#religio Romana
Text
Worshipping the gods doesn't have to be super serious devotion level worship all the time. I see some people worry about having "too many deities", but you don't have to have a close relationship with a deity to work with them or pray to them. In fact, it was more common in ancient times to NOT be devoted to any specific deity at all if you weren't some kind of religious figure, like a priest or priestess. Most of the time, there were certain deities that a person would favor, but their worship was not the in-depth type of devotion we see on witchblr a lot. In fact, ancient people sometimes went to a temple for a specific god once in their whole life to pray for something very specific and give offerings and then never needed that specific deity ever again. That's the very nature of these large pantheons. You will have favorites, but even then, you don't NEED to be devoted to them to ask for their help or pray to them.
I say this as mostly a Greco-Roman polytheist, but I'm sure it applies to other large pantheons as well. And, as always, certain gods may be an exception to the rule and require more, both historically and UPG-wise. But it is still a good general rule of thumb. There is no pressure to find a patron or become a devotee of any deity, unless you truly desire to do so.
785 notes
·
View notes
Text
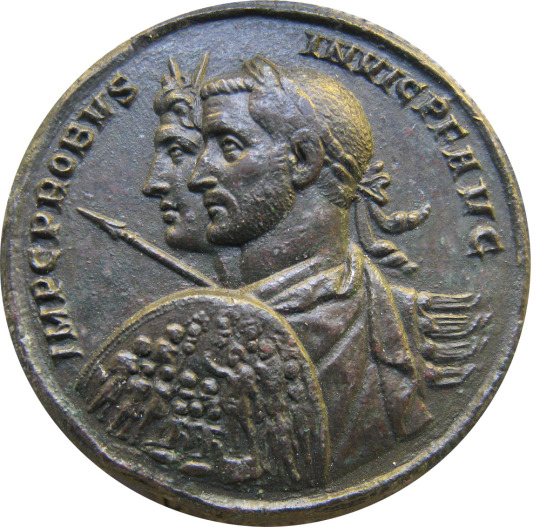

