#she was a teen when she married louis but during the revolution she was in her 30s. funny how people age over the span of several years!
Photo

« Plus scélérate qu’Agrippine
Dont les crimes sont inouïs,
Plus lubrique que Messaline,
Plus barbare que Médicis. »
- Pamphlet contre la reine. Vers 1785
Marie Antoinette was a teen queen. She had married the Dauphin when she was only fifteen. She was a pawn in the political design that included her Austrian parents of royal birth and the royals of France. When she came to France, she was surrounded by enemies, who were looking for ways to usurp the upper class.

The time was also ripe for the French Revolution. The growing dissent in the lower section of the society was gaining ground. Marie Antoinette’s profligate spending did not help either. The poor people of France were now impatient with the excesses of the royals and the upper middle class. They were looking for ways to implicate the King and the Queen for their misfortune. In 1793, Marie Antoinette was tried for treason, and publicly beheaded.

The real work of destruction had been done long before by satire, libel and rumour; Marie Antoinette had become dehumanised. The actual assault by a body of people inspiring each other with their bloodthirsty frenzy was the culmination of the process, not the start of it.
During the French Revolution, rumors were floated to taint the Queen, and justify the killing of the monarch. One of the stories that did the rounds then was that when the Queen asked her page why people were rioting in the city, the servant informed her that there is no bread. So, the Queen allegedly said, “S’ils n’ont plus de pain, qu’ils mangent de la brioche!” (then let them east cake!)

However, the ill-worded quote stuck on Marie Antoinette’s image for over 200 years. It was not until 1823, when the memoirs of Comte de Provence was published that the truth came out. Though the Comte de Provence was not exactly generous in his admiration for his sister-in-law, he did not fail to mention that while eating ‘pate en croute’ he was reminded of his own ancestress, Queen Marie-Thérèse.
In 1765, French philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau wrote a six part book titled Confessions. In this book, he recollects the words of a princess of his time, who said:
“Enfin je me rappelai le pis-aller d’une grande princesse à qui l’on disait que les paysans n’avaient pas de pain, et qui répondit : Qu’ils mangent de la brioche.” Which when translated in English says: “Finally I recalled the stopgap solution of a great princess who was told that the peasants had no bread, and who responded: “Let them eat brioche.”

Since this book was written in 1765, when Marie Antoinette was just a nine year old girl, and had not even met the future King of France, let alone marry him, it was unimaginable that Marie Antoinette had actually said the words. Marie Antoinette came to Versailles much later, in 1770, and she became queen in 1774.
Marie Antoinette, along with her King husband Louis XVI, became the scapegoat for the rising tide of rebellion. Marie Antoinette was aware of the public suffering, and often donated to several charitable causes, according to Lady Antonia Fraser, her biographer. She was sensitive to the suffering of the poor, and often driven to tears when she heard of the plight of the poor. However, despite her royal position, she either did not have the drive to remedy the situation, or probably lacked political finesse to protect the monarchy.

Marie Antoinette did not bear children in the initial years of her marriage, and this was projected as the queen’s promiscuous nature. Rumours flourished about her alleged affair with Axel Fersen, a Spanish count in court. Gossip flew thick inside the ornate walls of the Versailles palace, as Marie Antoinette was accused of participating in a crime that later came to be known as the “diamond necklace affair.”

But perhaps the most slanderous accusation that Marie Antoinette had to bear with was having an incestuous relationship with her own son. It may have broken the mother's heart, but on the face of it all, Marie Antoinette remained a stoic, and dignified queen who bore it all.
At the time of her trial, when the Tribunal asked her to respond to the accusation of having sexual relations with her son, she answered:
“If I have not replied it is because Nature itself refuses to answer such a charge laid against a mother.” She then turned to the crowd, who had gathered to witness her trial, and asked them: “I appeal to all mothers here present – is it true?”

Legend has it that when she spoke these words in court, the women in the audience were moved by her earnest appeal. However, the Tribunal, fearing that she may evoke public sympathy, hastened the legal proceedings to sentence her to death.
The unfortunate beheading of a queen wronged by her people is a story that will remain an everlasting blot in the history of humanity. She received a punishment far greater than her crime. As an Austrian wife of a French king, Marie Antoinette was destined for her doom even as she bore it all with dignity.

On October 16, 1793, as Marie Antoinette was taken in an open cart towards the guillotine, a priest asked her to have courage. These were her words she flung at the priest to reveal the stoic composure of a regal woman. “No one understands my ills, nor the terror that fills my breast, who does not know the heart of a mother.” A heartbroken Marie Antoinette spoke these words in 1789, at her beloved son Louis Joseph’s demise of tuberculosis.
#marie-antoinette#queen#quote#french#france#monarchy#king#bourbons#french revolution#history#execution#trial
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
History Bites: Best Royal Romances



