#off grid
Text
I feel like yall don't know bout earthships??
An earthship is a building that's built out of recycled materials (glass bottles, old tires, cans, etc..) and mostly Cob walls with solarpanels, wind turbines, greenhouses, and large water capture system to ensure all you need within the walls. All these components help regulate the temp for both plants and you creating a proper oasis from all of itnall
Here's a good dissection of one to give you an idea
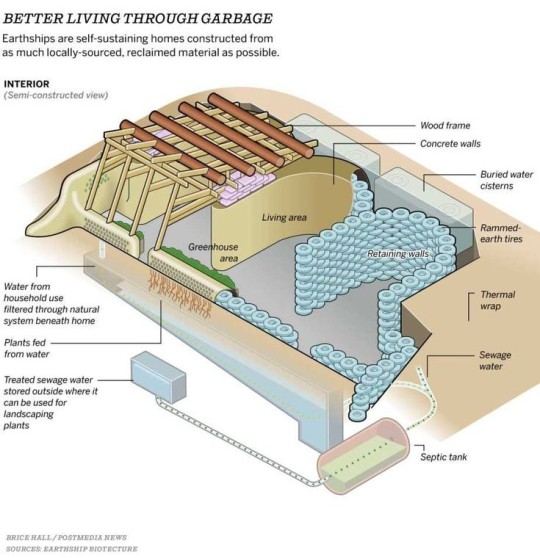
The most famous one, and one of the first ones ever made back in the 1970s by a small off grid group working together is The Phoenix which was built as the model for how cool these guys could be its now a place you can take tours or rent-
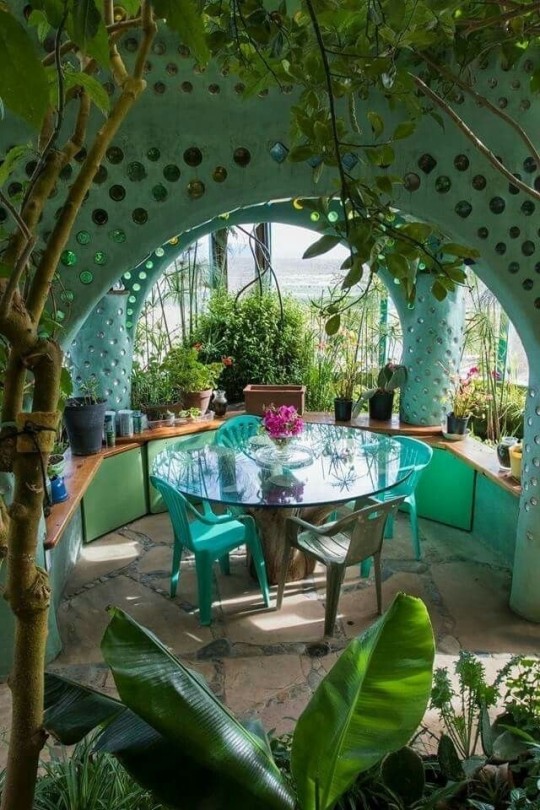
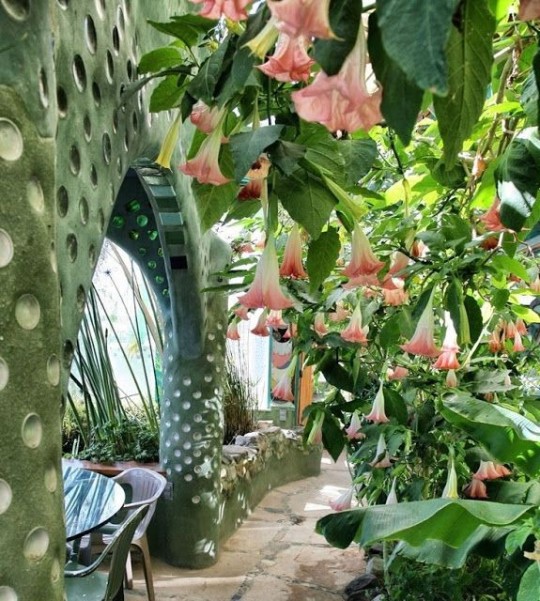





