#kabardino-balkaria
Photo

Beautiful swans in a shimmering lake in winter
Kabardino-Balkaria, North Caucasus! Russia ~ Zakharov Armen
#North Caucasus#Kabardino-Balkaria#Russia#lensblr#swans#landscape#nature#Edit: nature#winter wonderland#Fauna#Lake#mountains
279 notes
·
View notes
Text

Literally me /lh
#inside out#inside out fandom#inside out 2#inside out envy#inside out au#au#alternative universe#kabardino-balkaria#kabardian
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
okay I'm curious. this poll is for caucasians only
#i always felt culturally alienated from russians and slavic ppl in general for obvious reasons#but i wonder if that's the case for other ppl from caucasus#caucasus#circassia#dagestan#chechnya#ingushetia#kabardino-balkaria#karachay-circassia#adygea#armenia#georgia#also pls reblog to widen the scope!!
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
September 25th, 2022
The cries for help of Russia's national minorities: "We will stop existing"
"In small villages, with two or three streets, they have taken all the men" • Putin's draft mobilization punishes regions like Yakutia, Buryatia and Dagestan.
On the day after declaring partial mobilization in Russia, a member of the Duma [Russian Parliament] and ex-mayor of Jakutsk, in Siberia, protested that the number of reserves that each region has to send to the front [of the war in Ukraine] didn't match. She asked why regions like Novosibirsk only mobilize 0.27% of the men between ages 20 and 59 and, at the same time, Yakutia has to mobilize 1.66%. In addition, she added, why are precisely the most disadvantaged towns of the north of Yakutia where the proportion of men called to war is higher? "In villages of the Artic, with 300 inhabitants, they take 47 men. I know what it means to live in the north at -55°C [-67°F] and, without the men, families will have a very hard time. What is the logic behind these numbers? What kind of proportionality are we talking about?"
Yakutia, located north of the permafrost and almost 8,500 km away from Moscow, is a land rich in natural resources (diamonds, uranium, hydrocarbon...) and the immigration of workers for the extraction businesses has left Yakuts and Evens, the indigenous peoples, as a minority in the cities of the centre and south of the Republic. On the other hand, they are the majority in the towns of the north, from which they are now being sent en masse to the frontline.
We have talked to Aanis, a girl from a town of 500 inhabitants where 35 men have been called to war: "They've taken almost all young men from the town, of local ethnicities (Evens and Yakuts). It was very unexpected, nobody could have seen something like this coming. Before the mobilization, people from the town were not interested in the war, it's hard enough to survive. We were worried about everyday problems: hunting, how the vegetables were growing... Now everything has changed, we are shocked."
Nikolai, a man from a village in the north of Yakutia, answers resolutely when we ask what has happened: "We had never seen before what is happening now, not even in the Second World War. They have sent all the native men to the front." I ask him for more details: "My village is inhabited only by Yakuts and Evens. We're less than 500 people, out of which only 154 are of working age, including women. They have called to the front 65 people, almost all the men between ages 18 and 60." He adds that families don't know how they will survive this winter. "It reaches -60°C [-76°F], and we don't have centralised heating or water pipes. We use ovens to warm up and it's usually men who take care of that. We live from hunting. Who will hunt now? What will we eat? Nobody knows."
I ask him why does he think the authorities have decided to take them and not others: "Because we live in remote and very small villages, with no Internet; there are no lawyers here or organizations that defend us. Many of us don't speak Russian or English. They probably calculated that mobilizing us would have little repercussion: very few people would notice the absence of some minorities, even if they disappear completely. In fact, there's already few of us left.

