#Manitobatours
Text
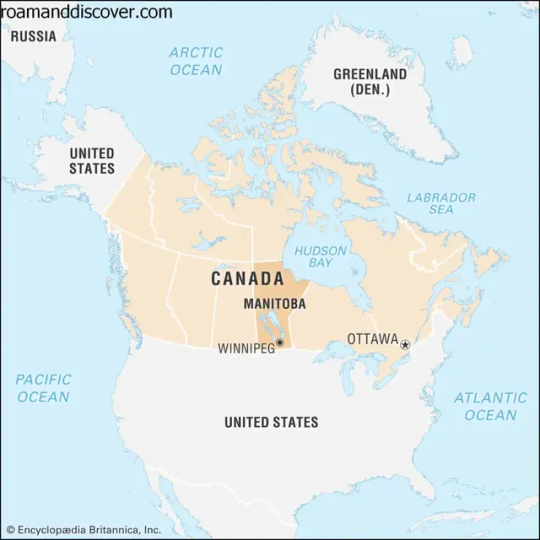
Manitoba

Manitoba is a province located in central Canada, known for its diverse landscapes, multiculturalism and rich history. It is home to many Indigenous communities and has a vibrant culture with a mix of European, Asian and Indigenous influences.
The name Manitoba comes from the Cree word "Manitou-wapow," meaning "the narrows of the Great Spirit," referring to the Lake Manitoba and Lake Winnipegosis region. The region was originally inhabited by Indigenous peoples for thousands of years before European contact in the 17th century.
The province has a fascinating history that includes the fur trade, the arrival of the first European settlers, as well as tensions between Indigenous peoples and Europeans. Today, Manitoba continues to evolve economically, socially and environmentally, and attracts tourists from all over the world.
Manitoba's geography includes the Canadian Shield, the Prairies, and the Hudson Bay Lowlands. The province is home to many species of wildlife, including polar bears, wolves, caribou and moose. the province produces large amounts of hydroelectric power from its many lakes and rivers, powering much of Canada's industry.
The climate in Manitoba varies depending on the region. The southern area experiences humid continental climate, while the northern region has a subarctic climate with short, cool summers and long winters. Manitobans enjoy many outdoor activities such as fishing, hunting, skiing, and snowmobiling in the wintertime.
The people of Manitoba are diverse and welcoming, with a mix of English, French, and Indigenous languages spoken throughout the province. The population has increased in recent years, largely due to immigration, making the province one of the most diverse in Canada.
If you're planning a visit to Manitoba, you'll find that there is an abundance of cultural and recreational activities, major cities and towns with friendly locals, and a variety of delicious cuisine. Manitoba is a great place to visit, live or work, and is a beacon of hope for all who strive to maintain the balance between economic progress and environmental stewardship.
Etymology in Manitoba
Manitoba is a province located in the heart of Canada, with a history that dates back thousands of years. The name "Manitoba" has an interesting origin and meaning behind it. It is derived from two words, "Manitou" and "Waba", which are derived from the languages of the Indigenous peoples who inhabited the region. The word "Manitou" translates to "the Great Spirit" or "the Creator Spirit", while "Waba" means "the Narrows" or "the Strait".
The origin of the name Manitoba can be traced back to the Cree and Ojibwe languages, which were spoken by the Indigenous peoples who lived in the region. The name was first recorded in 1688 on a French map of the Great Lakes region, and it was used to refer to the area around Lake Manitoba and Lake Winnipegosis.
The name "Manitoba" also has a rich cultural and historical significance for the Indigenous peoples of the region. The Great Spirit referred to in the name is an important figure in their spiritual beliefs, and the Narrows or Strait connects two important bodies of water, Lake Manitoba and Lake Winnipeg.
Today, Manitoba is known as the "Keystone of the West" and continues to honor its Indigenous heritage through its many cultural events and festivals. The name Manitoba represents the diverse and rich history of the province, and it is a symbol of the connection between the past, present, and future of the region.
History in Manitoba
Manitoba has a rich and diverse history, shaped by both Indigenous and European influences. The area that is now Manitoba has a long history of human habitation, with evidence of Indigenous peoples dating back over 8,000 years.
European exploration and settlement in the region began in the 17th century, with the arrival of French fur traders and French-speaking Métis people. British control of the area began in 1763 with the Treaty of Paris, which ceded much of what is now Canada to Britain.
The Red River Colony was established in 1811, and over the years it became an important hub for fur trading and agriculture. In 1869, a group of Métis people led by Louis Riel rebelled against the Canadian government, resulting in the establishment of the province of Manitoba in 1870.
The early years of Manitoba's history were marked by conflict between the predominantly English-speaking newcomers and the French-speaking Métis population, who felt that their rights and culture were being threatened by the influx of settlers from Eastern Canada. This conflict came to a head in 1885 with the North-West Rebellion, which was met with a strong military response from the Canadian government.
In the years that followed, Manitoba became a province in its own right, and its economy began to grow and diversify. It became known for its agricultural production, particularly wheat and other cereal crops, and its rich reserves of minerals and other natural resources.
Today, Manitoba continues to be a thriving and dynamic province, with a rich and diverse cultural heritage that reflects both its Indigenous and European roots. Its vibrant arts scene, excellent healthcare system, and strong economy make it an attractive destination for people from all over the world.
Indigenous history in Manitoba
Indigenous peoples have a long and rich history in the region now known as Manitoba. The province is home to many First Nations, Inuit, and Métis communities, each with their own unique culture and traditions.
Manitoba's Indigenous history dates back thousands of years. The first peoples to settle in the area were nomadic hunters and gatherers who migrated across the Bering Strait and down through North America. These early peoples made use of Manitoba's land and natural resources to survive and thrive.
