#aminoglycoside
Text
“If you ever prescribe an aminoglycoside, and the patient doesn’t come back complaining because it fucked up their digestion, it’s because they didn’t take it.”
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Amikacin Drug
Medical information for Amikacin on Pediatric Oncall including Mechanism, Indication, Contraindications, Dosing, Adverse Effect, Interaction, Renal Dose, Hepatic Dose.
#Amikacin#medication#medications#medicine#drug#drugs#drug information#medical information#drug index#drug center#pediatric dose#Antimicrobial - aminoglycoside
0 notes
Text
Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market New Innovations, Technology And Research 2022, Forecasts till 2029
The Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market size At USD 1325.9 million by 2029, exhibiting a CAGR of 2.4% during 2022-2029

Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market Overview
The Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market report is a comprehensive overview of the market, including a review of its major segments. Alliances are developed after thorough primary and secondary studies. By speaking with industry experts and collecting their data, in-depth market data is produced. The report provides a thorough account of many market factors, including trends, segmentation, growth prospects, chances, difficulties, and competitive analyses.
Get a Sample copy of the report:
https://pharmaresearchconsulting.com/reports/aminoglycosides-antibiotics-drug-market
List of Key Players Of Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market Report:
Jemicare, Teva, Novartis, Fangyuan-pharma, Aike Pharmaceutical, Cipla, Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, Sun Pharma, Hikma, Lannett Company,
Key Segments Covered in Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market
By Type, it is segmented into
Neomycin
Tobramycin
Gentamicin
Amikacin
Etimicin
Others
By Application, it is segmented into
Hospital
Clinic
Others
Competitive Landscape
Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market are showing an increasing amount of interest in creating unique products. In addition, several companies are collaborating, merging, and acquiring one another. In the upcoming years, all of these initiatives are anticipated to drive the global Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market to new heights.
The Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Drug Market Regional Analysis Covers
– North America: United States, Canada, and Mexico.
– South & Central America: Argentina, Chile, and Brazil.
– Middle East & Africa: Saudi Arabia, UAE, Turkey, Egypt and South Africa.
– Europe: UK, France, Italy, Germany, Spain, and Russia.
– Asia-Pacific: India, China, Japan, South Korea, Indonesia, Singapore, and Australia.
Get in Touch with Us: -
Phone No.+1 (704) 266-3234
Mail to: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Market shares, Size and Demand
The Global Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Market report presents insightful data for clients improving their simple management skills identifying with the global market along with market dynamics, segmentation, competition and local growth. The report describes the market size, market characteristics and market growth for the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics industry categorized by type, application and consumption sector.
It provides a comprehensive analysis of the aspects related to the pre and post covid market development 19 pandemic.
Prominent Players Covered in the Global Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Market Are:
Jemicare
Teva
Novartis
Fangyuan-pharma
Aike Pharmaceutical
Cipla
Pfizer
Fresenius Kabi
Sun Pharma
Hikma
Lannett Company
Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Market -Regional Analysis:
Geographically, this report is segmented into several key regions, with sales, revenue, market share and growth rate of the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics market in these regions, down to the forecast coverage.
North America (United States, Canada, and Mexico)
Europe (Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Russia, and Turkey, etc.)
Asia Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India, Australia, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia and Vietnam)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, etc.)
Some of the key questions answered in this report:
What is global? Sales Value, Production Value, Consumption Value, Import and Export of the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics Market?
What application/end user or product type can look for incremental growth prospects?
What are the different sales, Marketing and sales channels in the global industry?
What are the key market trends influencing the growth of the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics market?
Economic impact on the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics market industry and trend development of the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics market industry.
What are the market opportunities, market risk and market overview of the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics market?
What are the key drivers, restraints, opportunities and challenges of the Aminoglycosides Antibiotics market and how are they expected to be affect the market?
How big is the market for Aminoglycosides Antibiotics at regional and country level?
