#medical ethics
Text
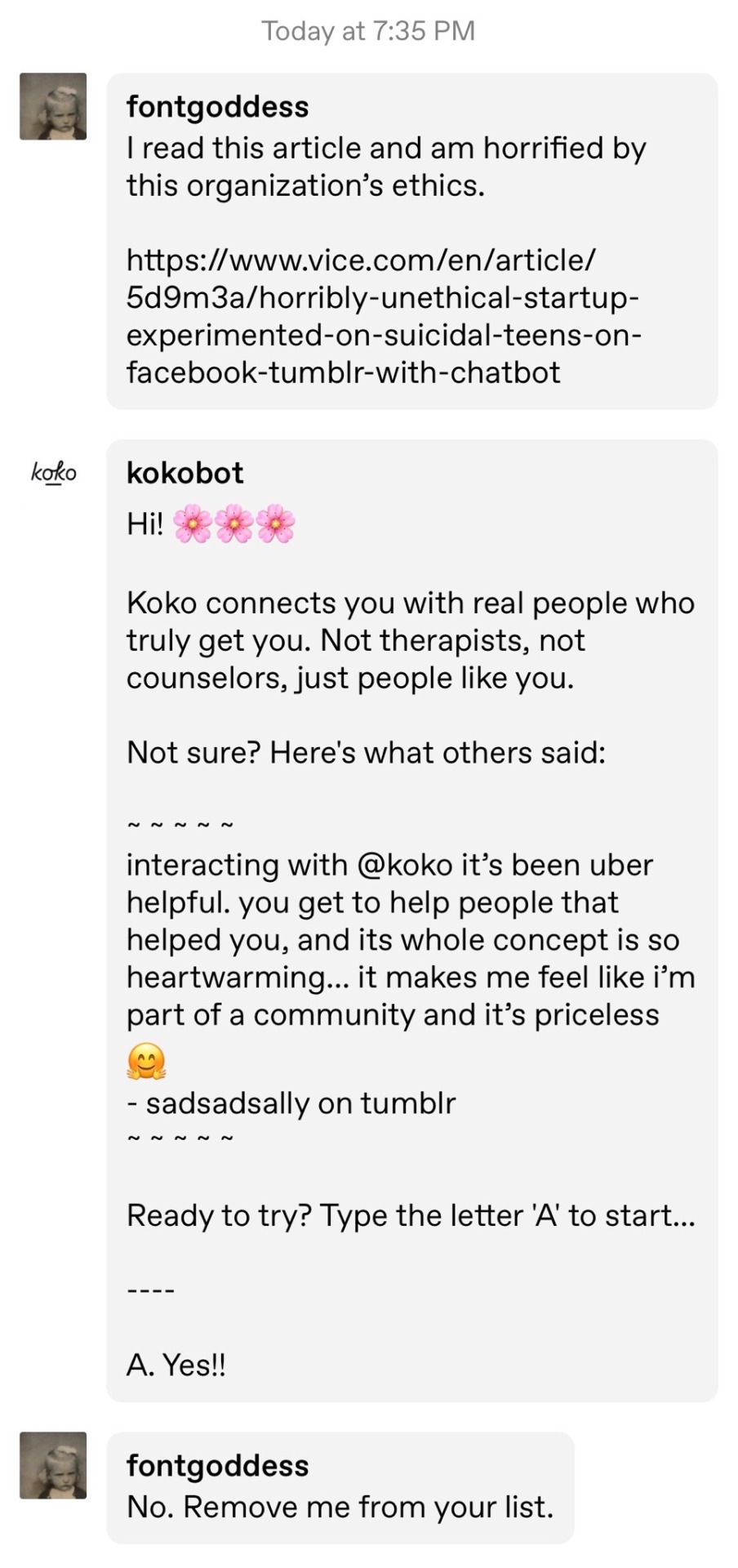
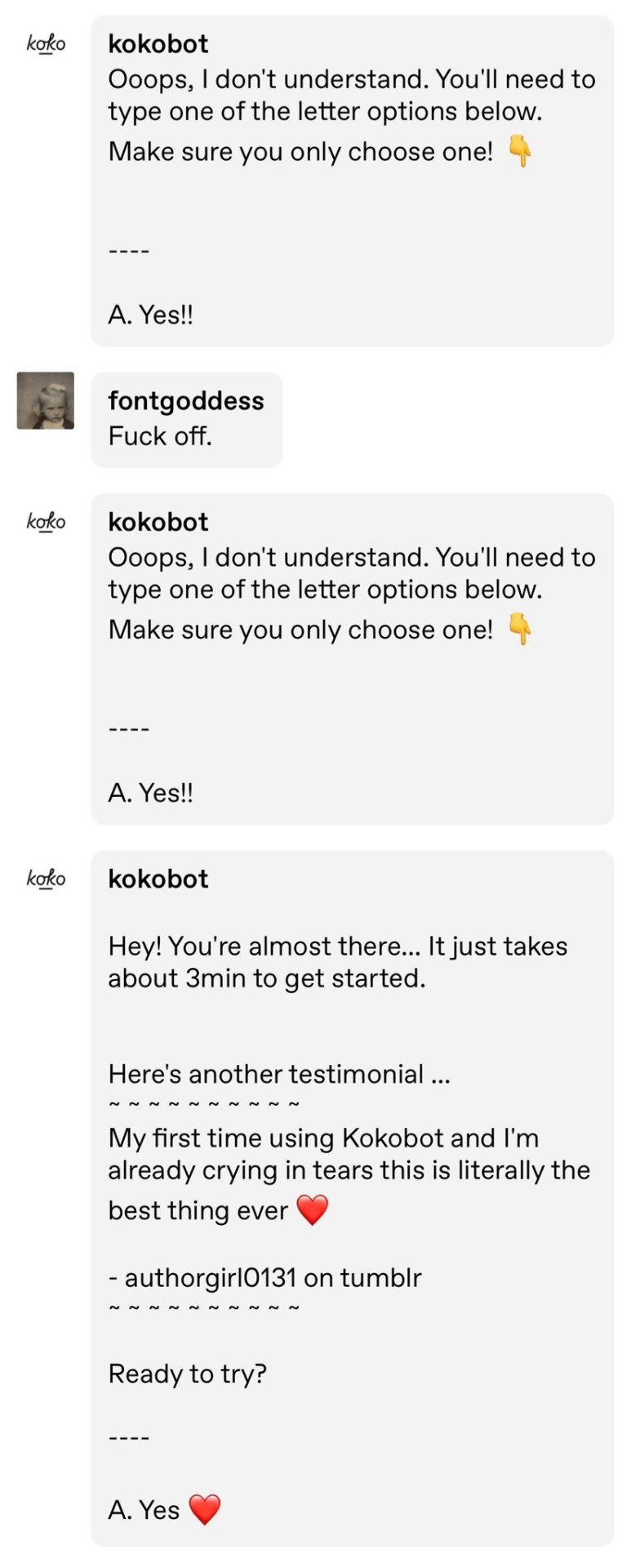
If I were running a chatbot that was being criticized for problems with consent, I would make sure that it understands the word “no” without having to be blocked and reported.
I’d also make it so that it didn’t send unsolicited messages to everyone sharing articles about its ethics lapses as if they want to use it.
Even for an old-school chatbot this is just staggeringly incompetent and a gigantic flashing warning sign that the organization should not be trusted with sensitive data and high-stakes interactions.
#koko#chatbot#mental health#medical ethics#ethics#suicide prevention#consent#trigger warning#kokobot
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you're a pharmacist and you refuse to fill a prescription due to "religious beliefs".... don't be a pharmacist. It's as simple as that.
My religious beliefs prevent me from eating pork. That's why I don't work as a food taster.
If you're a pharmacist, you're gonna have to fill all kinds of prescriptions. Birth control, Plan B, hormones...sorry but that's part of the job description.
You can't go into a job where part of the job description is filling prescriptions, and then cry about having to fill a prescription you "don't agree with."
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
before i succumbed to the house md brain worms in my freshman year medical ethics class we had to watch the house md episode “the tyrant” and write a paper about if it was ethical or not for chase to kill a dictator of a country who was about to commit genocide and like for the sake of the essay i had to say that chase was wrong for killing that guy but like…. this is the medical malpractice show about medical malpractice. hate crimes md. also this is a college essay. and it’s not chase’s job to play god. but like he did it anyway. maybe chase is the real villain. anyway i got like a B- the paper. because it was stupid and i didn’t care about it then. house md is a good show.
