#hard to work yourself up to the director's chair when all the entry positions involve standing for 14 hours at a time
Text

And in the Beginning There was... Light, Film Rolls, and Controversy.
Watching old movies has always been one of my favorite pastimes. I love the cracks in the film, the oddly tinted placements of color, the quick, scattered movements of the actors, and the slice of an intertitle. It all just makes sense when I think of those first filmmakers who were trying to make sense of their new medium. In my journey through film, I will start at the beginning. Well, sort of the beginning. Our main topic of discussion takes place in 1903. So we’ve skipped over a few years… 15 to be exact. I’ll sum them up now because if I miss a beat I’ll ruin the scene.
Let's start in October of 1888 when Louis Le Prince has just recorded the very first film. It’s short yet scenic; his family gathers in a garden and for the first time ever - they move. A man walks across the screen, the rigid bustles and day dress of two women sway as they turn away from the camera - ergo we have a moving image years before Edison would invent the kinetoscope. Of course, most don’t know of Le Prince and in school I never heard his name mentioned. In fact, I only heard of him through a Buzzfeed Unsolved video. So what happened? Why did history remember the names Edison and Lumière but not Le Prince?
There were many entries in the race to create the first film. And of course, there are arguments as to what cinema is in comparison to a bunch of still photographs played one after another. Strange, I think is this argument. For film is a series of stills or frames played one right after the other. Nevertheless, in 1878, we have the famous images of a galloping horse caught by twelve cameras set up by Muybridge to capture motion and to study animal locomotion. Motion but not a movie. What we needed was a camera that had a single lens capable of capturing a point of view. That’s what Le Prince did. Unfortunately, as history would see it, he mysteriously disappeared on a train to Paris in September 1890 right before his first public screening in New York carrying luggage that contained all of his work. Neither Le Prince or the luggage has ever been found. Quite the coincidence.
There are a few theories: Le Prince committing suicide, Le Prince’s own brother killing him, Le Prince fleeing due to his sexuality being outed but none have stuck... except one. Le Prince’s widow, Lizzie, believed Edison, his biggest competitor in the race, had him assassinated. The evidence? The discovery of Edison’s journal containing the following entry, which has been proven authentic. It read:
“Eric called me today from Dijon. It has been done. Prince is no more. This is good news but I flinched when he told me. Murder is not my thing. I'm an inventor and my inventions for moving images can now move forward.”
Take of that what you will.
Today, we are taught that Edison’s kinetoscope launched the novel medium of moving pictures into our familiar. When it was invented in 1891 by Edison and Dickson, the kinetoscope was a peepshow-like device with a "sight opening" on top that one viewer at a time could look into and watch a moving picture. Think about it like looking into a microscope - very different from how we view films now both in method and price, it was 50 cents for access to all films at a given venue.

In 1897, an improvement on Edison's device arose. Invented by the Lumière brothers, the cinematograph contained both a camera, projector, and hand crank. Now, audiences could sit and screen films. I'll circle back to Edison as he connects to our 1903 topic. But first, let's take a stop with the Lumière brothers.
Auguste and Louis Lumière are credited as the first filmmakers. Their documentary-esque films Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory and Arrival of a Train at La Ciotat are milestones in cinema. Known as travelogues or actualités, they showed the casual and working life of people in the mid to late 1890's. These shorts were even screened to audiences who jumped out of their seats at a train onscreen because they thought it would actually hit them. The Lumière Brothers took their screening all over the world, from Paris, to India, and China.
Watching these films, it's hard not to put yourself in the shoes of a passerby, a random person whose name we don't know, who exists in a few frames before disappearing to time. Like a fossil, it's interesting to examine what life was like back then. I love seeing the clothing. Everyone is so formal, at least compared to the laid back air of today. Even so, in the 1890’s people were moving away from the Victorian Era and into the “New Woman” Era. High necklines and longer sleeves were replaced by the open neck and short sleeves as morning turned to dusk. High chiffons under feathered hats were popular as was the shirtwaist style for work. All of these visible in the Lumière films.
Where we jump from reportage to fiction is where we jump from Lumière to Porter. And back to Edison, who had Porter working for him. Projectionist and electrician turned director, Edwin S. Porter was the brains behind many of the mechanics and techniques that have become so highly engrained in the making of films that the idea of them being novel seems almost impossible. In 1899, Porter became head of moving picture production at the Edison Manufacturing Company and throughout his career, which spanned about 15 years, he made more than 70 short films. So lets look at a few of them in detail.
