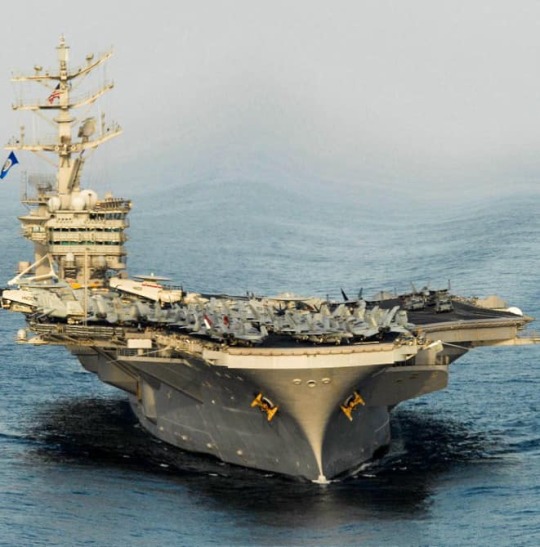
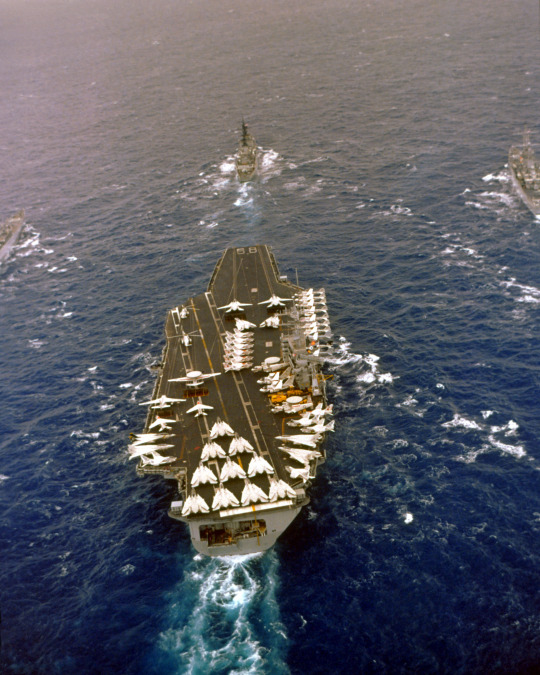
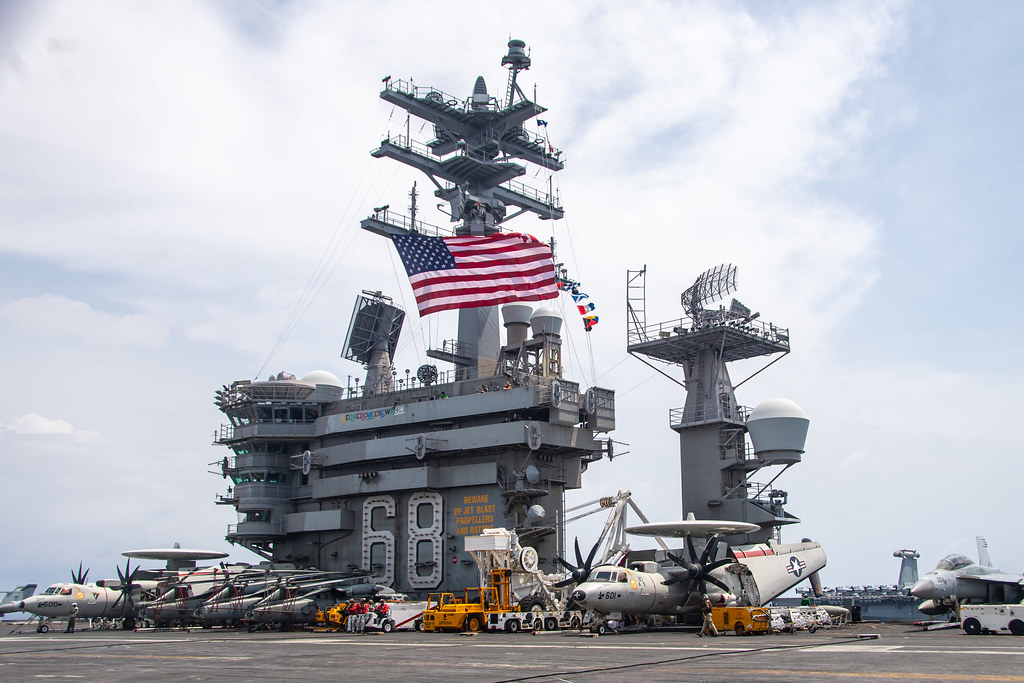
#USS Nimitz (CVN-68)
Text
Titans of the Sea: The Power and Influence of Nuclear-Powered Aircraft Carriers
Introduction