But now there is so many different styles and cool ideas for it! Now some of these are merely concepts


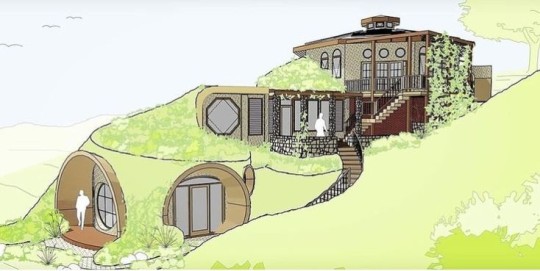

But you can adapt them to any weather for your particular light/weather/energy conditions.
The main thing about Earthships is typically they are illegal to build as the US government considers them waste sites due to the materials their built out of.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists have developed a new solar-powered system to convert saltwater into fresh drinking water which they say could help reduce dangerous the risk of waterborne diseases like cholera.
Via tests in rural communities, they showed that the process is more than 20% cheaper than traditional methods and can be deployed in rural locations around the globe.
Building on existing processes that convert saline groundwater to freshwater, the researchers from King’s College London, in collaboration with MIT and the Helmholtz Institute for Renewable Energy Systems, created a new system that produced consistent levels of water using solar power, and reported it in a paper published recently in Nature Water.
It works through a process called electrodialysis which separates the salt using a set of specialized membranes that channel salt ions into a stream of brine, leaving the water fresh and drinkable. By flexibly adjusting the voltage and the rate at which salt water flowed through the system, the researchers developed a system that adjusts to variable sunshine while not compromising on the amount of fresh drinking water produced.
Using data first gathered in the village of Chelleru near Hyderabad in India, and then recreating these conditions of the village in New Mexico, the team successfully converted up to 10 cubic meters, or several bathtubs worth of fresh drinking water. This was enough for 3,000 people a day with the process continuing to run regardless of variable solar power caused by cloud coverage and rain.
[Note: Not sure what metric they're using to calculate daily water needs here. Presumably this is drinking water only.]
Dr. Wei He from the Department of Engineering at King’s College London believes the new technology could bring massive benefits to rural communities, not only increasing the supply of drinking water but also bringing health benefits.
“By offering a cheap, eco-friendly alternative that can be operated off the grid, our technology enables communities to tap into alternative water sources (such as deep aquifers or saline water) to address water scarcity and contamination in traditional water supplies,” said He.
“This technology can expand water sources available to communities beyond traditional ones and by providing water from uncontaminated saline sources, may help combat water scarcity or unexpected emergencies when conventional water supplies are disrupted, for example like the recent cholera outbreaks in Zambia.”
In the global rural population, 1.6 billion people face water scarcity, many of whom are reliant on stressed reserves of groundwater lying beneath the Earth’s surface.
However, worldwide 56% of groundwater is saline and unsuitable for consumption. This issue is particularly prevalent in India, where 60% of the land harbors undrinkable saline water. Consequently, there is a pressing need for efficient desalination methods to create fresh drinking water cheaply, and at scale.
Traditional desalination technology has relied either on costly batteries in off-grid systems or a grid system to supply the energy necessary to remove salt from the water. In developing countries’ rural areas, however, grid infrastructure can be unreliable and is largely reliant on fossil fuels...
“By removing the need for a grid system entirely and cutting reliance on battery tech by 92%, our system can provide reliable access to safe drinking water, entirely emission-free, onsite, and at a discount of roughly 22% to the people who need it compared to traditional methods,” He said.
The system also has the potential to be used outside of developing areas, particularly in agriculture where climate change is leading to unstable reserves of fresh water for irrigation.
The team plans to scale up the availability of the technology across India through collaboration with local partners. Beyond this, a team from MIT also plans to create a start-up to commercialize and fund the technology.
“While the US and UK have more stable, diversified grids than most countries, they still rely on fossil fuels. By removing fossil fuels from the equation for energy-hungry sectors like agriculture, we can help accelerate the transition to Net Zero,” He said.
-via Good News Network, April 2, 2024
#water#water scarcity#clean water#saline#desalination#off grid#battery technology#solar power#solar energy#fossil fuels#water shortage#india#hyderabad#new mexico#united states#uk#united kingdom#good news#hope#aquifers
802 notes
·
View notes
Text
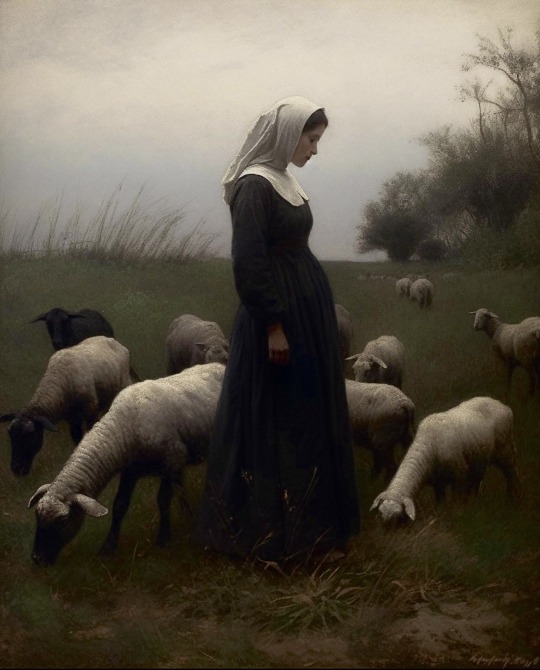
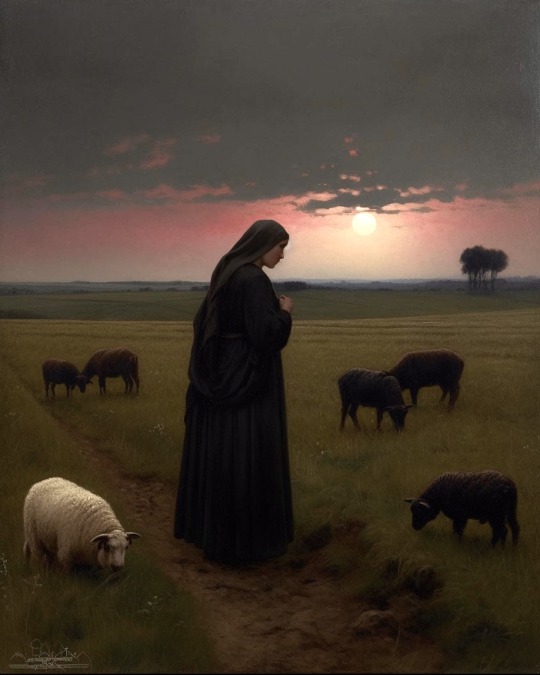



