#archaeology news
Text
An international team of researchers has discovered the oldest skeletal remains belonging to a stroke victim. The mummy, unearthed near Luxor in Egypt, belonged to a woman who lived about 2,700 years ago.
238 notes
·
View notes
Text




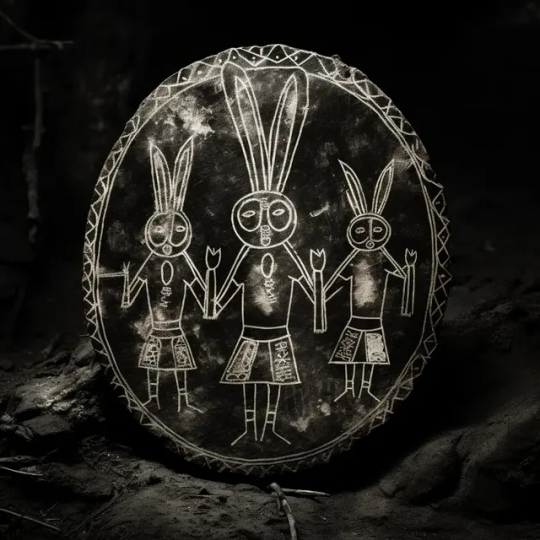
More Than Just Scent Marks.
Evidence of Hare cultures can be found throughout ages, across biomes, and within the traditions of the unlikeliest of critters.
No matter your nation, Hares have come closer than you think! And their influence runs further than you could imagine...
Visit frogiverse.com for more
#archaeology#educational#history#artifacts#fantasy#worldbuilding#culture#ancient artifacts#frogs#nature#archaeology news#history news#history memes#anthropology memes#pictographs#historical photos#turtles#tortoises#stoner#stones#pictograph#petroglyphs#glyphs
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
evidence shows that prehuman hominids were inventing new technology and building structures, before humans may have even existed
"Researchers from the University of Liverpool and Aberystwyth University used a new method called luminescence dating to date the wood, which is able to work out age by measuring the last time minerals were exposed to sunlight.
"They discovered that the structure was much older than they had expected, dating back at least 476,000 years.
"The earliest evidence of Homo sapiens is from around 300,000 years ago."
shattering our idea that pre-Babylonians were hunter-gatherers this evidence points to the need to redefine the term "stone age," as well as the entire idea that technological progress is linear and ever-increasing...
It looks like the rarity of ancient wooden structures is more to do with how difficult it is to preserve wood for eons; it's clearly a false assumption that ancient hominids were only using stone tools...
Given how difficult and rare it is for wood to be preserved, it's possible that wood use was much more ubiquitous in ancient prehistory. The amount of archaeology left to discover, potentially underwater, is unfathomable...
#archaeology news#another “peek-a-boo” moment for scientists#just because you can't find it yet doesn't prove it doesn't exist...
1 note
·
View note
Text
Indiana Jones and the academic beef
#cannot stop thinking about if the new movie is set in the 60s#what does Jones think about Binford and Processual Archaeology
6K notes
·
View notes
Text


‘Incredible’ Mosaics Were Found in an Ancient Luxury Home in Rome
Italy’s Culture Minister Gennaro Sangiuliano has called the works “an authentic treasure.”
Researchers working in the Archaeological Park of the Colosseum in Rome have shared their discovery of luxurious mosaic-tiled rooms found in an ancient home on the site, which they believe may have belonged to a Roman senator. Created from shells, glass, white marble, and Egyptian blue tiles, the mosaics have been described by Italy’s Culture Minister Gennaro Sangiuliano as “an authentic treasure”.
The “rustic” mosaics, found on the grounds surrounding the Colosseum in the heart of the city, date to the late Republican Age, in the last decades of the second century B.C.E., and show a series of figurative scenes. They once decorated a townhouse, or domus, owned by an upper class citizen. Italy’s Ministry of Culture have said that “due to the complexity of the scenes depicted” and their age, the mosaics are “without comparison.”