#house md#college things#medical ethics#medical malpractice the show#hate crimes md#my thoughts#essay writing#robert chase#at least house doesn’t purposefully kill patients#i don’t think#anecdote
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

[ID: A graphic that shows a realistic picture of a fetus. Underneath it, words read, “Know the facts about fetal pain.]
Fetal pain is real and have a right to access pain relief and proper health care in that regard. Parents also have a right to be fully informed of this reality when considering medical options that may physically harm the fetus.
AAPLOG Practice Guideline 2: Fetal Pain
63 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! Something I’ve been wandering is if there is no point where a brain is truly fully developed, then how do we gage what age should be the age of consent? /genuine I was wandering if you have thoughts on that because it’s something I feel pretty befuddled about
First, I'm sorry this answer is a little late, because I had to think about it a little bit. I think this question, which is a good one, has almost two answers -- one for an ideal youth-topia, and one for our current, ageist, kyriarchical, very-much-not-youth-topia world.
Also, heads up, I'm going to be talking about child abuse in a few paragraphs.
In an ideal world, I think children should begin having some say over their lives and bodies as soon as they're able to express their own opinions, but in conjunction with at least one trusted adult to provide guidance.
As the child gets older, the balance should gradually shift over time, with the child's opinion gradually carrying more "weight" over time.
