#megatherium
Text
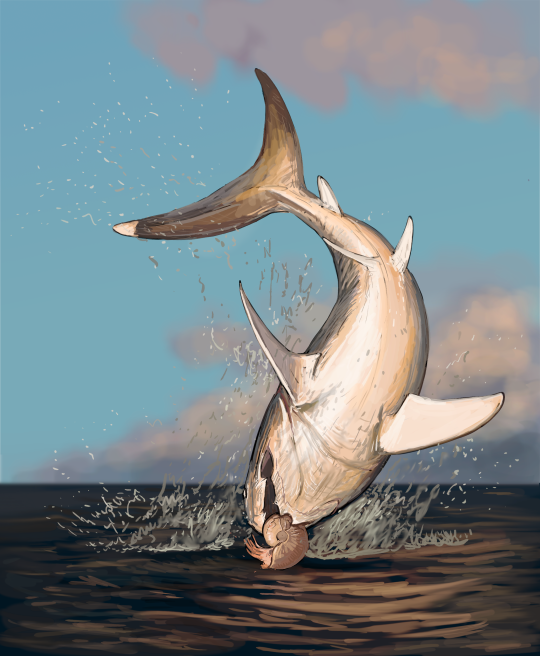




Results from the #paleostream! Dunkleosteus, Thoosuchus, Megatherium and Bennettazhia (with lots of guano)
#paleoart#sciart#temnospondyl#pterosaur#sloth#paleostream#guano#megatherium#smilodon#dunkleosteus#palaeoblr
843 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crystal Palace Field Trip Part 3: Walking With Victorian Beasts
[Previously: the Jurassic and Cretaceous]
The final section of the Crystal Palace Dinosaur trail brings us to the Cenozoic, and a selection of ancient mammals.
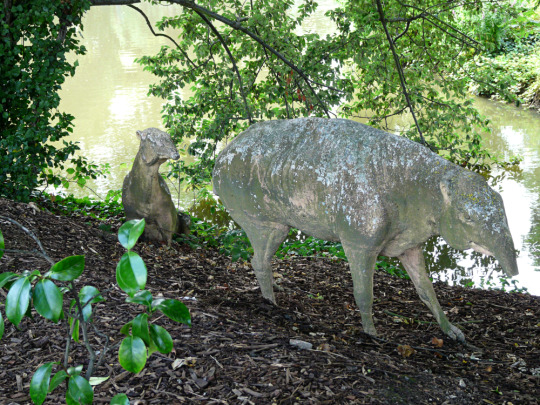

Image from 2009 by Loz Pycock (CC BY-SA 2.0)
Originally represented by three statues, there are two surviving originals of the Eocene-aged palaeotheres depicting Plagiolophus minor (the smaller sitting one) and Palaeotherium medium (the larger standing one).
The sitting palaeothere unfortunately lost its head sometime in the late 20th century, and the image above shows it with a modern fiberglass replacement. Then around 2014/2015 the new head was knocked off again, and has not yet been reattached – partly due to a recent discovery that it wasn't actually accurate to the sculpture's original design. Instead there are plans to eventually restore it with a much more faithful head.
These early odd-toed ungulates were already known from near-complete skeletons in the 1850s, and are depicted here as tapir-like animals with short trunks based on the scientific opinion of the time. We now think their heads would have looked more horse-like, without trunks, but otherwise they're not too far off modern reconstructions.
There was also something exciting nearby:

The recently-recreated Palaeotherium magnum!
This sculpture went missing sometime after the 1950s, and its existence was almost completely forgotten until archive images of it were discovered a few years ago. Funds were raised to create a replica as accurate to the original as possible, and in summer 2023 (just a month before the date of my visit) this larger palaeothere species finally rejoined its companions in the park.
Compared to the other palaeotheres this one is weird, though. Much chonkier, wrinkly, and with big eyes and an almost cartoonish tubular trunk. It seems to have taken a lot of anatomical inspiration from animals like rhinos and elephants, since in the mid-1800s odd-toed ungulates were grouped together with "pachyderms".

