#ancientworld
Text

“Hades”, digital, (#4 in my Olympians series)
OK, no 4, mr underworld..HADES! super fun piece to do. I didnt want him to feel evil, but the underworld is described as murky and deep, so it wasn’t going to be full of sunshine and rainbows. I love the idea of a silver and gold mine, as he is the god of wealth and precious minerals/metals. (hence the jewels in the bottom foreground)
Its apt that this piece is done now, as Persephone, his wife, has joined him (forcing Demeter to bring forth winter). Hades holds his bird tipped scepter, and his helmet (or cap) of invisibility (the same one he gave to Perseus as one of his magical items to go and slapy Medusa) .
Sitting Beside the throne is the three headed guard hound; CERBERUS, and in the deep, cavernous background we can the furies, those older, primordial creatures sent forth to punish bloodshed and murder with a family. (and who i cant wait to design and illustrate when i get back to the Oresteia’s second play “Euminides” (i.e. “furies”)
Next will be DEMETER, and I’m super excited about her piece, because i will bring in the Eleusinian mysteries/cult of Demeter into the portrayal somehow. Stay tuned folks! Thanks for looking! xoxo.
Want to own my Illustrated Greek myth book jam packed with over 130 illustrations like this? Support my book kickstarter "Lockett Illustrated: Greek Gods and Heroes" coming in early 2024.
#pagan#hellenism#greekmythology#tagamemnon#mythology tag#percyjackson#dark academia#greek#greekmyths#classical literature#percy jackon and the olympians#pjo#homer#classics#mythologyart#art#artists on tumblr#odyssey#literature#ancientworld#ancienthistory#ancient civilizations#ancient greece#the last olympian#greekgods#zeus#hesiod#hades
207 notes
·
View notes
Text



LADY Sarcasm ?.. - some skeptical expression:
Roman Floor Mosaic w| Tiles Depicting "Seasons"
From the Capannelle [area] on Via Appia Nuova [?], Rome
4-5 AD.
Sun 18 June 2023:
Palazzo Massimo, Museo Nazionale Romano | MNR PM
[2nd Floor]
• Web : https://museonazionaleromano.beniculturali.it/en/palazzo-massimo
• FB : https://www.facebook.com/MNRomano
• IG : @museonazionaleromano
• TW : @MNR_museo
MNR PM | @michael-svetbird Michael Svetbird phs©msp | 18|06|23 4960X4100 600 [I., II.]
The photographed object is the collection item of MNR PM and subject to copyrights.
[non commercial use | sorry for the watermarks]
What season is this, I'm wondering - 'Winter' I suspect ?..
#rome#palazzomassimo#museonazionaleromano#massimo#roman#mosaic#mosaics#ancient art#roman mosaic#seasons#personification#ancientportrait#antiquity#ancient history#archaeology#archeologia#ancient#ancient rome#ancientworld#ancientculture#heritage#museology#museum#mythology#archaeologyart#arthistory#photography#archaeologyphotography#museumphotography#michaelsvetbird
134 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Sensual Soirees of Ancient Roman Merchants
In the heart of ancient Rome, particularly before the establishment of the Empire, social and cultural dynamics unfolded that were distinctly different from those of later epochs. One facet of this era, often mentioned in literary and historical works, is the sensual feasts of the merchants, serving as a reflection of a more open attitude towards sensual and homoromantic relationships within certain social strata. These feasts offered not just a setting for culinary enjoyment but were also centers of cultural, business, and personal exchange.
At lavishly laden tables, adorned with exquisite dishes and exotic fruits, merchants displayed not only their wealth but also their far-reaching trade relationships. Music, poetry, and dance were integral parts of these gatherings, creating an atmosphere of freedom and openness, and thus fostering a culture of tolerance and acceptance.
These feasts were also a breeding ground for free and unbound conversations, often giving rise to deeper, personal relationships. In a world where personal connections and networks were of crucial importance, such events played a significant role both in private and in social life.
A vivid picture of this era is drawn in the literary works of the time, particularly in Petronius' "Satyricon," as well as in the poems of Catullus and Horace. Another example is found in the works of the poet Catullus. In his poems, he openly speaks about his feelings for a young man named Juventius. These poems are characterized by their emotional openness and direct description of his affection and longing.
Horace, a contemporary of Catullus, offers a somewhat different perspective in his poems. His works often reflect philosophical and ethical themes and show how culture and personalities influenced social life. Horace's poems, known for their elegance and subtle observations, convey an image of the social strata and the role that cultural events such as the merchants' feasts played in this context.
The "Satyricon," written by Petronius in the first century AD, is a key work that provides insight into the daily life and society of ancient Rome. This novel, often regarded as one of the first novels in world literature, illustrates the extravagant life of the Roman upper class. Particularly relevant are the descriptions of Trimalchio's feast, which reflect the decadence and excess of the time. The detailed accounts of the banquets and entertainments offer valuable insights into the cultural practices and social interactions typical of the merchants' feasts.
Catullus, a poet of the first century BC, is known for his passionate and often personal poems. His works illuminate the emotional depth and complexity of interpersonal relationships in Rome. Catullus' lyricism, ranging from passionate love to biting satire, illustrates the diversity of emotional expressions present in Roman society and reflects the atmosphere of openness found at the merchants' feasts.
Text supported by Chat GPT-4
Base Image generated with DALL-E, overworked with SD-1.5 inpainting and composing.
#AncientRome#HomoromanticHistory#AncientWorld#gayart#LGBTQ#gayhistory#loveislove#gaylove#manlovesman
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
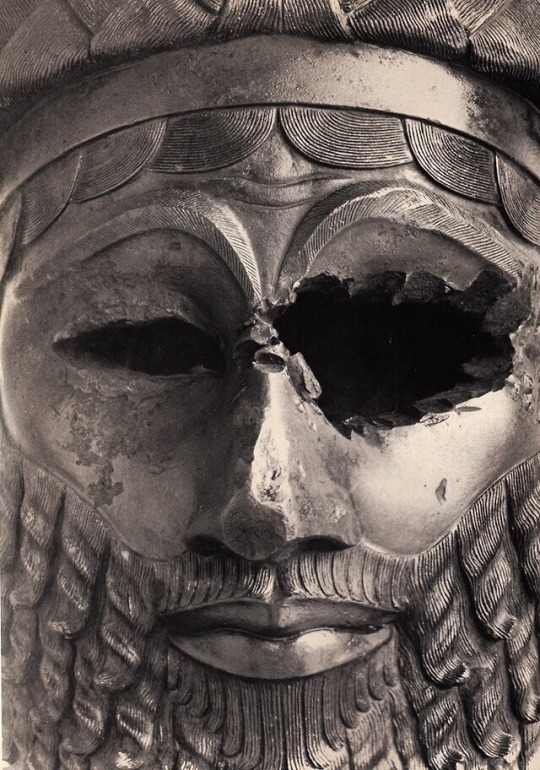