One mosaic depicts a coastal city with towers and porticos, with three large ships floating by on the ocean waves. The culture ministry believes this could be a reference to naval victories achieved by the owner of the home, which is believed to have been a Roman senator. This is supported by historical sources describing the area as having been occupied by such high-ranking members of society.
The decorated walls were likely located in the home’s dining rooms, where luxurious banquets would be hosted, and guests at these events were likely wowed with “spectacular water games,” according to the culture ministry, based on the presence of lead pipes set into the walls.
In the reception room, an extremely well preserved decorated stucco featuring landscapes and figures was also discovered. Other designs include vines and lotus leaves flowing from vases, musical instruments, and tridents.
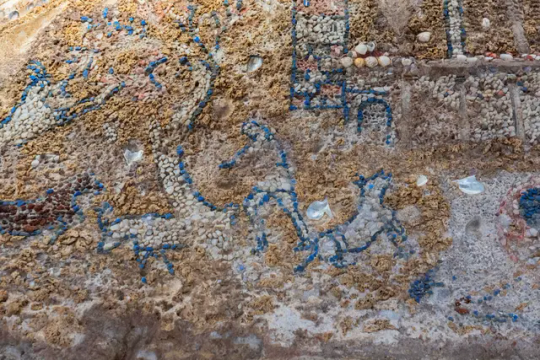


The mosaic walls were first discovered near the Colosseum in 2018, but excavation at the site will continue into 2024, and more rooms could be discovered. Alfonsina Russo, the Director of the Archaeological Park of the Colosseum, has said that once the domus is full uncovered, “we will work intensely to make this place, among the most evocative of ancient Rome, accessible to the public as soon as possible.”
By Verity Babbs.
#‘Incredible’ Mosaics Were Found in an Ancient Luxury Home in Rome#Archaeological Park of the Colosseum#Late Republican Age#second century B.C.E.#mosaic#roman mosaic#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient rome#roman history#roman empire#roman art
976 notes
·
View notes
Text
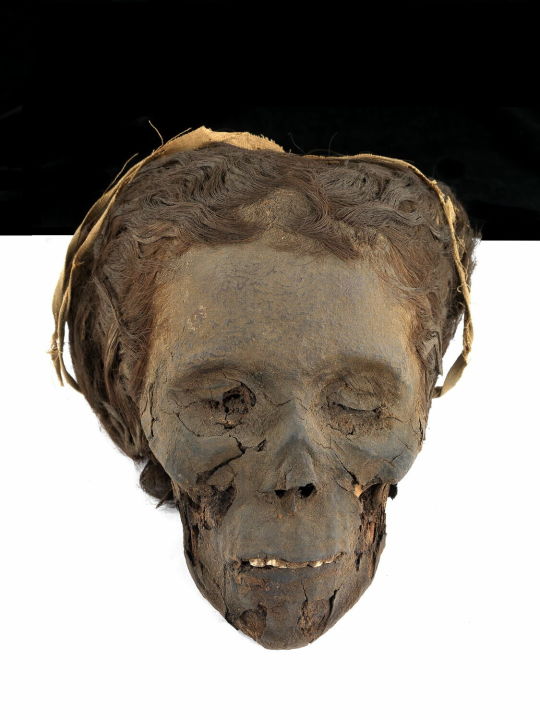
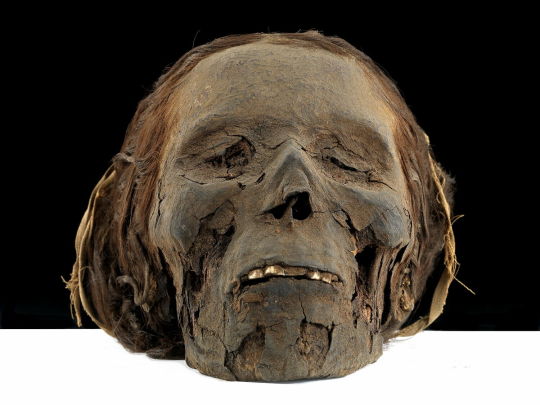
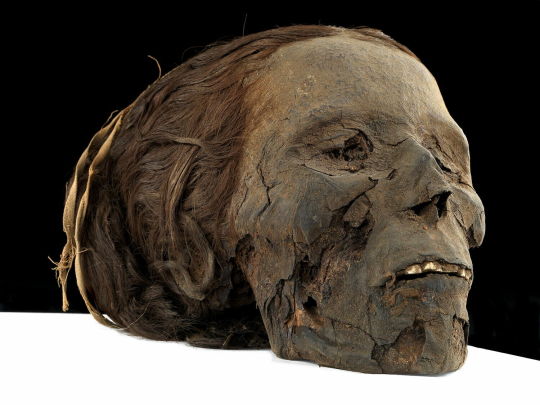
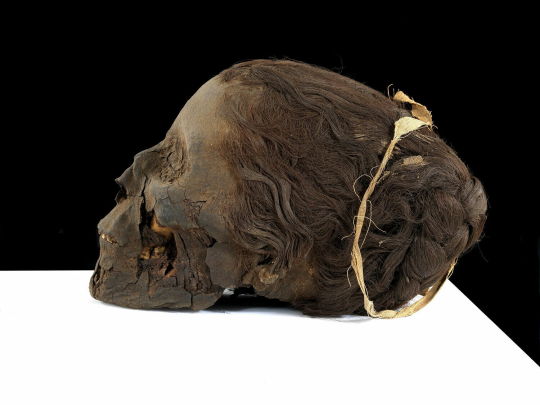
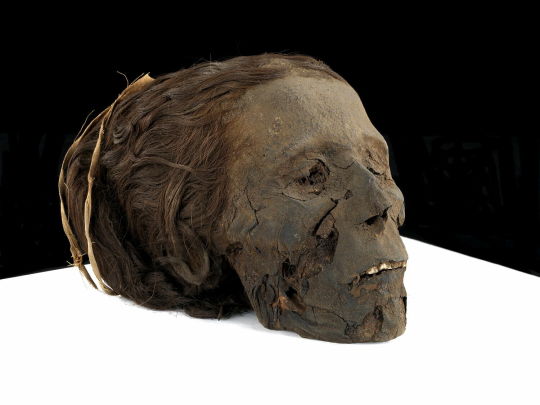