Then at some fixed end point, which should be no later than the late teens, the new young adult should have 100% autonomy with no oversight (they can still ask for advice -- which I specify because half the time this comes up, someone asks "What if a young adult wants their parents' advice!" and I have to say "Then they can call and ask, it's not illegal").
An adult will have to make pretty much all the decisions for a baby, because babies don't really know what's what.
A toddler's decision-making ability mostly maxes out at picking which toy they want to play with and then crying because actually they wanted the other one.
But a school-age child can start having some say in the decision-making process and can practice asking questions at the doctor's office, being included in the conversation, having things explained at their level, understanding things like "I know the shot hurts, but it will help keep you from getting sick later," or "I know you don't like taking pills, but they help your headache go away" or "If the pills don't help your headache go away, say so, and we'll ask the doctor for something that works better."
And a teenager can really start taking the lead in their own decisions, with guidance, especially if things like making thoughtful decisions, asking questions, weighing pros and cons, and doing research with reliable sources has already been practiced and modeled over the years. And by the time they're in their late teens, they should have sole final say in what happens to their bodies.
But. All of that is very much the "in an ideal world, youth-topia" answer.
We do not live in an ideal youth-topia. We live in a world where many (I'm being generous and not saying "most") adults in positions of influence over children and young people intend to manipulate or exploit them ("for their own good" or otherwise), and it can be really... extremely... difficult to keep kids from being abused or exploited by parents, families, doctors, capitalists, administrators, politicians, and others.
Most of the arguments I get into are about people wanting to raise the age of majority or some other minimum standard for ""real adulthood"" to some age higher than 18, usually invoking some spurious argument about "the brain."
And I will die on the hill that this is wrong and that 18 year olds should be considered full real adults with full bodily autonomy to do whatever they want no matter how unwise anyone thinks it is -- drink, smoke, take medicine, refuse medicine, have sex, have children, get married, have abortions, get their tubes tied, whatever.
Okay, but then you might say, what about 17 year olds? What about 16 or 15? Is an 18 year old really "more mature" than a 17 year old?
Well, no, of course not. The problem is that the legal status of minors is so absolutely abysmal that, within that legal status, it's hard to asses what "consent," let alone "informed consent," even means. It's not that I think a 17 year old isn't "mature enough" to choose to have surgery, say, but an 18 year old is "mature enough." It's that when you have zero (0) legal rights, having the right to make one (1) choice is really constrained.
Throughout the U.S. -- and I'm only going to be talking about the U.S. here because I can't confidently speak to any other country's laws -- it is legal, to varying degrees (and with even more varying degrees of enforcement), for parents to beat their minor children. It is legal, to varying degrees, for parents to restrict their minor children's movement. To restrict their food. To keep them in conditions barely above prison. To send them to "troubled teen" farms that are literally prison. Even if the mistreatment crosses into some threshold of legally actionable "child abuse," there is no guarantee that the law will be at all enforced. There is no guarantee that the abuse will be stopped. At most, the government will remove the child and place them in a foster home which is likely to be just as abusive if not moreso.
I'm not saying that minors shouldn't have the legal right to make more medical and general life choices than they currently do -- they absolutely should -- I'm saying that in the absence of certain basic physical safety guarantees, a technical on-paper "choice" doesn't mean much.
Like, I just said that I would fight for 18 year olds' right to be sterilized or get married, and also, I'm vehemently opposed to sterilization of minors and firmly support raising the minimum marriage age to 18.
That's not because I think decision-making maturity and wisdom magically kick in at the 18th birthday.
That's because an 18 year old can leave and file assault charges when their parent says "Sign this consent form or I'll beat you and send you to a prison farm."
So... with that in mind... I do think there are ways to protect minors' right to consent. I think people over 12 or 13 should have to give their own consent for any medical procedure that isn't an immediately life-threatening emergency. And ethical doctors shouldn't perform procedures on people they have reason to believe are being coerced.
As for minors seeking out medical procedures, I think we can look at some contextual questions like:
Is the need for this procedure urgent or time-sensitive? I.e. is there any reason it can't wait until the person is older?
Can someone interview the young person to try to assess whether they're being coerced?
Can the young person articulate the risks or give some indication that their choice is informed?
Can they talk about how the medicine/treatment/procedure makes them feel?
Do any adults benefit financially from the young person's decision? Are they having an undue influence over the young person?
(That isn't just about medical treatment, it's also questions like "Why are child beauty pageants a thing?" and "Why do 7 year olds play American tackle football?")
Have they been exposed to other points of view?
Obviously these are all really contextual questions that depend on people in power behaving ethically, which... is a lot to depend on.
So. That's my long answer. I guess.
Final note, mostly I'm talking about medical treatment in general and life decisions in general, but I wanted to quickly mention transition and gender-affirming care in particular.
I do support youth gender-affirming care. I didn't always. When I first heard about youth transition, I thought it was a risky thing that young people were going to be coerced into. I thought there would be parents coercing their gender non-conforming children into transitioning to the "other" binary gender and doing surgeries on them before they could object.