———

Next is Anoplotherium, an Eocene even-toed ungulate distantly related to modern camels.
(Apparently the sculpture closest to the water is a replica of a now-lost original, recreated from photo references in the same manner as the new Palaeotherium magnum. I can't find a definite reference for when this one was done, though – I'd guess probably during the last round of major renovations in the early 2000s, at the same time as the now-destroyed Jurassic pterosaur replicas?)
Anoplotherium commune is a rather obscure species today, but it was one of the first early Cenozoic fossil mammals to be recognized by science in the early 1800s. Depicted here as small camel-like animals, the three statues are positioned near the water's edge to reflect the Victorian idea that they were semi-aquatic based on their muscular tails.
Today we instead think these animals were fully terrestrial, using their tails to balance themselves while rearing up to reach higher vegetation. Their heads would also have looked a bit less camel-like, but otherwise the Crystal Palace trio are still really good representations.

———
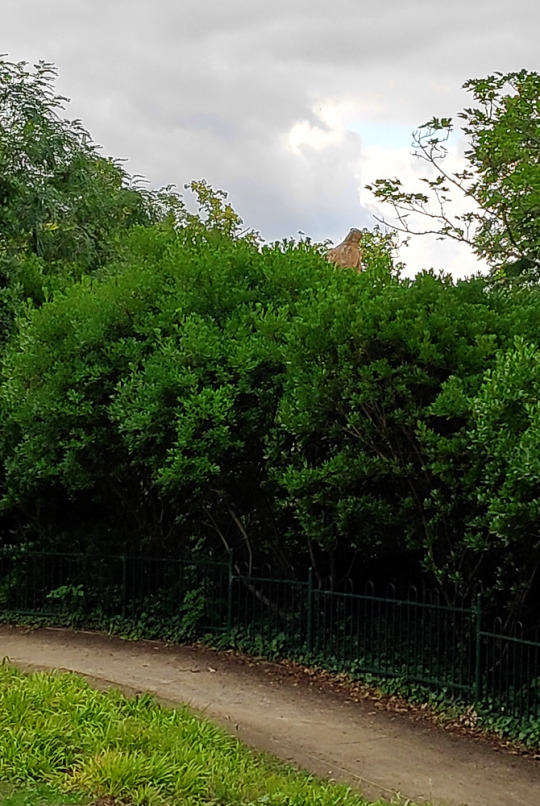

Next is a sculpture that's very easy to miss in the current overgrown state.
Who's that peeking over the bushes?
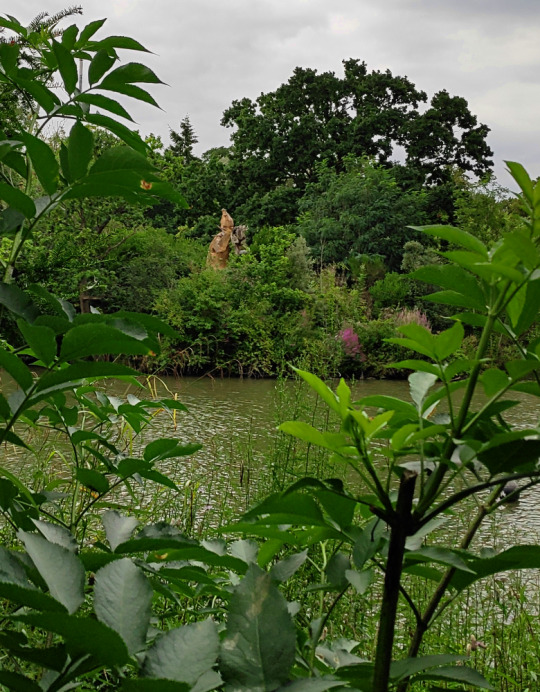

