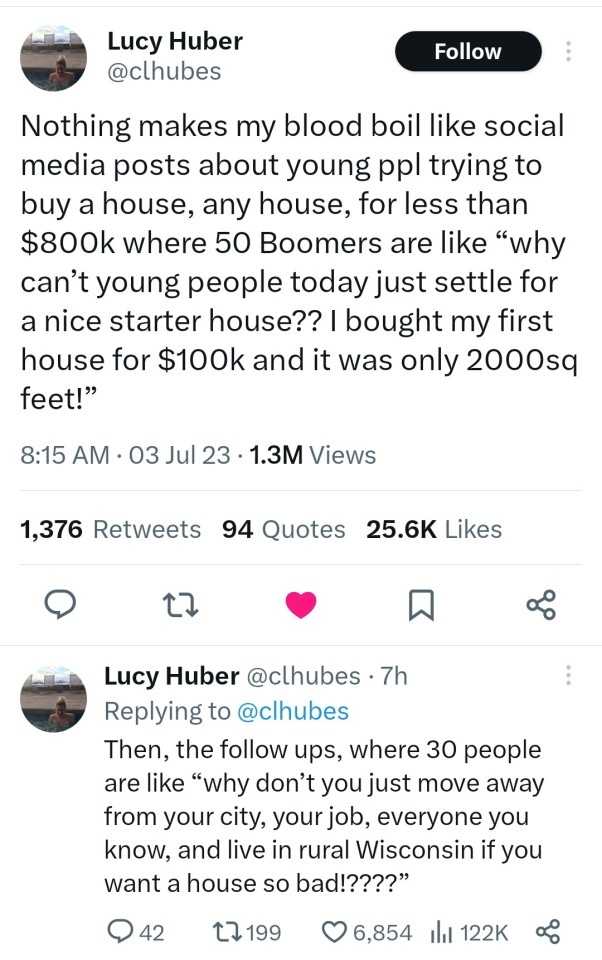
#housing & homelessness
Text
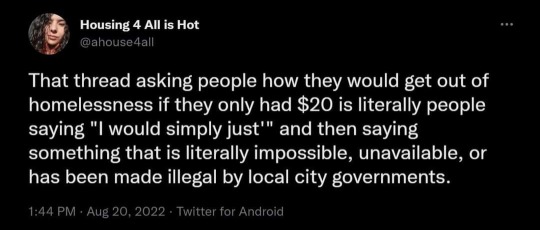


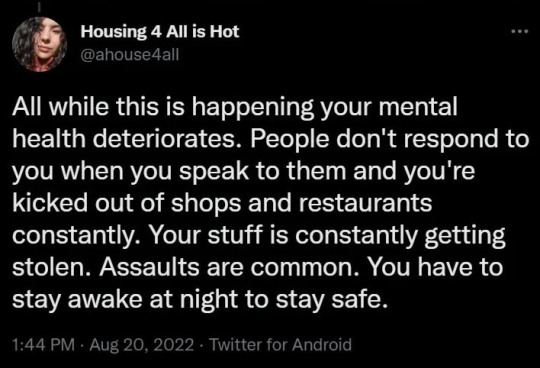


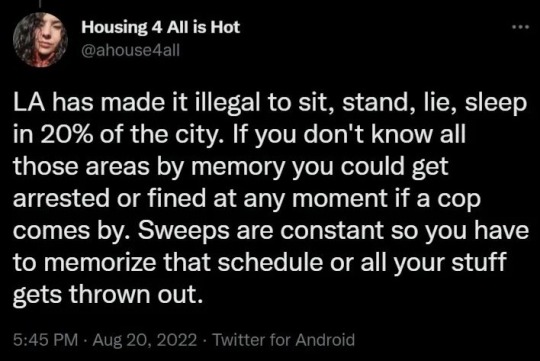


81K notes
·
View notes
Text

Source

Source
#end homelessness#homelessness#housing#housing crisis#news#current events#politics#us politics#government#public policy#progressive#the left#capitalism
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
DPXDC Prompt #90
Jason was frustrated with life, of course he was a revenant without a way to get revenge with Bruce’s no kill rule. Doesn’t say he can’t get others to kill for him, so when he gets captured by cultists he decides to take a leap of faith and make his wish to the Ghost King before the cultists can make their stupid wish about world domination or something.