Browse More Details On This Report at - https://www.businessresearchinsights.com/enquiry/request-sample-pdf/aminoglycosides-antibiotics-market-100818
Contact Us:
Business Research Insights
Phone:
US: (+1) 424 253 0807
UK: (+44) 203 239 8187
0 notes
Text
The global Aminoglycoside Antibiotics market size is estimated to be worth US$ 1090.4 million in 2022 and is forecast to a readjusted size of US$ 1324.9 million by 2030 with a CAGR of 3.3% during the review period
0 notes
Link
The global aminoglycosides market size is estimated to expand at a substantial CAGR during the forecast period, 2021–2028.
0 notes
Text


🫀 08.02.2024 [😶] // I didn't have any lecture today so I slept in until noon (as I am so so tired for the past weeks) and I wrote some of the notes i left unfinished. I still have some chapters to catch up before I forgot what my notes mean ahah (I still have 10/23 for the moment), which include (in no specific order) :
pharmacology of antihypertensives
public health of cardiovascular diseases
pharmacology of anticoagulants
the aminoglycosides
it's heavy subjects and even a one hour lecture takes so much time and effort to be understood, learned and remembered. And don't tell me wrong, I love doing it! I just wish I had more time :((
🎧 Red Wine Supernova - Chappell Roan
#dailylar#studyblr#french student#french studyblr#study#pharmacyblr#studyblr community#pharmacy student#pharma student
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers at McMaster University have discovered unique characteristics of a mechanism used by bacteria to resist an important class of antibiotics. The new research, published in Nature Chemical Biology, shows that resistance to aminoglycoside drugs—used to treat a variety of infections—is far more complex than initially thought.
Lead investigator Gerry Wright, professor of Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences at McMaster, says his lab observed never-before-seen versatility in ApmA, a long-studied bacterial resistance gene. The research showed that the gene can uncharacteristically enable bacteria to perform different functions against different antibiotics.
Of the hundred-or-more aminoglycoside resistance enzymes known to researchers, Wright says only this one has exhibited such nimble behavior.
"It's a unicorn," he says. "It looks different, it operates differently, and it belongs to an entirely different family of enzymes. It's completely different from all of the resistance mechanisms that we associate with this class of antibiotic."
Continue Reading.
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some help for fellow Phlebotomy students!
This is the saying that helps me remember the order of draw for venipuncture:
Yellow (blood cultures)
Light (PT, PTT, Coagulation)
Stop (Chemistry testing)
Green (Any plasma test except plasma cells)
Light (Blood group, Carbon Monoxide levels, CBC)
Go (Glucose, Lactic acid, Blood alcohol levels)
And then these are the tubes and their functions!
Yellow tube:
Blood cultures
Invert 8-10x
Light blue tube:
PT
PTT
Coagulation studies.
Always draw two.
Invert 3-4x
Red, tiger, or gold tubes:
Chemistry testing
Electrolyte panel:
Bicarbonate, carbon dioxide, chloride, potassium, sodium
Basic metabolic panels:
Electrolyte panel, BUN, creatinine, glucose, calcium
Drug monitoring:
Digoxin, vancomycin, aminoglycosides, phenobarbital, phenytoin, valproic acid, methotrexate, lithium, theophylline
Comprehensive metabolic panel
Basic metabolic panel, hepatic function panel
Hepatic function panel
ALT, AST, Bilirubin, albumin, total proteins
Total cholesterol
HDL, LDL
Lipid panel
HDL, LDL, TG
Thyroid profile
T3, T4, TSH
Individual tests
Folic acid, Vitamin B12, HIV, hCG
Invert 5-6x
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Capillary/Dermal Tubes:
Pink tube:
Blood bank studies
Rh typing
Pearl/white tube:
bDNA
Keep on ice.
Royal blue with purple or red stripe:
Toxicology
Heavy metal testing
Chain of custody.
Tan, royal blue (no stripe), or lavender:
Lead levels
Royal blue (plain):
Trace metal analysis.