Poster calling for a protest of the Free Yakutia Foundation: "Yakutia! Don't cry! RESIST!"
In Yakutia, women have taken the streets to protest. They stand their ground. And they have done so, shouting "no to genocide!"
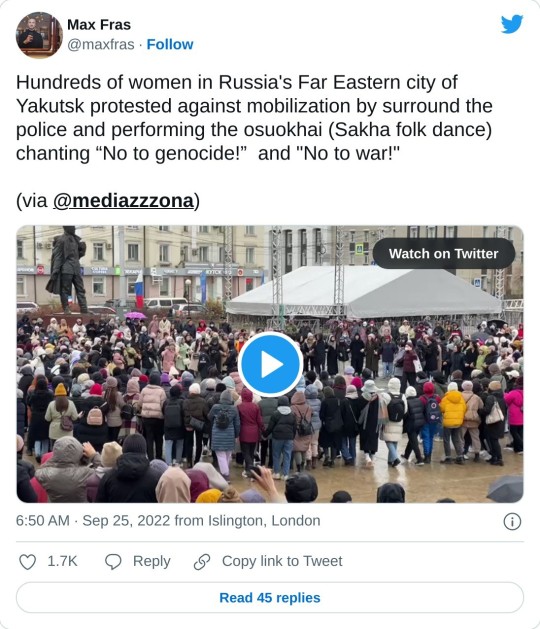
General mobilization in Buryatia
In Buryatia, a republic in the south of Siberia, bordering Mongolia, with a 35% native population of Mongolian origin (Buryats), their situation is just as harsh. "The mobilization in Buryatia is general, not partial", declares Aleksandra Garmazhapova, founder of a local NGO. Viktoriya Maladaeva, coordinator of the Free Buryatia Foundation, confirms it: "They're not calling up only reserves: they mobilize students, disabled people, and people who have never had any relation with the army. In small villages, with only two or three streets, they have taken all the men. There are families where they've called up the fathers and sons." She explains that many men were taken to the recruitment points during the night: "Then people started calling each other, and those who could drove their car to Mongolia. Others have hidden in the forests, in the taiga."
To answer to this situation, the ex-president of Mongolia (2009-2017) Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj published the following message: "I know that since the beginning of this bloody war, the ethnic minorities that live in Russia are the ones that have suffered the most: the Mongols of Buryatia, of Tuva and Kalmykia have suffered. They have been used as cannon fodder. We, the Mongols, will welcome you with open arms and hearts. Our borders will stay open."
To the question of why she thinks Buryatia is disproportionately affected by the mobilization, Maladaeva answers without a doubt: "Because we are an ethnic minority and for Putin we are worthless [...] And that's the same in other "ethnic republics": right now we're getting calls from activists from Kalmykia, Chuvashia, Yakutia, Tuva... On the contrary, in the Irkutsk region (where there is a Slavic majority without notable minorities), there's silence, even though it borders us. Why?"
Dead in combat
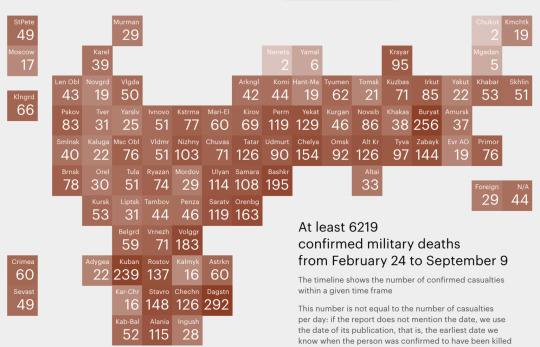
"Russian victims in Ukraine". Data compiled by Mediazona.
We must highlight that, until Putin signed the decree to mobilize reserves last Wednesday, going to fight in Ukraine was voluntary and paid. Those interested signed a contract with the Russian army and got paid a monthly salary between 130,000 and 200,000 rubles, depending on the region.
These salaries might not be much in Moscow, but they are a fortune in the most deprived areas. In the Russian capital city, the average monthly wage is about 115,009 rubles, three times the average monthly wage in Buryatia. If we look at unemployment rates, we see how it's 1.5% in Saint Petersburg while in Northern Caucasus republics, such as Ingushetia, it's as high as 30%. In the context of these economic inequalities, a result of highly centralized policies that center the economic wealth around the cities where political power resides and regulate the periphery to misery, it's no surprise that Buryats and Caucasians see an opportunity in an army wage, and knowing that in the worst of cases, if they die in combat, their families will receive (in theory) a compensation of 7 million rubles and a pension.
These economic reasons explain, in part, why the two regions with the most soldiers who died in combat in Ukraine are Buryatia and Dagestan (in the northern Caucasus). According to official data compiled by the Russian news portal Mediazona, 6,219 Russian soldiers have died in total in the war in Ukraine. From Buryatia, 256 have died (out of a total of 1 million inhabitants), and from Dagestan, 292 (out of 2.5 million inhabitants). These numbers contrast highly with the 17 dead soldiers from Moscow (12 million inhabitants) or the 49 deaths from Saint Petersburg (5 million inhabitants).
"We are the empire's trash"
Another factor that deepens the marginalization of minorities in Russia, that could have contributed to their disproportionate enlistment, is the prevailing racism in Russian society. Maria Viushkova, analyst of the Free Buryatia Foundation, declared in an interview: "The best alternatives in Buryatia for finding a job are either emigrating to South Korea or joining the army. For us, it's difficult to find work in other regions of Russia, where Buryats have to face discrimination and racism: they don't hire them, they don't house them, they limit their education. Often, Buryats who have tried their luck in other regions of Russia are forced to come back."
Aslan is a man from Kabardino-Balkaria, near Dagestan. He confirms that racism towards Caucasians is noticeable in Moscow, where he worked in some years: "It's constant. At work, first they looked badly at me, it took them a while to trust me. And when they knew me well, sometimes they spoke badly of Caucasians using a slur that they use to define us, "chernojopie" (black butts), not even realising I was there. In the subway, I have had problems with nationalists because of my looks. And my child has had quarrels with his friends for not being "Russian".
I ask him why he thinks it's them and Siberian minorities who are the most affected by this war. He's resolute: "Because we are the empire's trash to the Kremlin, and this is a way to get rid of us." And he adds: "But I don't understand why the Northern peoples don't rebel against Moscow, the empire has also wanted to destroy them. I think mobilization hasn't been as numerous in our republics in the Caucasus as it has in the Far East because they don't dare to, they know we'll stand up to them."
Aslan is probably right. The Caucasus is a potentially explosive region, where there was for years a Jihadist armed group made of young radicalized people with no hopes for the future. Authorities are not interested in feeding discontent and rage among these young people.
But in the Far East and in Siberia the situation is different, and the natives make a request of us. When I asked Nikolai, from the village in Yakutia that has been left with no young men, how could we help them, he said: "Please, report about the minority nations. If all men go to war, the genetic reserve of our people will be gone. In 20 years, or 40 years, our language will also go extinct. We will stop existing."
#war in ukraine#ukraine invasion#national minorities#ethnic minorities#russia#racism#yakutia#buryatia#dagestan#siberia#indigenous#evens#yakuts#tuva#kalmykia#kabardino-balkaria#caucasus#stateless nations#💬#genocide
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
Caucasus 1900 m above sea level ...
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Azerbaijani wedding in Russia.
Azerbaijani wedding in Russia.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Portrait of Kabardian Tovchenova. XIX в.
Портрет кабардинки Товченовой. XIX в.
Photographer A. Engel. (А.Энгель)
#Kabardino-Balkaria#Кабардино-Балкария#Kabardin#Кабардинцы#Adyghe#Адыги#Adyghe culture#Культура Адыги
17 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Russia.Kabardino-Balkaria
Россия. Кабардино-Балкария
Photo by ksuelbrus
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
Traditionalism vs. Assimilation Among Indigenous Peoples of Siberia.

