the pancreas produces insulin, either it is too little to enable cells to absorb insulin, or the cells themselves are resistant to insulin.
To control your glucose levels every day, do frequent self-testing with a home testing device known as 'glucometer'. This allows you observe your glucose levels. According to the readings obtained, you may modify your food, medicines, and actions.
To help provide some key information about diabetes here is a guide to some frequently asked questions.
Sadly, diabetes is a chronic condition; it is a life-long condition that as no cure. However, medications and proper diet will enable you to monitor your blood sugar levels and keep them at a minimum. A healthy lifestyle will also prevent further medical complications.

Generally, some telling symptoms of diabetes are: excessive thirst and urination, constant feeling of fatigue and hunger, sudden weight loss, slow healing of wound, recurring infection, and blurred vision.
People who have fat build up around the stomach may be at greater risk to diabetes, high blood, cholesterol, and heart disease.
When neglected, diabetes can cause major complications and long-term damage to certain organs such as the kidneys, nerves and the eyes.
Diabetics are definitely more prone to infections as white blood cells are impeded by too much sugar in the blood. White blood cells are responsible for fighting off infections in the body.
Eating sugary foods like cakes and chocolates will not cause diabetes. But it will aggravate a diabetic's existing condition.
The exact cause of diabetes may not be known, but there are links to genetic influence and most definitely poor health, lack of regular exercise, constant stress, and poor lifestyle habits are major factors that may lead to diabetes sooner or later.
Now that you have some basic idea on diabetes, start living healthy to prevent this disease.
You are not alone in fight against diabetes. We are with you, offering information, diabetic supplies and support for Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes and caregivers. Lifestyle tips, delicious diabetic recipes, answers for your queries, we deliver them right to your inbox. Together let's begin a journey of diabetes free life.
Find all you need to know about diabetes at
[Learn more by visiting her website]
#diabetes causes#diabetes cure#diabetes life expectancy#diabetes mellitus#diabetes oireet#diabetes symptoms#diabetes diet#diabetes recipes#diabetes treatment#diabetes facts#diabetes types#Diabetes supplement#Blood sugar supplement#Glucose support#Diabetic support supplement#Insulin resistance supplement#Blood sugar control supplement#Natural diabetes supplement#Pancreas support supplement#Diabetes management supplement#Metabolic health supplement#Chromium supplement for diabetes#Gymnema sylvestre supplement#Berberine supplement for diabetes#Cinnamon supplement for blood sugar#Alpha-lipoic acid supplement for diabetes#Magnesium supplement for diabetes#Vitamin D supplement for diabetes#Vitamin B12 supplement for diabetes#Zinc supplement for diabetes
0 notes
Text
#Diabetes Remedy#Diabetes Treatment#Type 2 Diabetes#Diabetes Cure#Cure Diabetes#Diabetes Diet#Diabetes Food#Diabetes Medicine#Diabetes Pills#Diabetes Causes#Diabetes Level#Check Diabetes#Diabetes Checking Machine#Diabetes Test#diabetics
0 notes
Text
Nutrient rich diet for diabetes control?
Nutrient-dense foods have a high concentration of vitamins and minerals in relation to their calories. Discover which superstars should add in your diet.
Nutrient-dense foods are high in vitamins and minerals yet low in sugar, salt, and saturated fat. As a result, they can give a high ratio of beneficial chemicals to calories. Consider them the polar opposite of “empty calorie” foods, which deliver quick energy but nothing else in the way of nutrients (and often leave you hungry soon after).
In other words, while low calorie density (items with the fewest calories per volume) may be desirable in a weight-loss diet, high nutrient density is always preferred. Some foods are both nutrient-dense and calorie-dense (think peanut butter and nuts), and they are fine to include in your diet as long as you don’t overdo it. So, which nutrition superstars should you include to your shopping list? Continue reading to learn about the greatest nutrient-dense foods to include in your balanced diet.
Why Should Nutrient-Dense Foods Be Included in Your Diet?
Essentially, nutrient-dense foods provide the greatest bang for your calorie dollars by supplying high-quality fuel that your body can use to carry you through the day. “They offer vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, water, fibre, and more without adding empty calories,” explains Dr. Soumya Hullannavar is a Lead Ayurveda Endocrine Specialist at Diabetes Reversal Clinics & EliteAyurveda Clinics
Focusing your diet on nutrient-dense foods may help you reduce your risk of a variety of health disorders associated with a poor diet, such as heart disease, obesity, and several malignancies. “Including nutrient-dense foods in your diet will help lower your risk for chronic diseases,” says Dr. Soumya. Consider it packed the maximum health advantages into each calorie.