~ Woman Mummy.
Date: 1550-332 B.C.
Period: New Kingdom, Late Period
Medium: Organic; Secondary Medium: Resin, linen (?)
#ancient#ancient art#history#museum#archeology#ancient egypt#ancient history#archaeology#mummy#woman mummy#late period#1550 b.c.#332 b.c.#new kingdom#hair
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Taos Pueblo, New Mexico, circa 1880.
789 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why was the ancient city of Ephesus suddenly abandoned? The recent discovery of a beautifully preserved business district full of coins, food, amphorae, lamps, and pilgrim souvenirs, deepens the mystery.
#Turkey#Byzantine#Sassanian#restaurant#coins#amphora#ancient Greek#ancient origins#ancient#history#archaeology news#archaeology
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
fiber art adventures in egypt
I recently got back from a trip to Egypt & finally got around to organizing some pictures to share. One of the things I was most excited about was seeing what I could find on fiber arts and textiles.
Dropping everything under a read more, 'cause this will be a long post haha
first visit: the National Museum of Egyptian Civilization (NMEC)
At the time of visiting, they had a special textiles exhibit. It covered Pharonic Egypt all the way up to modern times, although I only had time to check out the dynastic & a bit of the Coptic portion of the exhibit (which was what I was really hoping to see anyways)


Was super excited to see this diorama in person. I knew about it but had never seen good pictures of it. From the little I've seen of ancient Egyptian spinning, spinning with two spindles seems to be the norm rather than a master technique? It also shows up in tomb art, which the exhibit also shared:

They also used a different fiber preparation (splicing to create a rove of fiber, no traditional drafting to my understanding) so that probably made a difference? Regardless I really want to see if I can replicate the technique, especially because their spindles look so similar to modern spindles??