In History Bites, I pick the best moments of history and the antics historical figures in order to give you inspiration for your WIP. Think of History Bites like prompts, only juicer and 90% accurate (results may vary).
Love is one of the greatest reasons to do anything. Love will make people act strangely, become better people and level empires. In a world of arranged marriages and terrible spouses, some royals found happiness.
Antony and Cleopatra were the Ancient World's power couple. After Caesar's death, who had been Antony's mentor and the father to Cleopatra's son, Antony was sent to govern the Eastern Provinces. At Tarsus in Turkey, Cleopatra paid a visit to Antony. During the visit, Antony and Cleopatra got to know each other better and quickly things got romantic. It was not exactly the best thing for a Roman senator to have an Egyptian mistress and an odd thing for a famously intellectual Queen to take a notorious foolish hothead as her lover but the two were incredibly fond of one another. The two of them had three children, who Antony left the Roman Empire to in his will. The will was the final straw for Rome so it went to war with the couple, which ended in defeat. Antony committed suicide and Cleopatra sometime afterward.
Queen Victoria's marriage was an issue from the get go, because she needed a husband who was not her subject (because women were meant to obey their menfolk and a Queen shouldn't obey a subject) and one who was suitable. Victoria didn't like her cousin Albert when they met as teens but feel head over heels in love with him after they met again after Victoria became Queen. The two were rather smitten with each other and managed to pop out 9 kids. Victoria was distraught when Albert died and rarely wore anything but black for most of her life and rarely went out in public.
Josephine de Beauharnais was a wealthy French woman during the French Revolution which claimed the life of her first husband. Josephine caught the eye of the young Corsican soldier, Napoleon and the two quickly wed despite him being 6 years younger. Josephine was the perfect consort for Napoleon, she was an able diplomat and learned. When Napoleon was away, he often sent her raunchy letters which Josephine hilariously replied with nonchalance. Napoleon divorced Josephine because she was barren and he needed a heir. I doubt he stopped loving Josephine.
Charles II was not exactly the most monogamous of monarchs. The Merry Monarch and one of the few English Kings I think fondly of, had one declared mistress about five others. A friend of Charles saw Nell Gwyn playing on the London stage and decided to introduce her to his royal master, a wingman if you will. Nell and the King hit it off well because Nell wasn't as grasping as the other mistresses and knew how to make him laugh. She once took him fishing and when the monarch caught nothing, she tied a fried piece of fish to his line. She bore him too sons but felt as if Charles was not awarding them the right honours. When he came to visit them, she called one son over by saying "Come hither, you little bastard." Charles was angry at that but Nell reminded him that she had little else to refer to him by so Charles created a Dukedom for his sons. When Charles died, Nell remained monogamous to him telling one admirer than she would not "lay a dog where a deer that once lain."
Louis XIV was Charles's cousin and they shared a similar taste for mistresses. Madame de Montespan was married as Louis was but the two started a relationship together. Montespan was rather spoilt by Louis, earning the nickname "How much" by courtiers. Montespan and the King were together for a long period of time, having many children. A scandal came to light which involved a supposed witch and black masses where Montespan bought love potions and cursed the Queen. Montespan was lucky to avoid execution but she was dealt a personal blow: the King fell out of love with her. Montespan haunted the court as Louis moved on, keeping a bedroom for him at all times just in case he wished to visit. He never did. Louis moved on to the nanny of his bastard children by Montespan, the religious Madame de Maintenon. The two were kindred spirits and when the Queen died, Louis married Madame de Maintenon and the two lived the rest of their lives together.
Henry IV of France was married when he began a relationship with Gabrielle d'Estrees, a Catholic noblewoman during the Wars of Religion in France. Henry was increasingly fond of her despite their religious differences, even more than his wife at the time Marguerite of Valois. Gabrielle was a successful diplomat, going between the Protestant King and his Catholic nobility, smoothing relations by convincing Henry to become a Catholic. Gabrielle went to war with Henry, caring for his clothes and cooking his meals while on campaign. Henry was worried about her safety, especially when he saw bullet holes in her tent but Gabrielle refused to leave his side. Gabrielle sold her jewels to fund Henry's wars and once left the middle of a ball to rush to Henry's side. Her devotion led to Henry deciding to marry and crown her as his Queen. Gabrielle died suddenly before her wedding/coronation leaving Henry heartbroken.
Catherine the Great is on my list for worst marriages bur she found love after her husband was murdered. During her coup when she was making an important speech to rally the troops to her, a young cavalry officer named Grigory Potemkin offered her his own sword knot, a missing detail on her uniform. The two met years later and quickly fell in love. Catherine and Potemkin kept up their touching relationship throughout the wars with Turkey and Catherine's other lovers. They were incredibly close, Catherine giving him every honour and Potemkin helping her realise her dream of a navy. Potemkin died on the roadside, collapsing in front of his soldiers leaving Catherine heartbroken. It is rumoured by historians that the pair had been secretly married.
Have you ever seen bibles with King James written on the cover? Though King James was married and had sired numerous children with his wife, James had a string of noble young men as favourites, his favourite being George Villiers. James was incredibly fond of George, calling him "Steenie" after St. Stephen who canonically (no pun intended) had the face of an angel. When asked by Parliament about the close relationship, James replied that George was as close to him as Jesus was to his disciples. Though historians dispute whether they were actually gay (citing the fact that James had a wife and a loving relationship with her), it is entirely possible that James was bisexual. The two sent numerous letters to one another over the years, each rather touching
Inez de Castro is probably Portugal's most interesting Queen Consort. She was exhumed for her own coronation. Inez was the mistress of Prince Pedro and mother to his children. The King, Pedro's father, really did not want his son marrying his mistress so he had Inez murdered. Pedro was distraught at her death and hunted down the men who had done it, having their hearts torn out in revenge. He would never marry again so to make his children legitimate he had Inez exhumed and crowned Queen, forcing the nobility to kiss her hand and hail her as Queen. Nobody bothered Pedro about his kids again.
Though the film The Favourite (2017) is a skewed version of the relationship between Anne of England and Sarah Duchess of Marlborough, there is some proof to attest to the romantic relationship between the two. They knew each other from a young age and once escaped a house together to avoid the influence of Anne's father who at the time was embroiled in a battle to keep the throne against Anne's sister Mary. The two were incredibly close despite their rather differing personalities. Sarah did care for the Queen but had a habit of being quite abrasive and quick with cruel words which eventually ended the long lasting relationship between the two.
Peter I of Russia was an imposing man both in stature and in political policy. Peter dragged Russia toward Westernization and imposed radical reforms upon his country. Perhaps the greatest wave he made, was his marriage to Catherine, a laundress. Peter and Catherine were incredibly fond of each other, sharing an appetite of good living and each other. Peter did sleep about but Catherine joked about it in letters asking him whether he found any laundresses he liked. Peter fathered two daughters on Catherine but instead of handing control to them after he died he made his wife Empress Catherine I.
Perhaps my favourite royal romance story, is between Emperor Ai and his favourite Dong Xian. Emperor Ai and Dong Xian were chilling in bed together one day. Ai had to get up but Dong Xian was still asleep, laying on his sleeve. Rather than waking his lover, the Emperor cut off his own sleeve so he could get out of bed.
Emperor Hadrian is famous for his bitchin wall between Britannia and Caledonia. But Emperor Hadrian's greatest love would be the Greek Antinous. The emperor had Antonius come with him wherever he went and the two were fond of hunting and writing poetry. Antinous tragically drowned in the Nile, probably by accident but foul play cannot be ruled out.
Jeanne Antoinette Poisson or as you might know her Madame de Pompadour was told at nine years old that she would love a king. In her twenties it came true when she caught the eye of King Louis XV of France, earning her the title maîtresse-en-titre. Madame de Pompadour understood Louis in a way nobody else would. She knew how to read his emotions and knew how to keep him entertained. Though the two stopped sleeping together thanks to a medical condition Jeanne had, Louis kept her as his official mistress. Kings were not permitted to attend funerals so when Jeanne died, Louis couldn't go. He stood on his balcony in a downpour as her funeral carriage left Versailles, the only tribute he could pay the love of his life
Elizabeth Woodville's first husband was an early casualty in the Wars of the Roses, leaving her to care for two sons. Destitute, Elizabeth stood by the road to speak with the new York King of England. Edward IV was younger than her and was her enemy, yet the two fell in love and wed in secret. The court was furious at the marriage as Elizabeth was only the daughter of a baron. The marriage was extremely happy despite Edward's many mistresses and the unsettled times they lived in.
Elizabeth of York, Elizabeth Woodville's daughter, was a highly sought after bride in Europe. Henry Tudor, her uncle Richard's enemy, proposed to her from abroad declaring her would wed her in the Cathedral of Reims. Henry invaded England and won the crown at the Battle of Bosworth. He married Elizabeth and the two, despite being born enemies, lived a happy marriage together. Henry was distraught when Elizabeth died and never remarried.
Mary Tudor, the daughter of Elizabeth of York, was at one point Europe's most eligible and beautiful Princess. She was offered as a bride to the Prince of Spain and then the King of France, who she was married to. Mary was briefly Queen of France but her aged husband died soon after the wedding. Mary returned to England but she had a secret, she had hastily wed her brother's childhood friend, Charles Brandon. Henry VIII, her brother, got so cross that he fined and banished the two of them from court. But he quickly forgave them and the couple returned to court where they spent their short but happy marriage.
Elizabeth II & Prince Philip have been married for decades. The Queen was only eight when she met Philip and the two became friends, writing to each other during WWII. After WWII, Philip renounced his his Danish and Greek titles to marry Elizabeth, becoming Prince Consort and Duke of Edinburgh. Despite Philip's infamous faux pas and wild behavior, the two have a stable and loving relationship.
Edward III & Philippa of Hainault were only children when Edward's mother planned their marriage to gain the military might of Philippa's father. Their marriage was a happy one that produced 12 children. Philippa accompanied Edward to the battlefield many times.
Edward II is on my list for worst marriages but he was a romantic at heart. Edward was very close to a knight named Piers Gaveston. Edward's father didn't like this bond and sent Gaveston away. Edward's first act as king was to recall Piers and bestowed titles and land upon him like there was no tomorrow. Piers was seen as a bad influence and because of this he was killed by a group of rebelling nobles. Edward grieved for years and eventually went on a revenge war against the nobles who had killed his lover.
Despite being Nazi-Sympathizing assholes, no one could doubt that Wallis Simpson and Edward VIII did truly love one another. Edward was King and Wallis was an American divorcee (sound familiar?), and there were laws starting that he could not marry a divorcee. But Edward couldn't give her up do he gave up his throne for her and the two went off to live in France together.
Tsar Nicholas II and Empress Alexandra (then Princess Alix of Hesse) were never meant to be married. Alexandra's grandmother Queen Victoria did not approve of the autocracy of Russia and would have preferred that she marry into England. Alexandra herself dithered on whether to marry Nicholas as it meant a change in religion for her. In the end, the two decided to wed and they had a relatively close marriage. Some of their letters still survive.
#History Bites#best royal romances#writing#writing resources#writing reference#writing advice#writeblr#writer#writer's problems#spilled words#writer's life#characters#louis xiv#Charles ii#mary rose tudor#Elizabeth II#anne I of England#Catherine ii#Catherine I#Emperor ai#wallis Simpson#Emperor Hadrian#lgbt+ History#love#Madame de montespan#nell gwyn#george villiers
331 notes
·
View notes
Text
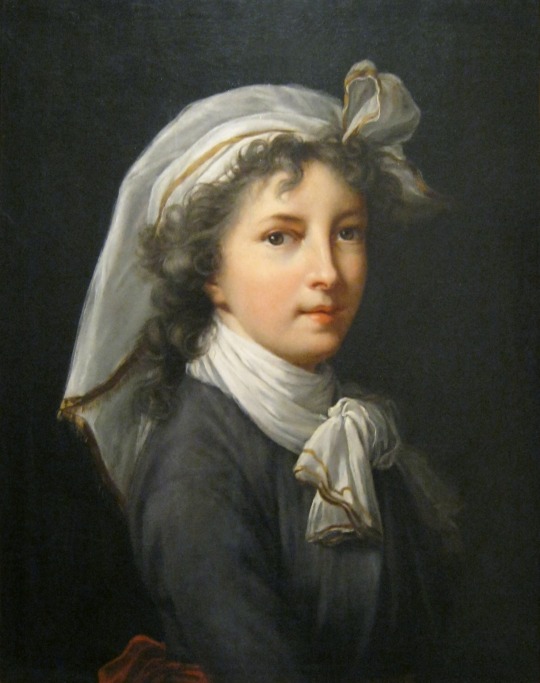
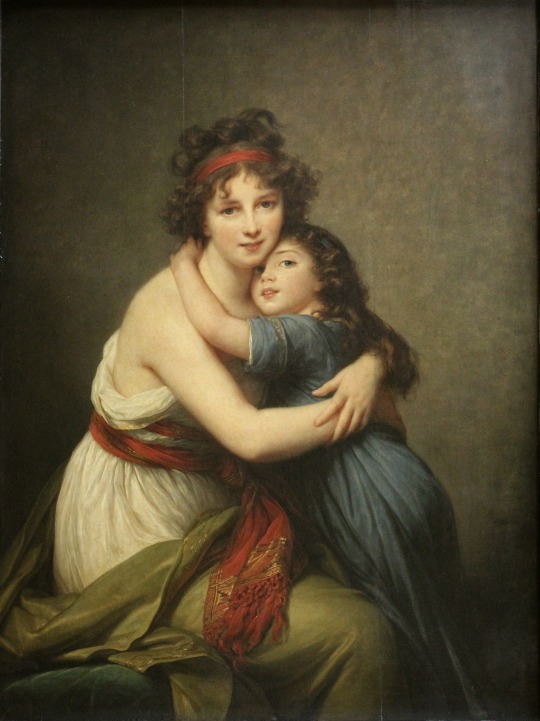
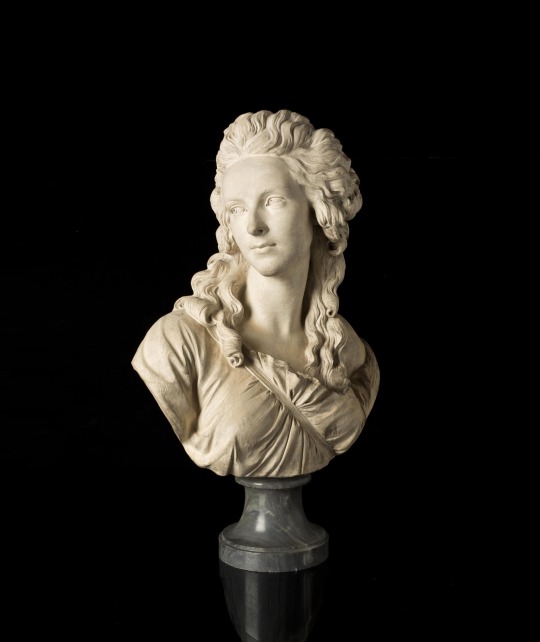








Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun (1755-1842).
18th and 19th-century French painter.
.
She was a prominent French portrait painter of the late 18th century and one of the most successful women artists (unusually so for her time), particularly noted for her portraits of women.
.
Her artistic style is generally considered part of the aftermath of Rococo with elements of an adopted Neoclassical style. Her subject matter and color palette can be classified as Rococo, but her style is aligned with the emergence of Neoclassicism. Vigée Le Brun created a name for herself in Ancien Régime society by serving as the portrait painter to Marie Antoinette. She enjoyed the patronage of European aristocrats, actors, and writers, and was elected to art academies in ten cities.
.
Vigée Le Brun created some 660 portraits and 200 landscapes. In addition to many works in private collections, her paintings are owned by major museums, such as the Louvre, Hermitage Museum, National Gallery in London, Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York, and many other collections in continental Europe and the United States.
.
Her father and first teacher, Louis Vigée, was a noted portraitist who worked chiefly in pastels. By the time she was in her early teens, Élisabeth was painting portraits professionally. In 1776 she married an art dealer, Jean-Baptiste-Pierre Lebrun. Vigée Le Brun began exhibiting her work at their home in Paris, the Hôtel de Lubert, and the Salons she held here supplied her with many new and important contacts. Her husband's great-great-uncle was Charles Le Brun, the first director of the French Academy under Louis XIV.
.
Her great opportunity came in 1779 when she was summoned to Versailles to paint a portrait of Queen Marie-Antoinette. The two women became friends, and in subsequent years Vigée-Lebrun painted more than 20 portraits of Marie-Antoinette in a great variety of poses and costumes.
In 1783, Vigée Le Brun was received as a member of the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture. She was one of only 15 women to be granted full membership in the Académie between 1648 and 1793. Her rival, Adélaïde Labille-Guiard, was admitted on the same day. Vigée Le Brun was initially refused on the grounds that her husband was an art dealer, but eventually the Académie was overruled by an order from Louis XVI because Marie Antoinette put considerable pressure on her husband on behalf of her portraitist.
.
In October 1789, after the arrest of the royal family during the French Revolution, Vigée Le Brun fled France with her young daughter, Julie. Her husband, who remained in Paris, claimed that Vigée Le Brun went to Italy "to instruct and improve herself", but she certainly feared for her own safety. In her 12-year absence from France, she lived and worked in Italy (1789–92), Austria (1792–95), Russia (1795–1801), and Germany (1801). She finally went back to France in 1802 but kept traveling.
She lost eyesight due to various strokes and endend up poor.
.
Famous paintings:
Self Portrait in a Straw Hat
Marie-Antoinette with a Rose
Marie-Antoinette and her Children
Self Portrait with Daughter
Portrait of Emma, Lady Hamilton, as Bacchante
#Élisabeth vigée le brun#Vigée le brun#Painter#18th century#19th century#french history#women history#women in history#History#marie antoinette#history crush#history hottie#history nerd#history geek#history lover#historical crush#historical babes#historical hottie#historical figure#historical
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
Joseph A. Harriss, The Elusive Marc Chagall, Smithsonian Magazine (December 2003)