I was wrong. I know that now, after learning more about how youth transition actually works. Doctors involved in gender-affirming care for youth really seem to be doing it right. They interview the young person. They make sure it's really what the person wants. They go slowly at first. The young person has ample time and opportunity to change their mind.
I think other forms of health care for youth
(looking at you, psychiatry) (looking at you, weight loss) (looking at you, reproductive health) should model themselves on the kinds of youth-affirming, consent-affirming practices that are standard in youth gender-affirming care.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
I got to yell at my students today about the importance of ethics and knowing history, featuring such highlights as "Nazis are bad" and "Deliberately infecting children with hepatitis is wrong".
#I love teaching intro classes#“Do you think *horrible thing we have strict rules about* really happened?”#Half the class shakes their head no#YES! IT HAPPENED AND IT WAS HORRIBLE!#That's why we bothered to make a rule about it!#I mean you could list anything and the Nazis probably tried it#not writing#medical ethics#Nazi human experimentation#Willowbrook hepatitis study
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
Could you elaborate on imperforate hymens? I didn't want to derail the reblog chain to ask about it but I've never heard of this medical issue before...
An imperforate hymen essentially means that, instead of a thin, semilunar membrane surrounding the vaginal opening, there’s a thick membre extending all the way across the area a normal hymen would occupy, completely blocking the vaginal opening. It’s a congenital condition that’s usually diagnosed around puberty, because menstrual blood gets trapped and can’t pass through. It’s easily removed by a minor surgery, which is essential to the girl’s health and well-being, because trapped, rotting blood is an excellent breeding ground for infections, and being trapped in the vaginal canal gives it easy access to spread quickly and viciously. These infections can be fatal.
In rural areas of Egypt (and other similar countries) male doctors routinely refuse to perform the simple operation because, and I quote, ‘it’s best to let her die than to defile her honour’. Which is vile and demonstrates perfectly the point the OP of that post was making about the extent of doctors’ ability to gatekeep healthcare based on personal belief.
164 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Bernard Lane
Published: Apr 14, 2024
Nine of the 15 gender clinics in a landmark international survey for the Cass review have admitted they do not routinely collect outcome data on their young patients.
This survey, together with a new evaluation of treatment guidelines for gender dysphoria, gives unprecedented insights into the workings of gender clinics around the world offering puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to minors.
In the 2022-23 survey, six clinics said they “routinely collected some outcome data”: one of these clinics gave no further detail; one noted the number of patients discontinuing treatment; another used measures of quality of life; two were taking part in cohort studies; and the sixth clinic repeated some baseline assessments. Nine clinics acknowledged “not routinely collecting outcome data.”
The report of the survey results1, published by researchers from the University of York earlier this month, identified clinics by country, not name. Of the clinics that took part, Australia and the Netherlands were prominent with five and four clinics respectively.
Poor data collection was central to the controversy over the London-based Tavistock youth gender clinic.
The Cass review had planned to run a data-linkage study—with help from adult gender clinics—to learn the outcomes of the Tavistock’s 9,000-odd former patients.
The missing long-term data would allow clinicians, young patients and parents to make informed decisions about treatment. The review said it was to be the largest study of its kind in the world.
However, six of the seven adult clinics refused to co-operate. One stated reason was that “the study outcomes focus on adverse health events, for which the clinics do not feel primarily responsible.”
Another adult clinic said, “The unintended outcome of the study is likely to be a high-profile national report that will be misinterpreted, misrepresented or actively used to harm patients and disrupt the work of practitioners across the gender dysphoria pathway.”
On April 12, however, The Times newspaper reported that the uncooperative adult clinics had “bowed to pressure to share [the] missing data”.
Mostly medical
In the York University international survey, ordered by the Cass review, all 15 youth gender clinics said they used a multi-disciplinary team, but researchers concluded there was a “paucity” of psychosocial therapy interventions such as psychotherapy or cognitive behaviour therapy. Five clinics did not offer any of these non-medical interventions in-house.
All gender clinics told researchers that “genital reconstructive surgery”—the creation of a pseudo vagina, for example—was “accessible only from age 18.” The youngest age for “masculinising chest surgery” (a double mastectomy) was reported as 16. In fact, there are documented cases in Australia of 15-year-olds approved for transgender mastectomy. Genital surgery is legally available to minors2 in Australia and practised in America.
“Only five clinics reported routine discussion of fertility3 preferences, and only two discussed sexuality4. Finland was the only country to report routinely assessing for history of trauma5,” the final Cass report says in its commentary on the survey.
In separate studies for the Cass review, three independent reviewers evaluated the quality of 21 guidelines for treatment of gender dysphoria in minors.
Included were international guidelines (from the Endocrine Society and the World Professional Association for Transgender Health or WPATH); documents from North America (for example, the 2018 policy statement from the American Academy of Pediatrics); from Europe (the guideline of the UK Royal College of Psychiatrists, for example, and Denmark’s); as well as guidelines from the Asia-Pacific and Africa.
“WPATH has been highly influential in directing international practice, although its guidelines were found by the University of York appraisal process to lack developmental rigour,” the Cass report says.