Going all the way around to the far side of the lake reveals a distant glimpse of the Pliocene-to-Holocene giant ground sloth Megatherium.
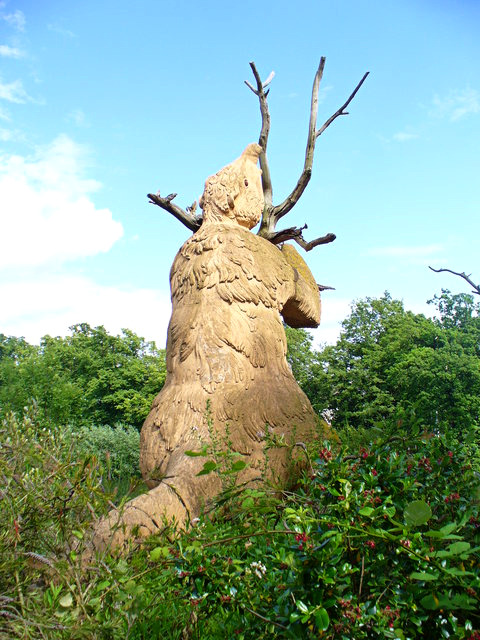

A better view of the Megatherium | "Tree Hugger" by Colin Smith (CC BY-SA 2.0)
Fossils of Megatherium americanum had been known since the late 1700s, but the 1854 Crystal Palace statue was still one of the first life reconstructions of this animal. Its anatomy is actually very close to our modern understanding, depicted with correctly inward-turned feet and sitting upright to feed on a tree with its tail acting as a "tripod".
However, we now know it didn't have a trunk-like nose, but instead probably had prehensile lips more like those of a modern black rhino.
Something weird also appears to have happened to the Crystal Palace Megatherium's hands. Early illustrations of the sculpture all consistently show it with the typical long claws of a sloth, but today it's missing its right hand and its left has only a strangely stumpy paw – suggesting that at some point in the intervening 170 years there was an unrecorded crude repair.

———
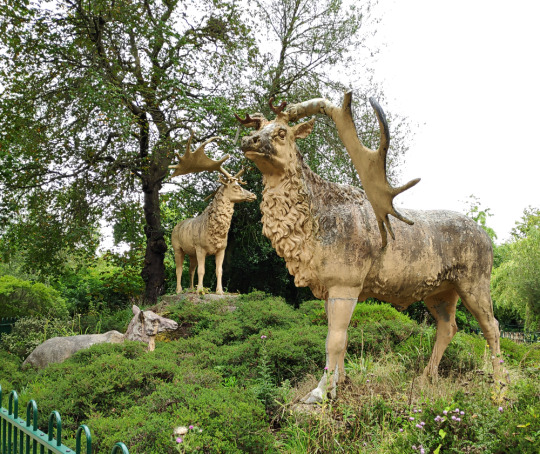

And finally we end the trail with three Megaloceros, the Pleistocene-to-Holocene "Irish Elk" that's actually neither exclusively Irish nor an elk.
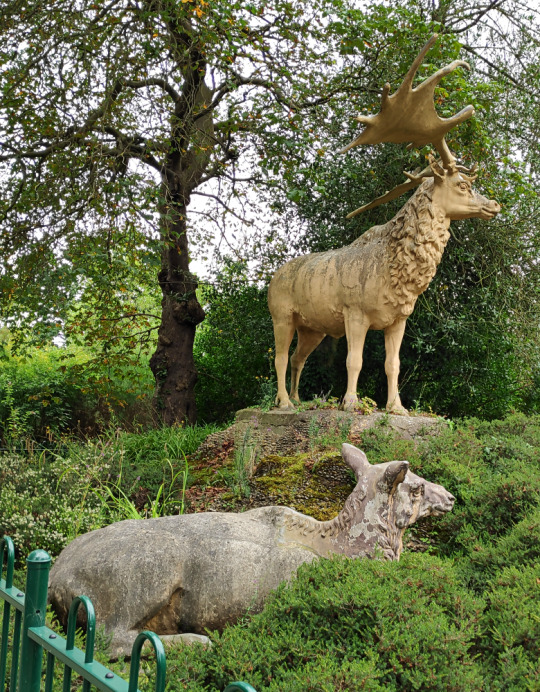

A closer look at the second stag and the doe.
There was originally a fourth giant deer sculpture in this herd, a second resting doe, but it was destroyed sometime during the mid-20th century. The stags also initially had real fossil antlers attached to their heads, but these were removed and replaced with less accurate versions at some point by the mid-20th century.
One of the stags' antlers suffered some damage in 2020, ending up drooping, and since then one antler has either fallen off or been removed.
In the 1850s Megaloceros giganteus was thought to be closely related to deer in the genus Cervus, and so the Crystal Palace reconstructions seem to be based on modern wapiti – specifically in their winter coats, fitting for ice age animals – since both the stags and the doe sport distinctive thick neck manes.

