#merozoite
Text
Adagrasib Sensitizes Polyhematoporphyrin-Mediated Photodynamic Treatment inside Cholangiocarcinoma through Focusing on xCT
Although Any. baumannii is considered as among the more threatening "superbugs'' for the health-related technique, minor is understood concerning the factors adding to their pathogenesis. In this function we all show that A. baumannii ATCC 17978 has the O-glycosylation system responsible for your glycosylation regarding multiple meats. 2D-DIGE and also bulk spectrometry methods discovered several Any Fluorouracil inhibitor . baumannii glycoproteins, regarding but unfamiliar operate. The actual glycan structure was resolute utilizing a mix of Microsoft and also NMR tactics along with consists of a branched pentasaccharide containing N-acetylgalactosamine, sugar, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, plus a kind regarding glucuronic chemical p. A glycosylation bad tension ended up being produced simply by homologous recombination. This particular stress would not present virtually any growth flaws, yet displayed the greatly diminished ability to create biofilms. Dysfunction with the glycosylation machines additionally led to diminished virulence by 50 percent contamination types, your amoebae Dictyostelium discoideum and the caterpillar with the insect Galleria mellonella, and lowered in vivo health and fitness in a computer mouse button model of peritoneal sepsis. Despite A. baumannii genome plasticity, the actual O-glycosylation machinery is apparently seen in just about all clinical isolates analyzed along with each of the genomes sequenced. This suggests the existence of a solid transformative strain in order to retain this technique. These types of outcomes jointly reveal which O-glycosylation in the. baumannii is necessary regarding entire virulence and so represents a manuscript targeted to add mass to fresh antibiotics.At any time there have been a truism that is that their a totally defensive Plasmodium falciparum malaria vaccine can be desperately needed. Each of our institute features devoted all its endeavours over the last Thirty years to be able to creating a fully protecting, small subunit-based, multiepitope, multistage (focusing on sporozoite as well as merozoite protein), chemical produced antimalarial vaccine, given that peptides with good joining activity to their equivalent host tissues (hard working liver cellular material or even crimson body cellular material) form the springboard pertaining to vaccine layout. Nevertheless, such maintained high activity joining peptides should be exclusively altered for you to render them straight into extremely immunogenic and protection-inducing peptides since they will be immunologically noiseless. These types of adjustments, reviewed in the Animations constitutionnel amount through H-1-NMR, enable them a much better squeeze into your MHC II-peptide-T-cell receptor complicated to stimulate an appropriate resistant result, providing the reasonable as well as logical method (reviewed with the solitary atom amount) pertaining to vaccine improvement, especially in the area of malaria.Background Babies using post-haemorrhagic ventricular dilatation (PHVD) have a superior likelihood of severe incapacity and also selleck chemicals llc parenchymal infarction boosts this specific threat. Present cranial ultrasound exam (CUS) markers of neurodevelopmental outcome are based on categorical features. Objective To analyze how much quantitative CUS proportions methylhexanamine associated together with seriousness of developing outcome along with the requirement for ventriculoperitoneal (Vice president) shunt from 2 years of age. Design 69 premature babies using PHVD had side ventricle area, intraventricular echodensity as well as parenchymal lesion sizes tested at the start of strategy to PHVD. Final result measures ended up the actual Bayley Scales regarding Infant Development-II along with functional potential from A couple of years old.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Population genomics of Plasmodium ovale species in sub-Saharan Africa
Plasmodium ovale curtisi (Poc) and Plasmodium ovale wallikeri (Pow) are relapsing malaria parasites endemic to Africa and Asia that were previously thought to represent a single species. Amid increasing detection of ovale malaria in sub-Saharan Africa, we performed a population genomic study of both species across the continent. We conducted whole-genome sequencing of 25 isolates from central and east Africa and analyzed them alongside four previously published west and central African genomes. Isolates were predominantly monoclonal (27/29), with their genetic similarity aligning with geography. Pow showed lower average nucleotide diversity (1.9x10-4) across the genome compared to Poc (2.8x10-4) (p < 0.0001). Signatures of selective sweeps involving the dihydrofolate reductase gene were found in both species, as were signs of balancing selection at the merozoite surface protein 1 gene. Differences in the nucleotide diversity of Poc and Pow may reflect unique demographic history, even as similar selective forces facilitate their resilience to malaria control interventions. http://dlvr.it/T5Tgvw
0 notes
Text
📆 2020 📰 The malaria parasite sheddase SUB2 governs host red blood cell membrane sealing at invasion
Malaria kills or disables hundreds of millions of people across the world, especially in developing economies. The most severe form of the disease is caused by Plasmodium falciparum, a single-cell parasite which, once inside a human host, forces its way into red blood cells to feed on a protein called haemoglobin. This invasion relies on P. falciparum being engulfed by the membrane of the red blood cell, which then seals off to form a compartment inside the cell where the parasite can feed and multiply. Invasion takes less than 30 seconds, and it involves P. falciparum losing the coat of proteins that covers its surface. An enzyme calls SUB2 cleaves or cuts off these proteins, but exactly why and how the shedding takes place during infection is still unclear.