The Ghost King accepts but wants a favor from him, what Jason wasn’t expecting was a kid with black hair blue eyes about 14, showing up on his doorstep saying he needed a place to crash and this was the ghost kings favor. Jason gets a message from his family just then, the Joker is confirmed dead. He doesn’t know why the Ghost King wants him to take care of a random teen but a deal is a deal.
#dp x dc prompt#dp x dc#dc x dp#danny fenton#danny phantom#jason todd#Jason makes a wish to the ghost king!#ghost king danny#Danny kills the Joker#Then Jason kind of adopts Danny#writing prompt#free to use#poor danny#homeless Danny got kicked out of his parents house and was on the run when he gets summoned by cultists#He recognizes a revenant and decides to take shelter with them
3K notes
·
View notes
Text


“The law, in its majestic equality, forbids rich and poor alike to sleep under bridges, to beg in the streets, and to steal their bread.”
Anatole France quote sticker seen on an anti-homeless sign in Victoria, British Columbia
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
as someone who has been chronically homeless for 9 years due to severe disability, the way housing is managed in america is just a joke. it's all about the profits for the landlord, nothing else matters. credit checks are a gate to keep out poor people. deposits are a gate to keep out poor people. you wanna apply for a low-income housing program? you HAVE to have a "severe" disability diagnosis and proof that you're too disabled to afford or apply for "normal" housing. this is a gate to keep out poor people.
people in positions to help house homeless people don't care because they're housed. there's no sense of urgency. they don't have to think about what it's like to go without a roof over their head. they get paid tens of dollars an hour to sit there and scoff at all of the "lazy poor and disabled people who should just get jobs and stop whining and expecting to have things handed to them." they get paid to ignore emails and take 2 hour long lunches to forget about how hard and scary the world really is.
how the FUCK are you supposed to work when you don't have a place to sleep at night, shower, or eat? come the fuck on. use your goddamn brain. this system is built off of abuse, lying and torture. nobody earns an "honest" day's pay, none of this is "honest" work. it's all built off of the backs of lying and stealing from someone who needs it more. jobs aren't given to the person who's the most qualified- they're given to the person who lied the most to make themselves sound good during the interview. jobs are given to people who are good at interviews, NOT people who are GOOD at what they do.
i don't know how to tell you that when the average person isn't making enough to eat, fuel their car or pay for their phone, they also can't afford the roof over their head. disabled people and low-income people are struggling even worse with this. i don't know how to tell people that you should care about this.
we are literally all the same species. we are all humans. you cannot look down on disabled, poor and addicted people because we're "scum" and "less than human". we're not. that's a lie you're being fed by capitalism to feel better about yourself so you'll keep blindly working. wake up. this is not how humans behave. you're being brainwashed. everyone needs a stable home. EVERYONE. especially if you want them to contribute to your stupid money machine.
capitalism makes no fucking sense. give people homes or get the fuck out of our way, because we're about to just start taking them. this is unsustainable. this is unliveable. this system doesn't fucking work. a system that leaves its people to starve and die while apartments, homes, condos, and hotel rooms stay empty and collect dust doesn't work. none of this shit works. fuck this fascist system. none of us are free.
