#whitehall mall
Text

American wasteland
#whitehall mall#sears#photography#dead mall#dead malls#deadmall#mall#malls#retail apocalypse#60s aesthetic#aesthetic#vaporwave aesthetic#vaporwave
124 notes
·
View notes
Note
You have been awfully quiet Mr Holmes, Did something happen?
-anon xxx
A nation.
#some people actually have a nation to run#dear anon#The Work never waits#mycroft replies#mycroft holmes#mycroft holmes replies#mycroft#pall mall#whitehall
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
El Desfile y Festival del Día de Año Nuevo de Londres está de regreso
El Desfile y Festival del Día de Año Nuevo de Londres está de regreso
Uno de los mayores espectáculos de Londres es el Desfile del Día de Año Nuevo, que tuvo lugar por primera vez en 1987.
Desde que comenzó, el desfile ha recaudado más de 2 millones de libras esterlinas para organizaciones benéficas locales y sigue siendo una importante contribución a la economía de la capital. Además de esto, el Desfile y Festival del Día de Año Nuevo de Londres se televisa en…

View On WordPress
#Charing Cross#Charing Cross y Westminster.#Desfile y Festival del Día de Año Nuevo de Londres#El Desfile y Festival del Día de Año Nuevo de Londres#Green Park#londres#Pall Mall#Parliament Square a través de Picccadilly Circus#Piccadilly#Piccadilly Circus#Regent Street#Trafalgar Square#West End#Westminster#Whitehall
0 notes
Text




The first rehearsal for the King's Coronation took place through central London - from Buckingham Palace to Westminster Abbey via the Mall and Whitehall - in the early hours of Tuesday morning | April 18th, 2023
233 notes
·
View notes
Text
It is as if you met a tram-car coming down a country lane. Mycroft has his rails and he runs on them. His Pall Mall lodgings, the Diogenes Club, Whitehall--that is his cycle. Once, and only once, he has been here.
Sherlock Holmes about his brother Mycroft in The Adventure of Bruce-Partington Plans
#quote#sherlock holmes#mycroft holmes#arthur conan doyle#acd sherlock#literary sherlock#books#myfragment
48 notes
·
View notes
Text






Three allied soldiers in Whitehall, walking with kit towards Trafalgar Square. 1939. Many buildings and public spaces in London underwent a change of usage before or during WW2, as society and the economy adapted to the needs of the war effort.
The third image shows a man walking near a brick pillbox in Northumberland Avenue. Pillboxes or British hardened field defences were small fortified structures constructed as a part of British anti-invasion preparations. Northumberland Avenue housed a number of military offices in two large requisitioned hotels during the Second World War. Image taken 19 June 1945.
Fourth image shows the Statue of King Charles I situated at the end of Whitehall, which is shielded by a combination of timber frame and corrugated steel sheeting to safeguard it from damage caused by air raids. A directional sign indicating the location of an above-ground public air raid shelter in Trafalgar Square is affixed to the structure. Additionally, traffic roadblocks are present at the structure's base.
Fifth image shows a machine gun position fortified with sandbags at the bottom of Admiralty Arch on the Mall during May 1940. The sixth and final image shows a large gathering on 15 August 1945 at the end of Downing Street. The crowd has assembled to hear the news of the end of the war in Japan (VJ Day). Note that many of the expectant people have climbed onto a nearby pillbox, which they are using as a vantage point.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Sunday Pictorial - May 18, 1947