Bronze Head of King Sargon of Akkad, 2306 B.C Material: Bronze . Dimensions: H: 12 in. (30.7 cm.) Location: Iraq Museum, Baghdad, Iraq (?).
583 notes
·
View notes
Text
There are undoubtedly millions of amazing artifacts from the ancient world that have served to shed light on the lives of our ancestors from many millennia ago. But some stand out for their uniqueness, their intrigue, or their ability to expand our knowledge about previously unknown aspects of our history.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Roman mosaic depicting a bird

ITEM
Mosaic depicting a bird
MATERIAL
Tesserae
CULTURE
Roman
PERIOD
3rd Century A.D
DIMENSIONS
400 mm x 440 mm x 40 mm
CONDITION
Good condition
PROVENANCE
Ex Swiss private collection, E.O., Geneve, acquired before 1990s
Roman mosaics are renowned for their intricate designs and enduring beauty, often depicting various motifs that reflect the cultural and artistic sensibilities of the time. Among these motifs, the depiction of birds holds particular significance in Roman art. Birds were commonly featured in Roman mosaics for their symbolic meanings, which varied depending on the species portrayed. The birds motif in Roman mosaics served both decorative and symbolic purposes, enriching the visual appeal of the artwork while conveying deeper layers of meaning to the viewer.
In Roman art, birds were frequently associated with themes of freedom, transcendence, and divine communication. Depictions of birds such as doves, eagles, and peacocks symbolized different aspects of Roman society and belief systems. For example, doves were often associated with peace and love, while eagles were emblematic of power and authority, often representing the Roman state and its military prowess. Peacocks, with their vibrant plumage, were symbols of immortality and resurrection in Roman mythology, associated with deities such as Juno and Hera.
The
Read the full article
#ancient#ancientart#ancienthistory#artefact#artifact#ancientartifacts#antiquities#antiquity#art#artobject#ancientrome#ancientworld#history#classical#archaeology#roman#mosaic#bird#tessera#tesserae#animal
3 notes
·
View notes
Link
#WalktheBible#Gospel#Scripture#Scroll#BiblicalArchaeology#discoveries#excavation#holyland#israel#archaeologylovers#travelhistory#arctic exploration#jewishheritage#historicplaces#scriptures#jews#middleeast#ancientworld#biblicalstudies#historybuff#discoverhistory#heritage#faith#religion#archaeology#ancientjudaism#biblehistory#deadseascrolls#qumran
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Monday's image: March 11, 2024
Egypt, New Kingdom, Ramesside, Statuette, Dynasty19-20, Pottery, red and black paint, 24 x 9.3 x 0.4 centimeters, 1295-1070 B.C., Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
#mc_embed_signup{background:#fff; false;clear:left; font:14px Helvetica,Arial,sans-serif; width: 600px;} /* Add your own Mailchimp form style overrides in your site stylesheet or in this style block. We recommend moving this block and the preceding CSS link to the HEAD of your HTML file. */
Subscribe to Monday's image
* indicates required
Email Address *
(function($) {window.fnames = new Array(); window.ftypes = new Array();fnames[0]='EMAIL';ftypes[0]='email';fnames[1]='FNAME';ftypes[1]='text';fnames[2]='LNAME';ftypes[2]='text';fnames[3]='ADDRESS';ftypes[3]='address';fnames[4]='PHONE';ftypes[4]='phone';}(jQuery));var $mcj = jQuery.noConflict(true);
#statuette#Egypt#NewKingdom#Ramesside#pottery#paint#sculpture#AncientWorld#MetropolitanMuseumofArt#NewYork#LeSoir#Brussels#Belgium#Gaza#Belgiumwantstoinfluencegenocideproceedings#Football#LeStandard#beatenbutsafe#Cycling#RemcoEvenepoel#happytohave'givenithisall'#TheTriumphof'Dalva'#LoveAccordingtoDalva#film#womeninfilm#EmmanuelleNicot#13thMagritteAwards#Belgianfilmawards#groupportrait#winners
0 notes
Text