#homelessness#housing#human rights#punk#trans punx#trans punks#queer punks#cripplepunk#cripple punk#crip punk#cpunk#our writing#about us#anticapitalism#antiwork#anti capitalism#anti work
782 notes
·
View notes
Text

#homeless#homeless people in edinburgh offered beds 250 miles away weeks after city declares housing emergency#homeless people#rent is theft#rent is too damn high#landlords are parasites#fuck landlords#landlords are scum#landlords are leeches#landlords are bastards#i’m a housing lawyer – landlords use new loophole to push out tenants in ‘bad faith’ evictions#landlords#i took my landlord to court over common rental problem that made my life hell and won $14#court dismisses assault on landlord and son who threw student out in his ‘jocks’ after no rent paid#we had to flee our home as it was invaded by mice & bedbugs – inspectors said it’s ‘deplorable’ but landlord won’t act#landlord#rental#rent#auspol#politas#ausgov#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich
855 notes
·
View notes
Text

Homelessness and unhoused people are issues that are no longer results individual character flaws. They are byproducts of policies, byproducts of capitalism, byproducts of corporate greed, and byproducts of myths regarding bootstrapping/meritocracy.
Punishment does not address housing.
Housing addresses housing.
428 notes
·
View notes
Text
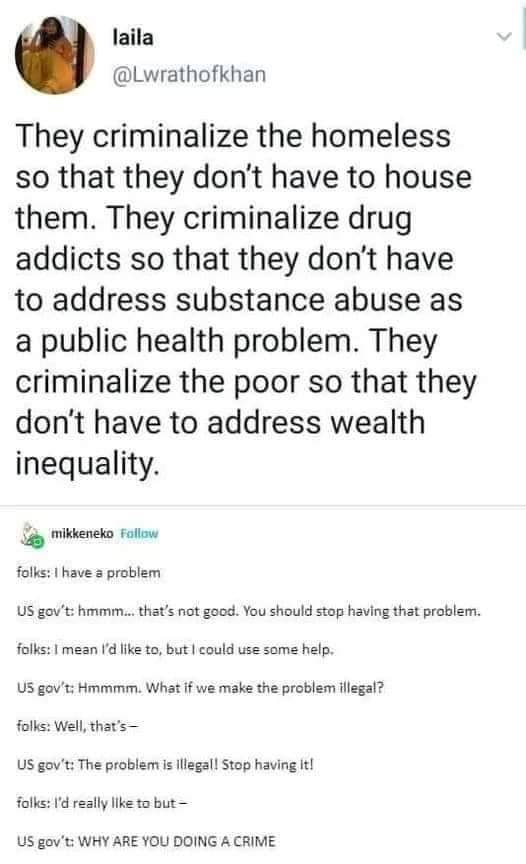
#human rights and civil liberties#poverty#classism#capitalism#homelessness#communism#fuck capitalism#late stage capitalism#housing rights#substance use#decriminalize drugs#decriminalised#crimes against humanity#class warfare
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


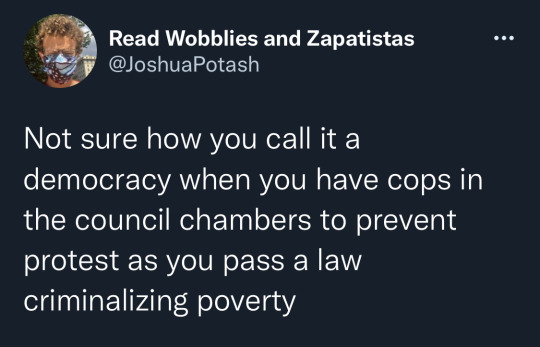
8.2.22. Los Angeles
LA City Council voted to criminalize sitting in public on 20% of LA’s land in an effort to strengthen police power and funnel more unhoused and Black and brown people into jails. Council members used police to clear the chamber of protesters, and nearly all people in the chamber, in order to pass the measure without protest.
[Image 1 shows a line of police officers with their backs turned to the city council bench, facing an empty council chamber minus one person sitting in a bench, possibly a journalist.]
#los angeles#defund lapd#abolish police#tweet#8.3.22#housing is a human right#homelessness#41.18#city council
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
Let People On Food Stamps Eat Hot Meals
Particularly on cold, rainy days (like today), while unhoused, sometimes all I want is a hot meal but it’s so difficult (if not impossible) to cook outside in the rain.