Over time, Indigenous communities in Manitoba developed complex societies and cultures. They established trade networks and formed alliances with neighboring nations. They also created sophisticated art forms, such as beadwork, quillwork, and birch bark biting.
The arrival of Europeans in the 17th century had a profound impact on Indigenous peoples and their way of life. Europeans brought with them diseases like smallpox, which devastated Indigenous populations. They also introduced new technologies, such as firearms and metal tools, which changed the dynamics of hunting and warfare.
Despite these challenges, Indigenous communities in Manitoba persisted. They adapted to the changing world and continued to hold onto their culture and traditions. Today, many Indigenous communities in Manitoba are actively working to preserve their language, art, and heritage.
One example of this is the Manitoba Indigenous Cultural Education Centre, which provides programs and services that promote Indigenous history, culture, and language. The centre works to increase understanding and appreciation of Indigenous peoples among non-Indigenous people in Manitoba.
In recent years, there has also been a growing movement to recognize and address the legacy of residential schools in Manitoba and across Canada. Residential schools were government-funded and church-run institutions that were designed to forcibly assimilate Indigenous children into European culture. The schools operated from the 1870s until the 1990s and had a devastating impact on Indigenous communities. Many survivors of residential schools have spoken out about the abuse they endured and the long-term effects it had on their families and communities.
Today, Manitoba's Indigenous peoples continue to play an important role in the province's cultural fabric. They have made significant contributions to the arts, literature, and sports, and continue to work towards greater recognition and respect for their rights and heritage.
European colonization in Manitoba
European colonization in Manitoba began in the 17th century when French fur traders arrived in the region. Through the fur trade, the French established relationships with Indigenous peoples, trading goods for furs. Eventually, the Hudson's Bay Company gained control of the region, leading to increased European influence and settlement.
The impact of European exploration and settlement on the region was significant. The arrival of Europeans brought new diseases that had devastating effects on Indigenous populations. The loss of life and culture cannot be understated.
As settlement increased, the fur trade began to decline in Manitoba. This led to the development of other industries, such as agriculture and mining. The construction of railroads and the development of transportation systems facilitated the growth of these industries.
However, the growth of European settlement in Manitoba was not without conflict. The Métis, a mixed-race group of Indigenous and European ancestry, faced discrimination and marginalization. This culminated in the Red River Rebellion in 1869-70, a significant event in Manitoba's history that led to the province's formation in 1870.
The impact of European colonization on Manitoba's culture and land is still felt today, with ongoing efforts by Indigenous peoples to reclaim their land and protect their culture. Manitoba is also home to various historical sites related to European colonization, such as the Lower Fort Garry National Historic Site, a former trading post and military fort established by the Hudson's Bay Company.
the impact of European exploration and settlement on Manitoba's history is complex and multifaceted. While it brought new industries and economic growth, it also had devastating effects on Indigenous populations and their way of life. Understanding this history is crucial to understanding Manitoba's culture and identity today.
Geology in Manitoba
Manitoba's geology consists of a mixture of ancient rocks and overlying sediments. The province has three main geological regions: the Canadian Shield, the Hudson Bay Lowland, and the Interior Plains.
The Canadian Shield, occupying the northeastern part of Manitoba, is an ancient mountain range consisting of igneous and metamorphic rocks that are over two billion years old. This region is rich in minerals and contains important deposits of copper, nickel, gold, and silver.
The Hudson Bay Lowland, located in the north-east corner of the province, is a flat, marshy region with low-lying valleys and rolling hills that was shaped by glaciers during the last ice age. This region contains vast peatlands, which are important for carbon sequestration and wildlife habitats.
The Interior Plains, extending across most of Manitoba, is characterized by flat to gently rolling hills and fertile agricultural land. This region consists of layers of sedimentary rocks deposited by ancient seas and contains important oil and gas deposits.
Manitoba's natural resources include minerals, oil, natural gas, timber, and hydroelectric potential. Mining is an important industry in the province, with companies extracting nickel, copper, and zinc from the Shield region. The oil and gas industry is also prominent, with discoveries of oil in southwestern Manitoba and natural gas in the southern part of the province.
Forestry is a significant industry in the Interlake region, where companies harvest softwood trees mainly for use in pulp and paper production. Manitoba's abundant water resources provide a source of hydroelectric power, with several hydroelectric dams located throughout the province.
- Manitoba's mineral resources:
- Copper
- Nickel
- Gold
- Silver
- Manitoba's oil and gas resources:
- Oil in southwestern Manitoba
- Natural gas in the southern part of the province
- Manitoba's forestry resources:
- Softwood trees primarily for pulp and paper production
- Manitoba's hydroelectric resources:
- Several hydroelectric dams located throughout the province