With his wild and whimsical imagery, the Russian-born artist bucked the trends of 20th-century art
David McNeil fondly remembers the day in the early 1960s his father took him to a little bistro on Paris’ Île St. Louis, the kind of place where they scrawl the menu in white letters on the mirror behind the bar, and masons, house painters, plumbers and other workingmen down hearty lunches along with vin ordinaire. Wearing a beret, a battered jacket and a coarse, checkered shirt, his father— then in his mid-70s—fit in perfectly. With conversation flowing easily among the close-set tables, one of the patrons looked over at the muscular, paint-splotched hands of the man in the beret. “Working on a place around here?” he asked companionably. “Yeah,” replied McNeil’s father, the artist Marc Chagall, as he tucked into his appetizer of hard-boiled egg and mayonnaise. “I’m redoing a ceiling over at the Opéra.”
Chagall, the Russian-born painter who went against the current of 20th-century art with his fanciful images of blue cows, flying lovers, biblical prophets and green-faced fiddlers on roofs, had a firm idea of who he was and what he wanted to accomplish. But when it came to guarding his privacy, he was a master of deflection. Sometimes when people approached to ask if he was that famous painter Marc Chagall, he would answer, “No,” or more absurdly, “I don’t think so,” or point to someone else and say slyly, “Maybe that’s him.” With his slanting, pale-blue eyes, his unruly hair and the mobile face of a mischievous faun, Chagall gave one biographer the impression that he was “always slightly hallucinating.” One of those who knew him best, Virginia Haggard McNeil, David’s mother and Chagall’s companion for seven years, characterized him as “full of contradictions—generous and guarded, naïve and shrewd, explosive and secret, humorous and sad, vulnerable and strong.”
Chagall himself said he was a dreamer who never woke up. “Some art historians have sought to decrypt his symbols,” says Jean-Michel Foray, director of the Marc Chagall Biblical Message Museum in Nice, “but there’s no consensus on what they mean. We cannot interpret them because they are simply part of his world, like figures from a dream.” Pablo Picasso, his sometime friend and rival (“What a genius, that Picasso,” Chagall once joked. “It’s a pity he doesn’t paint”), marveled at the Russian’s feeling for light and the originality of his imagery. “I don’t know where he gets those images. . . . ” said Picasso. “He must have an angel in his head.”
Throughout his 75-year career, during which he produced an astounding 10,000 works, Chagall continued to incorporate figurative and narrative elements (however enigmatic) into his paintings. His warm, human pictorial universe, full of personal metaphor, set him apart from much of 20th-century art, with its intellectual deconstruction of objects and arid abstraction. As a result, the public has generally loved his work, while the critics were often dismissive, complaining of sentimentality, repetition and the use of stock figures.
A major retrospective of Chagall’s unique, often puzzling images was recently on view at the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, following a highly acclaimed run at the Grand Palais in Paris. The first comprehensive exhibition of Chagall’s paintings since 1985 brought together more than 150 works from all periods of his career, many never before seen in the United States, including cloth-and-paper collages from the private collection of his granddaughter Meret Meyer Graber. The exhibition, says Foray, the chief organizer of the show, “offered a fresh opportunity to appreciate Chagall as the painter who restored to art the elements that modern artists rejected, such as allegory and narrative—art as a comment on life. Today he is coming back strong after a period of neglect, even in his home country.” Retrospectives are planned for 2005 at the Museum of Russian Art in St. Petersburg and at the State Tretiakov Gallery in Moscow.
Movcha (Moses) Chagal was, as he put it, “born dead” on July 7, 1887, in the Belorussian town of Vitebsk, near the Polish border. His distraught family pricked the limp body of their firstborn with needles to try to stimulate a response. Desperate, they then took the infant outside and put him in a stone trough of cold water. Suddenly the baby boy began to whimper. With that rude introduction to life, it’s no wonder that Marc Chagall, as he later chose to be known in Paris, stuttered as a boy and was subject to fainting. “I was scared of growing up,” he told Virginia McNeil. “Even in my twenties I preferred dreaming about love and painting it in my pictures.”
Chagall’s talent for drawing hardly cheered his poor and numerous family, which he, as the eldest of nine children, was expected to help support. His father, Khatskel-Mordechai Chagal, worked in a herring warehouse; his mother, Feiga- Ita Chernina, ran a small grocery store. Both nominally adhered to Hasidic Jewish religious beliefs, which forbade graphic representation of anything created by God. Thus Chagall grew up in a home devoid of images. Still, he pestered his mother until she took him to an art school run by a local portraitist. Chagall, in his late teens, was the only student who used the vivid color violet.Apious uncle refused to shake his hand after he began painting figures.
For all his subsequent pictorial reminiscing about Vitebsk, Chagall found it stifling and provincial—“a strange town, an unhappy town, a boring town,” he called it in his memoirs. In 1906, at age 19, he wangled a small sum of money from his father and left for St. Petersburg, where he enrolled in the drawing school of the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. But he hated classical art training. “I, poor country lad, was obliged to acquaint myself thoroughly with the wretched nostrils of Alexander of Macedonia or some other plaster imbecile,” he recalled. The meager money soon ran out, and although he made a few kopecks retouching photographs and painting signs, he sometimes collapsed from hunger. His world broadened in 1909 when he signed up for an art class in St. Petersburg taught by Leon Bakst, who, having been to Paris, carried an aura of sophistication. Bakst indulged Chagall’s expressive, unconventional approach to painting and dropped names, exotic to the young man’s ears, such as Manet, Cézanne and Matisse. He spoke of painting cubes and squares, of an artist who cut off his ear.
“Paris!” Chagall wrote in his autobiography. “No word sounded sweeter to me!” By 1911, at age 24, he was there, thanks to a stipend of 40 rubles a month from a supportive member of the Duma, Russia’s elective assembly, who had taken a liking to the young artist. When he arrived, he went directly to the Louvre to look at the famous works of art there. In time he found a room at an artists’ commune in a circular, three-story building near Montparnasse called La Ruche (The Beehive). He lived frugally. Often he’d cut a herring in half, the head for one day, the tail for the next. Friends who came to his door had to wait while he put on his clothes; he painted in the nude to avoid staining his only outfit. At La Ruche, Chagall rubbed shoulders with painters like Fernand Léger, Chaim Soutine, Amedeo Modigliani and Robert Delaunay. True to his nature as a storyteller, however, he seemed to have more in common with such writers as French poet Guillaume Apollinaire, who described Chagall’s work as “supernatural.” Another friend, Blaise Cendrars, a restless, knockabout writer, penned a short poem about Chagall: “Suddenly he paints / He grabs a church and paints with a church / He grabs a cow and paints with a cow.”
Many consider Chagall’s work during his four-year stay in Paris his most boldly creative. Reconnoitering the then-prevalent trends of Cubism and Fauvism, he absorbed aspects of each into his own work. There was his Cubist-influenced Temptation (Adam and Eve); the disconcerting Introduction, with a seven-fingered man holding his head under his arm; and the parti-colored Acrobat, showing Chagall’s fondness for circus scenes. At La Ruche he also painted his explosive Dedicated to My Fiancée, which he tossed off in a single night’s feverish work and later submitted to a major Paris exhibition. It took some artful persuasion on his part to convince the show’s organizers that the topsy-turvy mix of hands, legs and a leering bull’s head was not, as they contended, pornographic.
Returning to Vitebsk in 1914 with the intention of staying only briefly, Chagall was trapped by the outbreak of World War I. At least that meant spending time with his fiancée, Bella Rosenfeld, the beautiful, cultivated daughter of one of the town’s wealthiest families. Bella had won a gold medal as one of Russia’s top high-school students, had studied in Moscow and had ambitions to be an actress. But she had fallen for Chagall’s strange, almond-shaped eyes and often knocked on his window to bring him cakes and milk. “I had only to open the window of my room and blue air, love and flowers entered with her,” Chagall later wrote. Despite her family’s worries that she would starve as the wife of an artist, the pair married in 1915; Chagall was 28, Bella, 23. In his 1914- 18 Above the Town (one of his many paintings of flying lovers), he and Bella soar blissfully above Vitebsk.
In 1917 Chagall embraced the Bolshevik Revolution. He liked that the new regime gave Jews full citizenship and no longer required them to carry passports to leave their designated region. And he was pleased to be appointed commissar for art in Vitebsk, where he started an art school and brought in avant-garde teachers. But it soon became clear that the revolutionaries preferred abstract art and Socialist Realism— and how, they wondered, did the comrade’s blue cows and floating lovers support Marxism-Leninism? Giving up his job as commissar in 1920, Chagall moved to Moscow, where he painted decorative panels for the State Jewish Chamber Theater. But ultimately unhappy with Soviet life, he left for Berlin in 1922 and settled in Paris a year and a half later along with Bella and their 6-year-old daughter, Ida.
In Paris, a new door opened for Chagall when he met the influential art dealer Ambroise Vollard, who commissioned him to illustrate an edition of the poetic classic the Fables of La Fontaine. Chauvinistic French officials cried scandal over the choice of a Russian Jew, a mere “Vitebsk sign painter,” to illustrate a masterpiece of French letters. But that blew over, and Chagall went on to do a series of resonant illustrations of the Bible for Vollard.
Increasingly alarmed by Nazi persecution of the Jews, Chagall made a strong political statement on canvas in 1938 with his White Crucifixion. Then 51 and in his artistic prime, he por- trayed the crucified Christ, his loins covered with a prayer shawl, as a symbol of the suffering of all Jews. In the painting, a synagogue and houses are in flames, a fleeing Jew clutches a Torah to his breast, and emigrants try to escape in a rudimentary boat. Not long after, in June 1941, Chagall and his wife boarded a ship for the United States, settling in New York City. The six years Chagall spent in America were not his happiest. He never got used to the pace of New York life, never learned English. “It took me thirty years to learn bad French,” he said, “why should I try to learn English?” One of the things he did enjoy was strolling through Lower Manhattan, buying strudel and gefilte fish, and reading Yiddish newspapers. His palette during these years often darkened to a tragic tone, with depictions of a burning Vitebsk and fleeing rabbis. When Bella, his muse, confidante and best critic, died suddenly in 1944 of a viral infection at age 52, “everything turned black,” Chagall wrote.
After weeks of sitting in his apartment on Riverside Drive immersed in grief, tended to by his daughter, Ida, then 28 and married, he began to work again. Ida found a French-speaking English woman, Virginia McNeil, to be his housekeeper. A diplomat’s daughter, and bright, rebellious and cosmopolitan, McNeil had been born in Paris and raised in Bolivia and Cuba, but had recently fallen on hard times. She was married to John McNeil, a Scottish painter who suffered from depression, and she had a 5-year-old daughter, Jean, to support. She was 30 and Chagall 57 when they met, and before long the two were talking painting, then dining together. Afew months later Virginia left her husband and went with Chagall to live in High Falls, New York, a village in the Catskills. They bought a simple wooden house with an adjoining cottage for him to use as a studio.
Though Chagall would do several important public works in the United States—sets and costumes for a 1942 American Ballet Theatre production of Tchaikovsky’sAleko and a 1945 version of Stravinsky’s Firebird, and later large murals for Lincoln Center and stained-glass windows for the United Nations headquarters and the Art Institute of Chicago—he remained ambivalent about America. “I know I must live in France, but I don’t want to cut myself off from America,” he once said. “France is a picture already painted. America still has to be painted. Maybe that’s why I feel freer there. But when I work in America, it’s like shouting in a forest. There’s no echo.” In 1948 he returned to France with Virginia, their son, David, born in 1946, and Virginia’s daughter. They eventually settled in Provence, in the hilltop town of Vence. But Virginia chafed in her role, as she saw it, of “the wife of the Famous Artist, the charming hostess to Important People,” and abruptly left Chagall in 1951, taking the two children with her. Once again the resourceful Ida found her father a housekeeper— this time in the person of Valentina Brodsky, a 40- year-old Russian living in London. Chagall, then 65, and Vava, as she was known, soon married.
The new Mrs. Chagall managed her husband’s affairs with an iron hand. “She tended to cut him off from the world,” says David McNeil, 57, an author and songwriter who lives in Paris. “But he didn’t really mind because what he needed most was a manager to give him peace and quiet so he could get on with his work. I never saw him answer a telephone himself. After Vava took over, I don’t think he ever saw his bank statements and didn’t realize how wealthy he was. He taught me to visit the Louvre on Sunday, when it was free, and he always picked up all the sugar cubes on the table before leaving a restaurant.” McNeil and his half sister, Ida, who died in 1994 at age 78, gradually found themselves seeing less of their father. But to all appearances Chagall’s married life was a contented one, and images of Vava appear in many of his paintings.
In addition to canvases, Chagall produced lithographs, etchings, sculptures, ceramics, mosaics and tapestries. He also took on such demanding projects as designing stainedglass windows for the synagogue of the Hadassah-HebrewUniversityMedicalCenter in Jerusalem. His ceiling for the Paris Opéra, painted in 1963-64 and peopled with Chagall angels, lovers, animals and Parisian monuments, provided a dramatic contrast to the pompous, academic painting and decoration in the rest of the Opéra.
“He prepared his charcoal pencils, holding them in his hand like a little bouquet,” McNeil wrote of his father’s working methods in a memoir that was published in France last spring. “Then he would sit in a large straw chair and look at the blank canvas or cardboard or sheet of paper, waiting for the idea to come. Suddenly he would raise the charcoal with his thumb and, very fast, start tracing straight lines, ovals, lozenges, finding an aesthetic structure in the incoherence. Aclown would appear, a juggler, a horse, a violinist, spectators, as if by magic. When the outline was in place, he would back off and sit down, exhausted like a boxer at the end of a round.”
Some critics said he drew badly. “Of course I draw badly,” Chagall once said. “I like drawing badly.” Perhaps worse, from the critics’ point of view, he did not fit easily into the accepted canon of modernity. “Impressionism and Cubism are foreign to me,” he wrote. “Art seems to me to be above all a state of soul. . . . Let them eat their fill of their square pears on their triangular tables!”
Notes veteran art critic Pierre Schneider, “Chagall absorbed Cubism, Fauvism, Surrealism, Expressionism and other modern art trends incredibly fast when he was starting out. But he used them only to suit his own aesthetic purposes. That makes it hard for art critics and historians to label him. He can’t be pigeonholed.”
When he died in Saint Paul de Vence on March 28, 1985, at 97, Chagall was still working, still the avant-garde artist who refused to be modern. That was the way he said he wanted it: “To stay wild, untamed . . . to shout, weep, pray.”
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Karlie Kloss interview for British Vogue August 2019 by Elaine Welteroth (Part 2)
* If you have a fan accoun and repost it, please give credit.
The sun is finally up when we land in Los Angeles and discover, via text, that the Project Runway production meeting - the reason for our early cross-country flight - has been cancelled at the last minute. As I unleash a growl of annoyance, Karlie rests her hand on my shoulder and gives me a dose of the glass-half-full positivity that has defined her career: "Well, at least now maybe you can go get some sleep before the day..." I am reminded that I have never met a single soul more relentlessely cheerful than Kloss. It is not a persona: she is good to the core. "When you say that someone is nice it can sound pejorative but it's not," says her friend and mentor Diance von Furstenberg. "It is that honesty and eagerness that is resonating. Karlie is a good girl and a good role model for young girls."
Indeed, just ask around about her and you'll begin to wonder if she is the kindest person in fashion. But do not mistake her sweet nature, or her recent conversion to Judaism (the Kushner family are Modern Orthodox), for weakness. "Changing part of who you are for someone else can be seen as weak. But you know what? Actually, if you've been through that I've experienced, it requires you to be anything but weak," she says of her decision to convert. "It requires me to be stronger and self-loving and resilient. I really did not take this lightly. It wasn't enough to just love Josh and make this decision for him. This is my life and I am an independent, strong woman. It was only after many years of studying and talking with my family and friends and soul searching that I made the decision to fully embrace Judaism in my life and start planning for a future with the man I chose to marry."
The newly-weds recently put their immaculately decorated two-bedroom apartment in the East Village up for sale, looking for a new home in which to start their married life. Kloss first settled in New York five years ago, at the apex of her catwalk career, spending her hand-earned money on a place next to the Hudson river. At that point, she'd been working for five years, having been first scouted in St. Louis mall at the age of 13, when she was a coltish 5ft 8in and a burgeoning ballerina. Two years later, she landed her first New York Fashion Week show, with Calvin Klein, and her first editorial, an Arthur Elgort shoot with Teen Vogue. In the early days, Kloss travelled to jobs accompained by her physician father and her art direction mother, who protected her from the wilder aspects of the industry, but even as an adult, she has never been swept up in the party scene. Famously private, Kloss keeps a tight-knit circle of friends - albeit a high-profile one that includes Taylor Swift, Serena Williams and Derek Blasberg.
Once out of the airport, we part ways to shower. A few hours later we reunite on James Corden's set, where Kloss charms a rowdy audience with a little beauty trick she picked up backstage using a spoon to enhace Corden's lashes on live TV. Finally, after a scooter ride through Venice and a late dinner, jet lag strikes, and we decide to catch up on the phone a few days later, when she's managed to pull away from her hectic schedule for a meditative retreat with her husband in Wyoming.
In her Zen state, it's easy to see why she has so enthusiastically embraced the Jewish Shabbat, a day of rest that requires unplugging from work and completely disconnecting from the digiital world from sunset each Friday until nightfall on Saturday. She describes it as a "grounding force" in her otherwise non-stop lifestyle. "I think we all have a tendency to just keep going," she says on the phone. "Some people find grounding through meditation. Some find it through exercise. And to each their own, but for me, Shabbat has brought so much meaning into my life. It helps me reconnect to the actual world."
Kloss's studious approach to embracing Judaism reflects her insatiable curiosity. In 2015, long before the current wave of feminist hashtagivism, she enrolled in New York University's Gallatin School to study feminist theory. During this soul-searching period, she quit one of her most lucrative contracts, with the lingerie conglomerate Victoria's Secret. Bear in mind that this was before the rise of cancellation cuture, before walking away from a problematic company could earn a celebrity praise from the "woke" masses.
"The reason I decided to stop working with Victoria's secret was I didn't feel it was an image that was truly reflective of who I am and the kind of message I want to send to young women around the world about what it means to be beautiful," Karlie says. "I think that was a pivotal moment in me stepping into my power as a feminist, being able to make my own choices and my own narrative, whether through the companies I choose to work with, or through the image I put out to the world."
At the time, such a move may have felt risky and potentially damaging. But Kloss's star has only continued to soar - last year, Forbes named her the second most highly paid model in the world (Kendall Jenner pipped her to the top spot), and her fortune is estimated at $20 million. "In the modelling industry, every year is like a dog year," she says, smiling. "If you survive a year, it's like seven years in any other industry." If so, then she is a statesowman at just 26 - one whose enterprising embrace of new media put her on the front line of the digital revolution (she was one of the first major models with her own YouTube channel, in 2015) at a time when fashion was still resistan to change. I know because I was one of the magazine editors lurking around backstage the first season she showed up with a camera to capture her own getting-ready process in Hyperlapse to share with her growing following on social media. I found it innovative. Others found it bothersome, at best.
"I appreciate you using the word innovative. In the moment, I was a nuisance," Karlie laughs. "I got so many dirty looks at Paris Fashion Week. I remember getting yelled at and they would call my agency because I was Instagramming backstage." But she insists her rise hasn't been all selfies and sunshine. "I remember being 16 or 17 years old and afraid to say, "I don't want to wear this sheer top because I'm fully exposed and my mom is in the audience." I remember how it felt when I didn't say that I didn't want to do it, and how humilated I felt seeing those images and feeling sad that I didn't stand up for myself," she says. "Now I'm not trying to please anyone but myself."
The lesson she wants to share with other women? "Looking back at my late teens and early tweenties, I think I was fearful that I would lose a job or lose my position if I said I didn't want to do something. But I did not lose out on jobs, If anything, the more I exercised the power of my voice, the more I earned respect from my peers. And I earned more respect for myself. Only now do I have the confidence to stand tall - all 6ft 2in of me - and know the power of my voice," she says. "There are days when I wake up and I feel like I'm not this enough or too much that. We are all so critical of ourselves. But I love everything I do now, there is intention behind it."
13 notes
·
View notes
Photo
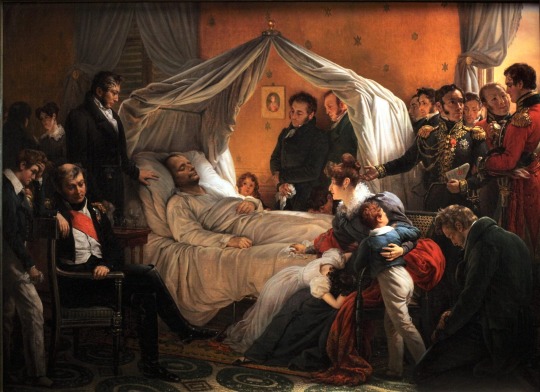
Vivant, il a manqué le monde ; mort, il le possède.
- François René de Chateaubriand (1768-1848), Vie de Napoléon, livres XIX à XXIV des Mémoires d’outre-tombe (posthume)
Of course we don’t have any photograph or film of Napoleon’s death on 5 May 1821 on Saint Hélène. But we do have the next best thing: a painting. Charles de Steuben depiction of Napoleon's deathbed and his faithful entourage that served as witnesses to his dying moments became the one of the most important paintings of the post-Napoleonic era but then faded from modern memory.
I first came across it by accident when I was in my teens at my Swiss boarding school. There were times I found myself with school friends going away on hiking trips around the high Alpine chain of the Allgäu Alps and we would drive through Lake Constance to get there, or we would hike around the Lake itself through the Bodensee-Rundwanderweg.
Perched high above Lake Constance and nestled in large parklands, stood Schloss Arenenberg which overlooks the lower part of Lake Constance. At first, it appears a relatively modest country house. But this was no usual pretty looking house. Arenenberg was owned by well-heeled families before it was sold to Hortense de Beauharnais, the adopted daughter and sister-in-law of the French Emperor himself, Napoleon Bonaparte. She had it rebuilt in the French Empire style and lived there from 1817 with her son Louis Napoleon, later Emperor Napoleon III, who is said to have spoken the Thurgau dialect in addition to French. This elegantly furnished castle then was once the residence of the last emperor of France.