The York researchers chart patterns of “circular” cross-referencing between guidelines to create a misleading impression of consensus in favour of the medicalised “gender-affirming” treatment approach.
“The guideline appraisal raises serious questions about the reliability of current guidelines. Most guidelines have not followed the international standards for [rigorous and independent] guideline development. Few guidelines are informed by a systematic review of empirical evidence [the gold standard for assessing the evidence supporting a health intervention] and there is a lack of transparency about how recommendations were developed,” the Cass report says.
“Healthcare services and professionals should take into account the variable quality of published guidelines to support the management of children and young people experiencing gender dysphoria. The lack of independence in many national and regional guidelines, and the limited evidence-based underpinning current guidelines, should be considered when utilising these for practice.”
The Cass report says it is “imperative” that gender clinic staff be “cognisant of the limitations in relation to the evidence base and fully understand the knowns and the unknowns.”
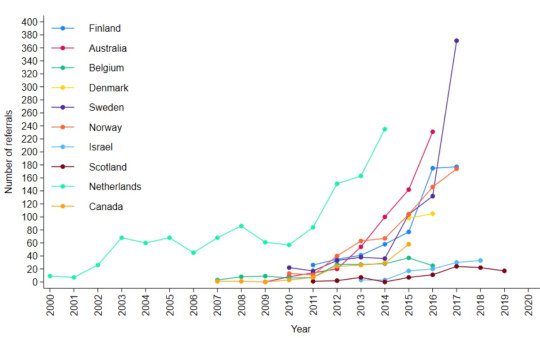
[ Chart: Number of youth gender clinic referrals over time by country. Source: Cass report ]
Bum steer
Staff at the Tavistock clinic misled patients and parents, or failed to correct their misconceptions, according to a new report from the Multi-Professional Review Group (MPRG) given oversight of treatment decisions from 2021.
These shortcomings of clinicians included playing down the extent of the unknowns of hormonal treatment; not explaining that puberty blockers are being used unlicensed and off-label; not challenging the reassuring but false parallel with the licensed use of puberty blockers for precocious (premature) puberty; not discussing the possibility that blockers will pause or slow psychosexual development; and not sharing figures showing the vast majority of children started on puberty blockers will go on to cross-sex hormones supposed to be taken lifelong.
The MPRG was also troubled by clinical documents showing misunderstanding of “the outcome of physical treatments” on the part of patients and parents.
In the York University study of treatment guidelines for gender dysphoria, only two were recommended for use by all three reviewers. These were recent, more cautious policies from Finland and Sweden. Both followed independent systematic reviews showing the evidence base for hormonal and surgical treatment of minors to be very weak and uncertain. Like the Cass review itself, the 2020 Finnish and 2022 Swedish guidelines recognise that puberty blockers are experimental and should not be routine treatment.
Although all the guidelines in the study agreed on the need for a multidisciplinary team to treat gender-distressed minors, the “most striking problem” shown by analysis of these documents was “the lack of any consensus6 on the purpose of the assessment process”, the Cass report says.
“Some guidelines were focused on diagnosis, some on… eligibility for hormones, some on psychosocial assessment, and some on readiness for medical interventions7.
“Only the Swedish and [the 2022] WPATH 8th version guidelines contain detail on the assessment process8. Both recommend that the duration, structure and content of the assessment be varied according to age, complexity and gender development.
“Very few guidelines recommend formal measures/clinical tools to assess gender dysphoria, and a separate analysis demonstrated that the formal measures that exist are poorly validated.”
Nor was there any consensus on “when psychological or hormonal interventions should be offered and on what basis.”
A survey of staff at the Tavistock clinic, undertaken as part of the Cass review, found specialists divided on whether or not “assessment should seek to make a differential diagnosis, ruling out other potential [non-gender9] causes of the child or young person’s distress.”
Arguing for an ambitious research program well beyond a possible clinical trial of puberty blockers, the Cass report says the field of youth gender dysphoria is one of “remarkably weak evidence” where health professionals are “afraid to openly discuss their views” because of vilification and bullying.
“Although some think the clinical approach should be based on a social justice model, the NHS works in an evidence-based way,” the report says.
“The gaps in the evidence base regarding all aspects of gender care for children and young people have been highlighted, from epidemiology through to assessment, diagnosis10 and intervention. It is troubling that so little is known about this cohort and their outcomes.
“Based on a single Dutch study, which suggested that puberty blockers may improve psychological wellbeing for a narrowly defined group of children with gender incongruence [or dysphoria], the practice spread at pace to other countries.
“Some practitioners abandoned normal clinical approaches to holistic assessment, which has meant that this group of [gender-distressed] young people have been exceptionalised compared to other young people with similarly complex presentations.”