On top of this, I’m physically disabled and chronically ill. Medically, I’m supposed to have assistance with making meals as part of in home care. But I can’t get in home care without a home.
I just finished making dinner for my partner and I, it took 2 hours (3 if you include clean up). My knees are burning, my back is aching in it’s core, I feel like I’m about to faint, and all my joints are screaming. But it’s the only way we could have a hot meal today and get some protein, which is vital for our health conditions.
People judge us for using what little funds we have on McDonald’s some days. Because sometimes, it’s the only hot meal we’ve had in days. And sometimes I’m physically unable to stand, move, and do all the actions needed to cook. Or I faint while cooking. Or the rain doesn’t let up. Or we don’t have access to a kitchen for the day. Or the fire danger outside is too high. The list goes on.
Without my own kitchen to use, I don’t get to sit down while I cook (right now, everything is wet from the rain), I can’t meal prep, I can’t stock up on freezer meals, I can’t use an oven or a microwave to reheat leftovers, I can’t just reach across the kitchen for a fridge item (we have a small amount of fridge space friends let us use), everything about cooking is exponentially harder.
And even if I had 24/7 access to an accessible, full kitchen, it’s not even physically safe to cook my own meals. Even then, having a pre-made, hot, ready-to-eat meal could keep me safe and give me independance.
And all the safety needs for hot meals aside, emotionally, hot meals are also life saving and comfort. Meals are a part of community, culture, love and art.
So many gatherings we have as communities center around food. Most people in the United States would think of ones that often hold great value to Western culture. Mother’s Day breakfast. Spaghetti fundraisers. Wedding cakes. Birthday dinners. Bake sales. Carnival treats. BBQs on weekends. Holiday roasts. Lunches with friends. Casseroles brought to grieving neighbors.
Our world revolves around food.
I firmly believe that no poor person could ever “take advantage” of a system designed to feed us by using food stamps on hot food. This restrictive rule serves no purpose but to punish the most vulnerable of poor people— unhoused, disabled, and those of us living in unsafe conditions.
It also serves to restrict our access to joy and comfort. The joy can sometimes come from the food itself, but also the joy from having shared experiences solidified by the sounds of laughter and forks clinking on plates. The comfort can sometimes also be from the food itself, but also the experience of being loved and cared for while your close friend brings you pizza from your favorite restaurant because you lost your drive to eat three weeks ago and they worry about you. They know you. Those slices of pizza bring color back into your world.
Poor people deserve to be able to have the comfort, joy, and care that goes into a hot meal. We deserve the autonomy to choose foods that are best for us ourselves. We deserve to be able to eat in ways that are accessible to us.
Above all, we deserve access to hot meals.
Originally posted to my blog on 6.3.22
#disability#chronically couchbound#disabled#cripple punk#cripplepunk#disabled pride#disability pride#unhoused#homelessness#poverty#homeless#housing crisis#houselessness#houseless#ebt#ebt food stamps#foodstamps#food stamps#food stamps ebt#poor#food pantries#food banks#food bank#homeless youth#disabled homeless#food sovereignty#poor rights#unhoused rights#homeless rights#chronic homelessness
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Paywall-free version
On the outskirts of Austin, Texas, what began as a fringe experiment has quickly become central to the city’s efforts to reduce homelessness. To Justin Tyler Jr., it is home.
Mr. Tyler, 41, lives in Community First! Village, which aims to be a model of permanent affordable housing for people who are chronically homeless. In the fall of 2022, he joined nearly 400 residents of the village, moving into one of its typical digs: a 200-square-foot, one-room tiny house furnished with a kitchenette, a bed and a recliner.
The village is a self-contained, 51-acre community in a sparsely populated area just outside Austin. Stepping onto its grounds feels like entering another realm.
Eclectic tiny homes are clustered around shared outdoor kitchens, and neat rows of recreational vehicles and manufactured homes line looping cul-de-sacs.
There are chicken coops, two vegetable gardens, a convenience store, art and jewelry studios, a medical clinic and a chapel.