Coin minted ca. 280 CE by the Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius Probus (r. 276-282). Probus is shown in the company of Sol Invictus ("Unconquered Sun"), a late form of the solar deity whose worship had been promoted by Probus' predecessor Aurelian. The birthday of Sol Invictus (Dies Natalis Solis Invicti) was traditionally celebrated on Dec. 25. On this coin, Probus, who was constantly on campaign during his brief reign, is shown prepared for battle with shield and spear, alongside Sol Invictus, who wears his characteristic radiant crown. Now in the National Museum of Denmark, Copenhagen. Photo credit: ChrisO/Wikimedia Commons.
#classics#tagamemnon#Ancient Rome#Roman Empire#ancient history#Roman history#Probus#M. Aurelius Probus#Roman religion#Ancient Roman religion#religio Romana#Sol Invictus#art#art history#ancient art#Roman art#Ancient Roman art#Roman Imperial art#coins#ancient coins#Roman coins#Ancient Roman coins#numismatics#ancient numismatics#Roman numismatics#National Museum of Denmark
307 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Non-Pagans Need to Know About Fiction Featuring Pagan Gods
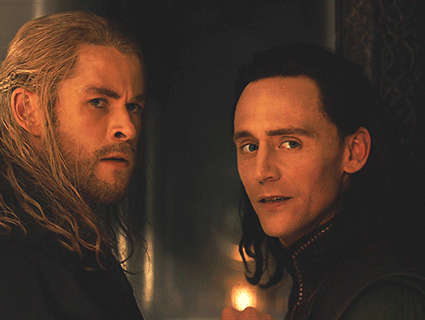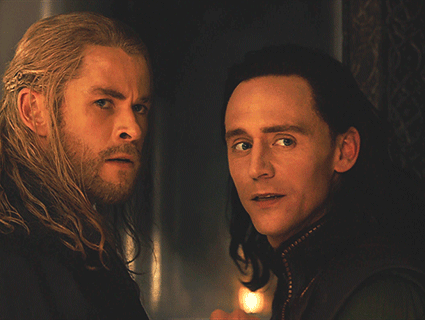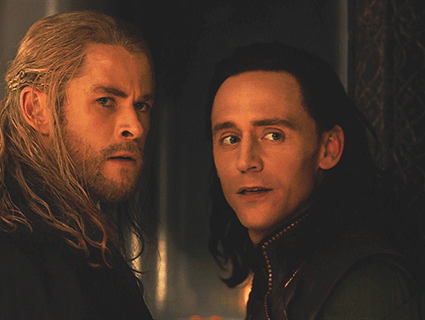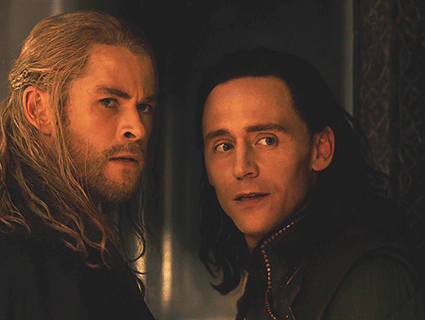
In light of Marvel's Loki show dropping a second season and a new Percy Jackson series on the horizon, I want to say some things about how fandom spaces can be respectful of real-life pagan religion.
Let's get one thing out of the way: literally no one is saying you can't enjoy fiction that uses pagan gods and heroes as characters. No one is saying, "Stop writing stories about our gods." In fact, many ancient cultures wrote fiction about their gods -- look at Greek theater or the Norse Eddas. The act of writing fiction about the gods is not offensive in itself.
But please remember that this is someone's religion.
The gods are not "just archetypes." Their myths are not "just stories." Their personalities are not a matter of artistic interpretation. For many pagans, the gods are very much real in a literal sense. I don't think Thor is a metaphor or a symbol -- for me, Thor is a real, autonomous spiritual being who exists outside of human perceptions of him, and who I have chosen to build a relationship with. Even if you are a hardcore atheist, I would hope you could at least be respectful of the fact that, to many modern pagans, the gods are both very real and very important.
When authors are not respectful of this fact, they reduce the gods, these very real objects of worship, to fictional characters. And here's the thing about fictional characters: they are fundamentally tools for authors to use to draw a desired emotional response from an audience.
Dracula's personality and behavior is wildly different depending on who is writing him, because different authors use Dracula to create different reactions in their audiences. In the 1931 film starring Bela Lugosi, he's equal parts alluring and disturbing, a symbol of America's mixed desire and disdain for foreigners. In Nosferatu, he's more strictly frightening and disgusting. In Francis Ford Coppola's movie, he's a tragic, romantic figure clinging to the last scraps of his humanity. In Netflix's Castlevania, he's an incredibly powerful being who has grown bitter and apathetic in his immortality. All of this is Dracula, and all of it is fine, because Dracula is not and never has been a central figure in anyone's religion.
Let's take a look at what happens when authors give this same treatment to real gods:
In Hellenic polytheism, Apollo is one of the most beloved gods, both historically and today. Apollo loves humanity, and humanity loves him back. He is the god of sunlight and of medicine, but also of poetry and song. He is one of humanity's most consistent defenders when one of the other gods gets wrathful. And while he does have dangerous or wrathful aspects of his own (he's also the god of disease, after all), he's also kind and soft with humanity in a way other gods often aren't, at least in some historic sources.
In the Lore Olympus comic series, Apollo is a villain. He's characterized as an abuser, a manipulator, and a violent man child. LO!Apollo is downright hateful, because the author wants us to hate him. Lore Olympus is a retelling of a myth about an abduction and forced marriage. Lore Olympus is also a romance. In order to get the audience to sympathize with Hades and root for his relationship with Persephone, Rachel Smythe needed to make someone else the villain. Apollo is the most obvious and extreme character assassination in Smythe's work, but several other gods (notably Demeter) also get the asshole makeover to tell the story Smythe wants to tell.
Here's where this becomes a problem: Hellenic polytheism is a fairly small religious community, while Lore Olympus is a massively popular webtoon with 1.3 billion views as of August 2023, print books available from major retailers, a TV adaptation in the works, and a very active online fandom. Rachel Smythe currently has a MUCH bigger platform than any Hellenic polytheism practitioner. Smythe and other authors are shaping how modern culture views the Hellenic gods, and that has a very real impact on their worshipers.
