#Ludlow Seguine Bull
Photo








An Egyptian Mathematics Science Saturday
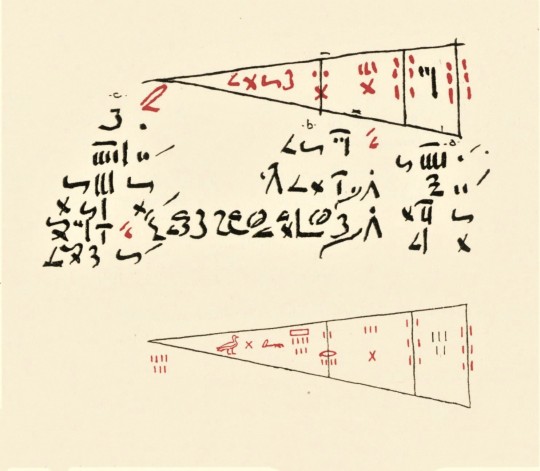
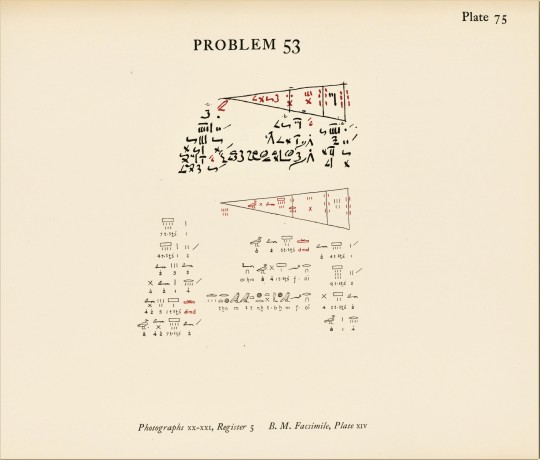
While Archimedes of Syracuse (287-212 BCE) is often considered the first to calculate the value of Pi (π), the Egyptians got pretty darn close a millennium and a half or so earlier, as evidenced by the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus. Copied by the scribe Ahmes sometime around 1650 BCE from an earlier text, the papyrus gives us a remarkable insight not only into Egyptian mathematics but also customs and culture, from taxation and farming practices to the exchange rate between beer and bread. It is named after Scottish antiquarian Alexander Henry Rhind, who acquired the papyrus sometime around 1858. Held by the British Museum since 1865, it is now suspected that the papyrus entered the antiquities market as a result of illegal excavations.
Our facsimile of the papyrus was the result of fifteen years of scholarship by mathematician Arnold Buffum Chace. The first volume was published in Oberlin, Ohio by the Mathematical Association of America in 1927, with the second volume following in 1929. All of the above images are from the second volume, which contains photographs of the papyrus, as well as transcription transliterations and literal translations by Chace. Chace was assisted in his work by mathematician Henry Parker Manning and Egyptologist Ludlow Seguine Bull. Also included in the second volume is a supplement to the “Bibliography of Egyptian Mathematics” from the first volume, both of which were prepared by Raymond Clare Archibald.
The first publication of the Rhind Papyrus was a translation into German in 1877 by August Eisenlohr. The Mathematical Association of America publication was part if a flurry of new scholarship surrounding the papyrus following advancements in scholarly understanding of Egyptian writing. In the preface to our edition, Chace notes the important 1923 translation by Eric Peet published by Liverpool University Press. Chace remarks that “Egyptologists ... will find philological matters fully discussed by Professor Peet,” while he intended for his work to be geared towards both mathematicians and the general public.
Both volumes were originally donated to the Library of the State Teachers College Milwaukee by the Carnegie Corporation of New York with their bookplate.
Check out more Science Saturday posts here.
-Olivia, Special Collections Graduate Intern
#Science Saturday#Rhind Papyrus#Rhind Mathematical Papyrus#Ahmes#Ahmose#Alexander Henry Rhind#Arnold Buffum Chace#Arnold Chace#Mathematical Association of America#Henry Parker Manning#Ludlow Seguine Bull#Raymond Archibald#August Eisenlohr#Eric Peet#Mathematics#Mathematics in Antiquity#Antiquities#Papyrus#olivia
34 notes
·
View notes