By a Special Contributor to the ‘Sunday Pictorial’
The tumult and the shouting dies. But for the King there can be no relaxation. When the cheering crowds disperse and go home, he has a tedious exacting job to do at his desk.
Throughout Britain this week the talk has been of our King and Queen. When they left for South Africa they were envied their promise of sunshine and non-austerity food.
Then, day after day, we heard of them giving a reception here, auditions there... It was work, hard work.
And now they are back… to work again in surroundings so familiar that they lack the excitement and glamour of the young Dominion.
Passers-by, looking up at the Royal Standard floating above Buckingham Palace, know that the King is back in London and try to imagine what he is doing. But all that emerges from behind those grey stone walls is a dull, factual Court Circular, with its list of people received, Privy Councils held, and ladies and gentlemen in attendance.
Now let’s go through the tall, double glass doors of the Privy Purse, the ‘business’ entrance of the Palace, on your right as you face it from the Mall, and see how the King’s day is planned, how the head of the Empire does his work.
In general control of the King’s official activities is his private secretary, holder of an office that has grown in importance greatly during the past three reigns until today it is often referred to as that of the ‘Sovereign’s Personal Prime Minister.’
The present private secretary is sparsely built, quizzical Sir Alan Lascelles, who holds the office not because he is first cousin to the Earl of Harewood, the King’s brother-in-law, but because of his long record as a servant of the Crown. He was assistant private secretary to the Duke of Windsor when he was Prince of Wales, private secretary to the Governor-General of Canada, and assistant private secretary to George V, Edward VIII and George VI.
Always an early riser, Sir Alan walks over from his house at St. James’s - which he has rent free as part of his salary - just after nine, and is firmly seated at his desk, with a good idea of the news of the day, by nine-thirty. At any moment after that a bell may ring, and an old-fashioned card indicator on the wall falls, showing the words ‘The King.’
Then Sir Alan, known to the King and Queen and to everyone else at the palace as Tommy, ‘goes up’ to the King. Those words are literally as well as constitutionally true, for the King’s business room - he does not call it his study - is on the first floor.
With the King, Tommy will go through the latest dispatches and messages from our Ambassadors abroad, reports from Whitehall, minutes from various Government departments, ‘submissions’ from the Prime Minister and from the Premiers of the Dominions, each of whom has the right of direct approach to the King.
Tommy knows more of what is going on all over the Empire and the world than anyone else, except the King. That’s part of his job.
It is his task to advise the King on every kind of problem, from whether he should accept an invitation to open an agricultural show, to what he should say in a Christmas broadcast, or whether and how he should intervene in some major crisis in public affairs.
Under Sir Alan are two assistant private secretaries, who take on the routine work, fixing details of programmes for provincial visits by the King and Queen, arranging for audiences and so on.
Part of their task is to furnish a short ‘aide-memoire’ for the King about everyone whom he receives in audience. The King has a really remarkable memory for faces and names, but he cannot be expected to remember details of each man’s career, of the interests and attainments of everyone he meets.
Another of their responsibilities is to furnish rough outline material for the King’s speeches, material which the King himself will later review and arrange.
Altogether there are about forty-five active members of the Royal Household in daily attendance at the Palace, not counting another fifty or more extra equerries, ushers, chaplains and holders of political appointments to the Household. They are the men - and women - who comprise the Court of St. James’s, the wheels in the smooth-running machine of British monarchy.
Today the Palace is run not as a great gentleman’s house, with everything in profusion regardless of cost, and kindly but not over-efficient amateurs holding important jobs, but on strict business lines.
In any business house it is true that if the boss is slack or unpunctual, the rest of the staff are likely to fall off in efficiency. That is true at the Palace as well, and the ‘boss’ - the King - is as hard working, as early rising as anyone on his staff.
Seven-thirty is his normal hour for rising, and he has his simple breakfast alone - bacon is his favourite dish, but the ration does not always run to it. Immediately afterwards he walks into his ‘business room,’ unlocks the red-leather dispatch boxes which have been brought in by the Page of the Presence - an old and trusted Palace servant - and settles down to read.
His papers may include a secret report from a British ambassador on the state of war-preparedness in the country to which he is accredited, and a memorandum on the miners’ attitude to nationalisation of the coalfields, as well as half a dozen other important matters. All of these the King reads and digests.
Presently he rings for his secretary, and the long morning procession begins, to end before lunch with perhaps a new ambassador coming to present his ‘letters of credence’ or a new bishop to do homage on bended knee before the secular head of the Established Church, or an Empire statesman or an outgoing Governor-General to have audience and stay to lunch.
Almost every day the King and Queen lunch together, usually with Princess Elizabeth at table as well, and over lunch the family discuss their plans, arrange theatre parties or dances, talk over the coming week-end at Royal Lodge, and chat of the everyday familiar things that are part of any family’s life.