This means "Apollo is an abusive asshole" is becoming a popular take online, and is even creeping into pagan communities. I've personally seen people be harassed for worshiping Apollo because of it. I've seen new pagans and pagan-curious folks who totally misunderstand the roles Apollo, Hades, and Persephone play in the Hellenic pantheon because of Lore Olympus and other modern works of fiction.
There are tons of other examples of this in modern pop culture, but I'll just rattle off a few of the ones that annoy me most: Rick Riordan depicting Ares/Mars as a brutish asshole hyped up on toxic masculinity; Rick Riordan depicting Athena as a mother goddess; Marvel depicting Thor as a dumb jock; Marvel depicting Odin as a cold, uncaring father; DC depicting Ares as purely evil; whatever the fuck the Vikings TV show was trying to do with seidr; the list goes on.
All of these are examples of religious appropriation. Religious appropriation is when sacred symbols are taken out of their original religious context by outsiders, so that the original meaning is lost or changed. It requires a power imbalance -- the person taking the symbols is usually part of a dominant religious culture. In many cases, the person doing the appropriation has a much bigger platform than anyone who has the knowledge to correct them.
When Rick Rioridan or Rachel Smythe totally mischaracterizes a Greek god to tell a story, and then actual Hellenic pagans get harassed for worshiping that god, that's religious appropriation.
Religious appropriation is a real issue. This isn't just pagans being sensitive. To use an extreme example: Richard Wagner and other German Romantic authors in the 19th century used the Norse gods and other Germanic deities as symbols in their work, which was a major influence on Nazi philosophy. Without Wagner, the Nazis would not have latched onto the Norse gods as symbols of their white supremacist agenda. To this day, there are white supremacist groups who claim to worship our gods or who use our religious imagery in their hate movement. We are still reckoning with the misinterpretation of our gods popularized by Wagner and other German Romantics almost 200 years ago.
Again, no one is saying you can't enjoy fiction based on pagan mythology. But there are a few things you can do to help prevent religious appropriation in fandom spaces:
Above all else, be mindful that while this may just be a story to you, it is someone's religion.
Recognize that enjoying fiction based on our gods does not mean you know our gods. You know fictional characters with the same names as our gods, who may or may not be accurate to real-life worship.
Do not argue with or try to correct pagans when we talk about our experience of our gods.
Don't invalidate or belittle pagan worship. Again, this mostly comes down to recognizing that our religion is totally separate from your fandom. We aren't LARPing or playing pretend. Our sacred traditions are real and valid.
If you see other people in your fandom engaging in religious appropriation, point out what they are doing and why it isn't okay.
Please tag your fandom content appropriately on social media. Always tag the show, movie, book, etc. that a post is about in addition to other relevant tags. This allows pagans to block these fandom tags if we don't want to see them and prevents fandom content showing up in religious tags.
For example, if I'm posting about Athena from the Percy Jackson books, I would tag the post #athena #athenapjo #percyjackson #pjo. You get the idea.
And if fiction sparks your interest and you want to learn more about the actual worship of the gods, you can always ask! Most pagans love talking about our gods and trading book recs.
If you are writing fiction based on real mythology, talk to people who worship those gods. Ask them what a respectful portrayal would look like. If possible, include a note in your finished work reminding audiences that it is a work of fiction and not meant to accurately portray these gods.
#btw hades is also not a villain in helpol#this post is just mostly discussing how lo villiainizes apollo#shoutout to my roman pagan husband for proofreading and offering feedback#this post is Approved By The Council#psa#long post#paganism#pagan#paganblr#heathenry#norse heathen#norse paganism#inclusive heathenry#hellenic polytheism#helpol#religio romana#roman polytheism#roman pagan#marvel#mcu#loki series#loki season 2#percy jackson#percy jackson and the olympians#pjo#lore olympus#religious appropriation#my writing#white supremacy mention#white supremacy tw
306 notes
·
View notes
Text
Please reblog for a bigger sample size! 🧡
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
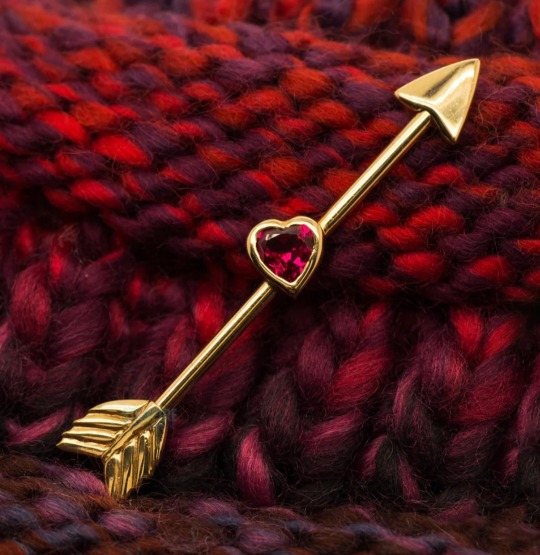
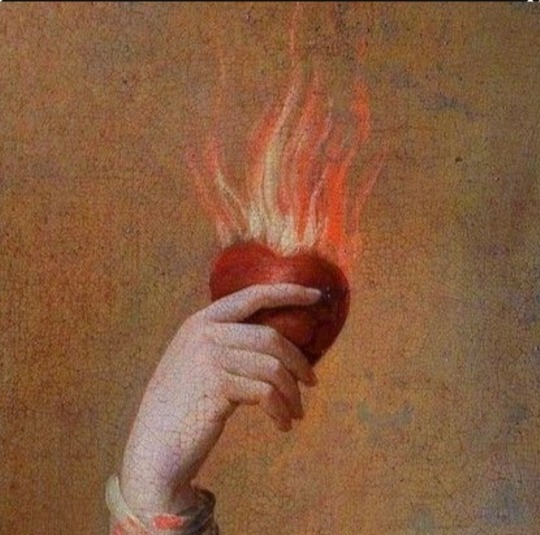
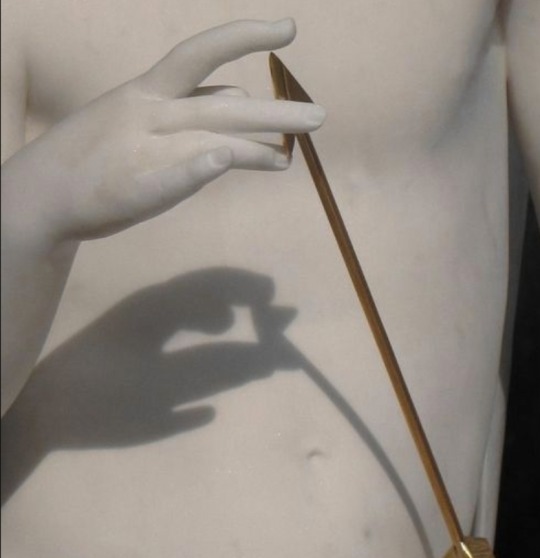