Sodium Heparin
Pale yellow:
Compatibility for transplant
DNA & Paternity testing.
Chain of custody
ACD
Capillary/Dermal Tubes END
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dark or light green tubes:
Any plasma test EXCEPT plasma cells
C reactive protein for inflammation
Immunoglobin A measures antibodies and tests for autoimmune diseases
Liver enzymes
Bone marrow disorders
Serum HCG
Gets spun!
Lithium heparin
Sodium heparin (Dark green)
Ammonium Heparin
Invert 8-10x
Lavender tubes:
Blood group (ABO)
Carbon monoxide levels
CBC
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
RBC
WBC
WBC w/ diff.
Platelets
Hemoglobin A1c
Rh typing
Sickle cell anemia
ANY blood cells
EDTA
Invert 8-10 times
Gray tubes:
Glucose
Glucose fasting and tolerance testing
Lactic acid
Do NOT use tourniquet
Patient does NOT need to make a fist
Blood alcohol levels:
DO NOT USE alcohol-based antiseptic
USE Chlorhexidine as an antiseptic.
Potassium Oxalate
Sodium Fluoride
Invert 8-10 times
Feel free to let me know if you have any questions, or if I missed something!! This is straight from my notebook, so it's highly likely that I missed something!
Have a wonderful day and stay safe!!
#phlebotomy#medical studies#studyblr#medical student#medical studyblr#medical stuff#order of draw#venipuncture
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
Common ototoxic medications
"FAV Q&A"
Furosemide (and other loop diuretics)
Aminoglycosides
Vancomycin
Quinine
Aspirin
#pharmacology#medicine#medical student#med school#medspo#revision#mnemonic#ototoxicity#medication#side effects#adverse effects#studyblr#student doctor#diuretics#medblr
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

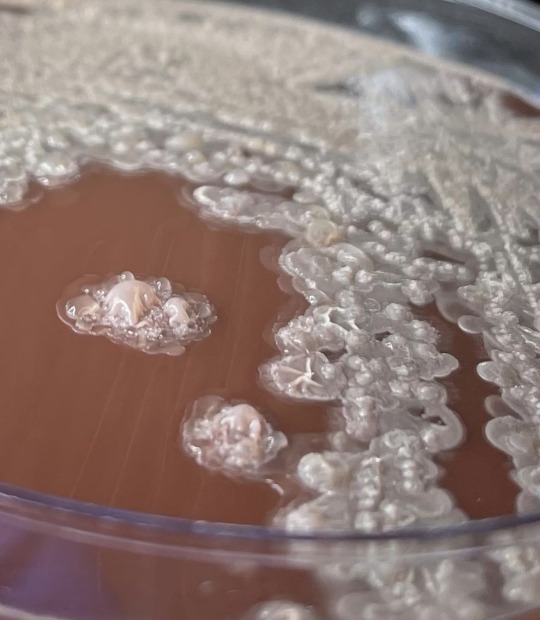
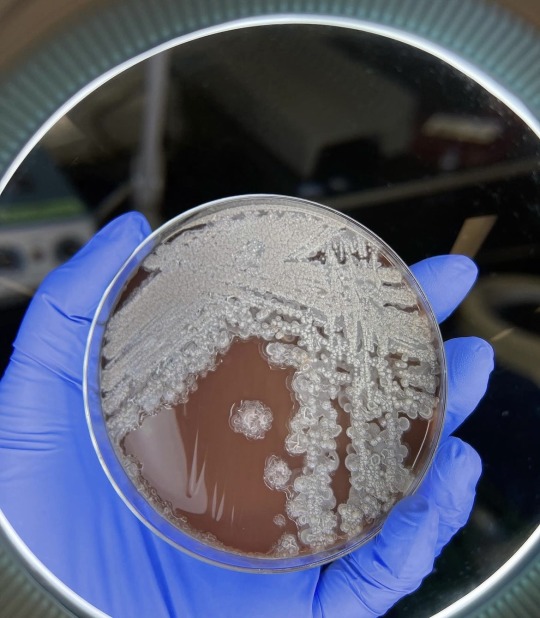

Bacillus licheniformis:
This is a gram positive bacterium commonly found in soil. It’s found on bird feathers especially chest and back plumage. It’s common in ground dwelling birds too. Is it harmful to man ? Yes it is has been found to cause infection in several cases of immunocompromised patients. It’s the causative agent of ventriculitis, ophthalmitis, bacteremia and endocarditis.