Roads run throughout, but residents mainly get around on foot or on an eight-passenger golf cart that makes regular stops around the property.
Mr. Tyler chose a home with a cobalt-blue door and a small patio in the oldest part of the village, where residents’ cactus and rock gardens created a “funky, hippie vibe” that appealed to him. He arrived in rough shape, struggling with alcoholism, his feet inflamed by gout, with severe back pain from nearly 10 years of sleeping in public parks, in vehicles and on street benches.
At first, he kept to himself. He locked his door and slept. He visited the clinic and started taking medication. After a month or so, he ventured out to meet his neighbors.
“For a while there, I just didn’t want to be seen and known,” he said. “Now I prefer it.”
Between communal meals and movie screenings, Mr. Tyler also works at the village, preparing homes for the dozen or more people who move there each month.
In the next few years, Community First is poised to grow to nearly 2,000 homes across three locations, which would make it by far the nation’s largest project of this kind, big enough to permanently house about half of Austin’s chronically homeless population.
Tiny-home villages for people who have been homeless have existed on a small scale for several decades, but have recently become a popular approach to addressing surging homelessness. Since 2019, the number of these villages across the country has nearly quadrupled, to 124 from 34, with dozens more coming, according to a census by Yetimoni Kpeebi, a researcher at Missouri State University.
Mandy Chapman Semple, a consultant who has helped cities like Houston transform their homelessness systems, said the growth of these villages reflects a need to replace inexpensive housing that was once widely available in the form of mobile home parks and single room occupancy units, and is rapidly being lost. But she said they are a highly imperfect solution.
“I think where we’re challenged is that ‘tiny home’ has taken on a spectrum of definitions,” said Chapman Semple. Many of those definitions fall short of housing standards, often lacking basic amenities like heat and indoor plumbing, which she said limits their ability to meet the needs of the population they intend to serve.
But Community First is pushing the tiny home model to a much larger scale. While most of its homes lack bathrooms and kitchens, its leaders see that as a necessary trade-off to be able to creatively and affordably house the growing number of people living on Austin’s streets. And unlike most other villages, many of which provide temporary emergency shelter in structures that can resemble tool sheds, Community First has been thoughtfully designed with homey spaces where people with some of the highest needs can stay for good. No other tiny home village has attempted to permanently house as many people.
Austin’s homelessness rate has been rapidly worsening, and the city’s response has whipped back and forth... In October [2023], the official estimate put the number of people living without shelter at 5,530, a 125 percent increase from two years earlier. Some of that rise is the result of better outreach, but officials acknowledged that more people have become homeless. City leaders vowed to build more housing, but that effort has been slowed by construction delays and resistance from residents.
Meanwhile, outside the city limits, Community First has been building fast. [Note from below the read more: It's outside city limits because the lack of zoning laws keeps more well-off Austin residents from blocking the project, as they did earlier attempts to build inside the city.] In a mere eight years, this once-modest project has grown into a sprawling community that the city is turning to as a desperately needed source of affordable housing. The village has now drawn hundreds of millions of dollars from public and private sources and given rise to similar initiatives across the country.
This rapid growth has come despite significant challenges. And some question whether a community on the outskirts of town with relaxed housing standards is a suitable way to meet the needs of people coming out of chronic homelessness. The next few years will be a test of whether these issues will be addressed or amplified as the village expands to five times its current size.
-via New York Times, January 8, 2024. Article continues below (at length!)
The community versus Community First
For Alan Graham, the expansion of Community First is just the latest stage in a long-evolving project. In the late 1990s, Mr. Graham, then a real estate developer, attended a Catholic men’s retreat that deepened his faith and inspired him to get more involved with his church. Soon after, he began delivering meals as a church volunteer to people living on Austin’s streets.
In 1998, Mr. Graham, now 67, became a founder of Mobile Loaves and Fishes, a nonprofit that has since amassed a fleet of vehicles that make daily rounds to deliver food and clothing to Austin’s homeless...