If there are important State guests at luncheon, the talk is naturally on a more serious plane, and Elizabeth, who meets as many of the important Palace visitors as possible, as part of her training, joins in the conversation.
After luncheon, the King likes to take a short stroll in the Palace gardens, sometimes with Elizabeth and her Corgi dog, sometimes alone. Then it is back to his desk till tea time.
Tea is another family gathering, after which, there is usually a final audience the King must give to the Prime Minister, the Foreign Secretary, or some other highly placed member of his Government.
Between then and dinner, the King sits at his desk tidying up the odds and ends left over during the day: for he is a man with a tidy mind, as befits a former naval officer, and he cannot bear leaving over things unfinished till the next day.
Often it is seven-thirty before he is finished - and that means that one or other of the secretaries, if not all three, is still on duty - and the royal dinner is served at eight.
There is just time to bath and dress - the King nearly always wears a dinner jacket and black tie - before he joins the Queen and the Princesses for what they all regard as the pleasantest part of the day.
In armchairs, the King and Queen and their daughters like to sit, the King reading a light book for relaxation, or looking at a sporting magazine, the Queen knitting or doing embroidery, and the Princesses reading or studying.
Even then, the King is not off duty. At any moment there may be a telephone call from Whitehall, a Government messenger may come to the Palace with urgent dispatches which the King must see at once.
Then the private line to Tommy’s house over at St. James’s comes into action, and if the matter is one of real gravity, the King’s secretary will leave his own home and rejoin his master for a conference that may go on till midnight.
For being the King-Emperor is a full-time job. He is, indeed, the servant of his own subjects and he is ready always to turn from his own recreations to the duty which is not of his own choice, but which he has accepted at all times with unflagging zeal.
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
The State Funeral of Her Majesty The Queen will take place at Westminster Abbey on Monday 19th September at 1100hrs BST. Prior to the State Funeral, The Queen will Lie-in-State in Westminster Hall for four days, to allow the public to pay their respects.
The Queen's Coffin currently rests in the Ballroom at Balmoral Castle. Her Majesty's Coffin will travel to Edinburgh tomorrow, Sunday 11th September, by road, to arrive at the Palace of Holyroodhouse, where it will rest in the Throne Room until the afternoon of Monday 12th September.
On the afternoon of Monday 12th September, a Procession will be formed on the forecourt of the Palace of Holyroodhouse to convey the Coffin to St Giles' Cathedral, Edinburgh. The King and Members of the Royal Family will take part in the Procession and attend a Service in St Giles’ Cathedral to receive the Coffin.
Her Majesty's Coffin will then lie at rest in St Giles' Cathedral, guarded by Vigils from The Royal Company of Archers, to allow the people of Scotland to pay their respects.
On the afternoon of Tuesday 13th September, The Queen's Coffin will travel from Scotland by Royal Air Force aircraft from Edinburgh Airport, arriving at RAF Northolt later that evening. The Coffin will be accompanied on the journey by The Princess Royal.
The Queen's Coffin will then be conveyed to Buckingham Palace by road, to rest in the Bow Room. On the afternoon of Wednesday 14th September, the Coffin will be borne in Procession on a Gun Carriage of The King’s Troop Royal Horse Artillery from Buckingham Palace to the Palace of Westminster, where The Queen will Lie-in-State in Westminster Hall until the morning of the State Funeral.
The Procession will travel via Queen’s Gardens, The Mall, Horse Guards and Horse Guards Arch, Whitehall, Parliament Street, Parliament Square and New Palace Yard. After the Coffin arrives at Westminster Hall, The Archbishop of Canterbury will conduct a short service assisted by The Very Reverend Dr David Hoyle, Dean of Westminster, and attended by The King and Members of the Royal Family, after which the Lying-in-State will begin.
During the Lying-in-State, members of the public will have the opportunity to visit Westminster Hall to pay their respects to The Queen. On the morning of Monday 19th September, the Lying-in-State will end and the Coffin will be taken in Procession from the Palace of Westminster to Westminster Abbey, where the State Funeral Service will take place.
Following the State Funeral, the Coffin will travel in Procession from Westminster Abbey to Wellington Arch. From Wellington Arch, the Coffin will travel to Windsor and once there, the State Hearse will travel in Procession to St. George’s Chapel, Windsor Castle via the Long Walk. A Committal Service will then take place in St George's Chapel.
191 notes
·
View notes
Text
“It is as if you met a tram-car coming down a country lane. Mycroft has his rails and he runs on them. His Pall Mall lodgings, the Diogenes Club, Whitehall—that is his cycle. Once, and only once, he has been here. What upheaval can possibly have derailed him?”
Mycroft continues to be the unruffled autistic king. I should start using “I have my rails and I run on them” for my comfort zone routines.
#letters from watson#the bruce partington plans#it wouldn’t be true though I’m constantly out of my comfort zone#i should take more after mycroft
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Details on the Coronation Procession
On the morning of the 6th May, Their Majesties will travel from Buckingham Palace in The King’s Procession to Westminster Abbey in the Diamond Jubilee State Coach. Created for Queen Elizabeth II to commemorate the 60th anniversary of Her late Majesty’s reign in 2012, the coach has only ever conveyed the Sovereign, occasionally accompanied by the consort or a visiting Head of State.