Eros: Greek God of love, lust, sex, desire, and procreation.
#pagan#deities#polytheism#polytheist#deity#paganism#greek god eros#god eros#eros god#hellenic polytheism#hellenic polythiest#hellenic deities#hellenism#hellenic pagan#religio romana#cupid#hellenic gods#deity moodboard#moodboard#devotional moodboard#god of love
199 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's kind of mind boggling to me how every time I see book recommendations for Hellenic or Roman polytheist I never see On the gods and the world by Sallust.
It may not teach practical ways of worship but it answers a lot of philosophical questions about the gods that I think we, as pagans, have at some point asked ourselves. Seriously, some of the points made by Reddit ath3ists are answered in this essay, like they're 2000 years behind.
It's very short (like 50 pages long) so if you can buy it, pirate it or get it from your local library I'd highly recommend it. Here's an audiobook in case you prefer that.
#paganblr#paganism#polytheist#helpol#hellenic polytheism#witchblr#roman paganism#cultus deorum#religio romana#pagan tips
138 notes
·
View notes
Text





Lararium and ritual by r.spadini on Instagram
#religio romana#roman paganism#roman polytheism#household shrine#household altars and shrines#religious shrines#lararium#southern european religions
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hypnos-Somnus is the silence and calmness of the night. He is the warmth of a blanket and coldness of other side of the pillow. He is tiredness, that comes at the end of the day and energy or comfortable laziness in the morning. He is pastel soothing blue, purple and white. He is slow and peaceful lo-fi. He is the blackness of the sleep or vivid visions of the dreams. He is red fields of blood on steppes or single little drops here and there on grass in form of wild poppies. He is this little crust of poppy's seeds in the bun filled with them. He is the certainty of the next day. He is the little white feathers that appear in every part of the city. He is the warmth of sweaters and pajamas. He is the smell of fresh cleaned sheets and much, much more.
He is so many than just sleep. And once you see it, it's hard to stop again. I hope that this year will be calmer, so I could give Him what He truly deserves.
But now, thank you, kind Hypnos-Somnus, that in my crisis days, where I couldn't get enough sleep, you helped me get some rest. That my bed was a safe space, that my pillows were soft. Thank you, that I didn't have any nightmares or stress dreams for a long time.
I thank you and honour you, Hypnos-Somnus, gentle God of sleep!
#Quday :: Hypnos-Somnus :: ⌞🌠☕️🖤⌝#A piece of my mind :: ⌞☔🍨🩷⌝#Hypnos deity#Hypnos worship#Hypnos devotee#Somnus deity#Somnus worship#Somnus devotee#Hellenic polytheism#Helpol#Religio romana
121 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok hear me out...
Aphrodite and Venus as goddesses of astronomy would make a lot of sense in the modern day.
-The planet Venus is theirs
-Venus is either the morning or evening star (we already have 2 gods for that but still)
-They are associated with Eos/Aurora
-✨️APHRODITE OURANIA✨️
-The most popular version of their birth is the castration of Ouranos (the sky)
-Some part of their cult (mainly that of Aphrodite Ourania) got mixed with the virgin Mary
-The sea literally touches the sky and (in my experience) is one of the best places to stargaze.
-Also sailors depended on the stars to navigate
-She helps sailors at sea (related to the last point)
I don't have any more ideas but IT MAKES SO MUCH SENSE TO ME
#aphrodite goddess#aphrodite#aphrodite worship#venus#venus goddess#helpol#religio romana#paganism#another wild strech from me
27 notes
·
View notes
Text




Saturnalia is coming on soon, so I'd like to speak some more on this peculiar, interesting festive occasion.
It is an Ancient Roman holiday of abundance, feasting, and celebration of harvest, which was supposed to be over by the time the festivities began. After the farmers gathered the crops, they'd celebrate Saturn, God of seed and sowing, for His generosity and richness of the harvest.
The festival, known for its abundant feasts and the peculiar tradition of switching roles of masters and servants, has a complicated history.