I took so many pictures of spindles, guys, and I fully intend to either have a few replicas made or to learn to make some myself. Also, although they were unlabeled... I'm pretty sure those are beaters for weaving? That was a bit of a trend with this trip, so much stuff was unlabeled :( I would've killed to at least get some date estimates for some of the stuff they had on display. I was nerding out in here though, and my family took a few pictures of how excited I was getting. A bit embarrassing, but eh haha
The exhibit also had a section on natural dyes used with a fun visual;
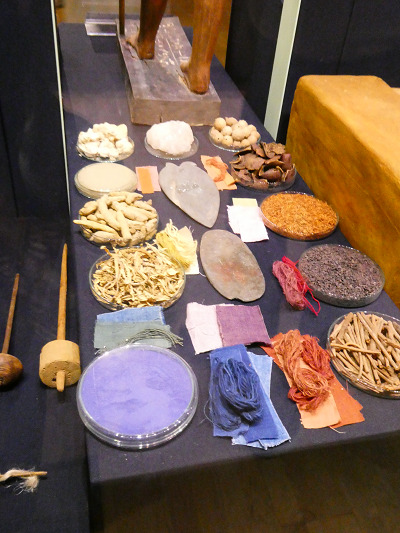

There was several diagrams specifically describing each dye source, but in the interest of not overloading on pictures I'll just list them out. For blues; woad, Yellows; turmeric, safflower, saffron, or yellow ochre; reds; madder, henna, pomegranate, and kermes. I originally thought kermes was another way to say cochineal, but it only seems to be distantly related.
next visit: Ramses Wissa Wassef Art Center
A small art center dedicated to hand-weaving wool and cotton tapestries. All of their work was museum quality & awe inspiring!!
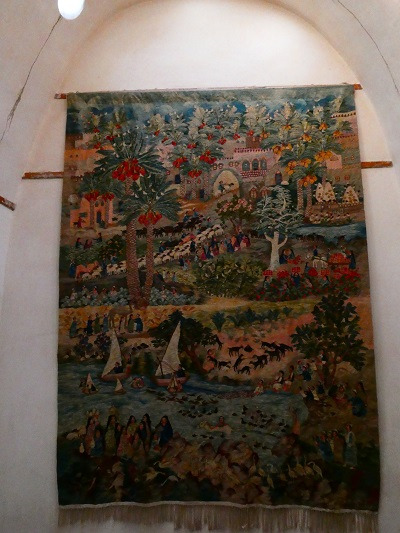



Was even invited to their back rooms to watch a few of their weavers working; no I don't have room to put a room-sized loom anywhere but heck do I want one now



Our guide that took us through talked a bit about the natural dyes they use (all of their dyes are dyed in house with what they grow in their dye garden!!!) and got excited to hear I was also interested in natural dyes! He seemed a bit disappointed I'd never worked with indigo and. while indigo scares me, I'll take it as a sign that maybe I should try some time this year haha.
final visit; the Egyptian Museum
we really had to rush through this one which was a huge shame because it's packed full of artifacts. Also, the lighting in there is atrocious, so apologies for the not great pictures ahead.
They had a fascinating display of textile tools, more than what the NMEC had;



(Hand for size reference) I want all of these spindles! So badly! But a few of them look so much like a few of the spindles I own already?? A few of them had a spiraling notch, that's so cool? But also, what's going on with the one with two whorls? I have no idea. I'm fascinated.


Look at these whorls!! Although again, I'm a bit confused; the lack of labeling strikes again. Unsure why some of these "whorls" have two holes, or what the metal object with the wooden handle is. The display implies sewing needles, and some of them do look like it, but others.... really don't look like sewing needles. I'm absolutely enchanted by this little whorl though. I think it has birds on it?