Nuclear-powered aircraft carriers represent the pinnacle of naval engineering and strategic military capability. The USS Nimitz (CVN 68), the lead ship of its class, exemplifies the power and versatility of these floating fortresses. Coupled with formidable aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet, the USS Nimitz and its counterparts serve as crucial assets in projecting military power and maintaining global security. This essay delves into the design, capabilities, and strategic importance of nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, with a special focus on the USS Nimitz and its fleet of F/A-18 Hornets.
Evolution of Nuclear-Powered Aircraft Carriers
The concept of nuclear-powered aircraft carriers emerged during the Cold War as nations sought to extend the reach and endurance of their naval forces. Unlike conventional diesel-powered ships, nuclear-powered carriers do not require frequent refueling, allowing them to remain deployed for extended periods and operate at higher speeds.
The USS Enterprise (CVN 65), commissioned in 1961, was the world’s first nuclear-powered aircraft carrier. Its success paved the way for the development of the Nimitz-class carriers. The USS Nimitz, commissioned in 1975, was the first of ten nuclear-powered carriers in this class. These ships have since become the backbone of the U.S. Navy, embodying the principles of sustained power projection and rapid response.
Design and Capabilities of the USS Nimitz
The USS Nimitz is an engineering marvel, measuring over 1,092 feet in length and displacing around 100,000 tons. It can accommodate a crew of approximately 5,000 personnel, including the ship's company and the air wing. Its flight deck spans about 4.5 acres, providing ample space for the launch and recovery of various aircraft.
Powered by two A4W nuclear reactors, the USS Nimitz can achieve speeds in excess of 30 knots. These reactors provide the ship with nearly unlimited operational range, limited only by the need for resupply of food and other consumables. The ship's propulsion system, combined with its advanced navigation and control technologies, enables it to maneuver effectively even in challenging conditions.
The USS Nimitz is equipped with a robust suite of defensive systems, including the RIM-7 Sea Sparrow and RIM-116 Rolling Airframe Missiles, which provide protection against aerial threats. Additionally, the Phalanx Close-In Weapon System (CIWS) offers a last line of defense against incoming missiles and aircraft. The ship’s radar and sensor systems ensure comprehensive situational awareness, enhancing its defensive and offensive capabilities.
The Role of F/A-18 Hornets
Fighters like the F/A-18 Hornet is a twin-engine, multirole fighter aircraft designed for carrier-based operations. Its versatility allows it to perform a wide range of missions, including air superiority, ground attack, reconnaissance, and close air support. The Hornet has been a mainstay of the U.S. Navy's air wings since its introduction in the 1980s and continues to be a vital component of carrier strike groups.
The F/A-18 Hornet’s design emphasizes survivability and versatility. It features advanced avionics, reduced radar cross-section, and electronic warfare capabilities, making it a formidable opponent in air combat. Its twin-engine configuration provides redundancy and improved performance, particularly important for operations from the demanding environment of an aircraft carrier.
One of the key advantages of the F/A-18 Hornet is its ability to switch roles rapidly. It can carry a diverse array of ordnance, from air-to-air missiles to precision-guided bombs, enabling it to engage both aerial and ground targets with high effectiveness. This flexibility is crucial for modern naval operations, where threats can emerge from multiple domains simultaneously.
Strategic Importance of the USS Nimitz
The USS Nimitz serves as a mobile airbase, capable of projecting power and deterrence far beyond U.S. territorial waters. Its presence in a region can significantly influence the strategic calculations of potential adversaries. The carrier’s ability to deploy a wide array of aircraft, including the F/A-18 Hornet, allows it to conduct sustained air operations over extended periods.
One of the primary missions of the USS Nimitz is to ensure freedom of navigation and the security of maritime trade routes. Given that a significant portion of global trade passes through strategic chokepoints like the Strait of Hormuz and the South China Sea, the carrier’s ability to operate in these areas is of paramount importance. Its deployment can reassure allies and deter aggression, contributing to regional stability.
In times of conflict, the USS Nimitz can serve as a command and control hub, coordinating the actions of various naval, air, and ground forces. Its air wing, centered around aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet, can perform a wide range of missions, from establishing air superiority to providing close air support for ground troops. The carrier’s versatility makes it a critical asset in both conventional and asymmetric warfare scenarios.
The Future of Carrier Aviation
While the USS Nimitz and its sister ships remain at the forefront of naval power, the future of carrier aviation is evolving. New classes of carriers, such as the Gerald R. Ford-class, incorporate advanced technologies like electromagnetic aircraft launch systems (EMALS) and advanced arresting gear (AAG). These innovations aim to improve the efficiency and capability of carrier operations, allowing for the deployment of next-generation aircraft.
Additionally, the integration of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) into carrier air wings represents a significant shift. Drones like the MQ-25 Stingray, designed for aerial refueling, will extend the range and endurance of manned aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet. This development will enhance the operational flexibility of carrier strike groups, allowing them to project power even further.
Furthermore, advancements in stealth technology and electronic warfare are likely to shape the future composition of carrier air wings. Aircraft like the F-35C Lightning II, with its advanced stealth and sensor capabilities, are expected to complement and eventually replace older platforms like the F/A-18 Hornet. These next-generation fighters will ensure that carrier strike groups remain at the cutting edge of military capability.
Conclusion

Nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, epitomized by the USS Nimitz, are critical instruments of naval power and global stability. Their ability to operate independently for extended periods, combined with the versatile capabilities of aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet, makes them indispensable to modern military strategy. As technological advancements continue to shape the future of carrier aviation, the legacy of the USS Nimitz and its contributions to naval warfare will endure, ensuring that these floating fortresses remain at the heart of American naval dominance for decades to come. The integration of new technologies and platforms will further enhance their operational effectiveness, enabling them to meet the evolving challenges of global security.
0 notes
Link
The Nimitz Carrier Strike Group left San Diego, Calif., on Saturday for a Western Pacific deployment, USNI News has learned. USS Nimitz (CVN-68) left its pier at Naval Station North Island at around 8 a.m. Saturday local time, according to ship spotters and headed out into the Pacific. In a Saturday statement to USNI News, …
1 note
·
View note
Text

An F/A-18E Super Hornet from the “Kestrels” of Strike Fighter Squadron (VFA) 137 launches from the aircraft carrier USS Nimitz (CVN 68).
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

A U.S. Navy Grumman A-6E Intruder from Attack Squadron 35 (VA-35) ‘BLACK PANTHERS’ approaches the USS Nimitz (CVN-68) for a landing on 27 June 1981. (U.S. Navy)
@kadonkey via X

19 notes
·
View notes
Text

U.S. Navy Lt. Rick Krystof watches an F-14A Tomcat catapult off the USS Nimitz (CVN 68) on Jan. 29, 1998.
Can you imagine being that close? Lt. Krystof is the "shooter" who is in charge of the launch and gives the signal for the cat to be fired. A split-second before this picture was taken, the wing passed right over his head. You'd feel the heat of the afterburners, and the sound would reach every inch of you.
The deck of an aircraft carrier is the most dangerous workplace in the world.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
CARRIER
Filmed in 2005, CARRIER is a 10-part series filmed aboard the USS Nimitz. CARRIER is a character-driven immersion in the high- stakes world of a nuclear aircraft carrier. The episodes follow a core group of characters as they navigate their jobs, families, faith, patriotism, love, the rites of passage and the war on terror.
youtube
The show does not focus only on the pilots and aircraft aboard the carrier, but it is an amazing look at the good, the bad, and the worse. The pilots are reoccurring but the main episode featuring carrier operations related to the aircraft can be viewed on Episode 7: Rites of Passage. To be blunt, I can only describe the show as ugly. The good times shown on the show are incredibly good, but overall it makes me sad. It feels like I’m watching an incredibly beautiful travesty. The show covers the stuff that you might not want to know about and it definitely is a reality check to what people go through to protect our country for us.
Regardless of your opinions of the military or any of the conflicts we have participated in (trust me when I say they don’t shy away from such topics) the show is worth a watch. I take comfort knowing that the truth always likes somewhere in the middle and I suggest you watch with the same mindset.
It’s not an easy watch, it’s not something I became obsessed with, but it’s still enthralling. If you watch any, I recommend Rite of Passage as it covers aviation more than some of the other episodes. Additionally, fans of the Fighter Pilot Podcast may recognize the familiar voice of Vincent “Jell-O” Aiello as one of the pilots on the show. He’s not featured often, but he does make an occasional appearance!
Watch the entire show FOR FREE at Archive.org(see link below).
NOTE!!!!!!!! The order of the episodes on the website are wrong!!!! Episode 10 is slotted after episode 1 so don’t make the mistake I did of watching them out of order!!!!
#we stan vincent jell o aiello#honestly heartbreaking#life on an aircraft carrier#carrier#documentary#fighter pilot podcast#give it a watch#top gun#aircraft carrier#Youtube#I like research#writing#mine#research#I like planes#and aircraft carriers#info
13 notes
·
View notes
Video
221004-N-DU622-1587 by U.S. Pacific Fleet
Via Flickr:
PACIFIC OCEAN (Oct. 4, 2022) An F/A-18F Super Hornet, from the "Kestrels" of Strike Fighter Squadron (VFA) 137, approaches for an arrested gear landing on the flight deck of aircraft carrier USS Nimitz (CVN 68). Nimitz is underway conducting operations. (U.S. Navy photo by Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Justin McTaggart)
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nuclear-Powered Aircraft Carriers and Their Role in Modern Naval Warfare
Introduction