The origins of Saturnalia are much of a mystery as the festival appears to be so Ancient that Roman sources mark it to be older than the city of Rome itself. Saturnalia existed in both Greek and Roman tradition, though it corresponded to the Greek Kronia, which was a similar, but not an identical festival.
Sources speak on different possible origins of the holiday: some mention the temple of Saturn, the largest of the recorded by the pontiffs, being erected in Rome, and thus starting the tradition; whereas others speak on the festival being brought from Greece. Either way, this Ancient tradition is associated with the liberation of the God of harvest.
Saturnalia was officially celebrated on December 17 and, in Cicero's ties, lasted for a week (inclusively), until December 23. The length of the celebration varied depending on the time period as Augustus shortened it to three days only for the sake of letting the civil courts stay closed for less, while Caligula extended the celebration to five days. The original festival, according to Macrobius, appeared to have lasted for only a day; fourteen days before the Kalends of January. The Julian reform shifted the date to the 17th, thus making it into sixteen days before the Kalends. Some believe that the timing for Saturnalia was symbolic, as next followed Winter Solstice, or symbolic Death of the Sun and Birth of the new one.
Regardless, even after the limiting of the festival, Saturnalia seemed to still be celebrated for a full week with the last day being dedicated to Sigillaria, named so after sigillaria, the small earthenware figurines sold in the cities on that day. The original day of celebration was in turn given to Ops, the consort of Saturn and the Deity of abundance and the fruits of the Earth. The celebration in Her honor was called Opalia, and two festivals tended to mix together with Ops' worshippers sitting down during prayer to touch Earth, mother of all.



Saturnalia involved various activities akin to feasts, parties, gift-giving, and ritual rites. The party traditionally started with the guests exclaiming, i Saturnalia, believed to be a shortening from ego tibi optimis Saturnalia auspico, or 'i wish you a happy Saturnalia'.
It is believed to be one of the most delightful periods of the year and one of the most beloved Roman festivals. People went into the streets celebrating, marching, setting up shows and street markets. People of all backgrounds could participate in it.
Among the general aspects of Saturnalia were activities such as gift giving, as people exchanged things such as candles, walnuts, dates, and honey. Masters served slaves, whereas slaves became free men as in memory of Saturn's reign when slavery did not exist. Servants walked the streets masked, in Frigio hats, or hats of liberation. The Saturnals were also celebrated in the army; the party was called the Saturnalicium castrense, when the low-rank soldiers sat next to the generals as equals and toasted together. Dice games and public gambling were allowed, but became prohibited again once Saturnalia ended. Mourning was abolished, while courts and schools were closed; starting war or enforce capital punishment was strictly prohibited. The festivities took such a great degree of chaos that some authors of the time report moving to remote suburban houses for the week of the Saturnalia to avoid the noise.
Saturn was one of the few celebrated Deities, as, in Roman times, Dis Pater and Proserpina were also believed to join the festive processions in winter time. They were to be appeased by gifts, festivities, and food; which was believed to make Them return to the Underworld where, as the Gods of subsoil, They would protect the crops and make them sprout in spring.
The official part of the feast consisted of a solemn sacrifice in the temple attended with bare head and during which the wool bandages that wrapped the feet of Saturn's simulacrum melted. A public banquet followed where all the guests exchanged toasts and wishes.
Further celebratory activities were split into days, and precise rites were done on each day of the festival.


At the beginning of Saturnalia, a rite of lectisternium was held. During the ritual, statues of Jupiter and 12 Olympians were seated in a dining position upon a special bed, or couch, and offered food, prayers, and gifts. They were spoken to with due respect and asked for protection of Rome and its people as well as for help with current affairs. After the first step, a procession was sent off to the Temple of Saturn and animal sacrifices were made at the site.
A banquet with cheeses, focaccia, olives, and wine was held, to which everyone was invited - all provided by the state.
Starting day one, no-work days began, and gifts as well as greeting cards were exchanged between the citizens. Myrtle, laurel, and ivy - symbolic elements of the Saturna - were given; the trees were respectively sacred to Venus, Apollo, and Bacchus. The first day was signified by banquets, during which the Princeps of Saturnalia, the ruler of the festivities, Princeps Saturnalicius, was elected. During the first day of the festival, people changed from togas to synthesis and pileus; a casual home robe and a cap like headdress.


