Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Baichi (Flacourtia indica) Morpho-physiological Characteristics and Yield

Abstract
An investigation was undertaken to evaluate the various morpho–physiological traits and yield contributing characters of baichi germplasms (GP) at Patuakhali Science and Technology University (PSTU). A number of baichi seedlings collected from different homesteads of Patuakhali coast were conserved at PSTU Germplasm Centre. Among the five survived germplasms (GP₁˗GP₅), two were male (GP₂ and GP₄) and the remaining three were female (GP₁, GP₃ and GP₅). The longest leaf length (4.45cm) was exhibited in GP₄. Maximum leaf blade width (2.83cm) was observed in GP₅. Although all the studied germplasms flowered at age 7, however, flower bud initiation started in male plants during the first week of February and continued to the last week of March and in female plants, it was started during the second week of February and continued to the mid of March. Length of flower bud was noticed among female genotypes of GP₅ (4.67mm), GP1 (4.65mm) and GP3 (4.62mm). Importantly, the flowers were apetalous in both male and female cases of all five germplasms. The highest fruit set (74.83%) and the fruit retention (80.88%) were recorded in GP₃ while the lowest fruit set (69.51%) and fruit retention (77.16%) were noticed in GP1. GP₅ had the biggest individual fruit size (11.24mm × 12.10mm), maximum edible portion (78.57%) and the highest fruit yield (10.5kg/plant) while the lowest individual fruit weight (1.19 gm) and fruit yield (8.6 10.5kg/plant) were observed in GP3. Based on the morpho–physiological traits among the three fruiting plants it may conclude that GP₅ was superior over other fruiting plants in relation to fruit size, edible part, individual fruit weight and yield. Therefore, a performance grading of the three female plants on the basis of yield can be as follows: GP₅ > GP₁ > GP₃.

Introduction
Flacourtia indica belonging to the family Selicaceae is one of the underutilized indigenous fruits of Bangladesh. Its common name is governor’s plum. It is locally known as baichi or “kantabohori” that is believed to be native to much of Africa and tropical and temperate parts of Asia. Baichi is an erect, branched, more or less spiny shrub or small tree. This species is dioecious in nature. Baichi produces fruit that is eaten fresh and has a pleasant rather sour taste. The fruits make a good jelly with the seeds and skin being discarded (Tredgold, 1986). The fruit can be fermented to produce wine. Fruits are used as appetizing, diuretic, and digestive, in jaundice and enlarged spleen. Barks are used for the treatment of intermittent fever and are also believed to be effective for arthritis. Roots are used in nephritic colic and gum is used in cholera (Kirtikar and Basu, 1998, Nazneen et al., 2002). The leaves and roots are used in herbal medicine for treatment of snakebite. Most parts of the plant are used for cough, pneumonia, and bacterial throat infection. After child birth among the poor the seeds is grind to powder with turmeric and rubbed all over the body to prevent rheumatic pains from exposure to damp winds. Pharmacological investigation includes the assessment of antihistaminic activity of ethanolic leaf extract of baichi in experimental guinea pig model (Tyagi et al., 2011). Gum is administered along with other ingredients in cholera. The glistening leaves of baichi can be very attractive when the tree is planted as an ornamental. When closely planted, it forms a close impenetrable barrier that serves as a hedge; it tolerates frequent trimming.

People of Bangladesh are generally poorly nourished despite substantial increase of food production in the country over past few decades. Most people suffer from mal–nutrition and resultant diseases. Ceaseless effort is therefore needed to improve the nutritional status and to increase food security, particularly for the rural poor (FAO, 1992). If minor food crops are properly utilized; they may help to contribute in food security, nutrition, health, income generation and environmental services (Kunkel, 1984). Wild fruits add variations in diets improve the palatability of staple foods and provide essential vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates and fats. Wild fruits of Flacourtia jangomas add variations in diets improve the palatability of staple foods and provide protein (3.9%), carbohydrates (21%), vitamin C (218mg), calcium (175mg), potassium (158mg), phosphorous (147mg), iron (118), and magnesium (57mg) per 100 gm dry weight basis (Hossain et al., 2011; Baruah and Neog, 2016).