The alterations made first by Queen Hortense and later by Empress Eugénie have been carefully preserved and the house still bears the marks of both women. Queen Hortense's drawing room is perfectly preserved and visitors can still admire her magnificent library (all marked with the Empress' cipher) containing over one thousand books. Likewise, in the room where the queen died, every object has been maintained in its original condition: pieces of furniture and personal belongings are gathered here to evoke her memory in a very touching manner. As for Empress Eugénie's rooms, they too have been very carefully preserved. Her private drawing room is a perfect illustration of the Second Empire style with sculptures by Carpeaux and portraits of the imperial family by Winterhalter.
After 1873, the Empress and the Imperial Prince brought the palace back to life by making regular summer visits, which they continued until 1878. However, on the tragic death of her son in 1879, Eugénie found it difficult to return to a place so full of painful memories. And so in 1906 she donated the estate to the canton of Thurgovie as a testimony of her gratitude for the region's faithful hospitality towards the Napoleon family. And in accordance with the Empress' wishes, the residence was turned into a museum devoted to Napoleon.
In what is now the Napoleonic Museum, the original furnishings have been preserved, and the palace gardens had been fully restored. This in itself might be worth a visit for the view over Lake Constance which is stunning. For Napoleonic era buffs though its the incredible art collection which is its real treasure. It houses an important art collection including works by the First-Empire artists Chinard Canova, Gros, Robert Lefèvre, Gérard, Isabey and Girodet-Trioson, and by the Second-Empire painters and sculptors Alfred de Dreux, Winterhalter, Carpeaux, Meissonier, Hébert, Flandrin, Detaille, Nieuwerkerke and Giraud.
But what caught my eye was this painting, ‘La Mort de Napoléon’ by Charles de Steuben. I didn’t know anything about it or the artist for that matter, but one of my more erudite school friends who, being French, was into Napoleonic stuff in a huge way, and she explained it all to me. Of course I knew a fair bit about Napoleon growing up because my grandfather and father, being military men themselves, were Napoleonic warfare buffs and it rubbed off onto me. I just knew about Napoleon the military genius. I never thought about him once he was beaten at Waterloo in 1815. So I never really engaged with Napoleon the man. And yet here I was staring at his last breath of mortality caught forever in time through art. Not for the first time I had mixed feelings about Napoleon Bonaparte, both the man and the myth (built up around him since his death).
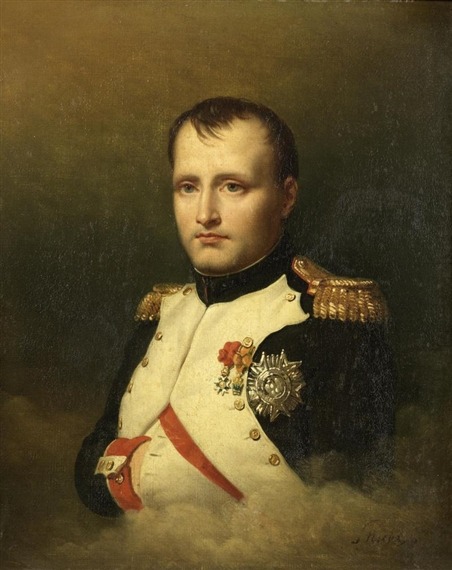