Nuclear-powered aircraft carriers represent the pinnacle of modern naval engineering and military strategy. Among these giants of the sea, the USS Nimitz (CVN 68) stands out as a quintessential example of American naval power. Alongside it, aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet play a crucial role in maintaining air superiority and providing versatile combat capabilities. This essay explores the design, capabilities, and strategic importance of nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, with a focus on the USS Nimitz and its accompanying fleet of F/A-18 Hornets.
The Evolution of Nuclear-Powered Aircraft Carriers
Nuclear power revolutionized naval engineering by providing ships with an almost unlimited range and endurance. Unlike conventional diesel or gas-turbine engines, nuclear reactors do not require refueling for many years, allowing aircraft carriers to stay at sea for extended periods. This capability is critical for maintaining a persistent military presence and quick response capability anywhere in the world.
The introduction of nuclear power to aircraft carriers began with the USS Enterprise (CVN 65) in the 1960s. This technological leap forward set the stage for the subsequent Nimitz-class carriers, which would become the backbone of the U.S. Navy's carrier strike groups. The USS Nimitz, commissioned in 1975, was the first of its class and remains a formidable asset in the Navy's arsenal.
Design and Capabilities of the USS Nimitz
The USS Nimitz is a marvel of engineering, measuring approximately 1,092 feet in length and displacing over 100,000 tons. It can accommodate a crew of over 5,000 personnel, including air wing and support staff. Its flight deck spans around 4.5 acres, providing ample space for the launch and recovery of various aircraft.
The ship's propulsion system consists of two A4W nuclear reactors, which drive four propeller shafts. This setup allows the USS Nimitz to achieve speeds in excess of 30 knots. The nuclear reactors provide the ship with virtually unlimited operational endurance, limited only by the need for resupply of food and other consumables.
The carrier's defensive capabilities are formidable, featuring multiple layers of protection against air, surface, and underwater threats. These include the RIM-7 Sea Sparrow and RIM-116 Rolling Airframe Missiles, as well as the Phalanx Close-In Weapon System (CIWS) for close-range defense.
The Role of F/A-18 Hornets
Fighters like the F/A-18 Hornet is a twin-engine, multirole combat aircraft capable of performing a wide range of missions, including air superiority, ground attack, and reconnaissance. The Hornet is highly versatile, making it an ideal aircraft for carrier-based operations. It has been a staple of the U.S. Navy's air wings since the 1980s and continues to be a critical component of carrier strike groups.
The F/A-18 Hornet's design emphasizes survivability, with features such as reduced radar cross-section, advanced avionics, and electronic warfare capabilities. Its twin-engine configuration provides redundancy and improved performance, allowing it to operate effectively from the cramped and sometimes harsh environments of aircraft carriers.
One of the key advantages of the F/A-18 is its ability to switch roles rapidly. For instance, it can carry a variety of ordnance, from air-to-air missiles to precision-guided bombs, enabling it to engage both aerial and ground targets with equal efficacy. This flexibility is crucial for modern naval operations, where threats can emerge from multiple domains simultaneously.
The Strategic Importance of the USS Nimitz
The USS Nimitz serves as a floating airbase, projecting power and deterrence far beyond the territorial waters of the United States. Its presence in a region can significantly alter the strategic calculus of potential adversaries. The carrier's ability to deploy a wide array of aircraft, including the F/A-18 Hornet, allows it to conduct sustained air operations over a prolonged period.
One of the primary missions of the USS Nimitz is to ensure freedom of navigation and the security of maritime trade routes. Given that a significant portion of global trade passes through strategic chokepoints like the Strait of Hormuz and the South China Sea, the ability of the Nimitz to operate in these areas is of paramount importance. Its deployment can reassure allies and deter aggression, contributing to regional stability.
In times of conflict, the USS Nimitz can serve as a command and control hub, coordinating the actions of various naval, air, and ground forces. Its air wing, centered around aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet, can perform a wide range of missions, from establishing air superiority to providing close air support for ground troops. The carrier's versatility makes it a critical asset in both conventional and asymmetric warfare scenarios.
The Future of Carrier Aviation
While the USS Nimitz and its sister ships remain at the forefront of naval power, the future of carrier aviation is evolving. New classes of carriers, such as the Gerald R. Ford-class, incorporate advanced technologies like electromagnetic aircraft launch systems (EMALS) and advanced arresting gear (AAG). These innovations aim to improve the efficiency and capability of carrier operations, allowing for the deployment of next-generation aircraft.
Additionally, the integration of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) into carrier air wings represents a significant shift. Drones like the MQ-25 Stingray, designed for aerial refueling, will extend the range and endurance of manned aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet. This development will enhance the operational flexibility of carrier strike groups, allowing them to project power even further.
Conclusion

Nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, epitomized by the USS Nimitz, are critical instruments of naval power and global stability. Their ability to operate independently for extended periods, combined with the versatile capabilities of aircraft like the F/A-18 Hornet, makes them indispensable to modern military strategy. As technological advancements continue to shape the future of carrier aviation, the legacy of the USS Nimitz and its contributions to naval warfare will endure, ensuring that these floating fortresses remain at the heart of American naval dominance for decades to come.
0 notes
Text
WoW.....
SOUTH CHINA SEA (Feb. 15, 2023)
The aircraft carrier USS Nimitz (CVN 68) steams alongside the Wasp-class amphibious assault ship USS Makin Island (LHD 8).
Nimitz Carrier Strike Group (NIMCSG) and Makin Island Amphibious Ready Group (MKI ARG), with embarked 13th Marine Expeditionary Unit (MEU),
are conducting combined expeditionary strike force (ESF) operations, demonstrating unique high-end war fighting capability, maritime superiority, power projection and readiness.
Operations include integrated training designed to advance interoperability between the two groups while simultaneously demonstrating the U.S. commitment to our alliances and partnerships in the Indo-Pacific region.
Nimitz is in U.S. U.S. 7th Fleet conducting routine operations. U.S. 7th Fleet is the U.S. Navy's largest forward-deployed numbered fleet, and routinely interacts and operates with Allies and partners in preserving a free and open Indo-Pacific region.
(U.S. Navy photo by Mass Communication Specialist Seaman Emma Burgess)
0 notes
Text
The Plundering of the South China Sea
September 18, 2023
We’re not going to mine our escape of the environment crisis.
Sailors observe the USS Nimitz (CVN 68) and USS Ronald Reagan (CVN 76) Carrier Strike Groups steam in development as the Nimitz Carrier Strike Force (CSF) in the South China Sea.
(3rd Class Dalton Reidhead/ Defense Department)
This short article initially appeared at TomDispatch.comTo remain on top of crucial short…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
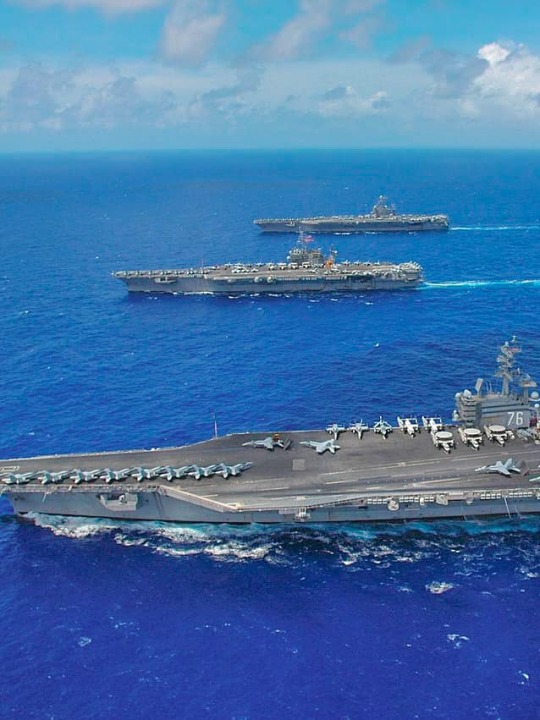