Manitoba's geology is diverse and provides significant economic benefits to the province through its vast mineral and natural resources. The Canadian Shield, Hudson Bay Lowland, and Interior Plains each have their unique geological makeup and natural resources, contributing to the province's rich landscape and economic prosperity.
Geography in Manitoba
Manitoba is a province located in the heart of Canada, bordered by Ontario to the east and Saskatchewan to the west. Its northern boundary is the 60th parallel, which it shares with the Northwest Territories. The province covers a total area of 649,950 sq. km.
The terrain in Manitoba is quite varied. The province is generally flat and featureless, with pockets of rolling hills and escarpments. The northeastern part of the province is dotted with lakes and boreal forests, while the south is predominantly covered in prairie grasslands. Manitoba is also home to several major rivers, including the Red, Assiniboine, and Winnipeg rivers.
One of the most notable landforms in Manitoba is the Manitoba Escarpment, which separates the province's southern prairies from the boreal forests to the north. The escarpment runs from western Manitoba into Minnesota and North Dakota.
Manitoba is also home to several major lakes, including Lake Winnipeg, which is one of the largest freshwater lakes in the world. The province also boasts several smaller lakes and reservoirs, including Lake Manitoba and Lake Winnipegosis.
The province's location in the center of North America has made it an important transportation hub. Several major highways and railways run through Manitoba, connecting the province with other parts of Canada and the United States.
Manitoba's geography is diverse and fascinating, with something to offer for everyone. Whether you are interested in exploring the prairies, boreal forests, or lakes and rivers of the province, Manitoba truly has it all.
Ecology in Manitoba
Manitoba is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, with a number of unique habitats and ecosystems that support a wide variety of plant and animal life. From boreal forests to grasslands, wetlands to tundra, the province is home to a range of ecosystems that support different types of life.
The boreal forest, which covers a significant portion of the province, is home to a number of tree species including black spruce, jack pine, and balsam fir. This forest is also home to a variety of wildlife, such as moose, caribou, and black bears.
The grasslands in southern Manitoba are home to some of the rarest and most endangered species in Canada, including the chorus frog, the loggerhead shrike, and the burrowing owl. These regions are also important habitats for prairie grasses, which play a critical role in preventing soil erosion and maintaining healthy soil ecosystems.
Wetlands are another important ecosystem in Manitoba, accounting for roughly 15% of the province's land area. These areas serve as crucial habitat for a wide range of waterfowl, such as ducks and geese, as well as other species like beavers and otters. They are also important for cleaning and storing water, and for mitigating the effects of floods.
The tundra in Manitoba's far north is characterized by harsh weather conditions and rugged terrain, but is nevertheless home to a number of native species such as lemmings, Arctic foxes, and polar bears.
Manitoba's waters are also teeming with life, supporting fish populations such as walleye, northern pike, and lake trout. The province is also home to a number of species of turtles, frogs, and salamanders.
Manitoba is a rich and diverse province when it comes to its ecology, and is home to many species of plants and animals that cannot be found anywhere else in Canada.
Biodiversity in Manitoba
Manitoba is home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, thanks to its wide range of habitats. From the boreal forest in the north to the prairie grasslands in the south, there is an abundance of flora and fauna to explore.
The province is home to over 320 bird species, including the iconic bald eagle and the great gray owl. Manitoba's waterways are also home to many species of fish, such as walleye, northern pike, and lake trout. In addition, the province has many wetlands, which serve as important habitats for waterfowl and other water-loving species.
On land, the province is home to many mammals, such as the black bear, moose, and beaver. Manitoba is also home to many species of reptiles and amphibians, including the western painted turtle and the northern leopard frog.
The province's flora is just as diverse, with over 1,400 species of plants. The boreal forest is home to many species of coniferous trees, such as spruce and pine, while the grasslands are dominated by prairie grasses and wildflowers, such as the iconic purple prairie clover.
Manitoba's biodiversity is not only important for its own sake, but also for the health of the region's ecosystems and the services they provide. Wetlands, for example, help to filter water and prevent flooding, while forests play an important role in storing carbon and mitigating climate change.
The province has several protected areas, such as Riding Mountain National Park, that are dedicated to conserving Manitoba's diverse ecosystems and the species that inhabit them. These areas provide opportunities for visitors to appreciate and learn about the province's natural wonders.
If you're interested in learning more about Manitoba's biodiversity, you may want to check out some of the province's nature reserves or parks. The Oak Hammock Marsh Interpretive Centre, for example, offers educational programs and exhibits about wetlands, while the Manitoba Museum has many exhibits about the province's flora and fauna.
Manitoba's biodiversity is a rich and fascinating subject, with many species of plants and animals to discover. Whether you're an avid nature enthusiast or just starting to explore the province's natural wonders, there is something for everyone to appreciate.