On the second day of the festival, Rome was still abundant with noise and feasts, to which everyone invited everyone. Stalls and juggles were in the streets alongside dancers and musicians. Celebrations were accompanied by the feast in honor of Epona, Celtic Goddess of horses, much adorned by the equites, whose importance during Saturnalia was due to Her connection to fertility and richness of feasts. The second day of Saturnalia, the 18th of December, marked the beginning of the triad of days of Mercatus, much similar to today's city fairs.


The third day of Saturnalia was the initial day of the celebration (before the reform of the calendar) and was devoted to the Goddess Ops, Deity of Sabine origin introduced to Rome under Titus Tatius. She was praised as the Deity of abundance, protector of rich harvest, giver of fruits of the Earth, and respected consort of the God Saturn. Her Temple at the Capitol hill was erected on that day, and thus received attention and became a center of worship of the Goddess as it was the anniversary of its establishment. Ops was prayed to and asked for blessings of harvest.


The fourth day of the Saturnian festivals, December 20, was dedicated to gift-giving and worship of the Lares, house guardian Deities of Ancient Rome. Terracotta figurines, sigillaria, were made out of paste, wax, or terracotta. Bronze statues were a rarity as bronze was expensive, while sigillaria made out of sweet dough were meant for the children. These statuettes were exchanged as gifts between the citizens as well as given to Saturn as offerings. He was seen as the God of time, and, thus, Death, and the figurines were to be given to Him as ways to redirect Death from coming for the giver, instead letting the figurine take it.


On the fifth day, Rome was filled with visitors from all across the Empire who came to see the city at its peak, blooming with festivals and street activities such as shops, shows, and a multitude of banquet spots. Fod, souvenirs, sigillaria (sigillaria<sigillum<signum+illum), clothes, ornaments and jewels were sold on the street. Artisans from all over the Empire offered goods made of leather, wood, terracotta, bronze, brass, silver and a special alloy of gold and silver, electrum.


On day six of the festivities Rome welcomed dancers, singers, and other performers from across the Empire who came to join the celebration as the entirety of the Empire was involved in it. Gift-exchanging with the guests, also known as xenia, was performed. Marcus Valerius Martialis wrote Xenia and Apophoreta for the Saturnalia, both of which were published in December and intended to accompany the "guest gifts" that were given at that time of year.


On the seventh - and last - day of the celebrations the Gods were thanked for everything given. The streets were full of torches and braziers, and the day passed between banquets and the baths decorated with ribbons and garlands for the occasion. Aulus Gellius relates that he and his Roman compatriots would gather at the baths in Athens, where they were studying, and pose difficult questions to one another on the ancient poets, a crown of laurel being dedicated to Saturn if no-one could answer them.
Saturnalia ended at sunset.
Sources in pinned.
#𓆩𝕍𓆪 ˣ 𝐅𝖊𝖗𝖎𝖆#hellenism#theoi#helpol#hellenic polytheism#roman polytheism#roman festival#religio romana#saturnalia#io saturnalia#witchblr
205 notes
·
View notes
Text
you do not have to have daily rituals and serious/taxing devotions to the gods, sometimes a gesture/thought of appreciation is enough. nor do you have to have long-lasting-in-depth relationships with deities, sometimes a small offering and prayer is enough. there's no such thing as "too many deities" when it comes to worship, the limit is what you can personally handle. worship is a unique experience among the individual. and the gods are meant to be experienced.
#templum :: 🪔#pagan community#pagan#paganblr#paganism#pagans of tumblr#roman pagan#spiritual#spirituality#religion#polytheism#roman polytheism#religio romana#roman pantheon#roman paganism#deity worship#worship#deity work
80 notes
·
View notes
Text