As is the case for many indigenous groups around the world, native peoples of Siberia struggle to fit into the modern global village while retaining their ethnic identity and cultural distinctiveness. Since the end of World War II, the indigenous peoples of Siberia have had a special legal status which allows for certain “affirmative action”-like quotas and benefits. However, the main aim of these policies was to integrate ethnic minorities into the all-Soviet people and to inculcate the “new Soviet man” mentality. Compulsory boarding schools, where children from different ethnic groups were brought together from the age of seven in a collectivist environment, often served as the hotbed of such Sovietization. The effect on native culture was disastrous. But, as James Forsyth in his A History of the Peoples of Siberia points out, “Russification began even before this, in kindergartens, where most nurses and teachers were Russian speakers. Even where some of them were natives, however, there were cases when children or the nurses themselves were reprimanded for using their native language” (here the parallels with Native North American languages are obvious). In the Soviet Union, it was believed that minority languages and cultures would die out under communism, and that “nationalism can only be bourgeois”. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, a number of new laws have been adopted whose goal is to preserve ethnic distinctiveness of indigenous peoples. But can the tables be turned?
#Adygea#Altai Republic#Bashkiria#Buryatia#Chechnya#Chuvashia#Dagestan#Ingueshtia#Kabardino-Balkaria#Kalmkia#Karachay-Cherkessia#Karelia#Khakassia#Komi Republic#Mari El#Mordovia#North Ossetia-Alania#Sakha Republic#Tatarstan#Tuva#Semi -autonomous regions#ethnic languages#Udmurtia#indigenous groups#russian language
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Circassian Day of Mourning (May 21)
On the day of the end of the Russian-Caucasian war of 1763–1864, on the day of memory and sorrow of the Circassians, we publish another album-manifesto from Jrpjej.
In addition to music, the album is accompanied by a pdf-zine with our reflection on Circassian songs of the 20th century and their relevance today
“Sefitse” is a line from the song “Quedzoqo Tole Tsiku.”
In the Adyghe language, “se”…