Jack and the Beanstalk (1902)
You'll see that a lot of the narrative ideas for these early films spun directly out of fairytales. For an audience, fairytales were a familiarity. Thus, they were able to stitch together what they already knew about the characters and stories and better understand these new moving pictures. And Porter knew this from his work as a projectionist. He knew what engaged the audience most. And that wasn't just story, it was technique. Porter's films were revolutionary for what would become known as editing, at that time just cutting film. Simplistic and impactful, he knew how to compact time and create magic. Objects and people appear and disappear in a single cut. The camera remains still, a wide shot, and on a tripod but what's in front of it changes slightly, making for magical realism. For example, once Jack makes it back down to earth after descending the beanstalk, he grabs an ax and starts chopping it down. He's got to do this or the giant chasing him will make it down too. So he swings the ax a few times with all his might. From a large beanstalk, ripe with leaves, reaching up to the sky, we immediately cut to a destroyed one. The fact that we end one cut with Jack in the same position as we start the next, keeps from disrupting the audience even though everything else onscreen has changed. We've condensed time, Jack has saved the day, and the Giant has fallen to his death. Porter would expand on this editing style, perfecting it, discovering cross-cutting.
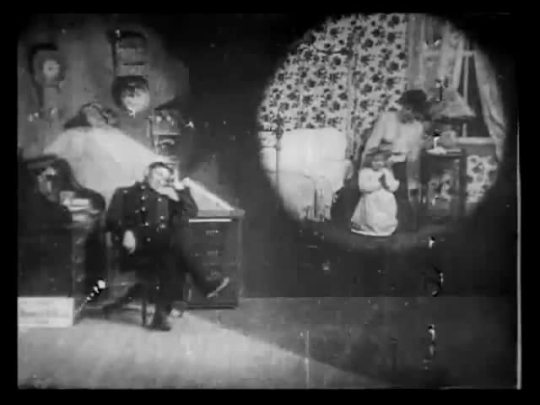
Life of an American Fireman (1903)
Cross-cutting or parallel action is so integral to editing that it happens in just about every film. Simply, two separate events are occurring - say, a woman trying to escape a fire inside of her house and firefighters rushing in a horse carriage to save her. These two events, perceived to be happening at the same time, are stitched together through editing so that the audience experiences both. Cut to the woman in her house as the fire inches closer to her. Cut to the firefighters rushing up the stairs. Will they get there? Will they save her? Cross-cutting serves to create tension and set the rhythm of a scene. Eventually, the two spatial points of view merge and the conflict should be resolved. This originates in Porter's films and Life of An American Fireman is the first one that shows it off.
Let's cut back to the first shot of this film, it's a trick shot. A sleepy fireman dreams of a mother putting her daughter to bed. Abruptly, the fire alarm is set off and he wakes up. Instead of cutting from the fireman dozing off in his chair to a separate shot of the mother, which would create confusion on whether the fireman was dreaming, Porter uses double exposure to frame the dream above the fireman shoulder. Double exposure had been employed by photographers since the 1860's to produce dreamy situations in otherwise ordinary places but in film, it first appears in Georges Méliès Four Heads are Better Than One. When we see the house aflame for the first time in Life of an American Fireman, the same mother and daughter from the dream pair reappear. The fireman's premonition connects back to the main drama of the story.

The Great Train Robbery (1903)
In this film we take the leap from a theatrical approach to cinematography, where the camera simply watches the action at a long-shot or observing eye, to being involved in the action. One way that Porter does this is by integrating the pan.
Panning is a technique that moves a camera side to side in a fixed location. We haven't taken the camera off of a tripod or stepped forward in anyway, we are simply turning left or right on the horizontal axis. If we took a step forward and followed a character or action we'd have a tracking shot. But we aren't there yet so plant your feet in the ground for now. Porter uses pans to reveal. The first pan is executed about six minutes into the film. The robbers jump off the caboose with their stolen goods and make a run for it. But where are they going? Queue the pan and we find out it's down some steep hills and into a forest. The subsequent shot is them in the thicket of a forest. Running passed the camera until all but one have exited camera left. But how will they get out? Queue the second pan to reveal horses - their getaway plan. This pan is masterfully done. I love the way Porter keeps his camera static and just observes the tumbling, running robbers until only one is left onscreen. Then and only then does he pan left to reveal the horses. By leaving only one person onscreen, not only does the audience have less to track but so does the camera. Simplifying the frame down to only the necessities of the action, one robber running away in a forest, amplifies the pan and makes the reveal feel complete - we reunite with the group of robbers and horses.