Moose
Climate in Manitoba
Manitoba has a continental climate characterized by cold winters and warm summers. The province experiences a wide range of temperatures throughout the year. On average, temperatures can dip down to -20°C (-4°F) in winter and rise to 25°C (77°F) in summer. The variation in temperature is due to Manitoba's location in the center of the North American continent and its distance from large bodies of water.
Winter in Manitoba can last around six months and is known for its frigid temperatures. During winter, the province experiences heavy snowfall which can lead to snowdrifts and icy conditions. The annual snowfall averages around 1.2 meters (4 feet). While winter can be bleak and harsh, it also provides ample opportunities for winter sports like skiing, snowshoeing, snowmobiling, and ice fishing.
Summer in Manitoba can be hot and humid with temperatures ranging from 20°C (68°F) to 30°C (86°F). In the summer, the daylight hours are longer, providing ample time for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, fishing, and boating.
Read the full article
1 note
·
View note
Photo

https://soiwasthinking.blog/2021/03/06/exploring-country-roads-with-brandy/ #iledeschenes #iledeschenesmanitoba #iledeschênes #manitoba #manitobaphotography #manitobatourism #hiking #hikingadventures #hikingwithdogs #hike #walk #walking #walkingthedog #countryroads #countryroad #skunks #dogs #dog https://www.instagram.com/p/CNy20XVHVV5/?igshid=6iseaisxrz9y
#iledeschenes#iledeschenesmanitoba#iledeschênes#manitoba#manitobaphotography#manitobatourism#hiking#hikingadventures#hikingwithdogs#hike#walk#walking#walkingthedog#countryroads#countryroad#skunks#dogs#dog
0 notes
Photo

So great working on an amazing project with @htfcwpg again! HTFC brought us on board to build these beautiful benches. We used salvaged 200 year old Manitoba Oak for the benches. The curved timbers were all cut from solid timbers! The new park is just another great reason to visit Gimli!⚓️ #Repost @htfcwpg (@get_repost) ・・・ #tbt to last week's opening of Gimli Viking Park! The new park gives the existing Viking an enhanced home and celebrates Gimli’s history and Canadian-Icelandic culture. We’re grateful for a wonderful collaboration with the Icelandic Festival of Manitoba, Betel Home, and the RM of Gimli. Special thanks to SMS Electrical Engineers, Crosier Kilgour Structural Engineers, Shelmerdine, Wood Anchor, Parr Metals, and Barkman Concrete. #woodanchor #gimli #benches #exteriordesign #landscapedesign #outdoorbench #park #exploremanitoba #exploregimli #manitobatourism (at Viking Statue, Gimli Manitoba)
#tbt#repost#manitobatourism#gimli#woodanchor#benches#park#exploregimli#exteriordesign#outdoorbench#exploremanitoba#landscapedesign
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Breakwater Artwork in Gimli . . . . . . . . . #manitobatourism #manitoba #travelmb #explorecanada #exploremb #lakelife #lake #canada (at Gimli, Manitoba)
0 notes
Photo