The stags from the other side.
We now know Megaloceros was actually much more closely related to modern fallow deer, and so probably resembled them more than wapiti. Cave art also shows that it had a hump on its shoulders, and even gives us an idea of what its coloration was.

———
…But wait!
There's actually one more thing.
A small statue sitting on the far side of the deer herd, missing its ears, and seemingly representing a Megaloceros fawn.
Except it's actually something very different and very special.
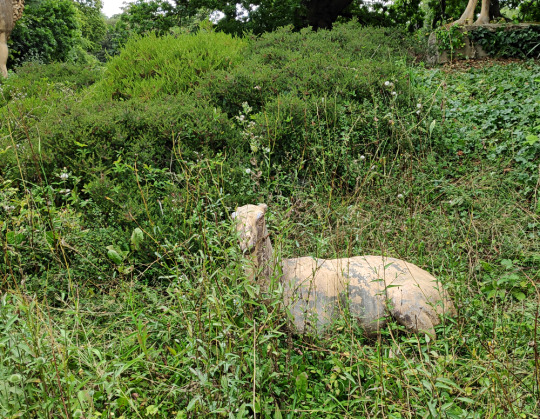

Ceci n'est pas un cerf.
Some recent investigation work revealed some surprising information about the Crystal Palace mammal statues – much like the nearly-forgotten large Palaeotherium, there was originally an entire group of four small Eocene-aged llama-like Xiphodon gracilis that had disappeared from living memory.
There was also no historic record of a fawn with the giant deer, but instead a suspiciously similar-looking sitting sculpture is illustrated among what we now known are the four missing Xiphodon in early records.

An 1853 illustration of the sculpture workshop. The four Xiphodon are shown in the center, directly in front of a Megaloceros stag and doe. (public domain)
Somewhere in the late 19th or early 20th century three of the Xiphodon must have been completely lost, and the remaining individual was misidentified as a fawn and placed with the giant deer herd.

———
Rediscovering a whole extra species among the Crystal Palace statues is exciting, but it also demonstrates just how much of these sculptures' history has gone completely undocumented.
The mammal statues especially seem to have suffered the most out of the "Dinosaur Court", being often overlooked, neglected, disrespected (at one point the Megatherium was inside a goat pen in a petting zoo!), and subjected to cruder repairs. A total of five original statues are now known to be missing from this Cenozoic section – the original large Palaeotherium, the three other Xiphodon, and the second Megaloceros doe – compared to the two pterosaurs lost from the Mesozoic island.
Hopefully the excellent recreation of the lost Palaeotherium magnum is the start of a long overdue new lease of life and conservation attention for all of the Crystal Palace sculptures. It was disappointing seeing them all in such an overgrown state, and with signs of ongoing disrepair in places such as the plant growing out of the big ichthyosaur's back.
But there has been some resurgence of interest and public attention in the Crystal Palace sculptures over the last few years, so with any luck these historic pieces of early paleoart will survive on to their 200th anniversary and beyond, to keep on reminding us of where things began and how far our understanding of prehistoric life has since come.
#field trip!#crystal palace dinosaurs#retrosaurs#i love them your honor#crystal palace park#crystal palace#palaeotherium#anoplotherium#xiphodon#ceci n'est pas un cerf#megaloceros#ungulate#megatherium#ground sloth#mammal#paleontology#vintage paleoart#art#proper art post tomorrow#this took longer than expected#also apologies for my potato-quality camera#i'm an illustrator not a photographer
321 notes
·
View notes
Text