More objects that I'm baffled by- the signage doesn't really indicate what some of this stuff is, if it's even known. Also confused by the object wrapped in white string in the right pic; it looks like a distaff but to the best of my knowledge the (ancient at least) Egyptians didn't use distaffs. It probably popped up in later times and was put in this display since it was still relevant, but I'm still not sure.
I have so many more pictures & thoughts but I'll save those for more specific future projects. I've been doing research outside this trip on ancient Egyptian spinning techniques and desperately want to go deeper into that, this trip just solidified how excited it makes me. If you made it all the way through this, many thanks for reading!
Bonus; look at this ancient linen 🥺

#hand spinning#archaeology#extant artifact#weaving#fiber arts#long post#letters from skylark#sorry for the overall low quality images in this post. Got a new camera and wasn't the best at using it this trip#also the raw image files were huge so I heavily downsized them to make sure this post wasn't a beast to load#would be happy to share the raw images if desired though
247 notes
·
View notes
Text
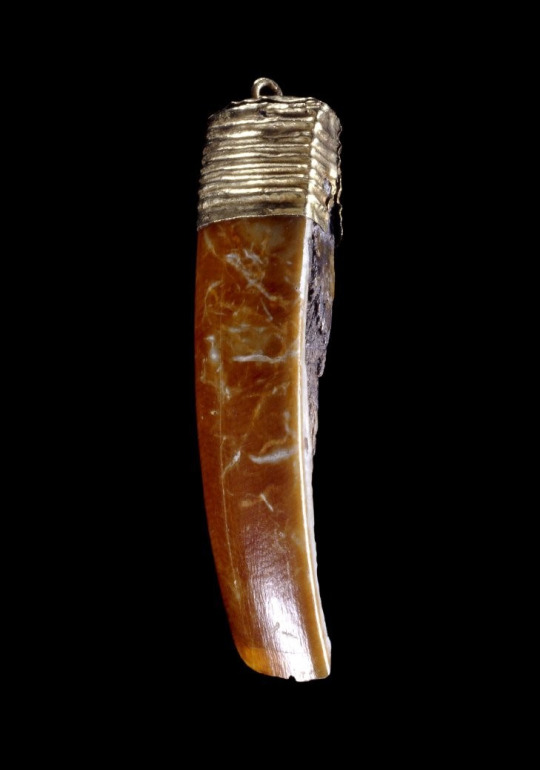

An Anglo-Saxon beaver tooth amulet discovered at the Wigber Low burial site in Derbyshire.
A 6th-century Anglo-Saxon riddle describes the beaver:
I am a dweller on the edge of steep stream banks, and not lazy at all, but warlike with the weapons of my mouth.
I sustain my life with hard labour, laying low huge trees with my hooked axes.
I dive into water, where the fish swim, and immerse my own head, wetting it in the watery surge.
The wounds of sinews and limbs foul of gore I can cure. I destroy pestilence and the deadly plague. I eat the bitter and well-gnawed bark of trees.
The Eurasian Beaver was hunted to extinction in Britain by the 16th century; since 2009, there has been an ongoing project to reintroduce them in Scotland.
#no idea there'd ever been beaver in Europe#no wonder they were so stoked to find more to kill in the New World#shiny objects#anglo-saxons#archaeology
290 notes
·
View notes
Video
Science Association Aranzadi has made a discovery that can be a landmark for the history of Basque language. In an Iron Age Vascon town of Irulegi, in the region of Aranguren (Nafarroa), an inscripted bronze hand from the 1st century BCE has surfaced. It’s the longest and oldest Basque text until now. It’s written in a variation of the Iberian alphabet, adapted by Vascons to our language. According to experts, the hand could have been a lucky charm to bring good luck and shoo bad luck away.
The first word reads sorioneku - please compare to nowadays Basque word zorioneko (for good luck, luckily).
THIS. IS. HUGE.
It’s the first Vasconic text - not single words - that has been found so omg, we’re super excited!!!