Talking to people like Mr. Johnston [a homeless Austin resident who Graham had befriended], Mr. Graham came to feel that housing alone was not enough for people who had been chronically homeless, the official term for those who have been homeless for years or repeatedly and have physical or mental disabilities, including substance-use disorders. About a third of the homeless population fits this description, and they are often estranged from family and other networks.
In 2006, Mr. Graham pitched an idea to Austin’s mayor: Create an R.V. park for people coming out of chronic homelessness. It would have about 150 homes, supportive services and easy access to public transportation. Most importantly, it would help to replace the “profound, catastrophic loss of family” he believed was at the root of the problem with a close-knit and supportive community.
The City Council voted unanimously in 2008 to lease Mr. Graham a 17-acre plot of city-owned land to make his vision a reality. Getting the council members on board, he said, turned out to be the easy part.
When residents near the intended site learned of the plan, they were outraged. They feared the development would reduce their property values and invite crime. One meeting to discuss the plan with the neighborhood grew so heated that Mr. Graham was escorted to his car by the police. Not a single one of the 52 community members in attendance voted in favor of the project.
After plans for the city-owned lot fell apart and other proposed locations faced similar resistance, Mr. Graham gave up on trying to build the development within city limits.
In 2012, he instead acquired a plot of land in a part of Travis County just northeast of Austin. It was far from public transportation and other services, but it had one big advantage: The county’s lack of zoning laws limited the power of neighbors to stop it.
Mr. Graham raised $20 million and began to build. In late 2015, Mr. Johnston left the R.V. park he had been living in and became the second person to move into the new village. It grew rapidly. In just two years, Mr. Graham bought an adjacent property, nearly doubling the village’s size to 51 acres and making room for hundreds more residents.
And then in the fall of 2022, he broke ground on the largest expansion yet: Adding two more sites to the village, expanding it by 127 acres to include nearly 2,000 homes.
“No one ever really did what they first did, and no one’s ever done what they’re about to do,” said Mark Hilbelink, the director of Sunrise Navigation Center, Austin’s largest homeless-services provider. “So there’s a little bit of excitement but also probably a little bit of trepidation about, ‘How do we do this right?’”
What it takes to make a village
Since he moved into Community First eight years ago, Mr. Johnston has found the stability that eluded him for so long. Most mornings, he wakes up early in his R.V., feeds his scruffy adopted terrier, Amos, and walks a few minutes down a quiet road to the village garden, where neat rows of carrots, leeks, beets and arugula await his attention.
Mr. Johnston worked in fast-food restaurants for most of his life, but he learned how to garden at the village. He now works full time cultivating produce for a weekly market that is free to residents.
“Once I got here, I said, This is where I’m going to spend pretty much my entire life now,” Mr. Johnston said.
Everyone at the village pays rent, which averages about $385 a month. The tiny homes that make up two-thirds of the dwellings go for slightly lower, but have no indoor plumbing; their residents use communal bathhouses and kitchens. The rest of the units are R.V.s and manufactured homes with their own bathrooms and kitchens.
Like Mr. Johnston, many residents have jobs in the village, created to offer residents flexible opportunities to earn some income. Last year, they earned a combined $1.5 million working as gardeners, landscapers, custodians, artists, jewelry makers and more, paid out by Mobile Loaves and Fishes.
Ute Dittemer, 66, faced a daily struggle for survival during a decade on the streets before moving into Community First five years ago with her husband. Now she supports herself by painting and molding figures out of clay at the village art house, augmented by her husband’s $800 monthly retirement income. A few years ago, a clay chess set she made sold for $10,000 at an auction. She used the money to buy her first car.
“I’m glad that we are not in a low-income-housing apartment complex,” she said. “We’ve got all this green out here, air to breathe.”
A small number of residents have jobs off-site, and a city bus makes hourly stops at the village 13 times a day to help people commute into town.
But about four out of five residents live on government benefits like disability or Social Security. Their incomes average $900 a month, making even tiny homes impossible to afford without help, Mr. Graham said.