Quiet Omens
— by xis.lanyx
#painting#art#artblr#rural#rural gothic#rural decay#ruralcore#cottagecore#artist#off grid#artists#oil on canvas#oil painting#ai generated#classical art#art gallery#art community#art blog#religious painting#religious imagery#religious art#southern goth#southern goth aesthetic#southern gothic
779 notes
·
View notes
Text
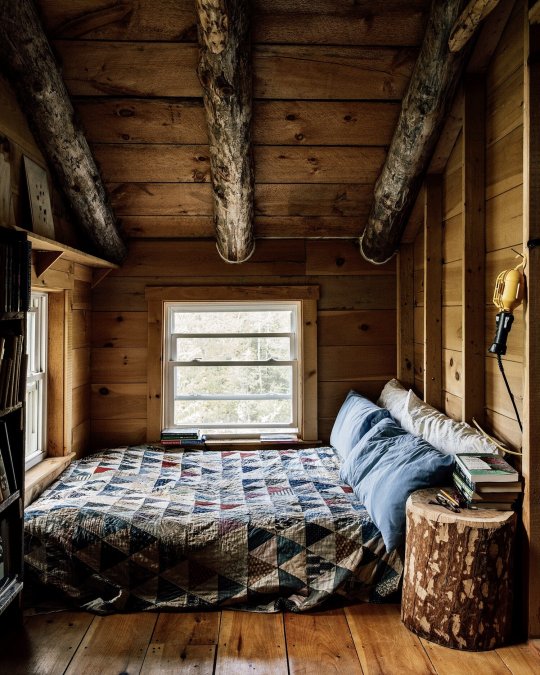