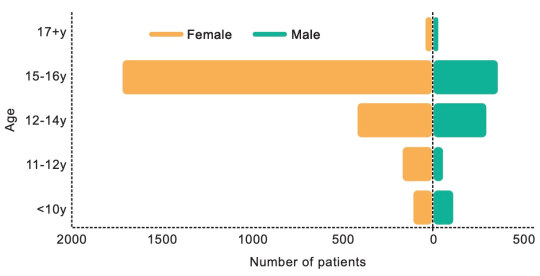
[ Chart: Age and sex on referral to the Tavistock clinic from 2018-2022. Source: Cass report ]
Who to trust?
The Cass report says the missing evidence “makes it difficult to provide adequate information on which a young person and their family can make an informed choice.”
“A trusted source of information is needed on all aspects of medical care, but in particular it is important to defuse/manage expectations that have been built up by claims about the efficacy of puberty blockers.
“The option to provide masculinising or feminising hormones from the age of 16 is available, but the [Cass] review would recommend an extremely cautious clinical approach and a strong clinical rationale for providing hormones before the age of 18. This would keep options open during this important developmental window, allowing time for management of any co-occurring [non-gender] conditions11, building of resilience, and fertility preservation, if required.”
The review stresses that “consent is more than just capacity and competence. It requires clinicians to ensure that the proposed intervention is clinically indicated as they have a duty to offer appropriate treatment. It also requires the patient to be provided with appropriate and sufficient information about the risks, benefits and expected outcomes of the treatment.”
“Assessing whether a hormone pathway is indicated is challenging. A formal diagnosis of gender dysphoria is frequently cited as a prerequisite for accessing hormone treatment. However, it is not reliably predictive of whether that young person will have long-standing gender incongruence in the future, or whether medical intervention will be the best option for them.”
Advocates for the gender-affirming approach assert that detransition and treatment regret are vanishingly rare, whereas suicide risk for those denied medical intervention is claimed to be very high.
The Cass report says: “It has been suggested that hormone treatment reduces the elevated risk of death by suicide in this population, but the evidence found did not support this conclusion.”
“The percentage of people treated with hormones who subsequently detransition remains unknown due to the lack of long-term follow-up studies, although there is suggestion that numbers are increasing.”
The report cites three reasons why the true extent of detransition is unlikely to be clear for some time—patients who decide medicalisation was a mistake may not wish to return to their former clinic to announce this fact; there is a post-treatment honeymoon period and clinicians suggest it may take 5-10 years before a decision to detransition; and the surge in patient numbers only began within the last decade.
Faced with uncertainty and a lack of good evidence, those with responsibility—from health ministers and hospital managers down to gender clinicians—rely on treatment guidelines supposed to advise on clinical practice according to the “best-available” evidence and expert opinion.
In the York University guideline analysis, the 21 documents were rated on six domains, the key two being the rigour of their development and their editorial independence.
“[Rigour] includes systematically searching the evidence, being clear about the link between recommendations and supporting evidence, and ensuring that health benefits, side effects and risks have been considered in formulating the recommendations,” the Cass report says.
Only the Finnish and Swedish guidelines scored above 50 per cent for rigour. Only these two documents, the Cass report says, link “the lack of robust evidence about medical treatments to a recommendation that treatments should be provided under a research framework or within a research clinic. They are also the only guidelines that have been informed by an ethical review conducted as part of the guideline development.”
“Most of the guidelines described insufficient evidence about the risks and benefits of medical treatment in adolescents, particularly in relation to long-term outcomes. Despite this, many then went on to cite this same evidence to recommend medical treatments,” the report says.
“Alternatively, they referred to other guidelines that recommend medical treatments as their basis for making the same recommendations. Early versions of two international guidelines, the Endocrine Society 2009 and WPATH 7th version guidelines, influenced nearly all the other guidelines.
“These two guidelines are also closely interlinked, with WPATH adopting Endocrine Society recommendations, and acting as a co-sponsor and providing input to drafts of the Endocrine Society guideline. The WPATH 8th version cited many of the other national and regional guidelines to support some of its recommendations, despite these guidelines having been considerably influenced by the WPATH 7th version.
“The circularity of this approach may explain why there has been an apparent consensus on key areas of practice despite the evidence being poor.”
Sometimes these gender-affirming guidelines seek to buttress a strong evidence claim with a citation to a study that is weak or involves a different patient group.
The Cass report notes that, “The WPATH 8th version’s narrative on gender-affirming medical treatment for adolescents does not reference its own systematic review [of the evidence], but instead states: ‘Despite the slowly growing body of evidence supporting the effectiveness of early medical intervention, the number of studies is still low, and there are few outcome studies that follow youth into adulthood. Therefore, a systematic review regarding outcomes of treatment in adolescents is not possible’.”
Despite WPATH insisting such an evidence review is not possible, this is precisely what health authorities and experts have undertaken since 2019 in several jurisdictions—Finland, Sweden, the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, Florida, Germany, and University of York research commissioned by the Cass review.
Yet in the 8th and current version of its guideline, WPATH makes the confident statement that, “There is strong evidence demonstrating the benefits in quality of life and well-being of gender-affirming treatments, including endocrine and surgical procedures… Gender-affirming interventions are based on decades of clinical experience and research; therefore, they are not considered experimental, cosmetic, or for the mere convenience of a patient. They are safe and effective at reducing gender incongruence and gender dysphoria”.