“Essentially 100 percent of the people that move into this village will have to be subsidized for the rest of their lives,” he said.
For about $25,000 a year, Mr. Graham’s organization subsidizes one person’s housing at the village. (Services like primary health care and addiction counseling are provided by other organizations.) So far, that has been paid for entirely by private donations and in small part from collecting rent.
This would not be possible, Mr. Graham said, without a highly successful fund-raising operation that taps big Austin philanthropists. To build the next two expansions, Mr. Graham set a $225 million fund-raising goal, about $150 million of which has already been obtained from the Michael and Susan Dell Foundation, the founder of the Patrón Spirits Company, Hill Country Bible Church and others.
Support goes beyond monetary donations. A large land grant came from the philanthropic arm of Tito’s Handmade Vodka, and Alamo Drafthouse, an Austin-based cinema chain, donated an outdoor amphitheater for movie screenings. Top architectural firms competed for the chance to design energy-efficient tiny homes free of charge. And every week, hundreds of volunteers come to help with landscaping and gardening or to serve free meals.
Around 55 residents, including 15 children, live in the village as “missionals” — unpaid neighbors generally motivated by their Christian faith to be part of the community.
All missionals undergo a monthslong “discernment process” before they can move in. They pay to live in R.V.s and manufactured homes distinguished by an “M” in the front window. Their presence in the community is meant to guard against the pitfalls of concentrated poverty and trauma.
“Missionals are our guardian angels,” said Blair Racine, a 69-year-old resident with a white beard that hangs to his chest. “They’re people we can always call. They’re always there for us.”
After moving into the village in 2018, Mr. Racine spent two years isolated in his R.V. because of a painful eye condition. But after an effective treatment, he became so social that he was nicknamed the Mayor. Missional residents drive him to get his medication once a week, he said. To their children he is Uncle Blair.
Though the village is open to people of any religious background, it is run by Christians, and public spaces are adorned with paintings of Jesus on the cross and other biblical scenes. The application to live in the community outlines a set of “core values” that refer to God and the Bible. But Mr. Graham said there is no proselytizing and people do not have to be sober or seek treatment to live there.
Mr. Graham lives in a 399-square-foot manufactured home in the middle of the village with his wife, Tricia Graham, who works as the community’s “head of neighbor care.” He said they do not have any illusions about solving the underlying mental-health and substance-use problems many residents live with, and that is not their goal.
“This is absolutely not nirvana,” Mr. Graham said. “And we want people to understand the beauty and the complexity of what we do. I wouldn’t want to be anywhere else on the face of the planet than right here in the middle of this, but you’re not fixing these things.” ...
From an experiment to a model
Community First has already inspired spinoffs, with some tweaks. In 2018, Nate Schlueter, who previously worked with the village’s jobs program, opened Eden Village in his hometown, Springfield, Mo. Unlike in Community First, every home in Eden Village is identical and has its own bathroom and kitchen. Mr. Schlueter’s model has spread to 12 different cities with every village limited to 50 homes or fewer.
“Not every city is Austin, Texas,” Mr. Schlueter said. “We don’t want to build a large-scale village. And if the root cause of homelessness is a loss of family, and community is something that can duplicate that safety net to some extent, to have smaller villages to me seemed like a stronger community safety net. Everybody would know each other.”
The rapid growth of Community First has challenged that ideal. In recent years, some of the original missional residents and staff members have left, finding it harder to support the number of people moving into the village. Steven Hebbard, who lived and worked at the village since its inception, left in 2019 when he said it shifted from a “tiny-town dynamic” where he knew everyone’s name to something that felt more like a city, straining the supportive culture that helped people succeed.
Mobile Loaves and Fishes said more staff members had recently been hired to help new residents adjust, but Mr. Graham noted that there was a limit to what any housing provider could do without violating people’s privacy and autonomy.
Despite these concerns, the organization, which had been run entirely on private money, has recently drawn public support. In January 2023, Travis County gave Mobile Loaves and Fishes $35 million in American Rescue Plan Act funds to build 640 units as part of its expansion.