31 days of pastel paleo critters (25-31, + bonus)!
25. Tyranosaurus
26. Amargasaurus
27. Citipati
28. Megatherium
29. Cryolophosaurus
30. Parasaurolophus
31. The Fighting Dinosaurs (Velociraptor + Protoceratops)
Bonus: The Spooky Dinosaurs
#paleontology#prehistoric animals#Tyranosaurus#Amargasaurus#Citipati#Megatherium#Cryolophosaurus#Parasaurolophus#Velociraptor#Protoceratops#dinosaur
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
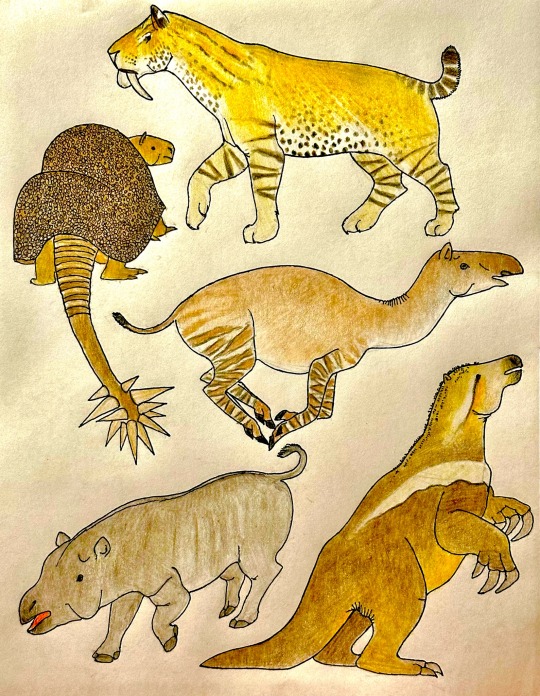
Sketches of some South American animals that were once part of the famous Pleistocene megafauna, from top to bottom: Smilodon populator, Doedicurus clavicaudatus, Macrauchenia patachonica, Toxodon platensis and Megatherium americanum
#paleoart#paleontology#pleistocenemegafauna#pleistocene#pleistocene south america#smilodonpopulator#smilodon#macrauchenia#megatherium#doedicurus#cenozoic life#cenozoology#cenozoic
141 notes
·
View notes
Text


Rancho La Brea mural by Charles R. Knight, 1925. From Terra: The Member's Magazine of The Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. Volume 31, No. 1. Fall 1992.
Internet Archive
#prehistoric#prehistoric mammals#felines#smilodon#xenarthra#megatherium#canines#dire wolves#american lions#birds#raptors#vultures#Charles Knight
295 notes
·
View notes
Text
does this to my mutuals
youtube
#g/t#giant tiny#personal#giants#giant ground sloth#megatherium#zoo tycoon 2#zoo tycoon 2 extinct animals#calvin baretto#Youtube
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
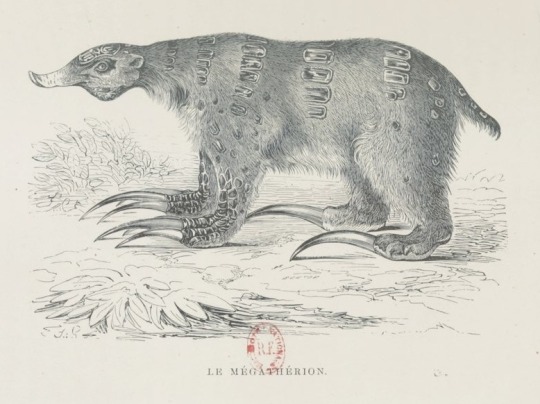
Megatherium from Paris avant les hommes [Paris Before Man] written and illustrated by Pierre Boitard, after Théodore Susemihl
Published posthumously as a novel with updated illustrations in 1861, first published in Musée des Familles – Lectures du Soir, 1836-1837 with art by Susemihl
https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6416941b/f291.item
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