If you have a chronic condition, you know that what you eat can have a big impact on your symptoms, energy level, and overall mood. A nutrient-dense eating plan can help you maintain a healthy lifestyle.
How Is Nutrient Density Determined?
According to a comprehensive study published in the journal Nutrition Reviews, various approaches for assessing the nutrient density of foods, commonly known as nutrient profiling, have been proposed. However, they all involve some combination of the following elements:
A food earns points for having “nutrients to encourage.” This contains the vitamins and minerals that human bodies require for healthy development and function (vitamins A, C, D, E, K, and B vitamins, as well as the minerals chloride, cobalt, copper, fluoride, iodine, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, sodium, and sulphur). Foods are also given points for protein, fibre, and maybe other healthful ingredients such as omega-3 fatty acids. The more of a nutrient’s recommended dietary allowance an item has, the more points it receives.
Points are deducted for “nutrients to limit,” which include added sweets, salt, and unhealthy fats (often saturated and trans fats), OR points are granted for their absence.
According to the Nutrient Reviews article, the points are then divided by a unit (typically 100 grams or 100 calories) to create a score.
Which Foods Are the Most Nutrient-Dense?
According to Derocha, fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, nuts and seeds, beans and legumes, and heart-healthy fats all fit the nutrient-dense food criterion. However, there are standouts in each area.
Here are some particularly nutrient-dense alternatives, listed alphabetically:
Asparagus. This vegetable is high in insoluble fibre, which helps lower cholesterol and aids digestion; vitamin K, which aids in blood clotting; and folate (folic acid), a B vitamin that can lessen the incidence of birth abnormalities (pregnant women should take plenty of it).
Avocados. They have at least 20 vitamins and minerals, are low in sugar, but abundant in unsaturated fat, and are thus an outlier among fruits. They also contain a lot of fibre.
Bell peppers. Each of these contains more vitamin C than an orange. Peppers are also high in fibre and anti-inflammatory antioxidants.
Berries. Berries are high in fibre and vitamins, but they’re also high in antioxidants, which originate from the phytochemicals (the plant chemicals that give berries their rich, vibrant colours). Berries that have been frozen retain their nutrients and can be consumed all year.
Broccoli. This cruciferous superfood is high in calcium, fibre, iron, potassium, vitamin C, and vitamin K.
Dark chocolate. Although it contains more calories than most nutrient-dense foods, dark chocolate contains antioxidants and minerals that make it a healthy choice. It contains flavanols, which are antioxidants with anti-inflammatory properties. To reap the most benefits, choose chocolate that has at least 70% cocoa.
Eggs. They include vitamins, minerals, protein, and choline, an important ingredient. Two-thirds of the fat in egg yolks is unsaturated, or “good” fat. The yolk carries the majority of the nutrients and fat, whereas the egg white is entirely protein. A large egg only has about 78 calories, the most of which come from the yolk.
Kale and other dark leafy greens. They contain vitamins A, C, and K, as well as calcium and protein. Fibre is also abundant in leafy greens. They can be eaten raw in salads or cooked with vegetable oils (or baked into chips for a crispy pleasure in the case of kale). Leafy greens, in addition to kale, include bok choy, collard greens, dandelion greens, mustard greens, spinach, and Swiss chard.
Legumes. Consider them nutritious powerhouses in a small package. Beans, chickpeas, edamame, lentils, peanuts, peas, and soybeans are examples of legumes (also known as pulses). They are high in fibre, folate, iron, magnesium, and potassium while being low in fat.
Liver. Although it is not for everyone, liver is one of the most nutrient-dense foods in the omnivore diet. This organ meat (often from a cow, chicken, duck, lamb, or pig) is high in protein and contains more than 100% of the RDA for a variety of vitamins and minerals such as iron, riboflavin (a B vitamin), vitamin A, and zinc.
Mango. This yellow-orange fruit contains fibre, folate, and vitamins A, B6, and C. The vibrant colour is due to beta-carotene, an antioxidant that may prevent cell damage. (Beta-carotene is a precursor to vitamin A, which means it is converted into the vitamin by your body.)
Nuts. Nuts, like legumes, pack a lot of nutrients into a small package. While they are abundant in fat, it is the good (unsaturated) form that is beneficial to your heart. Plant protein is also abundant in nuts. Antioxidants, calcium, fibre, omega-3 fatty acids, selenium, and vitamin E are just a few of the beneficial compounds found in nuts.