But WPATH “overstates the strength of the evidence” for its treatment recommendations, the Cass report says.
--
1 In the survey, there was one clinic each from Belgium, Denmark, Finland, Northern Ireland, Norway and Spain. The response rate was 38 per cent.
2 In Australia there is no good public data on trans surgery for minors.
3 Early puberty blockers followed by cross-sex hormones are expected to sterilise young people and may also impair future sexual function.
4 Some sizeable proportion of gender clinic patients might grow up in healthy bodies and accept their same-sex attraction were it not for trans medicalisation, according to testimony from detransitioners, clinicians’ reports and data.
5 Trauma from a history of sexual abuse, for example, or exposure to domestic violence is thought to be among the many possible underlying causes of what presents as gender dysphoria. The Multi-Professional Review Group (MPRG), given oversight of Tavistock treatment decisions from 2021-23, was troubled by the lack of curiosity by the clinic’s staff about the effect of a child’s “physical or mental illness within the family, abusive or addictive environments, bereavement, cultural or religious background, etc.”
6 Critics of the “gender-affirming” treatment approach say it is not mainstream medicine because the “trans child” in effect self-diagnoses while clinicians avoid differential diagnosis and attribute mental health disorders and other pre-existing issues to a “transphobic” society.
7 “In most cases [at the Tavistock clinic] children and parents were asking to progress on to puberty blockers from the very first appointment”, according to the MPRG.
8 In the MPRG’s opinion, the patient notes from the Tavistock “rarely provide a structured history or physical assessment, however the submissions to the MPRG suggest that the children have a wide range of childhood, familial and congenital conditions.”
9 Once referred to the Tavistock, patients typically were no longer seen by child and adolescent mental health services.
10 According to the MPRG, gender dysphoria in the diagnostic manual DSM-5 “has a low threshold based on overlapping criteria, and is likely to create false positives. Young people who do not go on to have an enduring cross-sex gender identity may have met the criteria in childhood. And early to mid-childhood social transition may be influential in maintaining adherence to the criteria. Sex role and gender expression stereotyping is present within the diagnostic criteria—preferred toys, clothes, etc—not reflecting that many toys, games and activities [today] are less exclusively gendered than in previous decades.”
11 The MPRG said it was “notable that until the child and family’s first appointment at [the Tavistock] they have received little, if any, support from health, social care, or education professionals. Most children and parents have felt isolated and desperate for support and have therefore turned for information to the media and online resources, with many accessing LGBTQ+ and [gender dysphoria] support groups or private providers which appear to be mainly ‘affirmative’ in nature, and children and families have moved forward with social transition. This history/journey is rarely examined closely by [Tavistock clinicians] for signs of difficulty [or] regret.”
==
Critics have described "gender affirming care" - that is, sex-trait modification - as "medical experimentation." This is incorrect. In a medical experiment, you actually collect data and monitor the participants in the experiment. They don't do that. They're cowboys violating all medical ethics - "first, do no harm" - for ideology, money or both.
#Bernard Lane#Cass review#Cass report#Dr. Hilary Cass#Hilary Cass#gender affirming care#gender affirming healthcare#gender affirmation#medical scandal#medical malpractice#sex trait modification#medical corruption#World Professional Association for Transgender Health#WPATH#ethics violations#medical ethics#unethical#gender ideology#gender identity ideology#queer theory#intersectional feminism#religion is a mental illness
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
I had somewhat forgotten what it was like to take classes that are emotionally challenging. The "hard" sciences can be intellectually difficult, but we weren't covering material that breaks my heart or enrages me.
Anyway, I'm off to finish a documentary about the horrific racism and medical cruelty of the decades (!) of Tuskegee syphilis "research."
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
White supremacy is so dynamic and insidious. You see that today with abortion rights. Roe v. Wade gave some legal protection but even with it being the law of the land, so many people did not have access to abortion. There were still medically unnecessary tests, waiting periods, and violence against abortion seekers and providers. Legislation alone does not protect people’s humanity. We organize around the world we deserve; not just our survival and the absence of abuse, but the presence of love, joy, and pleasure.
Kelly Davis quoted in an article by Thalia Charles at Rewire News Group. Less Than Half of States Ban Pelvic Exams Without Consent
But more states have stepped up recently to ban nonconsensual pelvic exams on unconscious or sedated patients.
New Voices for Reproductive Justice
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
RE: not everyone should get an MRI. Getting the MRI contrast dye put in you isn't harmless! You need to have the energy to flush it out of your system and all that.
Besides, there are other ways to diagnose issues, and the more you avoid invasive (because x-rays and MRIs ARE still invasive) procedures the better.