On 5 May, 1821, at 5.49pm in Longwood House on the remote island of St Helena, in the words of the famed French man of letters, François-René de Chateaubriand, ‘the mightiest breath of life which ever animated human clay�� came no more. To the British, Dutch, and Prussian coalition who had exiled Naopleon Bonaparte there in 1815, he was a despot, but to France, he was seen as a devotee of the Enlightenment.
In the decade following his demise, Napoleon’s image underwent a transformation in France. The monarchy had been restored, but by the late 1820s, it was growing unpopular. King Charles X was seen as a threat to the civil liberties established during the Napoleonic era. This mistrust revived Napoleon’s reputation and put him in a more heroic light.
Fascination with the French leader’s death led Charles de Steuben, a German-born Romantic painter living in Paris, to immortalise the momentous event. Steuben’s painting depicts the moment of Napoleon’s death and seeks to capture the sense of awe in the room at the death of a man whose legendary career had begun in the French Revolution. It was this, ultimate moment that Steuben wished to immortalise in a painting which has since become what could almost be described as the official version of the scene.
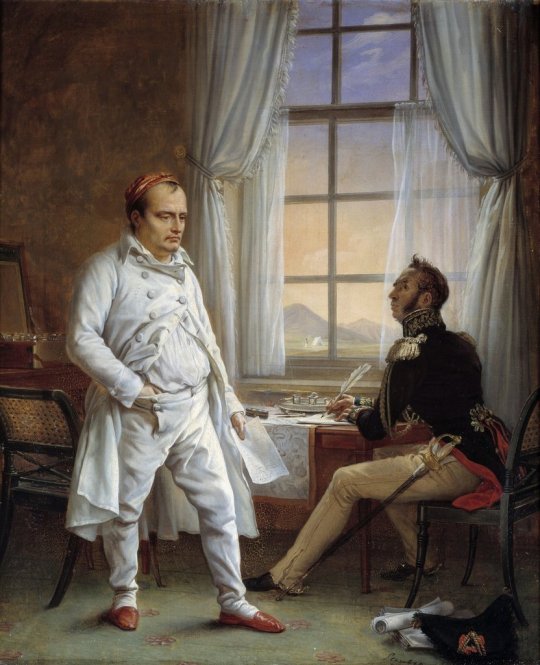