Sarker et al. (2015) reported a wide range of fruit diversity in Patuakhali coast of Bangladesh, of which most species were minor ones. Despite the many beneficial characteristics baichi is overlooked as a fruit plant and there is no organized orcharding and no recognized cultivars for this fruit crops. As a result baichi is in the verge of extinction. The main reasons for the under–utilization of germplasm, according to curators, scientists and other users of plant genetic resources, is the lack of adequate passport, characterization, and evaluation data; people cannot use genetic resources that lack essential information. Therefore, the accurate documentation of information about the origin, characterization, and performance of this germplasm is essential for effective conservation and use (Biodiversity, 2007). Considering the problem statements, the present study was undertaken with the objective to find out the morpho–physiologically improved baichi germplasm (s) with higher yield contributing traits.
Source : Baichi (Flacourtia indica) Morpho-physiological Characteristics and Yield | InformativeBD
0 notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Link
#Botanicals#Phytochemicals#Ethanolic crude#Ethanol leaf extracts#Momordica#Moringa#Tabernaemontana#Mollugo
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Endoparasites in Sardinella lemuru and Glossogobius guiris from Caraga, Philippines
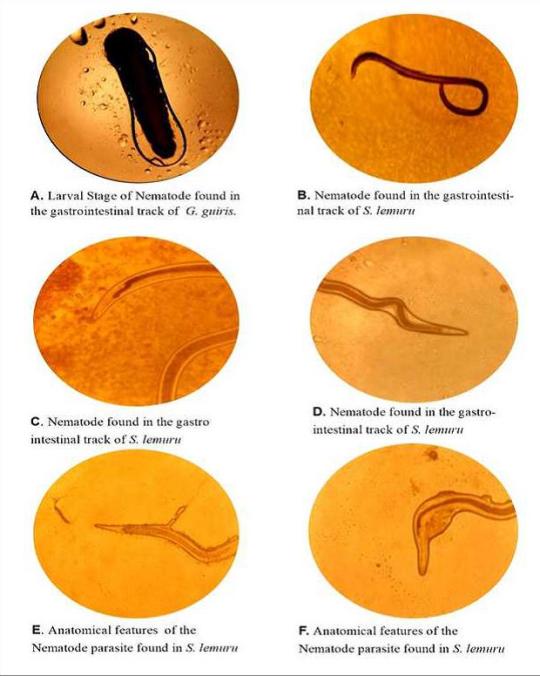
Abstract
Fish often serves as a staple food and protein source. Most Filipinos depend on fishing activities as a means of living. Fish parasites are diverse and pervasive organisms affecting a variety of hosts, including commercially important fish. Despite being utilized for commercial purposes, limited studies on fish parasitism are done in the Caraga region and are published in the Philippines. This study is one of the few conducted on the prevalence of parasites from the coast of Cabadbaran City and Lake Mainit in Jabonga, Agusan Del Norte, Phils. The two areas were the major fishing ground for different fish varieties sold in the local market. Two fish samples were collected: Glossogobius guiris (n=100) and Sardinella lemuru (n=100). Standardized protocols for fish parasite investigation were adopted. From the collected fish samples, the gastrointestinal tract was subjected, then examined and isolated. Of the 200 individuals, there were 2 found infected withG. guiris and 8 infected withS. lemuru. The recorded parasite was identified as Nematodes and was mostly observed in marine fish species (S. lemuru) when compared to freshwater fish (G. guiris). This implies that the occurrence of these parasites may vary depending on the fish type, maturity, diet composition, and location. A significant difference p=0.0003 was observed in the length-weight and prevalence of fish parasites and infers that size structure is associated with parasitic rate. Thus, the importance of conducting fish parasites could give an understanding of how this ubiquitous organism affects commercially important fish and awareness to the fish-eating community.

Introduction
In the Philippines, fish livelihood activities greatly contribute to the local and national economies. Fishing has produced a large contribution to the country’s development, with the recorded input of an estimated 4.33 billion dollars to the country’s financial resources (BFAR, 2016). Due to this record, there is a need for intensive management of fishery activities to maintain the economic stability of the country. Along with this is the careful assessment of the quality of harvest as its Philippine catch value increases over time (Anticamara and Go, 2016). Fish is successfully marketed according to a range of customer key standards (Saeed et al., 2022), and such requirements are qualities that are largely influenced by environmental factors (Fritrianiet al., 2019).