The god Hesperus sits on a throne and holds a tall torch. Around him are Apollo-Helios (identifiable by his halo), Aphrodite (crowned), and other deities. Wall painting in the Fourth Style from the exedra of the House of M. Gavius Rufus (VII.2.16) at Pompeii; now in the National Archaeological Museum, Naples. Photo credit: ArchaiOptix/Wikimedia Commons.
#classics#tagamemnon#Ancient Rome#Roman Empire#Pompeii#Greek religion#Ancient Greek religion#Hellenic polytheism#Roman religion#Ancient Roman religion#religio Romana#Dionysus#Dionysos#Helios#Aphrodite#art#art history#ancient art#Roman art#Ancient Roman art#Roman Imperial art#wall painting#fresco#Fourth Style#NAM Naples
522 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pagan Wedding Flowers (and other plants) Cheat Sheet
Flowers have been associated with weddings for almost as long as humans have been getting married. In fact, the use of flowers in ritual may actually be older than humans! Neanderthal graves in Iraq suggest that Neanderthals buried their dead with flowers. There are mentions of flowers in our earliest recorded accounts of weddings, such as in Egypt, Greece, and Rome.
Historically, couples would have used whatever flowers were available to them. While some cultures had flowers they preferred for weddings because of their symbolism, couples would have been limited by what grew in their area and by what was in bloom at the time of their ceremony. To be truly as historically accurate as possible, consider using flowers you grew or foraged yourself. Bonus points for native blooms!
For those who aren't into growing or gathering your own wedding flowers, modern florists and greenhouses allow us to choose from a wide range of flowers, many of which aren't native to our homes. This makes it much easier to choose flowers based on their symbolism, history, or cultural meaning.
Historic Wedding Flowers + Plants
Roses have been the flower of choice for Western weddings pretty much forever, and with good reason. The rose is associated with several ancient goddesses of sex, fertility, and/or romance, such as Inanna, Ishtar, Aphrodite, and Venus. (Later, medieval Christians would also associate this flower with the Virgin Mary.) Including the goddess's flowers in a wedding may have been a way of invoking her blessing on the union. Sappho called rose "Queen of the Flowers."
Roses are held in a high regard in pretty much every culture with access to them. They're strongly associated not only with love, but also with beauty, wholeness, blessings, and even spirituality.
Rose was included in wedding celebrations in Ancient Hellos (Greece) and Rome. It is associated with the planet Venus and the water element.
Wheat was also a popular inclusion in weddings in ancient Greece and Rome. Hellenic brides would carry sheaths of wheat or another grain to invoke fertility and good fortune. Wheat was strongly associated with agrarian goddesses like Demeter, Persephone, Ceres, and Proserpina. Carrying wheat may also have been a way of expressing a wish for the marriage to produce many children. Pliny the Elder explicitly says in his Natural History that wheat was included in weddings to honor Ceres.
In modern occult systems, wheat is associated with fertility, the conception of children, and wealth. It is associated with the planet Venus and the element of earth.
Olive branches also featured in Hellenic weddings. Olive was an important crop in the ancient Mediterranean, and olive branches were a symbol of peace and friendship. Olive was also used in the victors' crowns in the Olympic Games. In Athens, the olive tree was a symbol of Athena. It was also carried by worshipers of Apollo when they visited the Oracle at Delphi. Olive was also important to the Romans, who associated it with Mars in his aspect as a protector of peace.
In modern magic traditions, olive is associated with beauty, healing, stamina, wealth, fertility, protection and of course, peace. It is associated with the sun and the fire element.
Orange blossoms were included in Hellenic weddings as a sign of happiness. These strongly scented white flowers also sometimes appeared in Roman weddings. Thousands of years later, Queen Victoria wore a crown of orange blossoms at her wedding, but for her they were a symbol of chastity.
In modern systems, orange is associated with joy, partnership, sweetness, and good luck. It is associated with the sun and the fire element.
Hawthorn appeared in weddings in ancient Rome. Pliny the Elder said that Roman bridal processions included a hawthorn torch dedicated to the goddess Ceres. In Rome, hawthorn was more generally associated with love and good luck.
In Celtic cultures, especially Ireland, hawthorn was believed to be a fairy tree. For this reason, cutting a hawthorn tree or bringing hawthorn branches inside was considered bad luck.
The blooming of hawthorn trees was used to determine the date of Bealtaine, and hawthorn boughs were often decorated with flowers, ribbons, and egg shells to make a May bush, which was placed by the front door for good luck. In Britain, hawthorn wood was used to carve maypoles. Hawthorn flowers may be especially appropriate for a May wedding or handfasting.
In modern occultism, hawthorn is associated with protection, healing (especially healing the heart), romantic love, fertility, granting wishes, and happiness. It is still strongly associated with weddings and marriage. It is associated with the planet Mars and the fire element.
Lotus may have featured in ancient Kemetic (Egyptian) weddings. The lotus was an important symbol in Kemetic religion, and was associated with the sun, rebirth, and the creation of the world. Lotus flowers featured in festivals to honor Hapi, the androgynous god of the Nile. The lotus is used in art to represent Upper Egypt. An Egyptian poem from 1100 BCE connects the lotus to marriage.
Lotus flowers were also popular in ancient Chinese weddings, and they're still used by some Chinese couples today. In Chinese culture, lotus represents purity, honor, and long life.
In modern traditions, lotus is associated with protection, spirituality, and blessings. It is associated with the moon and the water element.
Yellow flowers were used in pre-Christian Ireland for blessings and protection. The exact flower used for these rituals is not specified, so it seems like the color was what mattered. Modern pagans looking to carry on this tradition have lots of yellow flowers to choose from. Some popular choices include yellow roses (see above), yellow amaryllis (associated with creativity, playfulness, and joy), chrysanthemum (associated with long life, optimism, and protection), marigold (associated with happiness, rebirth, and vitality), and/or daffodils (associated with love, fertility, and luck).
Modern Wedding Flowers
We've gone over some of the flowers that were popular in historic pagan weddings, but it's also easy to pagan-ify the flowers that are most popular in modern weddings. Here's a quick rundown of some popular wedding blooms and their neopagan and occult symbolism:
Peony is associated with purification, healing, prosperity, and success. In ancient Rome, peony was believed to be sacred to Mars. It is associated with the sun and the fire element.
Dahlia is associated with mystery, occult wisdom, and transformation. It is associated with the moon and the water element.
Lilac is associated with balance, peace, romance, protection from evil, and attracting friendly spirits. It is associated with Venus and the water element.
Sweet Pea is associated with comfort, charm, and sweetness. It is associated with Venus and the water element.
Hydrangea is associated with healthy boundaries, breaking negative patterns, hex breaking, and protection. It is associated with water and with both the moon and Neptune.
Tulip is associated with beauty, desire, gratitude, love, prosperity, and simplicity. It is associated with Venus and the earth element.
Orchid is associated with beauty, elegance, sexuality, fertility, and romance. It is associated with Venus and the water element.
Lily is associated with spirituality, beauty, harmony, and protection from the evil eye. It is associated with Venus and the water element.
Carnation is associated with beauty, love, rebirth, strength, and healing. Carnations are associated with same-gender love and especially love between men because of Oscar Wilde's fondness for them. They are associated with the sun and the fire element.
Gardenia is associated with love, peace, healing, and spirituality. It is associated with the moon and the water element.
Resources:
"New Neanderthal remains associated with the ‘flower burial’ at Shanidar Cave," Cambridge University Press
"History of Wedding Flowers" by Benna Crawford
The Roman Wedding by Karen K. Hersch
"The Olive in the Ancient Mediterranean" by Mark Cartwright
"The History, Mythology, and Offerings of Hawthorn" by Meghan Pivarnik
Where the Hawthorn Grows by Morgan Daimler
Temple of the Cosmos by Jeremy Naydler
The Magic of Flowers by Tess Whitehurst
The Magic of Trees by Tess Whitehurst (see my disclaimer about Whitehurst's books, but these are some of her better ones)
Cunningham's Encyclopedia of Magical Herbs by Scott Cunningham
#the great handfasting project#handfasting#pagan wedding#wedding magic#queer wedding#pagan#paganism#pagan witch#hellenic polytheism#hellenism#religio romana#cultus deorum#roman polytheism#kemetic paganism#kemetic polytheism#irish paganism#irish pagan#irish folklore#wicca#wiccan#flowers#flower magic#correspondences#love magic#love spell#green witchcraft#green witch#witch#witchblr#witchcraft
502 notes
·
View notes
Text
(For Venus ⬇️) (For Apollo⬇️)