To investigate, Collins, Hackett et al. deactivated the gene which codes for SUB2, and examined how mutant P. falciparum would survive and multiply. Without the enzyme, the parasites failed to shed many of their proteins, including some that were not previously known to be removed by SUB2. The majority of the genetically modified parasites also failed to invade red blood cells. In particular, most of the host cells ruptured, suggesting that the protein coat needs to be discarded for the engulfing process to be completed properly. When the enzyme-free mutants did manage to make their way into a red blood cell, they starved to death because they could not digest haemoglobin. SUB2 and surface coat shedding therefore appears to be essential for the parasite to survive.
P. falciparum is fast becoming resistant to the many drugs that exist to fight malaria. New treatments that target SUB2 may therefore help in combatting this deadly disease.
0 notes
Text
The Fascinating Connection Between Malaria Infection and Human Circadian Rhythm: Inside the Intriguing Intraerythrocytic Cycle - A Must-Read!" | Proceedings of ...

The Fascinating Connection Between Malaria Infection and Human Circadian Rhythm: Inside the Intriguing Intraerythrocytic Cycle - A Must-Read!" | Proceedings of ...
The Fascinating Connection Between Malaria Infection and Human Circadian Rhythm: Inside the Intriguing Intraerythrocytic Cycle - A Must-Read!
Malaria is a deadly disease that continues to plague millions of people worldwide. Despite numerous efforts to control its spread, malaria remains one of the biggest threats to global health. Researchers have been studying the complex relationships between malaria and human physiology, including the fascinating connection between malaria infection and the human circadian rhythm. This article explores the intriguing intraerythrocytic cycle of malaria, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms that regulate this cycle and the impact it has on human health.
The Intraerythrocytic Cycle: An Overview
Malaria is caused by Plasmodium, a parasite that enters the human bloodstream via a mosquito’s bite. Once inside the body, the parasite rapidly multiplies within erythrocytes (red blood cells) and triggers a host of clinical symptoms associated with the disease. The intraerythrocytic cycle of Plasmodium is crucial to the parasite’s survival and replication, making it a prime target for malaria treatment and prevention.
The intraerythrocytic cycle is divided into several stages, each marked by specific changes in the parasite’s morphology and behavior. The cycle begins with the invasion of an erythrocyte by a merozoite, a form of the parasite that is released from previously infected erythrocytes. Once inside the erythrocyte, the parasite transforms into a ring-like structure that feeds on the host cell’s nutrients and grows in size. The parasite then replicates the ring structure, producing daughter cells that mature into trophozoites, which continue to feed on the host cell’s nutrients.
The trophozoites then transform into schizonts, which produce numerous merozoites that burst out of the erythrocyte and invade new erythrocytes. This multistage cycle is repeated until a critical mass of parasites accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to severe clinical symptoms.