x
#home#home interior#home design#home decor#cabin#cottage#bedroom#wood#wooden#wooden beams#bed#cozy#window#off grid#rustic#1k
5K notes
·
View notes
Photo
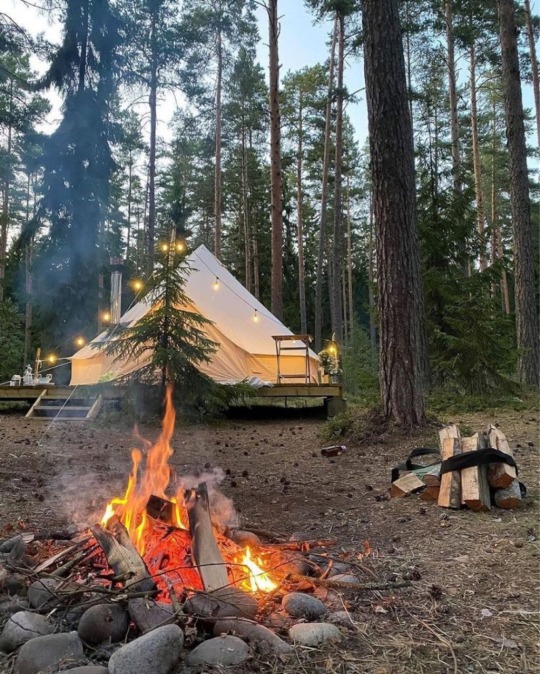

#camping#bell tent#canvas tent#round tent#hot stove#aesthetic#camping aesthetic#hiking#bush craft#fire#fire aesthetic#wood#wood aesthetic#forest#forest aesthetic#forest core#off grid#off grid property#self sufficiency
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

304 notes
·
View notes
Text

114 notes
·
View notes
Text

Love waking up on those early autumn mornings. Who wouldn’t want to wake up every day to look out your window and see trees, mountains, and lakes as far as the I can see.
www.TheOffGridCabin.com
#off the grid#offgrid#offthegrid#off grid#homestead#diy tiny home#fall season#autumm#autumn#fall#leaves
206 notes
·
View notes
Text
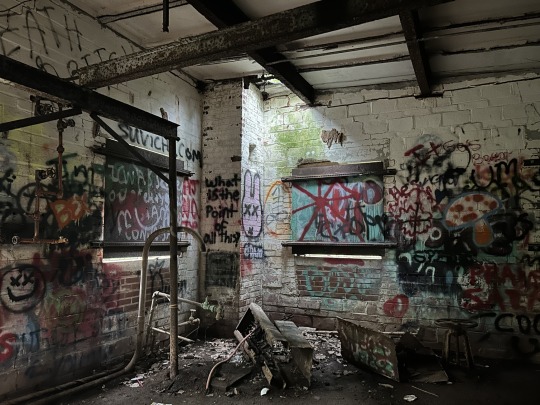

#voidcore#liminal spaces#feverdreamcore#liminal#liminalcore#nostalgiacore#fever dream#nostalgic#grungecore#off grid#abandoned#abandonedcore#lostcore#rural photography#ruralcore#rural decay#woods#art#photography#mine#small town gothic#rural america
61 notes
·
View notes
Text