US Navy 100506-N-8421M-124 The aircraft carriers USS Ronald Reagan (CVN 76), USS Nimitz (CVN 68) and USS Carl Vinson (CVN 70)
163 notes
·
View notes
Text

An E/A-18G Growler from the "Cougars" of Electronic Attack Squadron (VAQ) 139 makes an arrested landing aboard the aircraft carrier USS Nimitz (CVN 68), Aug. 25, 2023.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
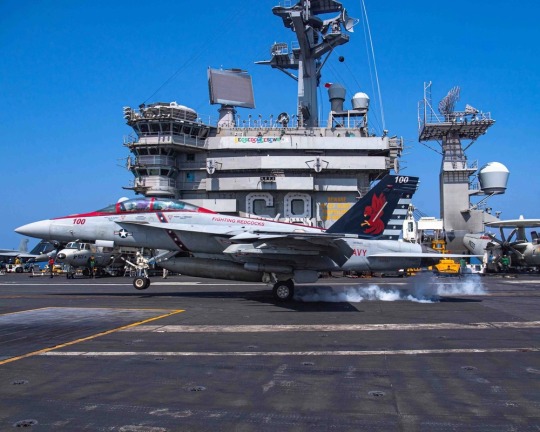

USS Nimitz records 350,000 hooked landings
Fernando Valduga By Fernando Valduga 04/23/23 - 10:23 am in Military
The USS Nimitz (CVN 68), the oldest U.S. commissioned nuclear aircraft carrier in the world, successfully completed its 350,000th hooked aircraft landing while sailing in the South China Sea, a milestone that took almost 48 years to achieve.
The Nimitz is the first active U.S. Navy aircraft carrier in the fleet to reach this milestone. USS Dwight D. Eisenhower (CVN 69) has the next largest total of hooked landings, currently at 326,600.
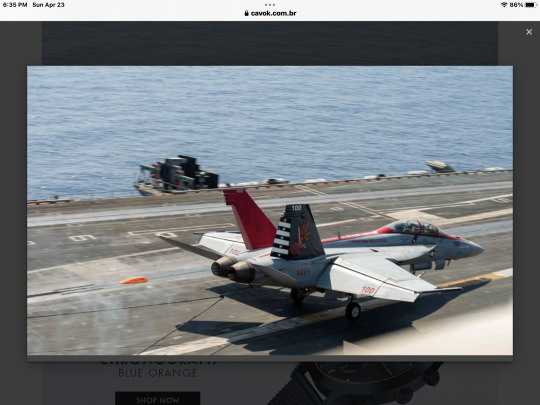
Captain Craig Sicola, commander of the Nimitz, and Commander Luke Edwards, commander of the Strike Fighter Squadron (VFA) 22 "Fighting Redcocks" piloted the landing of the F/A-18F Super Hornet of the VFA 22 on the morning of April 22.
“I am honored and proud to land this historic landmark for our ship. I dedicate this landing to the numerous naval aviators who flew before me, and it is a privilege to promote the proud tradition of service that this distinguished aircraft carrier incorporates," said Sicola. "For the shipyard maintenance teams who dedicate countless hours to prepare this warship for the sea, for the thousands of dedicated sailors on board who sacrifice themselves for their country and for the families at home who support us along the way - 'teamwork is a tradition' at Nimitz and we could not have fulfilled this mission without the unwavering commitment to this historic ship."

As the first in its class, the Nimitz is the namesake of all the aircraft carriers of the Nimitz class of the Fleet. Over the decades, tens of thousands of sailors have embarked on the Nimitz to fulfill missions around the world. Since commissioning almost 50 years ago, Nimitz has sailed in 30 deployments and served in numerous operations and missions.
Nimitz serves as the flagship of the Nimitz Carrier Strike Group (NIMCSG). NIMCSG is currently in a regular deployment in the U.S. 7th Fleet operations area.