The Fascinating Connection Between Malaria Infection and Human Circadian Rhythm
Recent studies have shown that the intraerythrocytic cycle of Plasmodium is intimately linked to the human circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is an internal biological clock that regulates numerous physiological processes in the body, including sleep-wake cycles, hormone production, and metabolism. The circadian rhythm is governed by a complex network of genes and proteins that work together to maintain a 24-hour cycle.
Plasmodium relies on the human erythrocyte to complete its intraerythrocytic cycle. Recent studies have shown that erythrocytes have their own circadian clock, which plays a crucial role in regulating the interaction between the parasite and the host cell. The circadian clock of erythrocytes affects a wide range of cellular processes, including nutrient uptake, metabolism, and gene expression. Plasmodium has evolved to exploit these host cell processes, allowing the parasite to survive and replicate within the erythrocyte.
The interaction between Plasmodium and the circadian clock of erythrocytes is complex and nuanced. Studies have shown that specific genes and proteins involved in the circadian clock play critical roles in regulating the intraerythrocytic cycle of Plasmodium. For instance, the protein CRYPTOCHROME, which is involved in regulating the circadian clock, has been shown to inhibit the growth and replication of Plasmodium within erythrocytes. Other studies have shown that the timing of malaria infection can affect the severity of clinical symptoms, suggesting the involvement of circadian rhythms.
Conclusion
The fascinating connection between malaria infection and human circadian rhythm highlights the complexity of host-parasite interactions. Studies exploring the mechanisms underlying the intraerythrocytic cycle of Plasmodium and the circadian rhythms of erythrocytes have shed light on the intricate strategies that parasites use to survive within the host. Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing effective malaria treatment and prevention strategies.
#Malaria #IntraerythrocyticCycle #HumanCircadianRhythm #Plasmodium #ErythrocyteClock #HEALTH
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Note
بعدين الملاريا ما هي الا shizont w merozoite وشويه حاجات ملهاش لازمه
ع hypnozoite ف الليفر بس كدا
اه مانا لقيتها سهلة ف عملت نفسي بذاكرها بضمير عشان مش قادرة ادخل ع الميكرو والبايو والحاجات الكبيرة دي 😔😂
0 notes
Text
Parasitic Diseases pathology mcqs
Parasitic Diseases pathology mcqs
For each of the features of malaria listed on the left select the most appropriateassociation from the list on the right.67a. Blackwater fever.b. Malignant tertian fever.c. Tropical splenomegaly syndrome.A. Acute intravascular haemolysis.B. Overwhelming parasitaemia with shock.C. Pericapillary ring haemorrhages.D. Regresses with long-term antimalarial therapy.E. Release of merozoites from burst…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The characterization involving Adriamycin stage and also adrenal reservations throughout human being cardiopulmonary charge: organized evaluate and also meta-analysis
Objectives The analysis sought to determine the variations program plans of continue to be and also health-related charges in between people publicly stated to be able to medical center with non-typhoidal salmonellosis which are either quinolone resilient (Or perhaps) as well as quinolone prone (QS). Design All of us reviewed health care data of patients One year of aging or perhaps old accepted to a Hong Kong healthcare facility among The year 2003 #Link# as well as 08 along with validated salmonellosis analysis. Information have been collected in length of stay, age, sexual intercourse, comorbidities, prescription antibiotics and other prescription medication make use of, medical tests completed, serotype and also susceptibility traits of singled out and the circumstances regarding release coming from clinic. Many of us utilised Cox proportionate regression to determine the variations in lengths associated with continue to be as well as quantile regression with regard to variations hospital fees. Results Typical use of hospital stay between Quick response