The gilded crown on the top of the Diamond Jubilee State Coach was carved from oak from HMS Victory, and the coach’s interior is inlaid with samples of woods, metals and other materials from buildings and places with specific connections to Britain and its history; Royal Residences including Buckingham Palace, Kensington Palace, Windsor Castle and the Palace of Holyroodhouse; cathedrals including St Paul’s and Westminster Abbey; and historic ships, such as the Mary Rose. The coach will be drawn by six Windsor Greys.
The King’s Procession, accompanied by The Sovereign’s Escort of the Household Cavalry, will depart Buckingham Palace through the Centre Gate, and proceed down The Mall, passing through Admiralty Arch and south of King Charles I Island, down Whitehall and along Parliament Street. The King’s Procession will travel around the east and south sides of Parliament Square to Broad Sanctuary to arrive at the Sanctuary of Westminster Abbey, where the Coronation Service will begin at 11 o’clock.

The procession from Westminster Abbey to Buckingham Palace, The Coronation Procession, will be much larger in scale, taking the same route in reverse. The Coronation Procession will include Armed Forces from across the Commonwealth and the British Overseas Territories, and all Services of the Armed Forces of the United Kingdom, alongside The Sovereign’s Bodyguard and Royal Watermen.

Their Majesties will travel in the Gold State Coach. The coach, last seen during the Pageant of the Platinum Jubilee of Queen Elizabeth II in June 2022, was commissioned in 1760 and was first used by King George III, to travel to the State Opening of Parliament in 1762. The coach has been used at every Coronation since that of William IV in 1831. The coach will be drawn by eight Windsor Greys and, due to its weight of four tonnes, will travel at walking pace.

Upon returning to Buckingham Palace following the Coronation Service, Their Majesties will receive a Royal Salute from the United Kingdom and Commonwealth Armed Forces who have been on parade that day. The Royal Salute will be followed by three cheers from the assembled service personnel, as a tribute from the Armed Forces on parade to The King and The Queen Consort on the day of Their Majesties’ Coronation.
41 notes
·
View notes
Photo
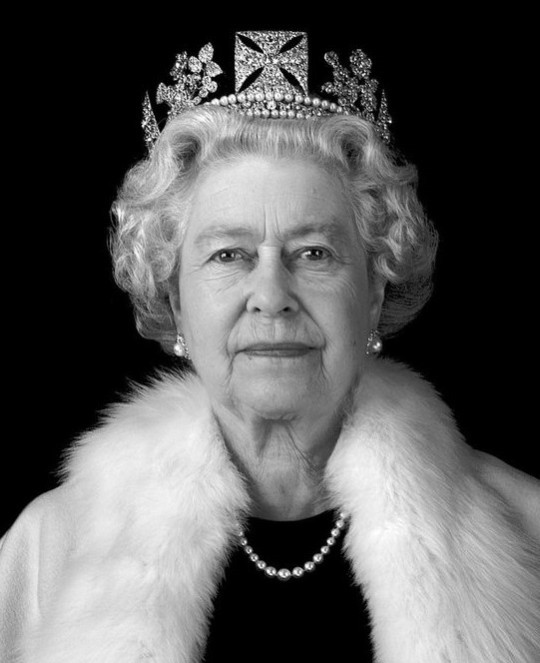