“As we sail the South China Sea, we celebrate this once-in-a-lifetime achievement, 350,000 hooked landings, more than a hundred years of innovation on the U.S. aircraft carrier and the determination, sacrifice and winning spirit of all naval airmen of the past and present and our sailors,” said Rear Admiral Christopher Sweeney, commander of Carrier Strike "This milestone is proof of the nation's commitment to fly, sail and operate around the world, promoting peace and security, just as "Old Salt - the NIMITZ" has done for the last 48 years."
The 350,000th catrapo represents a significant moment in the history of the ship. The first hooked landing of the Nimitz was made in 1975, the same year as the ship's commissioning. Captain Bryan Compton, Nimitz's first commanding officer, made history by completing the first landing.
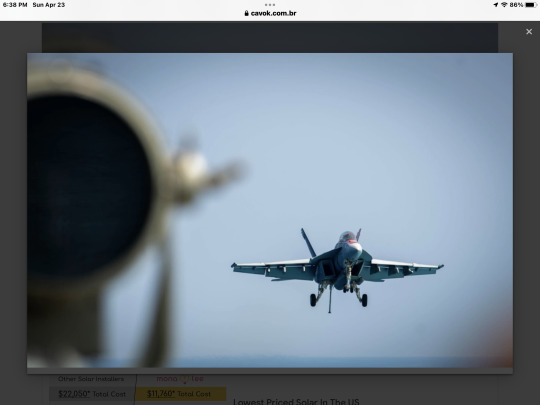
Although the ship has sailed in several oceans and docked in several locations, the constant over the decades has been the tenacity of the ship's crew day after day - without which not a single landing would have been possible.
"Although aircraft are critical to our mission, the aviators and maintainers who fly and operate our aircraft are truly the reason for our success," said Captain Christopher Hurst, commander of Carrier Air Wing (CVW) 17. "This milestone shows the accuracy and operational excellence of our sailors to perform hundreds of thousands of landings in Nimitz."

Nimitz's aircraft launch and recovery equipment division (ALRE) is responsible for the operation and maintenance of the ship's catapults and stopping equipment.
"We have been looking forward to reaching this milestone for a long time," said Robert Reed, companion of the aviation foreman (equipment), Robert Reed, chief non-commissioned officer of the ALRE division. "The sailors made all this possible by garrisoning our equipment and ensuring the proper execution of our mission. Your dedication and determination are inspiring and I am proud to be part of the Nimitz team. This landing could not have been made without their commitment to the ship."
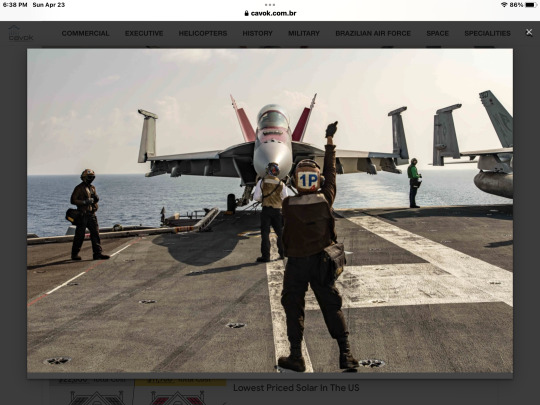
Before celebrating the historic 350,000th landing hooked aboard the Nimitz, the cockpit personnel quickly returned to work. The sailors redefined the detention cable, taxied aircraft out of the landing area and redefined the deck - there were still more aircraft to land. The powerful Nimitz had to prepare for catrapo number 351,001.
Tags: Military Aviationaircraft carrierUSN - United States Navy/US NavyUSS Nimitz
Fernando Valduga
Fernando Valduga
Aviation photographer and pilot since 1992, he has participated in several events and air operations, such as Cruzex, AirVenture, Dayton Airshow and FIDAE. He has works published in specialized aviation magazines in Brazil and abroad. Uses Canon equipment during his photographic work throughout the world of aviation.
Related news
MILITARY
How military airfields could fix themselves with a new type of concrete
23/04/2023 - 16:00
INTERCEPTIONS
Swedish and Danish air forces work together to escort Russian Il-20 aircraft over the Baltic Sea
23/04/2023 - 14:00
MILITARY
Why now is the ideal time for Egypt to transfer its MiG-29M/M2 to Ukraine
23/04/2023 - 12:00
MILITARY
Italy unveils plans to convert Gulfstream jets
23/04/2023 - 11:26
MILITARY
Decisive combat effectiveness, exclusive lethality of Gripen E
23/04/2023 - 00:03
MILITARY
U.S. Army MQ-1 Gray Eagle surveillance drone crashes in Iraq
04/22/23 - 4:00 PM
homeMain PageEditorialsINFORMATIONeventsCooperateSpecialitiesadvertiseabout
Cavok Brazil - Web Creation Tchê Digital
Commercial
Executive
Helicopters
HISTORY
Military
Brazilian Air Force
Space
Specialities
Cavok Brazil - Web Creation Tchê Digital
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
What’s The Difference Between the Gerald R. Ford-Class and The Nimitz-Class Carriers?
By Dan Doyle
The centerpiece of naval warfare today is the carrier and its strike group. These modern carriers project an immense amount of power anywhere in the world. They do this with speed and efficiency. At present, the United States Navy has 11 active carriers. They are made up of Enterprise- and Nimitz-class carriers, as well as carriers from the newest class, the Gerald R. Ford class.
These carriers are extremely valuable assets, as they are extremely effective deterrents to any potential adversaries. They are designed to bring powerful air support to U.S. and coalition forces afloat, in the air, or on shore, and they can do this rapidly, anywhere in the world.