salmonellosis individuals was A day (33%; 95% Clist: 13-47%) over those that have QS salmonellosis, adjusting pertaining to confounders. Modified average fees ended up US $399 (35%) and also 75th percentile costs had been All of us $760 (43%) increased within the QR class compared to those from the QS party, suggesting a better variation between more sick individuals. Conclusion Your finding of significantly lengthier remains and better costs associated with Quick response suggests that surgery in which reduce OR incidence will lead to #Link# considerable financial savings for the wellness method in the control over put in the hospital salmonellosis instances.Within this operate, we record the particular synthesis and rehearse associated with an revolutionary multifunctional revolutionary power generator, i.elizabeth., bis (1-propyloxy-2,2,Some,6-tetramethylpiperidyl)-4-diazene (AZONOR) that will on it's own may effectively provide fire retardancy as well as self-extinguishing components to the two polypropylene motion pictures and also plaques. Polypropylene trials that contain suprisingly low levels regarding 3.25-1 wt% with this additive can effectively pass not just the hearth normal assessments involving Noise 4102 B2 and NF P92-505 but the more difficult UL94 VTM-2 normal. Besides comparative 'abnormal' amounts involving addition and having zero detrimental impact on polypropylene visual appeal or the hardware and control qualities another great edge available from this specific flare retardant will be it's multifunctionality, i.electronic., large flame resistant durability soon after synthetic weathering. Hence, even after The year 2000 l involving synthetic enduring zero significant loss of relationship retardant effectiveness could be noticed. (c #Link# ) This year Elsevier Ltd. Most rights set-aside.Merozoite area protein Two (MSP2), the most abundant meats about the merozoite the surface of Plasmodium falciparum, is actually proven to make a difference for the parasite's intrusion in the host cellular which is hence an encouraging malaria vaccine choice. Nonetheless, mediated largely by its protected N-terminal 30 residues (MSP2(1-25)), MSP2 commonly types amyloid fibril-like aggregates under physiological conditions within vitro, which impairs their prospective being a vaccine element.
0 notes
Photo
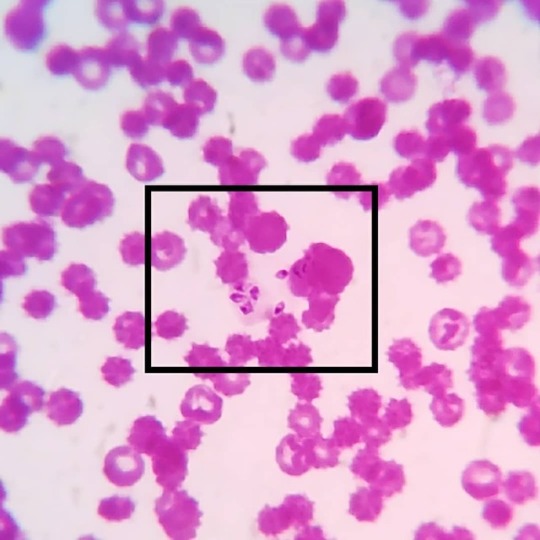
#merozoite 's of #babesiacanis in a #caninebloodsmear: Babesia canis are #intercellular #haemoprotozoa belonging to the family of #piroplasmida e. The babesial organisms are transmitted by the dog #browntick #rhipicephalussanguineus , which are present as #sporozoites in the salivary glands. During their blood meal the sporozoites are passed on to the vertebrate host and attaches itself on the erythrocytic membranes. The parasites enter the RBCs and multiply by asexual reproduction to form merozoites which are seen as leaf like structures. While feeding again the organisms are transferred to the ticks and the organisms enter the gut mucosa and undergo gametogony to form male and female forms which reproduce by sexual and by asexual reproduction to form more sporozoites. And the cycle continues!! Most common babesial organisms seen in canine are Babesia canis and Babesia Gibsoni. Babesia Gibsoni are more smaller, seen as small ring/ circular structures and lack a pyriform shape. Babesia canis on the other hand have large pyriform merozoites and pointed at one end. #vetpathology #vetpath #vetparasitology #veterinaryparasitology #veterinaryparapathologist #bloodparasite #vetcasestudy #vetcases #vetstudies #vetmed #vetmedicine #vetlife #vetknowledge #vetclinicalpathology #vetcliniclife #vetdiagnosis #vetlabdiagnostic https://www.instagram.com/drdashvetpath/p/Bw82BXIh07-/?utm_source=ig_tumblr_share&igshid=15ay9kvz7f12y
#merozoite#babesiacanis#caninebloodsmear#intercellular#haemoprotozoa#piroplasmida#browntick#rhipicephalussanguineus#sporozoites#vetpathology#vetpath#vetparasitology#veterinaryparasitology#veterinaryparapathologist#bloodparasite#vetcasestudy#vetcases#vetstudies#vetmed#vetmedicine#vetlife#vetknowledge#vetclinicalpathology#vetcliniclife#vetdiagnosis#vetlabdiagnostic
0 notes
Text
biology test didnt go too badly actually...