Pomegranates. They’re high in fibre, folate, potassium, and vitamins B6, E, and K. Red seeds are delicious as a snack or sprinkled on oatmeal, salads, or yoghurt. The white flesh is edible, although it tastes bitter.
Potatoes. Potatoes are abundant in vitamin C and were once credited with preventing scurvy. They are also high in fibre and potassium. In fact, a baked potato with skin is the single finest meal source of potassium, with almost 900 mg of this vital mineral that aids in blood pressure regulation.
Pumpkin. This squash family member, like carrots and mango, receives its orange colour from beta-carotene. Pumpkins are also high in fibre and contain more potassium per cup than bananas!
Quinoa. This is a seed that is commonly referred to as a grain. It’s packed with fibre, folate, magnesium, phosphorus, and thiamin (another B vitamin). It’s very high in protein, especially when compared to other cereals.
Salmon. This fatty fish contains a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, which may help reduce the risk of heart disease. Anchovies, herring, mackerel, sardines, and trout are also high in omega-3.
Seaweed. This marine plant is the richest supplier of iodine, which is beneficial to thyroid health. Seaweed also contains a significant amount of calcium, copper, and iron.
Sweet potatoes are a type of potato. They include a lot of protein, vitamin A, and beta-carotene. Eat them baked, boiled, or mashed, just not fried, like regular potatoes.
Yams. Yams are a root vegetable similar to sweet potatoes, but starchier and more similar in taste and texture to potatoes. Sweet potatoes have less fibre, vitamin C, and potassium than yams.
How to Increase the Nutrient Density of Your Diet
There are numerous simple replacements that can help you add more nutrient-dense meals to your diet while substituting less healthy options. The American Heart Association offers the following suggestions:
On pizza and sandwiches, use vegetable toppings instead of meat.
Brown rice should be used instead of white rice.
Replace sugary drinks with coffee, unsweetened tea, or water.
Try replacing sour cream with plain nonfat Greek yoghurt in baked potatoes, chilli, tacos, and other recipes.
Instead of chips, snack on nuts or veggies. If you’re looking for something crunchy to dip in salsa or guacamole, try carrot or celery sticks, cucumber slices, or radishes.
Instead of sugary sweets, serve fruit for dessert.
Consider working with a registered dietitian (R.D.) or registered dietitian nutritionist (R.D.N.) if you need assistance getting started or want more individualised eating advice targeted to your health situation. “They can provide personalized recommendations for helping you eat a balanced diet,” adds Dr. Soumya.
Our Outlook –
How are we able to Treat Diabetes Completely?
“Madhumeha” is the term for Diabetes in Ayurveda, which means ‘Sweet urine’. The manifestation of diabetes is through thirst or urination. According to Ayurveda, due to accumulation of Vata Dosha. Vata dosha accumulates in the large intestine and travels to the pancreas, which hampers its functioning.
Sometimes, Pitta Dosha also leads to diabetes. This is when Pitta gets accumulated in the small intestine before moving to the liver and may cause damage to pancreas. As the main constituent of Pitta is Agni, it burns out pancreas leading to Diabetes.
If the above things are taken into consideration, the treatment of Diabetes in Ayurveda starts with proper cleansing of the body and balancing of doshas. The treatment includes herbal combinations that are prepared based on individual Prakruti and Vikruti analysis. Ie. The treatment is based on a person’s body composition & which dosha is dominant. The treatments like Dhara, Udwarthanam, Thalam, etc are followed to reverse diabetes. The treatment also includes Panchakarma & Yoga procedures to address the root cause of disease. We have seen many patients successfully reversing Diabetes and now living a healthy life.
Unlike other treatment procedures that jump straight to symptom management, we address the root-cause of the disease. Our treatment for Diabetes has proved to achieve a near cure and symptom-free state. We focus on diet, use of potent herbs, meditation, massage with herbal oils and yoga. These classical ayurveda practices have proven & shown sustained results in our Diabetes Treatment.
The author, Dr. Soumya Hullannavar is a Lead Ayurveda Endocrine Specialist at Diabetes Reversal Clinics & EliteAyurveda Clinics. With over 15 years of experience in treating endocrine & diabetes cases
Visit diabetesreversal.clinic for additional details.
know how diabetes can be reversed naturally
#diabetes#diabetes reversal#ayurveda#diabetes diet#diabetes cure#type 2 diabetes#diet plan#low carb diet
0 notes