There is no question that Steuben’s painting became the most famous and most iconic depiction of Napoleon’s death in art history. In another painting, executed during the years 1825-1830, Steuben was to give a realistic view of the emperor dictating his memoirs to general Gourgaud. This same realism also pervades his version of Napoleon’s death, and it is totally unlike Horace Vernet’s, Le songe de Bertrand ou L’Apothéose de Napoléon (Bertrand’s Dream or the apotheosis of Napoleon) which, although painted in the same year, is an allegorical celebration of the emperor’s martyrdom and as such the first stone in the edifice of the Napoleonic legend.
And what a legend Napoleon’s life was turned into for time immemorial. Napoleon declared himself France’s First Consul in 1799 and then emperor in 1804. For the next decade, he led France against a series of European coalitions during the Napoleonic Wars and expanded his empire throughout much of continental Europe before his defeat in 1814. He was exiled to the Mediterranean island of Elba, but he escaped and briefly reasserted control over France before a crushing final defeat at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.
Napoleon’s military prowess earned him the fear of his enemies, but his civil reforms in France brought him the respect of his people. The Napoleonic Code, introduced in 1804, replaced the existing patchwork of French laws with a unified national system built on the principles of the Enlightenment: universal male suffrage, property rights, equality (for men), and religious freedom. Even in his final exile on St. Helena, Napoleon proved a magnetic presence. Passengers of ships docked to resupply would hurry to meet the great general. He developed strong personal bonds with the coterie who had accompanied him into exile. Although some speculate that he was murdered, most agree that Napoleon’s death in 1821, at the age of 51, was the result of stomach cancer.
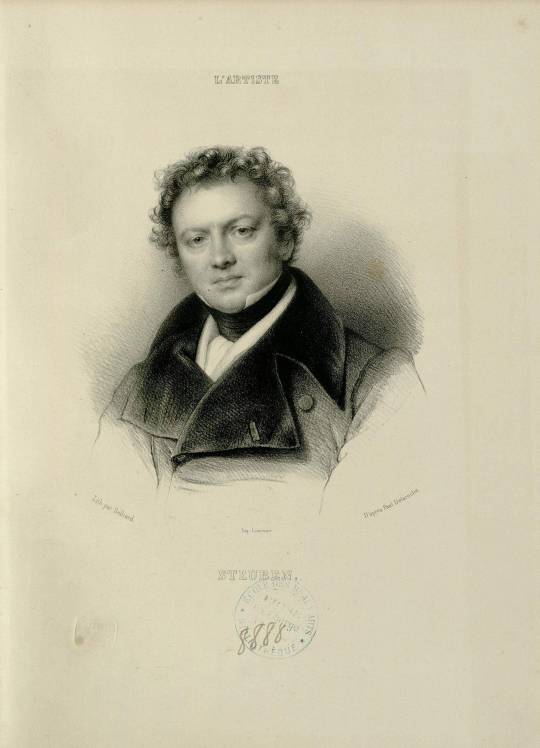

By contrast, Charles de Steuben was born in 1788, his youth and artistic training coinciding with Napoleon’s rise to power. He was the son of the Duke of Württemberg officer Carl Hans Ernst von Steuben. At the age of twelve he moved with his father, who entered Russian service as a captain, to Saint Petersburg, where he studied drawing at the Art Academy classes as a guest student. Thanks his father's social contacts in the court of the Tsar, in the summer of 1802 he accompanied the young Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna of Russia (1786–1859) and granddaughter of Frederick II Eugene, Duke of Württemberg, to the Thuringian cultural city of Weimar, where the Tsar's daughter two years later married Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (1783–1853). Steuben, then fourteen years old, was a Page at the ducal court, a position for which the career prospects would be in the military or administration. The poet Friedrich Schiller was a family friend who at once recognised De Steuben's artistic talent and instilled in him his political ideal of free self-determination regardless of courtly constraints.
At the behest of Pierre Fontaine in 1828 de Steuben painted La Clémence de Henri IV après la Bataille d'Ivry, depicting a victorious Henry IV of France at the Battle of Ivry. De Steuben's Bataille de Poitiers, en octobre 732, painted between 1834 and 1837, shows the triumphant Charles Martel at the Battle of Tours, also known as the Battle of Poitiers. He painted Jeanne la folle around the same time and he was commissioned by Louis Philippe to paint a series of portraits of past Kings of France.