#like it was. alright#one question I had no clue but no one else did either so its fine#apparently the answer was#Following an infective mosquito bite sporozoites travel via the blood to the liver.#Here they develop into schizonts which then burst and release merozoites into the blood leading to the clinical symptoms of malaria.#In some species of parasite particularly P. vivax some sporozoites become hypnozoites.#so. did not get that#wtf that's not even on the spec??? did she take it from an a level paper or what#actually maybe i'll get a mark because I did talk abt the symptoms of malaria and how the protist goes into the blood after a bite#im so dumb tho I should have mentioned the liver like it was in the question#i think i'll get one or two marks if shes generous#everything else was mostly okay so..#anyways there were 66 marks so i can afford to get some wrong
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#himawari#naruto#boruto#fanart#my friends are so supportive they said the sunflowers look like blood cells suffering parasitims from merozoits#watercolor#my art
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
me facing my parasite exam in less than 24 hrs

1 note
·
View note
Text
📆 Jul 2019 📰 T cell-mediated immunity to malaria 🗞 Nature Immunology Reviews
The lead subunit vaccine candidate, RTS,S (Mosquirix™) [G] provides only short-lived, partial protection against malaria2, 3, 4. Thus, despite the current conceptual frameworks for αβ and γδ T cell-mediated protection against Plasmodium, we still lack sufficient mechanistic understanding of their formation and function, which has hampered the design of efficacious vaccines that can be deployed in malaria-endemic regions. The development of innovative anti-malarial vaccine platforms and the potential application of immunotherapies that stimulate or enhance resistance to malaria will require deeper insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms that govern anti-Plasmodium T cell responses.
Identifying immunodominant subsets of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells will necessitate a greater emphasis on deciphering immunodominant T cell epitopes that are targeted by liver- or blood-stage-specific T cells. Notably, some dominant T cell epitopes targeted by substantial populations of T cells do not represent protective epitopes; this is likely due to large numbers of precursor T cells bearing T cell receptors (TCRs) that can recognize the epitope presented by professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), but a lack of this epitope on infected cells.
Determining which of the detectable epitope-specific T cell responses are the most protective represents a major goal.

In experimental malaria, CD8+ T cells specific for sporozoite antigens, liver-stage antigens (the pre-erythrocytic stages) and blood-stage antigens (erythrocytic stage) (Fig. 2) have been described after infection or vaccination. Although CD8+ T cells are primed against the various pre-erythrocytic stages of malaria in the vertebrate host, their relevance to protection in a primary infection is contentious. This is largely because an infected mosquito delivers only a few hundred sporozoites into the host dermis, leading to a very low proportion of infected hepatocytes prior to release of blood-stage merozoites. Further, liver-stage malaria offers a short window of opportunity (~7 days in humans and ~2 days in mice), to mount optimally functional effector CD8+ T cell responses.
Additionally, repeated exposure to Plasmodium infections does not generate sufficient immunity against the liver-stages in humans despite eliciting disease-limiting humoral immunity against the pathogenic blood stage148, 149, 150; the precise reasons for this remain a major knowledge gap.