114 notes
·
View notes
Text

Reddit meets the wild men of the woods
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
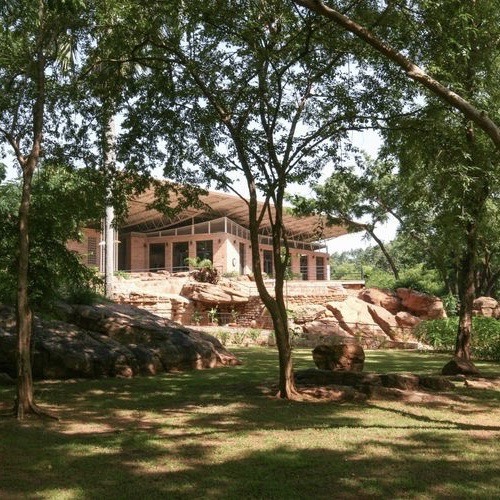
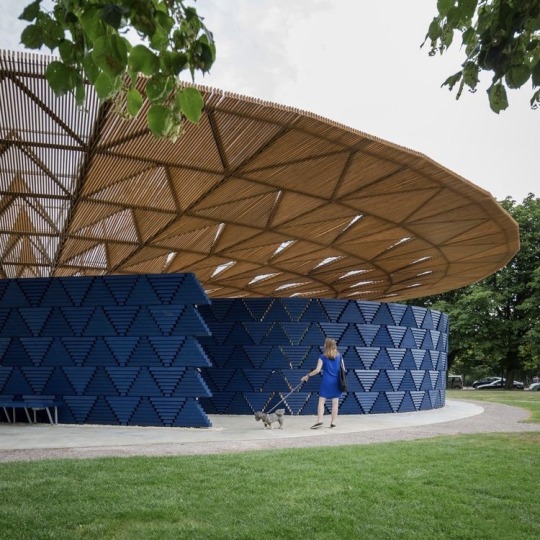
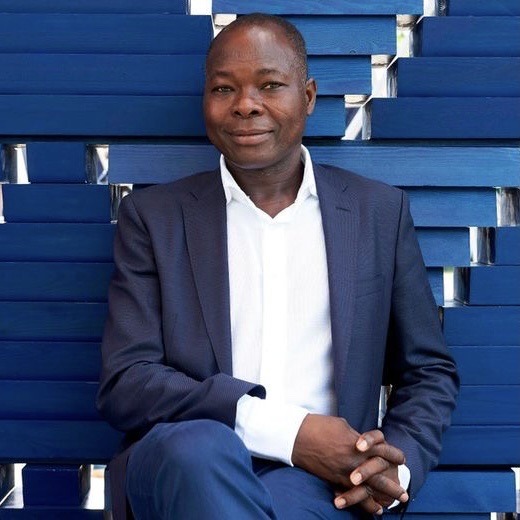








This is Francis Kéré, an architect from Burkina Faso and at least in my eyes, the patron saint of "afro solar punk". He builds using local, sustainable materials, and uses the education he received in Germany to improve on traditional methods already known. His first project was a school in his home village, built to enable other children to receive an education like he once was. The school has a self-cooling mechanism that does not require AC and was built cost effectively together with the community. This year he won the Pritzker Prize. You know what, just watch his TED Talk, I highly recommend it.
#solar punk#solarpunk#afro solar punk#off grid#traditional african living#rural african living#african architecture#sustainable#sustainability
2K notes
·
View notes
Text





#my photos#small town#southern gothic#rural america#rural aesthetic#southern#off grid#american gothic#fall aesthetic#mine#woodland
47 notes
·
View notes
Text

Calming sea.
#nature#sea#ocean#atlantic ocean#landscape photography#landscape#clouds and sea#light beams#mother nature#off grid#explore#adventure#light on the sea
53 notes
·
View notes
Text

242 notes
·
View notes
