Text
Behavior management
Non pharmacological
1. Tell show do
Tell – Explain procedure with age appropriate language
Show – Demonstrate procedure
Do – Perform procedure
Communication should be gentle, addressing the child. Use euphemism (eg. call LA “sleeping juice”, rubber dam “umbrella”) and smile. Have positive reinforcement.
2. Behavior modelling – Show other children getting procedures and how they behave
3.…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
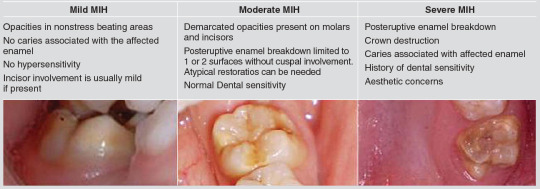
Molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH)
Clinical appearance of enamel hypomineralization of systemic origin affecting one or more permanent first molars (PFM) that are frequently associated with incisors
Etiology:
Oxygen shortage + low birth weight
Parental risks – infection, maternal psychological stress
Complications during delivery
Respiratory diseases and oxygen shortage of ameloblasts
Children born with poor general…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Dental fluorosis
Developmental disturbance of dental enamel, caused by successive exposure to high concentrations of fluoride – 1.5 mg/l (1.5 ppm) in drinking water – during tooth development , leading to enamel with lower mineral content of increased porosity
Etiopathogenesis:
Direct inhibitory effect on enzymatic action of ameloblasts leading to defective matrix formation and subsequent…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Prescribing Drugs
How to prescribe
1. Formulation of drug: PO, IV, IM, PV, PR
2. Name of drug: Paracetamol, Amoxycillin
3. Dosage: mg, g, avoid decimals
4. Frequency: OD, BD, TDS, Nocte, PRN (state minimum dose interval in PRN)
5. Duration: 5/7, 2/52, 3/12
Eg. PO Augmentin 625mg BD x 5/7
1-5 years: 1/4 of adult dose
6-12 years: 1/2 of adult dose
Calculating Drug dosage
Use the app Dental Drugs (App…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
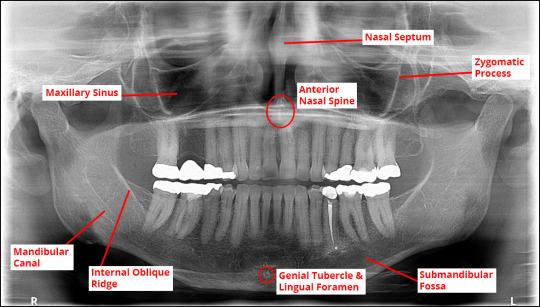
Radiology: X-Ray positions
Bilateral bite wing (BBW)
Patient head straight so occlusal plane is parallel to the floor
Bite should be normal
X-ray central beam:
Vertical angulation: +10°
Horizontal angulation:
Premolar BBW: 30° from mid-sagittal plane, aimed at inner canthus of the eye
Molar BBW: 60° from mid-sagittal plane, aimed at outer canthus of the eye
Watch video
Intraoral periapical (IOPA)
Identification…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Dental instruments
Download Medicos Dental Material App on:
App store
Play store
This app has instruments, their name and use and tray set ups for all dental procedures
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Chronology of tooth development and eruption
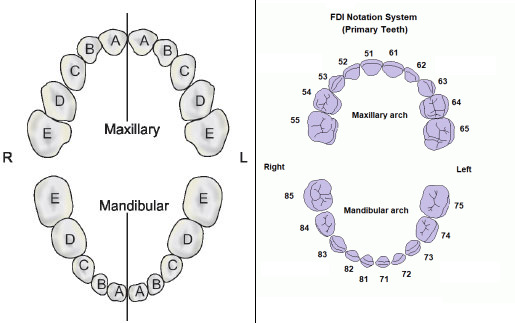
Primary teeth
Sequence of eruption: A-B-D-C-E
ToothArchCalcification(Weeks in utero)Crown completion (Months)Eruption(Months)Root completion(Years)ACIMaxMand141.52.51081.5BLIMaxMand162.53111321.5CCMaxMand17919203DM1MaxMand1565.5162EM2MaxMand1918111029273Primary teeth development and eruption
Permanent teeth
Sequence of eruption:
Maxilla: 6-1-2-4-5-3-7-8
Mandible:…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Tooth extraction
Patient positioning when extracting teeth
Maxillary teeth: 3 inch below shoulder level of operator and 45 degree chair angulation
Mandibular teeth: At elbow level of operator and 90 degree chair angulation
1st, 2nd and 3rd quadrant: Right front of patient
4th quadrant anterior teeth: Right front of patient
4th quadrant posterior teeth: Behind right side of patient/ just right side
Tooth…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Extraction forceps
Maxillary extraction forceps
Maxillary anterior forceps – Incisors and canines
©Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons of India
Maxillary premolar forceps – Premolars
©Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons of India
Maxillary molar forceps – Molars
©Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons of India
Maxillary cow horn forceps – Molars with extensive loss of coronal…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Radioanalysis of impacted teeth
Canine localization
Parallax in horizontal plane: Two IOPA or USO + IOPA
Parallax in vertical plane: OPG (↑8°) + USO (↓65-70°) to horizontal plane
SLOB: Same Lingual Opposite Buccal
If in line with arch, will not move
Can do CBCT
Third molars
X-rays used:
IOPA – difficult due to gagging
OPG
Oblique lateral view
Lower/upper oblique occlusal view – buccolingual position
CBCT
1.…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Trauma and fractures
Classification of dentoalveolar injuries
Injuries to dental hard tissues and pulp
Enamel infraction – incomplete crack of enamel, no loss of tooth structure
Enamel fracture – loss of tooth structure involving enamel only
Enamel dentine fracture – loss of enamel and dentine, pulp not involved
Complicated crown fracture – crown fracture involving pulp
Complicated crown root fracture – enamel,…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Local Anesthesia
Techniques of administrating LA
1. Inferior alveolar nerve block: Mandibular posterior teeth
Picture
Between pterygomandibular raphe and coronoid notch (feel with thumb)
Insert from contralateral side, 1cm above occlusal plane
Contact bone, withdraw slightly and give LA
2. Mental nerve block: Mandibular anterior teeth
Picture
Between 1st and 2nd premolar
3. Anterior, middle, posterior…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Soft tissue cysts
Dermoid cyst:
Etiology: Epithelial tissue implanted into another structure
Commonly: Face, inside skull, lower back, ovaries
Clinical: Mature skin with sweat glands, hair follicle, sebum, blood, fat, bone, cartilage, nails, teeth
Benign, solitary, expand slowly due to accumulation of epithelial debris and glandular secretion
Non tender
Can rupture
Picture
Epidermoid cyst: Lined with…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Soft tissue radiopacities and dystrophic calcifications
Calcification is soft tissues i.e. heterotopic ossification
1. Dystrophic calcification
Degenerated, diseased, dead tissue
Normal calcium and phosphate levels
Localized to site of injury (trauma, infection, inflammation) eg. cysticercosis parasite
a. Chronically inflamed cysts – eg. Residual cyst
b. Calcified lymph nodes
Cervical tuberculosis adenitis
Sarcoidosis
Cat scratch…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Maxillary sinus radiology
1. Inflammatory
a. Retention cyst – Mucosal gland blocked
b. Mucocele
Sinus opening in nasal passage blocked (allergy/cold)
Sinus filled with thick viscous fluid
Radiology: Clouding/opacification of whole sinus, sclerotic border still intact
If bacterial infection – destroy sclerotic wall
Picture
c. Sinusitis
Mucosa lining thickened – opaque thickening on sclerotic border
Long standing…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Radiology of lesions
Radiolucent lesions
A. Periapical radiolucency
Apical periodontitis – widened PDL at root apex
Bone cyst – UL/ML – round at periapex or scalloped between PM and M roots
Periapical abscess or granuloma
Periapical COD – early
Radicular cyst
Scar – dense fibrous tissue in RCT treated tooth
B. Pericoronal radiolucency (impacted teeth)
AOT
Ameloblastoma – UL/ML – resorbed roots
Ameloblastic…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
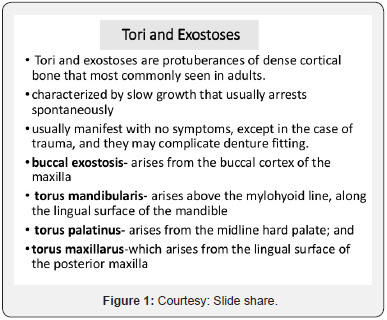
Exostosis, enostosis and tori
Exostosis
Overgrowth of mature bone from periosteal surface extending outwards
Picture
Enostosis
Overgrowth of bone from endosteal surface extending into marrow space
Picture
Tori
Bony overgrowths, not a neoplasm
Picture
View On WordPress
0 notes