The long reign of Queen Elizabeth II was marked by her strong sense of duty and her determination to dedicate her life to her throne and to her people.
She became for many the one constant point in a rapidly changing world as British influence declined, society changed beyond recognition and the role of the monarchy itself came into question.
Her success in maintaining the monarchy through such turbulent times was even more remarkable given that, at the time of her birth, no-one could have foreseen that the throne would be her destiny.
Elizabeth Alexandra Mary Windsor was born on 21 April 1926, in a house just off Berkeley Square in London, the first child of Albert, Duke of York, second son of George V, and his duchess, the former Lady Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon.
Both Elizabeth and her sister, Margaret Rose, who was born in 1930, were educated at home and brought up in a loving family atmosphere. Elizabeth was extremely close to both her father and her grandfather, George V.
At the age of six, Elizabeth told her riding instructor that she wanted to become a "country lady with lots of horses and dogs".
She was said to have shown a remarkable sense of responsibility from a very early age. Winston Churchill, the future prime minister, was quoted as saying that she possessed "an air of authority that was astonishing in an infant".
Despite not attending school, Elizabeth proved adept at languages and made a detailed study of constitutional history.
A special Girl Guides company, the 1st Buckingham Palace, was formed so that she could socialise with girls of her own age.
Increasing tension
On the death of George V in 1936, his eldest son, known as David, became Edward VIII.
However, his choice of wife, the twice-divorced American Wallis Simpson, was deemed to be unacceptable on political and religious grounds. At the end of the year he abdicated.
A reluctant Duke of York became King George VI. His Coronation gave Elizabeth a foretaste of what lay in store for her and she later wrote that she had found the service "very, very wonderful".
Against a background of increasing tension in Europe, the new King, together with his wife, Queen Elizabeth, set out to restore public faith in the monarchy. Their example was not lost on their elder daughter.
In 1939, the 13-year-old princess accompanied the King and Queen to the Royal Naval College at Dartmouth.
Together with her sister Margaret, she was escorted by one of the cadets, her third cousin, Prince Philip of Greece.
Obstacles
It was not the first time they had met, but it was the first time she took an interest in him.
Prince Philip called on his royal relatives when on leave from the navy, and by 1944, when she was 18, Elizabeth was clearly in love with him. She kept his picture in her room and they exchanged letters.
The young princess briefly joined the Auxiliary Territorial Service (ATS) towards the end of the war, learning to drive and service a lorry. On VE Day, she joined the Royal Family at Buckingham Palace as thousands gathered in The Mall to celebrate the end of the war in Europe.
"We asked my parents if we could go out and see for ourselves," she later recalled. "I remember we were terrified of being recognised. I remember lines of unknown people linking arms and walking down Whitehall, all of us just swept along on a tide of happiness and relief."
After the war, her desire to marry Prince Philip faced a number of obstacles.
The King was reluctant to lose a daughter on whom he doted, and Philip had to overcome the prejudice of an establishment that could not accept his foreign ancestry.
But the wishes of the couple prevailed and on 20 November 1947 the couple married in Westminster Abbey.
The Duke of Edinburgh, as Philip had become, remained a serving naval officer. For a short time, a posting to Malta meant the young couple could enjoy a relatively normal life.
Their first child, Charles, was born in 1948, followed by a sister, Anne, who arrived in 1950.
But the King, having suffered considerable stress during the war years, was terminally ill with lung cancer, brought about by a lifetime of heavy smoking.
In January 1952, Elizabeth, then 25, set off with Philip for an overseas tour. The King, against medical advice, went to the airport to see the couple off. It was to be the last time Elizabeth would see her father.
Elizabeth heard of the death of the King while staying at a game lodge in Kenya and the new Queen immediately returned to London.
"In a way, I didn't have an apprenticeship," she later recalled. "My father died much too young, so it was all a very sudden kind of taking on and making the best job you can."
Personal attack
Her Coronation in June 1953 was televised, despite the opposition of Prime Minister Winston Churchill, and millions gathered around TV sets, many of them for the first time, to watch as Queen Elizabeth II made her oath.
With Britain still enduring post-war austerity, commentators saw the Coronation as the dawn of a new Elizabethan age.
World War Two had served to hasten the end of the British Empire, and by the time the new Queen set off on a lengthy tour of the Commonwealth in November 1953, many former British possessions, including India, had gained independence.
Elizabeth became the first reigning monarch to visit Australia and New Zealand. It was estimated that three-quarters of Australians turned out to see her in person.
Throughout the 1950s, more countries hauled down the union flag and the former colonies and dominions now came together as a voluntary family of nations.
Many politicians felt that the new Commonwealth could become a counter to the newly emerging European Economic Community and, to some extent, British policy turned away from the Continent.
But the decline of British influence was hastened by the Suez debacle in 1956, when it became clear that the Commonwealth lacked the collective will to act together in times of crisis. The decision to send British troops to try to prevent Egypt's threatened nationalisation of the Suez Canal ended in an ignominious withdrawal and brought about the resignation of Prime Minister Anthony Eden.
This embroiled the Queen in a political crisis. The Conservative Party had no mechanism for electing a new leader and, after a series of consultations, the Queen invited Harold Macmillan to form a new government.
The Queen also found herself the subject of a personal attack by the writer Lord Altrincham. In a magazine article, he claimed her court was "too British" and "upper-class" and accused her of being unable to make a simple speech without a written text.
His remarks caused a furore in the press and Lord Altrincham was physically attacked in the street by a member of the League of Empire Loyalists.
Nevertheless, the incident demonstrated that British society and attitudes to the monarchy were changing fast and old certainties were being questioned.
From 'the Monarchy' to 'the Royal Family'
Encouraged by her husband, notoriously impatient with the court's stuffiness, the Queen began to adapt to the new order.
The practice of receiving debutantes at court was abolished and the term "the Monarchy" was gradually replaced by "the Royal Family".
The Queen was once more at the centre of a political row when in 1963, Harold Macmillan stood down as prime minister. With the Conservative Party still to set up a system for choosing a new leader, she followed his advice to appoint the Earl of Home in his place.
It was a difficult time for the Queen. The hallmark of her reign was constitutional correctness, and a further separation of the monarchy from the government of the day. She took seriously her rights to be informed, to advise and to warn - but did not seek to step beyond them.
It was to be the last time she would be put in such a position. The Conservatives finally did away with the tradition that new party leaders just "emerged", and a proper system was put in place.
By the late 1960s, Buckingham Palace had decided that it needed to take a positive step to show the Royal Family in a far less formal and more approachable way.
The result was a ground-breaking documentary, Royal Family. The BBC was allowed to film the Windsors at home. There were pictures of the family at a barbecue, decorating the Christmas tree, taking their children for a drive - all ordinary activities, but never seen before.