Then four months later came a significant surprise: The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development approved the use of federal housing vouchers, which subsidize part or all of a low-income resident’s rent, for the village’s tiny homes. This will make running the village much more financially sustainable, Mr. Graham said, and may make it a more replicable blueprint for other places.
“That’s a big deal for us, and it’s a big deal on a national basis,” Mr. Graham said. “It’s a recognition that this model, managed the way that this model is, has a role in the system.”
Usually, the government considers homes without indoor plumbing to be substandard, but, in this case, it made an exception by applying the housing standards it uses for single-room-occupancy units. The village still did not meet the required ratio of bathrooms per person, but at the request of Travis County and the City of Austin’s housing officials, who cited Austin’s “severe lack of affordable housing” that made it impossible for some homeless people with vouchers to find anywhere else to live, HUD waived its usual requirements.
In the waiver, a HUD staffer wrote that Mr. Graham told HUD officials over the phone that the proportion of in-unit bathrooms “has not been an issue.” But in conversations with The Times, other homeless-service providers in Austin and some village residents said the lack of in-unit bathrooms is one of the biggest problems people have with living there. It also makes the villages less accessible to people with certain disabilities and health issues that are relatively common among the chronically homeless....
Mr. Graham said that with a doctor’s note, people could secure an R.V. or manufactured home at the village, although those are in short supply and have a long waiting list. He said the village’s use of tiny homes allowed them to build at a fraction of the usual cost when few other options existed, and helps ensure residents aren’t isolated in their units, reinforcing the village’s communal ethos.
“If somebody wants to live in a tiny home they ought to have the choice,” Mr. Graham said, “and if they are poor we ought to respect their civil right to live in that place and be subsidized to live there.” But he conceded that for some people, “this might not be the model.”
“Nobody can be everything for everyone,” he said.
By the spring of 2025, Mr. Graham hopes to begin moving people into the next phase of the village, across the street from the current property. The darker visions some once predicted of an impoverished community on the outskirts of town overtaken by drugs and violence have not come to pass. Instead, the village has permanently housed hundreds of people and earned the approval and financial backing of the city, the county and the federal government. But for the model to truly meet the scale of the challenge in Austin and beyond, Chapman Semple said, the compromises that led to Community First in its current incarnation will have to be reckoned with.
“We can build smaller villages that can be fully integrated into the community, that can have access to amenities within the community that we all need to live, including jobs and groceries,” Chapman Semple said. “If it’s a wonderful model then we should be embracing and fighting for its inclusion within our community.”
-via New York Times, January 8, 2024
#housing crisis#unhoused#homelessness#homeless#housing#affordable housing#austin texas#austin#texas#texas news#united states#usa#poverty#cost of living#tiny home#tiny house#social support#community#good news#hope
371 notes
·
View notes
Text

Source


Source
#capitalism#housing crisis#homelessness#end homelessness#politics#us politics#government#the left#progressive#news#current events
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
We ask your questions so you don’t have to! Submit your questions to have them posted anonymously as polls.
#polls#incognito polls#anonymous#tumblr polls#tumblr users#questions#housing#homelessness#polls about people
429 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Without shelter people die"
Seen on an anti-homeless barrier in Seattle
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
have never understood why squatting is considered a crime. loitering too. sir you have been arrested for the crime of....chilling. and hanging out. and taking a little nap
#also homeless encampments are never in the way of anything and yet the cops still harrass them. its fucked up#like we straight up push people out of existence. and for what#i know im not saying anything new here im just mad abt htis#like!!! if its space nobodys using for shit who cares! who cares omg. if we arent gonna house people we shld at least let them exist#like theyre already having a hard enough time man.#im sick of how ppl around where i live talk abt the homeless problem as though homeless people are the problem that needs to be solved#like no empathy no self awareness these 'normal' ppl want the unhoused dead or in prison and dont get how ghoulish they sound. anyways
361 notes
·
View notes