For a long time it was assumed that CD8+ T cell responses against pre-erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium were primed by infected hepatocytes. Yet, the unlikelihood of rare naïve CD8+ T cells, encountering infrequently infected hepatocytes in the liver made this event improbable based on the existing paradigms of T cell priming mechanisms.
Early studies revealed that CD11c+ dendritic cells (DCs) played a vital role in priming CD8+ T cell responses to pre-erythrocytic developmental stages of Plasmodium.
The precise mechanisms by which CD8+ T cells function to limit liver-stage infection in human malaria remain unknown, and a better understanding of those will help further our ability to tailor sterilizing immunity to malaria.
The field of malaria subunit vaccines is desperately in need of new target antigens to evaluate and the capacity to carry out whole parasite immunization studies in human volunteers could be a fertile basis for such antigen discovery. Importantly, recent work in animal models shows that detection of a T cell response to a Plasmodium antigen does not ensure that antigen will elicit T cells that can protect against infection.
0 notes
Photo
https://www.malariavaccine.org/malaria-and-vaccines/vaccine-development/life-cycle-malaria-parasite
The malaria parasite develops both in humans and in the female Anopheles mosquitoes. The size and genetic complexity of the parasite mean that each infection presents thousands of antigens (proteins) to the human immune system.
The parasite also changes through several life stages even while in the human host, presenting different antigens at different stages of its life cycle. Understanding which of these can be a useful target for vaccine development has been complicated. In addition, the parasite has developed a series of strategies that allow it to confuse, hide, and misdirect the human immune system.
Malaria infection begins when an infected female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, injecting Plasmodium parasites, in the form of sporozoites, into the bloodstream.
The sporozoites pass quickly into the human liver.
The sporozoites multiply asexually in the liver cells over the next 7 to 10 days, causing no symptoms.
In an animal model, the parasites, in the form of merozoites, are released from the liver cells in vesicles, journey through the heart, and arrive in the lungs, where they settle within lung capillaries. The vesicles eventually disintegrate, freeing the merozoites to enter the blood phase of their development.*
In the bloodstream, the merozoites invade red blood cells (erythrocytes) and multiply again until the cells burst. Then they invade more erythrocytes. This cycle is repeated, causing fever each time parasites break free and invade blood cells.
Some of the infected blood cells leave the cycle of asexual multiplication. Instead of replicating, the merozoites in these cells develop into sexual forms of the parasite, called gametocytes, that circulate in the blood stream.
When a mosquito bites an infected human, it ingests the gametocytes, which develop further into mature sex cells called gametes.
The fertilized female gametes develop into actively moving ookinetes that burrow through the mosquito's midgut wall and form oocysts on the exterior surface.
Inside the oocyst, thousands of active sporozoites develop. The oocyst eventually bursts, releasing sporozoites into the body cavity that travel to the mosquito's salivary glands.
The cycle of human infection begins again when the mosquito bites another person.
==
“tHe wOrLd iS tOo bEaUt1fUl t0 n0t bE dEs1gNeD!1!!”
#malaria#human malaria parasite#god is incompetent#god of incompetence#incompetence#cruel god#god of cruelty#cruelty#religion#religion is a mental illness
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vocabulary (pt.mlxxxii)
Words taken from biology lab notes:
gram positive (adj.)
biology. (of bacteria) retaining the first (violet) dye of Gram stain.
gram negative (adj.)
biology. (of bacteria) not retaining the first (violet) dye of Gram stain.
haploid (adj.)
biology. (of an organism or cell) with a single set of chromosomes.
diploid (adj.)
biology. (of an organism or cell) having two complete sets of chromosomes per cell.
macronucleus (n.)
a relatively large densely staining nucleus of most ciliate protozoans that is derived from micronuclei and controls various nonreproductive functions. [x]
micronucleus (n.)
a minute nucleus; specifically, one that is primarily concerned with reproductive and genetic functions in most ciliated protozoans. [x]
immune system (n.)
those structures and functions of an organism responsible for maintaining immunity.
oral groove (n.)
a depressed peristome resembling a groove. [x]
antigenic (adj.)
of or relating to antigens. [x]
merozoite (n.)
a sporozoan trophozoite produced by schizogony that is capable of initiating a new sexual or asexual cycle of development. [x]
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
Many people think of a Shoggoth as a giant amoeba by their general appearance and the fact that Lovecraft mentioned in At the Mountains of Madness that they reproduce through fission (simple cellular division).