Life in the French capital was a repeated source of internal conflict for Steuben. The allure of bohemian Paris and his military-dominated upbringing made him a wanderer between worlds. As an official commitment to his adopted country he became a French citizen in 1823. However, the irregularity of his income as a freelance artist was in contrast to his sense of duty and social responsibility. To secure his family financially, he took a job as an art teacher at École Polytechnique, where he briefly trained Gustave Courbet. In 1840 he was awarded a gold medal at the Salon de Paris for his highly acclaimed paintings.
The love of classical painting was a lifelong passion of Steuben. He was a close friend to Eugène Delacroix, the leader of the French Romantic school of painting, whom he portrayed several times. Steuben was also part of this artistic movement, which replaced classicism in French painting. "The painter of the Revolution," as Jacques-Louis David was called by his students, joined art with politics in his works. The subjects of his historical paintings supported historical change. He painted mainly in sharp colour contrasts, heavy solid contours and clear outlines. The severity of this style led many contemporary artists - including Prud'hon - to a romanticised counter movement. They preferred the shadowy softness and gentle colour gradations of Italian Renaissance painters such as Leonardo da Vinci and Antonio da Correggio, whose works they studied intensively. Steuben, who had begun his training with David, felt the school was becoming increasingly rigid and dogmatic. Critics praised his deliberate compositions, excellent brush stroke and impressive colour effects. But some of his critics felt that his pursuit of dramatic design of rich people also showed, at times, a pronounced tendency toward the histrionic.

The portrayal of key moments in Napoleon’s dramatic military career would feature among some of Steuben’s best known works. But it is this death scene that Steuben is most remembered for.
Using his high-level contacts among figures in Napoleon’s circle, Steuben interviewed and sketched many of the people who had been present when Napoleon died at Longwood House on St. Helena. He wanted to attempt o give the most accurate representation of the scene possible. Indeed, the painter interviewed the companions of Napoleon’s captivity on their return to France and had them pose for their portraits. Only the Abbé Vignali, captain Crokat and the doctor Arnott were painted from memory. The Grand maréchal Bertrand made sketches of the plan of the room, noting the positions of the different pieces of furniture and people in the room. All the protagonists within the painting brought together some of their souvenirs and in posing for the painter, each person can be seen contributing to a work of collective memory, very much with posterity in mind.
Painstakingly researched, Steuben painted a carefully composed scene of hushed grief. Notable among the figures are Gen. Henri Bertrand, who loyally followed Napoleon into exile; Bertrand’s wife, Fanny; and their children, of whom Napoleon had become very fond.
The best known version of “La Mort de Napoléon” was completed in 1828. French writer Stendhal considered it “a masterpiece of expression.” In 1830 the installation of a more liberal monarchy in France further boosted admiration of Napoleon, who suddenly became a wildly popular figure in theatre, art, and music. This fervour led to the diffusion of Steuben’s deathbed scene in the form of engravings throughout Europe in the 1830s. As Napoleon’s stock arose within French culture and arts, so did Steuben’s depiction of Napoleon’s death. It became a grandeur of vision that permeated Steuben’s masterpiece of historical reconstruction.
Initially forming part of the collection of the Colonel de Chambrure, the painting was put up for auction in Paris, on 9 March 1830, with other Napoleonic works, notably Horace Vernet’s Les Adieux de Fontainebleau (The Fontainebleau adieux) and Steuben’s Retour de l’île d’Elbe (The return from the island of Elba). The catalogue noted that the painting had already been viewed in the colonel’s collection by “three thousand connoisseurs” – which alone would have made it a success -, but its renown was to be further amplified by the production of the famous engraving. The diffusion of this engraving by Jean-Pierre-Marie Jazet (1830-1831, held at the Musée de Malmaison), reprinted and copied countless times throughout the 19th century, made the scene a classic in popular imagery, on a level of popularity with paintings such as Millet’s Angelus.
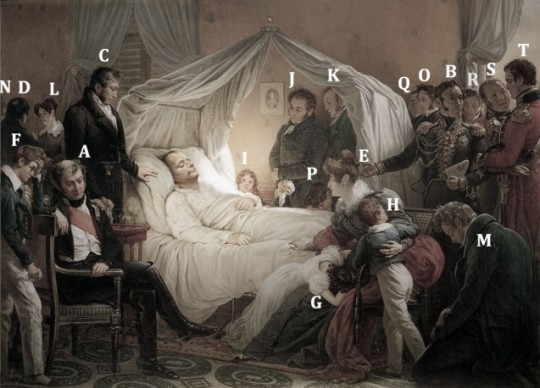
A / Grand Marshal Henri-Gatien Bertrand. Utterly loyal servant of Napoleon’s to the last. His memoirs of the exile on St Helena were not published until 1849. Only the year 1821 has ever been translated into English.
B / General Charles Tristan de Montholon. Courtier and companion of Napoleon’s exile. Montholon managed to ease Bertrand out and become Napoleon’s closest companion at the end, highly rewarded in Napoleon’s will, which Montholon helped write. Montholon’s untrustworthy memoirs were published in 1846/47.
C / Doctor Francesco Antommarchi. Corsican anatomy specialist. Sent by Napoleon’s mother from Rome to St Helena to be Napoleon’s personal physician on the expulsion of Barry O’Meara. Napoleon disliked and distrusted Antommarchi. Antommarchi’s untrustworthy memoirs were very influential and published in 1825.
D / Angelo Paolo Vignali, Abbé. Corsican assistant-chaplain, sent by Madame Mère from Rome to St Helena in 1819.
E / Countess Françoise Elisabeth “Fanny” Bertrand and her children: Napoléon (F), who carried the censer at Napoleon’s funeral; Hortense (G); Henry (H); and Arthur (I), youngest by six years of all the Bertrand children and born on the island. She was wife of the Grand Marshal, very unwilling participant in the exile on St Helena. Her relations with Napoleon were difficult since she refused to live at Longwood. She spoke fluent English. Was however very loyal to Napoleon.
J / Louis Marchand. Napoleon’s valet from 1814 on and one of his closest servants. As Napoleon noted in his will, “The service he [Marchand] rendered were those of a friend”.
K / “Ali”, Louis Étienne Saint-Denis. Known as “the Mamluk Ali”, one of Napoleon’s longest-serving and intimate servants; He became Librarian at Longwood and was an indefatigable copyist of imperial manuscripts.
L / Ali’s English (Catholic) wife, Mary ‘Betsy’ Hall. She was sent out from England by UK relatives of the Countess Bertrand to be governess/nursemaid to the Bertrand children. Married Ali aged 23 in October 1819.
M / Jean Abra(ha)m Noverraz. From the Vaud region in Switzerland. Very tall and imposing figure that Napoleon called his “Helvetic bear”. He was himself ill during Napoleon’s illness.
N / Noverraz’s wife, Joséphine née Brulé. They married in married in July 1819, and she was the Countess Montholon’s lady’s maid. Noverraz and Saint-Denis had a fist fight for the hand of Joséphine.
O / Jean Baptiste Alexandre Pierron. The cook, dessert specialist, long in Napoleon’s service and who had accompanied Napoleon to Elba.
P /Jacques Chandelier. Iincorrectly identified on the picture as Santini who had left the island in 1817. A cook, from the service of Pauline Bonaparte, Napoleon’s sister, who arrived on St Helena with the group from Rome in 1819.
Q /Jacques Coursot. Butler, from the service of Madame Mère, Napoleon’s mother, he arrived on St Helena with the group from Rome in 1819.
R / Doctor Francis Burton. Irish surgeon in the 66th regiment who had arrived on St Helena only on 31st March 1821. He is renowned for having made Napoleon’s death mask (with ensign John Ward and Antommarchi).
S/ Doctor Archibald Arnott. Surgeon in the 20th regiment. Brought in to tend to Napoleon in extremis on 1 April 1821.
T/ Captain William Crokat. A Scot, orderly officer at Longwood for less than a month, having replaced Engelbert Lutyens on 15 April. He received the honour of carrying the news of Napoleon’s death back to London and also the reward, namely, a promotion and £500, privileges of which Lutyens was deliberately deprived by the governor.
#charles de steuben#art#painting#napoleon#bonaparte#st helena#life#death#chateaubriand#french#france#emperor#artist#aesthetics#war#politics#society#culture#arts#personal
33 notes
·
View notes