Sources: 1 & 2
#euskadi#euskal herria#basque country#pais vasco#pays basque#euskera#euskara#basque#language#history#archaeology#news#video#omfg#nafarroa#linguistics
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
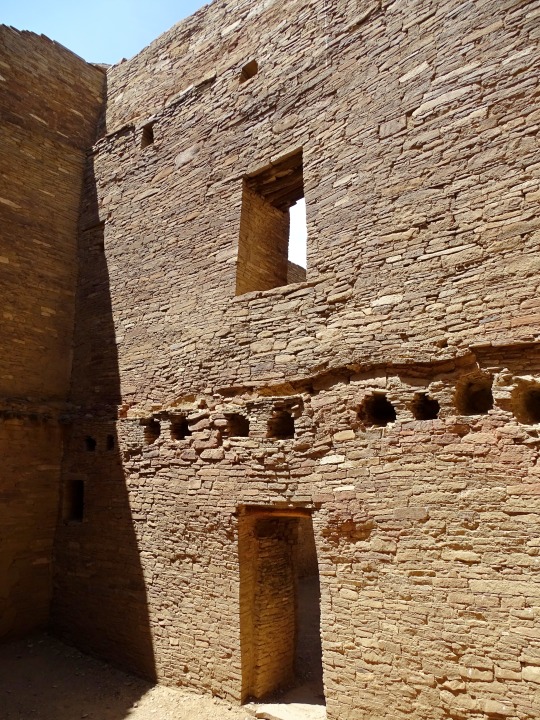



Pueblo Bonito, in Chaco Canyon, was occupied from 828 and 1126 CE. It was the largest of the great houses in what may have been a ceremonial center.
Explore Chaco:
#travel#architecture#history#wandering#original photography#chaco canyon#archaeology#ancestral puebloans#ancient architecture#native american#new mexico#chaco culture#national park service#national park#lensblr#photography#wanderingjana
251 notes
·
View notes
Text
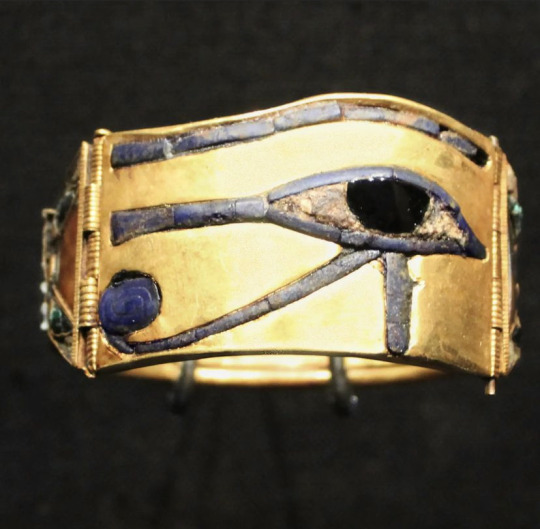

Bangle of Tutankhamen
Gold and jewels inlay Udjat Eye
18th Dynasty, New Kingdom
#art#archaeology#ancient#egyptian art#egyptology#ancient egypt#ancient jewelry#gold jewelry#jewelry#gold#jewels#tutankhamen#tutankhamun#tutankamon#new kingdom
222 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Chilean paleontologists have released their findings on a new duck-billed dinosaur named Gonkoken nanoi, which inhabited Chilean Patagonia in the late Cretaceous, in the late age of the Dinosaur, approximately 70 mya.
The name Gonkoken nanoi means similar to koken or swan in Tehuelche language, the indigenous people that inhabited the region where this species was found, and nanoi in honort to Mario “Nano” Ulloa, who helped during expeditions. It is estimated that it could have measured between 3.5 and 4 meters in length and weighed between 600 kilograms and one ton.
Chilean Patagonia could have been a refuge for these primitive forms of hadrosaurs, which would have migrated to the Southern Hemisphere long before more advanced forms, and it is believed these hadrosaur may have even reached Antarctica, when it was connected to South America.
3D Reconstruction by Christopher Chávez
Reference (Open Access): Alarcón-Muñoz et a., 2023. Relict duck-billed dinosaurs survived into the last age of the dinosaurs in subantarctic Chile. Science Advance
#new species#dinosaur#hadrosaur#Gonkoken nanoi#sciblr#science blr#science#biology#archaeology#fossil#gonkoken
530 notes
·
View notes
Link
Since I haven’t seen it on tumblr yet, here’s an article on a major piece of Sumerian news - the recent discovery of the palace and temple at Girsu! Girsu was, for a time, the capital city of Lagash, its political peak occurring roughly halfway through its more than four millennia of occupation. The temple was dedicated to the city’s patron deity, Ninngirsu, a god of agriculture and warfare.
#sumerian news#sumerian#sumerian archaeology#sumerian mythology#archaeology#girsu#also I just realized this is my 1500th post on this blog! exciting
427 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gigantic Skull of Prehistoric Sea Monster Found on England’s ‘Jurassic Coast’
The remarkably well-preserved skull of a gigantic pliosaur, a prehistoric sea monster, has been discovered on a beach in the county of Dorset in southern England, and it could reveal secrets about these awe-inspiring creatures.
Pliosaurs dominated the oceans at a time when dinosaurs roamed the land. The unearthed fossil is about 150 million years old, almost 3 million years younger than any other pliosaur find. Researchers are analyzing the specimen to determine whether it could even be a species new to science.
Originally spotted in spring 2022, the fossil, along with its complicated excavation and ongoing scientific investigation, are now detailed in the upcoming BBC documentary “Attenborough and the Jurassic Sea Monster,” presented by legendary naturalist Sir David Attenborough, that will air February 14 on PBS.