A prevalent problem in aquatic animals is parasitism which contributes to high mortalities among fish stocks (Edeh & Solomon, 2017). This special interaction between organisms involves a parasite harming a host or limiting its abundance. The impact of these organisms stretches out to an ability to wipe out other species due to their ability to cause wide epidemics, especially for disease-causing parasites (Frainer et al., 2018). Parasites are classified into ectoparasites, parasites on the external part of the host and endoparasites, parasites within the host’s body. Such endoparasites may be located within the flesh and organs of the host organism (Edeh & Solomon, 2017). Flagellates, amoebae, and Haplosporidia are examples of these parasites, to name a few (Lucas etal., 2019). The existence of these harmful organisms affects fish quality such that a study made byRamos, 2020 proved that some of these parasite-infested fish products are commercialized.
Despite their ability to cause diseases, fish are also known to be effective bioindicators. In an evaluation performed by Fierro etal., 2019, fishes were proven to present information on human agricultural activities to which their setting is subjected, as well as the water pollution in the same setting. In addition, fish examination gives information on the health and environmental disturbances by assessment of the inner organs and tolerance. Fish had also been used in a different study by (Gutiérrez and Agudelo, 2020) in assessing the accumulation of coal and mercury in Colombian waters, which gave significant results. Many factors contribute to the results of these bioassessments, namely, the increase in population (Rabadon & Corpuz, 2021), as well as climate change and the pollution that is brought about by the same factor (Wu etal., 2019).
Moreover, the fish-size relationship and the occurrence of parasites in fish products reduce the value and quality to drop, thus changing the marketability of the fish (Abollo etal., 2001; Levsen et al., 2005; Karl, 2008; Llarena-Reino etal., 2013; D’Amico et al. 2014; Llarena-Reino et al., 2015).
Fish parasite infection and pollution develop in ineffective energy and nutrient consumption and an escalation in energy expenditure of fish through respiration, impacting reproduction and growth (Marcogliese and Pietrock, 2011; Khan, 2012; Shea- Donohue et al., 2017; FAO 2020). More importantly, the risk posed by fish-borne parasitic zoonoses to human health (Quiazon, 2015) is estimated to be high, especially since fish is the staple food of fishing communities and eating raw fish is common practice in the region (Soares Magalhães etal., 2014; Tenorio and Molina, 2021).
This study utilized Sardinella lemuru (Tamban) and Glossogobiusguiris (Pidjanga), which is a commercially important fish in the Caraga region and the Philippines as well. Being ranked second in terms of volume in fish production, it is considered to be one of the most abundant fish and an affordable source of protein in the country (Labrador et al., 2021). These fish have a good hold on the economy of the Philippines and can affect the state of that part of the country. However, according to a study (Pohle, 2013), consumers have the trend in food without assessing the quality and information of the said product. In this case, consumers are at risk of diseasecausing factors brought upon by the products they buy due to their lack of awareness and lack of assessment from the food industry (Ziarati etal., 2022). In support of this information, the American Society has found that about 260,000 people have reported being sick from consuming fish products. Likewise, Barrett etal., 2017 also recorded 857 outbreaks causing about 4800 illnesses with hospitalizations and deaths in the same country due to polluted fish.
Further, due to their availability and precise identification of species, fish assessments prove to be convenient and useful in scientific investigations. It is also imperative to perform with scientifically proven and applicable methods along with the locallyobtained samples. More importantly, there is a need to use a preventive approach in the maintenance of fish health in our aquatic resources (Assefa & Abunna, 2018). Moreover, Cook, 2017, infers that the foundation of sustainability rests upon three factors which are social, economic, and environmental. There were no studies conducted in the region utilizing the fish samples. Thus, the study aims to provide baseline information to address the gap. Lastly, the focus of the study is to determine the prevalence of endoparasites in Sardinella lemuru and Glossogobius guiris. While this also touches on the protection and conservation of our water resources as well as the health of the fish-consuming community.
Source : Endoparasites in Sardinella lemuru and Glossogobius guiris from Caraga, Philippines | InformativeBD
0 notes