Yep. And the operation and maintenance of these machines is expensive and highly specialized. MRIs are giant magnets and X-Ray machines have radioactive cores, which can be very dangerous if used improperly, which is why you need to have the resources to train and pay radiologists. I'm all for universal healthcare, and people who have a genuine need for these diagnostics should be able to get them, but it's absolutely reckless and irresponsible to demand that everyone gets them 'just because'. These machines use a lot of energy and for machines that use radioactive elements, are also a huge environmental concern when it comes to disposal. I shudder to think of the environmental toll of all the extra energy expenditure if everyone got MRIs and X-rays and CT scans, etc etc as regularly as going to their GP. In medicine it's all about making sure the benefit outweighs the risk.
For example, when TB was a lot more widespread in developed countries, chest x-rays were performed much more regularly because the benefit of detecting TB before it could spread and get worse outweighed the risk of radiation exposure. Now, thankfully we don't have to worry about TB as much in developed countries, so there's no need to perform regular chest x-rays in healthy patients.
Just being curious is not a valid reason to perform these tests.
34 notes
·
View notes
Note
You mentioned your medical ethics class in your tags on the healthy autistic behaviors post and having more thoughts on it and now I'm intrigued so if you'd like to elaborate on that, consider this a formal invitation
Ok SO there’s this whole thing we’re going over thats honestly also the core of the class and it’s this: Disabilities are socially enforced because disabilities are labeled disabilities if you cannot function “normally” we also get into the word Normal and how Normal actually means Average.
Our society is built around what the average person can achieve, but if you know anything about statistics its that Average especially over a large population is exceedingly rare. In our efforts to cater to this Average we’re actually harming the majority. Take wheelchair accessibility for example, a supposed outlier of the population. And yet you know who else benefits from ramps and easy access to elevators? Elderly, mothers with small children, people with leg injures and more. Theres so much more than Average out in the world yet we build so much around the assumption everyone is around middle age and perfectly healthy.
So basically those “Negative” traits that are actually healthy were labeled as negative because of how they clash with the view of whats normal or expected of people. However! Normal does NOT equal healthy. Looking at health and labeling disabilities based on how people are failing to meet normality can be VERY problematic. It’s the whole “whats normal for me isn’t normal for you”
So like these psychologists are coming at this the only way they know how: “What about you doesn’t function in our society and how can we change YOU to fit in it.” Sometimes not in an actively malicious mindset but it’s still harmful because at the end of the day they’re telling autistic people is “What comes naturally to you doesn’t allow you to function in society how we’ve decided people should function and therefore it is bad.”
I probably could have worded all this better but it’s 3:00am and I just got home from work. Thank you for asking me to ramble on about this.
#i could go on#but I am so very sleepy#also capitalism is a huge HUGE part of whats acceptable in society#like ugh#autism#medical ethics
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Because of pro-choice doctors wrongfully denying life and health saving measures for pregnancy problems (such as premature induction, mismanaging infections/hemorrhage, etc), and causing harm to women and families as a result, I feel the need to share this resource with you. It shows how to report a doctor/other staff member for malpractice and what that will look like.
No human being, pro-choice, pro-life or otherwise, deserves to have their life at risk for a political agenda. No abortion restriction allows for this gross mistreatment of patients.
We all have a part to play in the fight against obstetric violence, abuse, and negligence. If you are a victim, your role can include seeking a support system to give you medical justice. If you are not a victim, inform yourself of the procedure involved, how it looks in your state, and having those resources ready to share for victims who may need it.
I haven’t been too happy with how AAPLOG has been avoiding commentary on these sad cases of medical malpractice, but they have been sharing information on medical procedures for pregnancy complications. They also have testimonies from pro-life care providers, who call out the BS that these new laws are preventing them from saving lives. You can visit them at aaplog.org
308 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reporting on Long Covid Taught Me How to Be a Better Journalist
Covering long Covid solidified my view that science is not the objective, neutral force it is often misconstrued as. It is instead a human endeavor, relentlessly buffeted by our culture, values and politics. As energy-depleting illnesses that disproportionately affect women, long Covid and M.E./C.F.S. are easily belittled by a sexist society that trivializes women’s pain, and a capitalist one that values people according to their productivity. Societal dismissal leads to scientific neglect, and a lack of research becomes fodder for further skepticism. I understood these dynamics only after interviewing social scientists, disability scholars and patients themselves, whose voices are often absent or minimized in the media. Like the pandemic writ large, long Covid is not just a health problem. It is a social one, and must also be understood as such. […]
In covering conditions like long Covid and M.E./C.F.S., many journalistic norms and biases work against us. Our love of iconoclasts privileges the voices of skeptics, who can profess to be canceled by patient groups, over the voices of patients who are actually suffering. Our fondness for novelty leaves us prone to ignoring chronic conditions that are, by definition, not new. Normalized aspects of our work like tight deadlines and phone interviews can be harmful to the people we most need to hear from.
Ed Yong, New York Times, Dec. 11, 2023
Excellent article and the comments are full of people praising not just this article, but all the Covid 19 coverage by Ed Yong.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Medical ethics convention"
AKA
"Should we selectively abort disabled people, sterilize them in their teens, or just euthanize them outright? "
5 notes
·
View notes