Also just realized i never posted this
Mother ground sloth carrying her child on her back.
#paleoart#cenozoic#ground sloth#Megatherium#sloth#i guess???#i love ground sloths so much wish modern sloths went this hard#i guess we have anteaters for that#also the colors on this were inspired by anteaters also the carrying young on her back is a behavior in anteaters and sloths#so i think its reasonable to believe ground sloths also did this#and more importantly its cute#also i have beef with the ice age sloth for gaslighting society into thinking anceint sloths werent cool#dragon draws creatures
26 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Some critters n creatures!
255 notes
·
View notes
Text
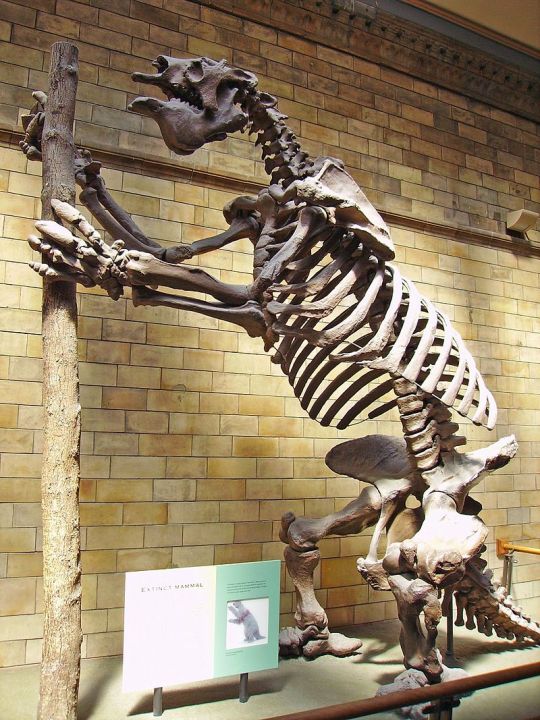
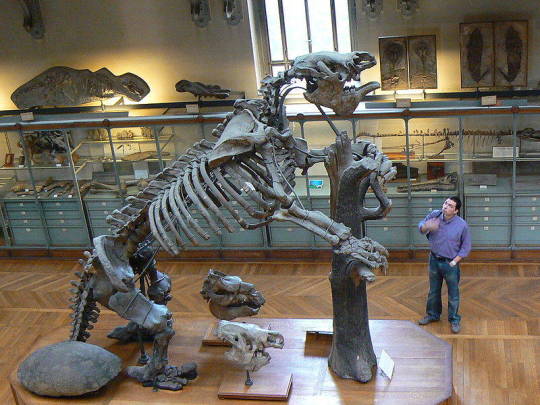








Megatherium known as the giant ground sloth or the megathere is an extinct genus of ground sloth which lived throughout South America from the Pliocene to Pleistocene some 5 million to 12,000 years ago. The first known remains of Megatherium consisting of a mostly complete skeleton were discovered in 1788 by Manuel Torres, on the bank of the Luján River in Argentina. The fossil was shipped to Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales in Madrid the following year, where it remains. It was reassembled by museum employee Juan Bautista Bru in 1795 and subsequently described by Georges Cuvier in 1796. Cuvier assigned the fossil the scientific name Megatherium americanum from the Greek méga 'great' and theríon 'beast' and americanum being a reference to the Americas. In the centuries to follow dozens of well preserved specimens have been recovered representing some 8 species considered valid: M.�� americanum, M. altiplanicum, M. gallardoi, M. istilarti, M. medinae, M. parodii, and M. sundti which are separated into the two sub-genuses of Megatherium and Pseudomegatherium. With the largest species reaching some 20ft (6m) in length, 7ft (2.1m) tall when on all fours, and 8,400 to 10,100lbs (3,810 to 4580kgs) in weight, megatherium surpassed most modern elephants in size making it not only one of the largest xenathrans but one of the largest mammals known to have ever existed. Megatherium had a robust skeleton with a large pelvic girdle and a broad muscular tail. Its large size enabled it to feed at heights unreachable by other contemporary herbivores. Rising on its powerful hind legs and using its tail to form a tripod, Megatherium could support its massive body weight while using the curved claws on its long forelegs to pull down branches. These large animals likely lived in small groups feeding during the day before spending there nights resting inside of caves and large burrows the animals likely dug using there massive claws. Megatherium became extinct around 12,000 years ago during the Quaternary extinction event, which also claimed most other large mammals throughout the world. The extinction coincides with the settlement of the Americas, and multiple kill sites where M. americanum was slaughtered and butchered, suggesting that human hunting helped caused the sloths extinction.
Art belongs to the following creators:
Megatherium Mother and Baby: Mark Witton
https://www.redbubble.com/i/art-board-print/Megatherium-by-MarkWitton/40411556.TR477
Megatherium: Brian Engh
Lost World - Megatherium: Rob Brunette
https://www.artstation.com/artwork/3dbQXY
#pleistocene pride#pleistocene#pliestocene pride#pliestocene#cenozoic#ice age#stone age#giant sloth#sloth#ground sloth#giant ground sloth#megatherium#pliocene#south america#megafauna#prehistoric#prehistoric animals
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