View On WordPress
#Adyghe (people)#Bulat Khalilov#Caucasian Knot (website)#Circassian Day of Mourning (May 21)#Circassian folk music#Circassian genocide#Circassians#Jrpjej (folk music group)#Kabardino-Balkaria#Nalchik#Ored Recordings#Russo-Circassian War#Timur Kodzoko
0 notes
Text



Mountain Jews of Nalchik, Kabardino-Balkaria (southern Russia), ca. late 19th century
347 notes
·
View notes
Text



Kabardino-Balkarian Republic, Russia, by Olivier Duport (source)
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
#grunge#alternative#aesthetic#punk#rock#emo#goth#grunge girl#photography#hipster#alt girl#alt fashion#alt style#arab#arab girl#palestanian#kabardino balkaria#emo fashion#grunge fashion#grunge style
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

“Bataraz and Pako” by Kabardian artist Zaurbek Bgazhnokov, 2020-2021. From the Nart sagas
Source: https://pinterest.com/pin/636766834842897946/
#illustration#kabardines#kabarda#kabardino balkaria#caucasus#russia#northwest caucasian#2020s#circassians
0 notes
Text
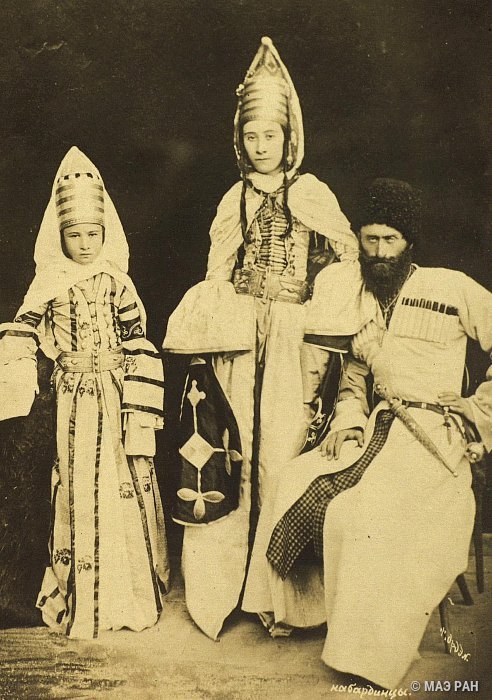

Noble Kabardians. 1890s
Знатные Кабардинцы. 1890s
From Kunstkamera archive.
Photographer A. Engel. (А.Энгель)
#Adyghe#Адыги#Kabardino-Balkaria#Кабардино-Балкария#Kabardin#Кабардинцы#non-russian#indigenous russia#indigenous russian#caucasian#Adyghe culture#Культура Адыги
14 notes
·
View notes