Critics claimed that Richard Cawston's film destroyed the mystique of the royals by showing them to be ordinary people, including scenes of the Duke of Edinburgh barbecuing sausages in the grounds at Balmoral.
But the film echoed the more relaxed mood of the times and did much to restore public support for the monarchy.
By 1977, the Silver Jubilee was celebrated with genuine enthusiasm in street parties and in ceremonies across the kingdom. The monarchy seemed secure in the public's affection and much of that was down to the Queen herself.
Two years later, Britain had, in Margaret Thatcher, its first woman prime minister. Relations between the female head of state and female head of government were sometimes said to have been awkward.
Scandals and disasters
One difficult area was the Queen's devotion to the Commonwealth, of which she was head. The Queen knew the leaders of Africa well and was sympathetic to their cause.
She was reported to have found Thatcher's attitude and confrontational style "puzzling", not least over the prime minister's opposition to sanctions against apartheid South Africa.
Year by year, the Queen's public duties continued. After the Gulf War in 1991, she went to the United States to become the first British monarch to address a joint session of Congress. President George HW Bush said she had been "freedom's friend for as long as we can remember".
However, a year later, a series of scandals and disasters began to affect the Royal Family.
The Queen's second son, the Duke of York, and his wife Sarah separated, while Princess Anne's marriage to Mark Phillips ended in divorce. Then the Prince and Princess of Wales were revealed to be deeply unhappy and eventually split up.
The year culminated in a huge fire at the Queen's favourite residence, Windsor Castle. It seemed a grimly appropriate symbol of a royal house in trouble. It was not helped by a public row over whether the taxpayer, or the Queen, should foot the bill for the repairs.
The Queen described 1992 as her "annus horribilis" and, in a speech in the City of London, appeared to concede the need for a more open monarchy in return for a less hostile media.
"No institution, city, monarchy, whatever, should expect to be free from the scrutiny of those who give it their loyalty and support, not to mention those who don't. But we are all part of the same fabric of our national society and that scrutiny can be just as effective if it is made with a measure of gentleness, good humour and understanding."
The institution of monarchy was very much on the defensive. Buckingham Palace was opened to visitors to raise money to pay for the repairs at Windsor and it was announced that the Queen and the Prince of Wales would pay tax on investment income.
Abroad, the hopes for the Commonwealth, so high early in her reign, had not been fulfilled. Britain had turned its back on its old partners with new arrangements in Europe.
The Queen still saw value in the Commonwealth and was deeply gratified when South Africa, where she had come of age, at last threw apartheid aside. She celebrated with a visit in March 1995.
At home, the Queen sought to maintain the dignity of the monarchy while public debate continued on whether the institution had any future.
Death of Diana, Princess of Wales
As Britain struggled to find a new destiny, she tried to remain a reassuring figure, and with a sudden smile could lighten a solemn moment. The role she valued above all was that of symbol of the nation.
However, the monarchy was shaken and the Queen herself attracted unusual criticism after the death of Diana, Princess of Wales, in a car accident in Paris in August 1997.
As the public crowded around the palaces in London with tributes of flowers, the Queen seemed reluctant to provide the focus that she had always tried to do during great national moments.
Many of her critics failed to understand that she was from a generation that recoiled from the almost hysterical displays of public mourning that typified the aftermath of the princess's death.
She also felt as a caring grandmother that she needed to comfort Diana's sons in the privacy of the family circle.
Eventually, she made a live broadcast, paying tribute to her daughter-in-law and making a commitment that the monarchy would adapt.
Losses and celebrations
The deaths of the Queen Mother and Princess Margaret, in the Queen's Golden Jubilee year, 2002, cast a shadow over nationwide celebrations of her reign.
But despite this, and the recurring debate over the future of the monarchy, a million people crowded into The Mall, in front of Buckingham Palace, on the evening of the jubilee.
In April 2006, thousands of well-wishers lined the streets of Windsor as the Queen performed an informal walkabout on her 80th birthday.
And in November 2007, she and Prince Philip celebrated 60 years of marriage with a service attended by 2,000 people at Westminster Abbey.
There was yet another happy occasion in April 2011 when the Queen attended the wedding of her grandson, William, Duke of Cambridge, to Catherine Middleton.
In May that year she became the first British monarch to make an official visit to the Irish Republic, an event of great historical significance.
In a speech, which she began in Irish, she called for forbearance and conciliation and referred to "things we wish had been done differently or not at all".
Referendum
A year later, on a visit to Northern Ireland as part of the Diamond Jubilee celebrations, she shook hands with the former IRA commander Martin McGuinness.
It was a poignant moment for a monarch whose much-loved cousin, Lord Louis Mountbatten, had been killed by an IRA bomb in 1979.
The Diamond Jubilee brought hundreds of thousands of people on to the streets and culminated in a weekend of celebrations in London.
The referendum on Scottish independence, in September 2014, was a testing time for the Queen. Few had forgotten her speech to Parliament in 1977 in which she made clear her commitment to a United Kingdom.
"I number kings and queens of England and of Scotland, and princes of Wales among my ancestors and so I can readily understand these aspirations. But I cannot forget that I was crowned Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland."
In a remark to well-wishers at Balmoral on the eve of the Scottish referendum, which was overheard, she said she hoped people would think very carefully about the future.
Once the result of the vote was known, her public statement underlined the relief she felt that the Union was still intact, although recognising that the political landscape had changed.
"Now, as we move forward, we should remember that despite the range of views that have been expressed, we have in common an enduring love of Scotland, which is one of the things that helps to unite us all."
On 9 September 2015 she became the longest reigning monarch in British history, surpassing the reign of her great-great-grandmother Queen Victoria. In typical style she refused to make any fuss saying the title was "not one to which I have ever aspired".
Less than a year later, in April 2016, she celebrated her 90th birthday.
She continued with her public duties, often alone after the retirement of the Duke of Edinburgh in 2017.
There were continued strains on the family - including her husband's car accident, the Duke of York's ill-judged friendship with convicted American businessman Jeffrey Epstein and Prince Harry's growing disillusionment with life in the royal family.
These were unsettling moments, presided over by a monarch who demonstrated that she was still firmly in control. There was also the death of Prince Philip in April 2021, in the midst of the coronavirus pandemic, and her Platinum Jubilee a year later.
Although the monarchy might not have been as strong at the end of the Queen's reign as it was at the start, she was determined that it should continue to command a place of affection and respect in the hearts of the British people.
On the occasion of her Silver Jubilee, she recalled the pledge she had made on a visit to South Africa 30 years before.
"When I was 21, I pledged my life to the service of our people and I asked for God's help to make good that vow. Although that vow was made in my salad days, when I was green in judgement, I do not regret, or retract, one word of it."
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at http://justforbooks.tumblr.com
100 notes
·
View notes
Text