PHOTO: WIKIPEDIA/UNITED STATES NAVY
USS NIMITZ (CVN 68)
The Nimitz- and Ford-class aircraft carriers are presently the largest warships in the world. The USS Gerald R. Ford (CVN 78) is the first of its class and is now on active duty. There are two more being built at this time. They are the USS John F. Kennedy (CVN 79) and the Enterprise (CVN 80). There is one more on order, the USS Doris Miller (CVN 81).
The latter Ford-class carrier is to be named after Doris Miller, the first African American to be awarded the Navy Cross in WWII. He was a Mess Attendant 2nd Class when the ship he was serving on at Pearl Harbor was hit by bombs on December 7, 1941. During the attack, he helped several of his wounded shipmates and manned an anti-aircraft machine gun, for which he had no training. Despite the lack of formal training on the anti-aircraft machine gun, he shot down 4-6 of the attacking Japanese planes. Miller would be killed in action later in the war when the ship he was then serving on, the escort carrier USS Liscome Bay, was sunk by a torpedo near the Gilbert Islands.

PHOTO: FLICKR/OFFICIAL U.S. NAVY PAGE
USS GERALD R. FORD (CVN 78)
The nuclear-powered Nimitz- and Ford-class carriers are designed for a 50-year service life with a single mid-life refurbishing necessary during that long life. But there are some significant differences between these two classes as well.
The USS Gerald R. Ford has two reactors that can generate 600MW of electrical power vs. the Nimitz-class ships that have one reactor that produces 200MW of electrical power. Another major difference is that the Gerald R. Ford has an electromagnetic catapult system that can generate 25% more sorties (flights) than the Nimitzes’ steam-powered catapult system. The Ford also has a dozen electromagnetic weapons elevators, which makes the movement of planes and armaments much faster and more efficient. This, again, makes the Ford capable of arming and launching more aircraft more quickly.

PHOTO: GETARCHIVE/DEFENSE VISUAL INFORMATION DISTRIBUTION SERVICE
THE FORD-CLASS AIRCRAFT CARRIER USS GERALD R. FORD (CVN 78) AND THE NIMITZ-CLASS AIRCRAFT CARRIER USS HARRY S. TRUMAN (CVN 75) TRANSIT THE ATLANTIC OCEAN JUNE 4, 2020.
A third difference between the Nimitz- and Ford-class carriers is that the USS Gerald R. Ford is equipped with technologically more advanced radar systems. It has an AEGIS-style X-Band AN/SPY-3 Aegis radar and S-Band Volume Surveillance Radar, capable of search, track, and multiple missile illumination. This makes it possible to detect incoming aircraft and missiles at a greater distance.
Lastly, the Gerald R. Ford also has more sophisticated defensive armaments. It has two MK.29 missile launchers with eight ESSMs each. It has two Rolling AirFrame missile launchers, as well as four Phalanx Close-In Weapons systems for defense against attacking aircraft, missiles, and small ships.

PHOTO: FLICKR/OFFICIAL U.S. NAVY PAGE
USS GERALD R. FORD (CVN 78)
Because Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carriers are so new and so much more sophisticated than the Enterprise and Nimtz-class carriers, they have experienced a number of glitches in the various high-tech systems that have been deployed in the design. Those have been worked out, and the USS Gerald R. Ford has recently been deployed fully to the fleet and is on active duty. Those improvements will, of course, be incorporated into the two Ford-class carriers currently under construction and the third that is on order. These Ford-class carriers will eventually completely replace the former Enterprise- and Nimitz-class carriers.
These massive, fast, powerful ships will continue to be the centerpiece of the U.S. Navy’s mission for decades to come. There is nothing quite like a U.S. Navy Carrier Strike Group to protect the freedom of the seas and to deter potential adversaries from threatening that freedom.
0 notes