Another beautiful fall morning at the cottage with @trvltodiscover . #discovercanada #traveltodiscover #manitobatourism #riverton #interlake #canadasheartbeats #explorecanada #igerscanada (at Riverton, Manitoba)
#discovercanada#canadasheartbeats#igerscanada#manitobatourism#explorecanada#riverton#interlake#traveltodiscover
0 notes
Photo

Dinner at the park with the family. #exploremb #wanderlusting #travelmanitoba #manitobatourism #picnic #wanderlust #familygoals (at Kildonan Park Playground)
0 notes
Photo

https://soiwasthinking.blog/2020/08/11/trappist-monastery-provincial-park/ Trappist Monastery Provincial Park. Our Lady of the Prairies. #monastery #trappist #trappistmonastery #trappistmonks #trappistmonk #trappistmonasteryruins #ruins #monk #monks #history #historic #historichomes #historical #stnorbert #manitoba #manitobaphotography #manitobaphotographer #manitobatourism #travelphotography #travel #travelmanitoba #hiking #hikingadventures #hike #hikingwithdogs #hikingtrails #peace #peaceful #meditation https://www.instagram.com/p/CDyitZ3H_Jb/?igshid=1kofa582hyu3v
#monastery#trappist#trappistmonastery#trappistmonks#trappistmonk#trappistmonasteryruins#ruins#monk#monks#history#historic#historichomes#historical#stnorbert#manitoba#manitobaphotography#manitobaphotographer#manitobatourism#travelphotography#travel#travelmanitoba#hiking#hikingadventures#hike#hikingwithdogs#hikingtrails#peace#peaceful#meditation
0 notes
Photo

https://soiwasthinking.blog/2020/08/11/trappist-monastery-provincial-park/ Trappist Monastery Provincial Park. Our Lady of the Prairies. #monastery #trappist #trappistmonastery #trappistmonks #trappistmonk #trappistmonasteryruins #ruins #monk #monks #history #historic #historichomes #historical #stnorbert #manitoba #manitobaphotography #manitobaphotographer #manitobatourism #travelphotography #travel #travelmanitoba #hiking #hikingadventures #hike #hikingwithdogs #hikingtrails https://www.instagram.com/p/CDyic9SHuQD/?igshid=1janh80wxj48w
#monastery#trappist#trappistmonastery#trappistmonks#trappistmonk#trappistmonasteryruins#ruins#monk#monks#history#historic#historichomes#historical#stnorbert#manitoba#manitobaphotography#manitobaphotographer#manitobatourism#travelphotography#travel#travelmanitoba#hiking#hikingadventures#hike#hikingwithdogs#hikingtrails
0 notes
Photo

While me and my sister in law waiting for Aurora Borealis. . . . . . #aurora #auroraborealis #nightphotography #longexposure #ridingmountain #ridingmountainnationalpark #travelmanitoba #manitoba #manitoba411 #manitobatourism #manitobaphotography #manitobaphotographer #lakelife #canada #travelcanada🇨🇦 #deptheffect #depthobsessed #inspomb #sony6000 #sonya6000 (at Riding Mountain National Park)
#manitoba411#sony6000#canada#depthobsessed#nightphotography#lakelife#inspomb#ridingmountainnationalpark#travelcanada🇨🇦#auroraborealis#longexposure#aurora#ridingmountain#travelmanitoba#manitobatourism#deptheffect#sonya6000#manitoba#manitobaphotography#manitobaphotographer
0 notes
Photo

Almost there, the leaves are falling. Snow flakes coming up! ❄️☃️❄️. . . . . . . . . #manitoba #manitoba411 #manitobatourism #manitobaphotography #manitobaphotographer #wpg #wpgnow #wpgofinstagram #ywg #yourmanitoba #ywgphotographer #travel #travelwinnipeg #travelmanitoba #travelcanada🇨🇦 #travelblogger #canada #canada150 #visualabassadors #deptheffect #depthobsessed (at The Forks)
#travelcanada🇨🇦#manitoba#manitobaphotographer#canada#deptheffect#wpgofinstagram#travelwinnipeg#yourmanitoba#manitobaphotography#ywgphotographer#canada150#travelblogger#travel#depthobsessed#visualabassadors#manitoba411#travelmanitoba#wpg#wpgnow#ywg#manitobatourism
0 notes