Treatment: it is sensitive to antibiotics such as cefepime, carbapenems, aminoglycosides and vancomycin.
…. Health is wealth …
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Enterococcus faecalis
As per wiki, "not to be confused with enterococcus faecium."
why in god's name are they so similarly named. I do not know. but it does change management.
Faecalis is more susceptible to penicillin and ampicillin. Faecalis is more virulent and more likely to cause IE than faecium. Faecium is also more likely to be resistant to ampicillin and vancomycin --> in the US: 80% to vanc, and 90% resistant to ampicillin.
It's a nosocomial common bug, so there aren't any cool case reports. If you walk into a ward, odds are you'll find someone with this. Not as common as staph or strep though.
Image source: bacteria under the microscope

E. Faecalis is gram positive cocci, (purple spheres), previously part of the streptococcus umbrella - if it makes it easier to remember - both appear in chains or pairs (rather than clusters like staph). Similar to strep it is catalase negative. Facultative anaerobe, so it will grow in both bottles. Faecalis is far more common than faecium, both live in the gut (think faeces). They grow at high salt concentrations, 6% (normal saline on the wards is 0.9%) and are usually non haemolytic.
Key thing to be aware of is that it can be a healthy part of your gut or genital tract but under the right circumstances for it - it can become pathogenic/disease causing. Further key thing: intrinsically resistant to bactericidal antibiotics hence they require synergism between a combination or prolonged duration in severe cases. like IE.
It's considered an opportunistic infection (for the lay public, it means when you're unwell or immunosuppressed, it becomes a problem). Increasingly it is a nosocomial infection (hospital acquired), 60% of cases in the US were acquired in hospital. They survive very harsh environments, including ethanol and can survive 10 mins at 60 degrees celsius and on surfaces from days to months. They are killed at 80 degrees or with 70% ethanol.

Similar to staph and strep, it can cause a variety of infections, including:
Infective endocarditis --> 3rd most common cause, 90% are faecalis other 5% are faecium (after staph aureus and strep viridans), subacute course, now more associated with TAVIs (elderly/frail/multimorbid patients). high mortality, 10-35%
UTIs - cause up to 20% of UTIs, but usually associated in hospital setting and with catheters/devices etc.
wound infections & OM (rarely)
line associated --> always replace lines if you can in sepsis, one cause of bacteraemia is the line
2nd or 3rd most common cause of nosocomial Utis, sepsis and wound infections (less often: diabetic ulcers, prosthetic joints)
less common: meningitis - and usually associated with shunts and neurosurgical procedures --> anything to do with devices and hospital. Mortality risk of 20%
odd association: strongyloides hyperinfection (remember this increases risk for bacteraemia), as post earlier.
sepsis/bacteraemia mortality risk is 25%
bottom line: high mortality in severe disease
Epidemio:
more likely to be found in the elderly populations who are multi-morbid and less independent in their activities of daily living.
Special powers:

No toxins (like staph or strep), but have inherent antibiotic resistance or are amenable to this and are very durable/hardy. Ability to form biofilms - hence attraction to lines and devices and staying there. This limits abx penetration allows them to persist. They gain resistance by their ability to pick up and transfer mobile gene elements like plasmids via conjugation etc. Abx including: cephalosporin, clinda, TMP-SMX, aminoglycosides like gent.