(Black candle for Queen Persephone. Black Pomegranate candle for Queen Hera. ⬇️)

Hi! I just wanted to show some of my shrines I’ve dedicated to my deities! (Hestia has her own shelf, but I need to clean it [and I also wanna remake it] so I won’t show it yet :])
#girlblogging#hellenic polytheism#hellenism#hellenismos#helpol#pagan#witchblr#witchcraft#goddess venus#goddess hera#goddess hestia#goddess persephone#god apollo#religio romana#roman polytheism
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Digital Altar: Eros ❤️

#pagan#deities#polytheism#polytheist#deity#paganism#hellenic polythiest#hellenism#hellenic deities#religio romana#greek god eros#God Eros#hellenic pagan#hellenic gods#hellenic polytheism#greek deity#greek god#greek mythology#greek myth#greek polythiesm#greek pagan#greek paganism#Digital Altar#Psyche#Psyche and Eros#Eros and Psyche#God of Love#devotional#e-shrine#e shrine
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
We have pop pagan music
So last week I made a post about how we as pagans don't really have pop music to listen to that relates to our beliefs and myths. All pagan music is pretty much folk, metal or reenactments of ancient and medival music. Nothing wrong with it, but some of us like to be basic from time to time.
Then I realised... That's not true. There's plenty of pop songs that reference the gods and the myths even though the singers themselves may not be polytheists and that's why I created this playlist. Here you can listen to mostly upbeat but also some pop ballads that you could relate to as a polytheists.
Of course I'm accepting recommendations but please only recommend songs of genres that are pop-adjacent (pop, pop-rock, K-pop, J-pop, dance pop...) or mainstream (r&b, rap, trap, hip hop). It'd be especially thankful in recommendations from other faiths like Kemetism, Norse, Celtic, etc. since I don't know much about those. Any language is good.
#paganblr#paganism#polytheist#helpol#witchblr#hellenic polytheism#roman paganism#pagan music#religio romana#norse paganism#germanic paganism#kemetism#irish paganism#slavic paganism#Spotify
74 notes
·
View notes