Sears at Whitehall Mall is coming down
#whitehall mall#sears#photography#dead mall#retail#dead malls#deadmall#mall#malls#shopping mall#shopping malls#retail apocalypse#dead mall series#pennsylvania#lehighvalley#lehigh valley#allentownpa
61 notes
·
View notes
Note

I should be listening to you Mr Holmes, but I'm sorry if I'm stealing pictures instead
I noticed.
#mycroft holmes#mycroft#mycroft replies#mycroft bbc#mark gatiss#mycroft holmes replies#whitehall#pall mall
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Why not? It is as if you met a tram-car coming down a country lane. Mycroft has his rails and he runs on them. His Pall Mall lodgings, the Diogenes Club, Whitehall—that is his cycle. Once, and only once, he has been here. What upheaval can possibly have derailed him?”
Loving the extended tram/rails metaphor
“It recalls nothing to my mind. But that Mycroft should break out in this erratic fashion! A planet might as well leave its orbit. By the way, do you know what Mycroft is?”
[…]“But Jupiter is descending to-day. What on earth can it mean? Who is Cadogan West, and what is he to Mycroft?”
And also the planet metaphor, which is basically a roundabout way for Holmes to call his brother fat.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
New ceremonial details about the Coronation of The King and The Queen Consort, posted by the Royal Family account:
On the morning of the Coronation, Their Majesties will travel from Buckingham Palace in The King’s Procession to Westminster Abbey in the Diamond Jubilee State Coach – which was created in 2012 for Queen Elizabeth II’s Diamond Jubilee.