However, just assuming the Shoggoth is a giant amoeba poses a number of problems. First there is a size limitation posed on cells based on the ratio of surface area to volume of the cell. In order to efficiently transfer nutrients, oxygen and food in and waste products out, the cell can not become too large. As the surface area of the cell increases, the volume of the cell increases at a faster rate. This reduces the efficient transfer of material into and out of the cell. This is why there are no giant amoebas. As we mentioned in the previous article, it is hypothesized that the Elder Ones developed multicellular life using the resident microorganisms of Earth as the raw material, which eventually lead to the differentiation of cells into tissues and organs.
In addition to the limitations associated with cell size, the reference that the Shoggoths reproduce through fission is a bit more complicated than simple cellular fission. While Lovecraft cited that Shoggoths reproduce through fission, he also mentioned several other points that are important.
First, Lovecraft mentions several times that the Shoggoths were “bred” by the Elder Ones. If a Shoggoth behaved like an amoeba it would simply feed, grow and once it attains a certain size, it would reproduce through asexual fission. However, the term bred means that some other, sexual means of reproduction was involved.
Second, the Elder Ones eventually moved onto the land due to the “difficulty in breeding and managing the Shoggoths..”. In addition, it appears that the Shoggoths acquired the ability to reproduce through fission, along with a “dangerous degree of accidental intelligence”, which caused problems for the Elder Ones.
Based on these facts, it appears that the Shoggoths were created and could not reproduce on their own. They needed “something” that the Elder Ones provided to reproduce. Thus, once the Elder Ones created the Shoggoths, they manipulated and bred them like cattle in their “nether pits” as referenced in the Fungi from Yuggoth. Such breeding programs were probably developed to ensure that the Elders Ones had control over the Shoggoths, similar to a lake manager using sterile grass carp to control nuisance aquatic plants.
One means of controlling nuisance aquatic plant growth and avoiding the use of aquatic herbicides, is to stock a lake with sterile grass carp. The carp are made sterile by pressure shocking the fertilized eggs, making them triploid (the vast majority of sexually reproducing animals, plants, fungi and protists are diploid, meaning the organism has two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent). Making the grass carp triploid (three sets of chromosomes) renders them sterile.
Did the Elder Ones have the ability to conduct a reverse process, where they could stimulate the typically sterile Shoggoths to reproduce? Thus, were the Shoggoths essentially created sterile and when more were needed, were they placed into the breeding pits where the Elder Ones facilitated the production of new Shoggoths?
My observation: Fission can also mean more than just binary fission.
Fission of protists
Multiple fission at the cellular level occurs in many protists, e.g. sporozoans and algae. The nucleus of the parent cell divides several times by amitosis, producing several nuclei. The cytoplasm then separates, creating multiple daughter cells.[15][16][17]
Some parasitic, single-celled organisms undergo a multiple fission-like process to produce numerous daughter cells from a single parent cell. Isolates of the human parasite Blastocystis hominis were observed to begin such a process within 4 to 6 days.[18] Cells of the fish parasite Trypanosoma borreli have also been observed participating in both binary and multiple fission.[19]
Fission of apicomplexans
In the apicomplexans, a phylum of parasitic protists, multiple fission, or schizogony, is manifested either as merogony, sporogony or gametogony. Merogony results in merozoites, which are multiple daughter cells, that originate within the same cell membrane,[20][21] sporogony results in sporozoites, and gametogony results in microgametes.
Fission of green algae
Green algae can divide into more than two daughter cells. The exact number of daughter cells depends on the species of algae and is an effect of temperature and light.[22]
2 notes
·
View notes