Depending on which version of the film you watch, you might be surprised by waves of color among a sea of black and white. Tinting whole films blue, amber, or sepia has been around since the origins of moving pictures, but in The Great Train Robbery, Porter selects specific actions or objects to tint. This was all done by hand.
Color is one big manipulator. Think of light blue and you'll likely picture endless summer skies; an air of calm. How about Green? I picture the tangled tree webs of a jungle - adventure, growth, the smell of dew on fresh leaves, nature. Now red. Explosions, fire, burst of emotion. Yellow? A bright, morning sun, a blooming sunflower, happiness, positivity, a new start. Early filmmakers used color to bring attention to specific objects, people, and actions. They used it to draw out an emotion from the viewer. They used it to connect themes of violence, love, and happiness. And they used it to spice up their frame.
Porter hand paints the explosion of a train lockbox bright orange and a deep red. The smokey pops from gunshots are also a fiery red. The dress of a dancing woman is bright yellow. The coat of another girl is a rich purple. The addition of color cultivates realism but also gives the film a flair of the imaginary.

So, we have the creative process of tinting to enhance the visual characteristics of a story and we have panning to push forward the important aspects of a narrative. Let's add a few more ingredients to our recipe.
Because the story cuts back and forth between the robbers, the operator, and the posse of men who will eventually hunt down the robbers, it has parallel action. Three separate storylines, integrated through the edit, that coverage at the end. Now that we have the way in which the story is cut and delivered, how about some specific effects?
In shots where the action occurs inside the prop train, which is not moving but the audience is meant to believe it is, Porter uses double exposure to ground his location in reality. He filmed exterior, moving shots and layered them onto the static train shots. In the '30s this would become known as "rear projection".
Additionally, Porter creatively placed his camera in new ways to produce frames that diverged from the typical wide shot; bringing the viewer closer into the action. For example, at about 2 minutes and 50 seconds in, the camera is propped on top of the engine car roof while a sneaking robber crawls passed and kills a fireman.
At last we arrive at the final shot. Diverging from the narrative, Porter set this up to look like a wanted poster. It is filmed in a medium close-up, which serves to focus all attention on the subject by filming them waist-up, having them fill up most of the frame, and blocking out the surrounding environment. The robber points his revolver right at the camera and shoots six times. If you've ever seen Goodfellas, Martin Scorsese recreates this at the end with Joe Pesci. Seemingly, the purpose was to shoot the audience. To tell them even though all of these robbers were killed in the end, their spirit doesn't die. It says "I'm warning you- it's still dangerous out there." Funny enough, this wasn't even the original intention. The shot was promotional and where it ended up in the film was entirely up to the projectionist. It could've just as well been placed at the beginning if they wanted. Even so, the break in the fourth wall and punch of dramatics that ended the film still prevail through cinema history today. Completing the recipe for one the first Westerns, ripe with shootouts, chase sequences, bandits, and suspense.
The Kleptomaniac (1905)
When moving pictures are void of sound and spoken dialogue it's a bit difficult to understand what characters are doing onscreen. Heightened emotional and physicalized acting made up for this. Through facial expressions and over the top, exaggerated body movements, audiences could connect the dots to figure out what was going on in a scene. But in 1903, Porter directed Uncle Tom's Cabin and introduced intertitles, words that would appear printed onscreen. Early iterations of intertitles read like book chapters. They described the main action that was about to take place in the scene. In Uncle Tom's Cabin some examples include: "The Escape of Eliza", "Rescue of Eva", and "Tom and Eva in the Garden. In The Kleptomaniac, intertitles state location and give context to where we are, which is helpful because without them, I don't think I could follow what was going on - at all.
Location is such a main element in this film that intertitles are practically non negotiable. "Leaving Home", "Arriving at the Store", "Home of Thief", and "Court Room Scene", prepare us with the information that is necessary to fully understand the purpose of each scene. The department store shot isn't clear-cut. It could've been a mail room or an office. If we miss that it's a department store that our main character is visiting (and stealing from), we miss the connection to the thief stealing food later on in the film and thus miss the whole theme of class disparities. The intertitles supplement for lack of onscreen information and sound. They would be used regularly in the silent era, branching into dialogue intertitles and expositionary intertitles before dying out with the advent of sound.
2 notes
·
View notes