It is becoming more notorious for resistance particularly vancomycin resistant enterococcus faecalis (also not to be confused with VRE - Patients who were recently hospitalised or institutionalized are often swabbed for this, but this is actually E. faecium they're referring to). increased risk for this include previous antibiotics use (eg cephalosporins, vancomycin), due to disrupted gut biome, and exposure risk - more likely to occur if you've been recently hospitalised, require routine access to the wards (i.e. dialysis) etc. Also increased association with devices (like pacemakers), diabetics and stomach acid suppression from PPIs.
Investigations
Relevant imaging i.e. CT for abdominal collections, and culture/staining. sensitivities are an absolute must including aminoglycoside resistance, pencillin and vanco, which most labs will automatically do anyway when it's identified, teams just gotta remember to chase. other possibilities include PCR or 16s rRNA sequencing
Interesting additional work up: Colonoscopies. Some reports are starting to recommending doing this routinely if no source is found in cases of bacteraemia or IE. As there is an increasing association with neoplasms from the gut. Similar to guidelines for strep bovis.
Management
in general UTIs, wound infections etc, most are susceptible to penicillins and ampicillin, so you can treat with either.
Management of beta lactam resistant enterococcus:
- resistant against beta lactams --> refer to immunology for desensitisation, vanco is not as effective against enterococci, duration is 6 weeks in severe infection
Vanco resistant (your local infectious diseases team will be involved)
daptomycin, linezolid --> equally effective, tigecycline (last resort/salvage)
Treatment in IE --> synergism is key for bacteriocidal effect (durability)
in case of bacteraemia, try the denova calculator to determine risk of IE - Duration of symptoms, Embolizations, Number of positive cultures, Origin, valve disease, and Auscultation murmurs
if susceptible, it's intermittent doses of benzylpenicillin or continuous infusion at 2.4 g IV plus gentamicin (if concerning for kidneys, shorten the duration to 2 weeks) for approx 4-6 weeks
--> unless there's high level resistance to aminoglycosides
or if resistant as above options
issue with aminoglycosides -> ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity, requires frequent monitoring and caution in elderly
Resources:
Pathogen data sheet - Canadian government
StatPearls
Australian therapeutic guidelines - paywall, unless you're at an Australian hospital/medical school
Uptodate - always the gold standard, but is behind a paywall unless you have institutional access
Wikipaedia
#infectious diseases#internal medicine#medblrs#medblr#microbiology#infectious disease#enterococcus#enterococci#e faecalis#enterococcus faecalis
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Q. Why do we treat neonates with "Amp & Gent"?
A. Ampicillin is a penicillin that covers Group A Streptococcus, Group B Streptococcus, and Listeria monocytogenes.
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside that covers Escherichia coli and Methicillin Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus.
Together they have synergy against Enterococcus spp.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ah! so the antibiotics in patho are based off of aminoglycoside antibiotics!! I knew i recognised the -mycin ending...

neomycin is the only real one though - monomycin and ferromycin are made up. but ferro- suggests that the antibiotic contains an iron atom somewhere, and that feeds into a working theory i have about heme and othersuch iron-containing molecules in humans and bulls rather nicely...
bwahahah... holy shit...
Aminoglycosides are thought to work by inhibiting protein synthesis inside bacteria. Kill rates of bacteria are increased when higher concentrations of aminoglycosides are present; however, the margin between a safe and a toxic dose is narrow and monitoring is often needed, although once daily dosing increases the safety window. Impairment of kidney function and hearing loss are the most common side effects of aminoglycosides. Aminoglycosides tend to be used when other less toxic antibiotics are contraindicated or ineffective.
(aminoglycoside drug class page)
No wonder taking them fucks you up so bad ingame :D :D :D man i wish theres were like... penicillins or literally any other group of antibiotics to compare effectivity...
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
The global Aminoglycosides Antibiotics market size is estimated to be worth US$ 1051.5 million in 2021 and is forecast to a readjusted size of US$ 1244.9 million by 2030 with a CAGR of 2.4% during the forecast period 2022-2030.
0 notes