The King’s Procession, accompanied by The Sovereign’s Escort of the Household Cavalry, will depart Buckingham Palace and proceed down The Mall, passing through Admiralty Arch and Trafalgar Square, down Whitehall and along Parliament Street to Westminster Abbey.
The procession from Westminster Abbey to Buckingham Palace – The Coronation Procession - will take same route in reverse and will feature Armed Forces from across the Commonwealth and the British Overseas Territories, and all Services of the UK’s Armed Forces.
Their Majesties will travel in the Gold State Coach, which was commissioned in 1760 and was first used by King George III to travel to the State Opening of Parliament in 1762, and has been used at every Coronation since that of William IV in 1831.

101 notes
·
View notes
Text
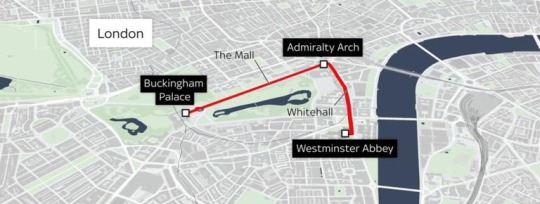


Further details about the Coronation were released by Buckingham Palace this weekend.
Their Majesties will travel from Buckingham Palace in The King’s Procession to Westminster Abbey in the Diamond Jubilee State Coach, drawn by six Windsor Greys and will be accompanied by The Sovereign’s Escort of the Household Cavalry.
The King's Procession will depart Buckingham Palace through the Centre Gate, and proceed down The Mall, passing through Admiralty Arch and south of King Charles I Island (the roundabout by Trafalgar Square), down Whitehall and Parliament Street. It will proceed along the south side of Parliament Square to the Sanctuary of Westminster Abbey, where the Coronation service will commence at 11 o'clock.
The Coronation Procession after the service will be more elaborate. The King and Queen will return to Buckingham Palace in the Gold State Coach drawn by eight Windsor Greys via the same 1.3 mile route.
The Coronation Procession will include Armed Forces from across the Commonwealth and the British Overseas Territories, and all Services of the Armed Forces of the United Kingdom, alongside The Sovereign’s Bodyguard and Royal Watermen.
After arriving back at Buckingham Palace, the King and Queen will receive a Royal Salute from the United Kingdom and Commonwealth Armed Forces who have been on parade that day... followed by Three Cheers from the assembled service personnel.
16 notes
·
View notes