it's been a while, take some paleoart as compensation!
(Gomphothere, Titanis, Megatherium, Thylacoleo, Glyptodon, Toxodon)
#i am sure this is not totally accurate paleoart i was going more for style than substance anyway#but still! enjoy!#other#paleoart#paleontology#thylacoleo#gomphothere#titanis#megatherium#toxodon
110 notes
·
View notes
Text

Started out as bad puns ended in silly geese.
#himorenart#digital art#sketches#illustration#paleoart#megatherium#mammoth#paraceratherium#chalicotherium#prehistoric#prehistoric valentine's
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
Titanoboa is cool but I LOVE the visual of Megatherium roaming the earth. Sloths are already so weird (affectionate), I love a world where they are just.......... Godzilla-sized (not really but you know what I mean).
They'd eat all the trees. But they'd look cute doing it.
17 notes
·
View notes
Photo



#070 - Foleander
#071 - Synthesloth
#072 - Xenarthere
(redesigns)
#fakemon#pokemon#normal type#grass type#sloth#ground sloth#two toed sloth#megatherium#xenarthra#megafauna
179 notes
·
View notes
Photo



Was messing around with photoshop brushes and had a fun idea of a side scrolling adventure game in a sort of cave painting style with various prehistoric creatures as the boss fights, I think that’d be fun.
(Fun lil detail, the back drop for this is a picture of the other side of my fossil of a shrimp)
#My art#Game idea#Cave Paint Adventure#Paleoart#short faced bear#Woolly Rhino#Gigantopithecus#Megatherium#Woolly Mammoth#Triceratops#Quetzalcoatlus#Ankylosaurus#Diplodocus#T. Rex#Tyrannosaurus Rex#To be clear the dinos are there cause of magic or time travelling aliens I don't think dinos and humans were around at the same time dghhgvf
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
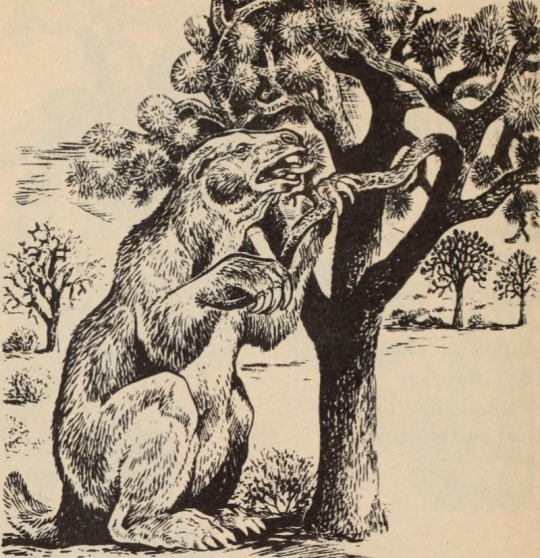

Megatherium. Animal Ghosts. Edited by Claudia Clow. Illustrated by Walt Disney Productions. 1971.
Internet Archive
113 notes
·
View notes