Such was the enormous size of the carnivorous marine reptile that the skull, excavated from a cliff along Dorset’s “Jurassic Coast,” is almost 2 meters (6.6 feet) long. In its fossilized form, the specimen weighs over half a metric ton. Pliosaurs species could grow to 15 meters (50 feet) in length, according to Encyclopaedia Britannica.
The fossil was buried deep in the cliff, about 11 meters (36 feet) above the ground and 15 meters (49 feet) down the cliff, local paleontologist Steve Etches, who helped uncover it, said in a video call.
Extracting it proved a perilous task, one fraught with danger as a crew raced against the clock during a window of good weather before summer storms closed in and the cliff eroded, possibly taking the rare and significant fossil with it.
Etches first learned of the fossil’s existence when his friend Philip Jacobs called him after coming across the pliosaur’s snout on the beach. Right from the start, they were “quite excited, because its jaws closed together which indicates (the fossil) is complete,” Etches said.


After using drones to map the cliff and identify the rest of the pliosaur’s precise position, Etches and his team embarked on a three-week operation, chiseling into the cliff while suspended in midair.
“It’s a miracle we got it out,” he said, “because we had one last day to get this thing out, which we did at 9:30 p.m.”
Etches took on the task of painstakingly restoring the skull. There was a time he found “very disillusioning” as the mud, and bone, had cracked, but “over the following days and weeks, it was a case of …, like a jigsaw, putting it all back. It took a long time but every bit of bone we got back in.”
It’s a “freak of nature” that this fossil remains in such good condition, Etches added. “It died in the right environment, there was a lot of sedimentation … so when it died and went down to the seafloor, it got buried quite quickly.”



Fearsome top predator of the seas
The nearly intact fossil illuminates the characteristics that made the pliosaur a truly fearsome predator, hunting prey such as the dolphinlike ichthyosaur. The apex predator with huge razor-sharp teeth used a variety of senses, including sensory pits still visible on its skull that may have allowed it to detect changes in water pressure, according to the documentary.
The pliosaur had a bite twice as powerful as a saltwater crocodile, which has the world’s most powerful jaws today, according to Emily Rayfield, a professor of paleobiology at the University of Bristol in the United Kingdom who appeared in the documentary. The prehistoric marine predator would have been able to cut into a car, she said.
Andre Rowe, a postdoctoral research associate of paleobiology at the University of Bristol, added that “the animal would have been so massive that I think it would have been able to prey effectively on anything that was unfortunate enough to be in its space.”
By Issy Ronald.


#Gigantic Skull of Prehistoric Sea Monster Found on England’s ‘Jurassic Coast’#Dorset England#pliosaur#jurassic#fossil#prehistoric#dinosaur#paleobiology#palaeontologists#archaeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#Sir David Attenborough#nature#naturalist
589 notes
·
View notes