Step back in time and explore the wonders of Pangaea! 🌍✈️ Where ancient landscapes meet timeless adventures. Experience a world before borders, where every destination is within reach. 🏞️🦕
#TimeTravel#AncientWorld#UnexploredEarth#RetroTravel#ContinentalJourney#PrehistoricAdventures#WorldWithoutBorders
0 notes
Video
Ancient ruins
0 notes
Link
How does this make you feel? Share with us!
#graphicdesign#grimoire#gothic#darkartist#darkart#emo#occult#witch#sorcerer#magic#dreaming#vintage#gold#mysterious#darkmood#journal#secrets#egyptian#ancientworld#mandala#ornate
0 notes
Text

Anubis is an ancient Egyptian deity associated with mummification, the afterlife, and the protection of graves. He is often depicted as a jackal or a man with the head of a jackal. Anubis played a significant role in Egyptian mythology and religious beliefs.
In Egyptian mythology, Anubis was considered the son of Nephthys and Osiris or sometimes of Seth and Nephthys. He was closely associated with death and the process of embalming and mummification. Anubis was believed to oversee the weighing of the deceased person's heart against the feather of Ma'at, the goddess of truth and justice, in the Hall of Ma'at during the judgment of the soul. He would determine the fate of the deceased based on the outcome of this judgment. If the heart was found to be heavier than the feather, it meant the person had led an immoral life, and their heart would be devoured by Ammit, a creature with the head of a crocodile, the front body of a lion, and the rear body of a hippopotamus.
Due to his role in the afterlife, Anubis was also considered a protector of graves and cemeteries. Ancient Egyptians believed that he guarded the tombs and guided the souls of the deceased to the realm of the dead. As a result, Anubis was commonly depicted on the walls of tombs and burial sites, usually in the form of a jackal or as a human figure with a jackal head.
Anubis had a significant presence in ancient Egyptian religious practices. He was invoked during funeral ceremonies and mummification rituals to ensure the proper preservation and protection of the deceased. Anubis was also venerated as a guardian and protector of the living, with people seeking his assistance and favor in various aspects of their lives.
Thanks as always for looking! Xoxo
#pagan#hellenism#tagamemnon#mythology tag#percyjackson#dark academia#greek#classical literature#percy jackon and the olympians#pjo#homer#iliad#classics#mythologyart#art#artists on tumblr#odyssey#literature#ancientworld#ancienthistory#ancient civilizations#ancientgreece#olympians#egypt#ancientegypt#egytpianmythology#egyptiangod#egyptiangods
308 notes
·
View notes
Text



ARTEMIS Type Naples:
"The Goddess of the hunt is shown advancing rapidly, her quiver slung around her body.
With her left hand she lifted an edge of her dress, whilst in her right she held a bow and arrows.
Statue in the archaizing style of the early Imperial period, also known from other examples.
Augustan Period [early 1st cent. AD]."
[txt ©MNR Palazzo Massimo]
White fine-grained greek marble with traces of red paint on the robe, inserted eyeballs were made of different material.
Probable provenance - residential building [Caserta, Campania ?], was stolen [1994] from the area of Caserta, recovered [2001] in Switzerland.
1 AD.
Palazzo Massimo, Museo Nazionale Romano | MNR PM
[2nd Floor, Sala VIII.]
• Web : https://museonazionaleromano.beniculturali.it/en/palazzo-massimo
• FB : https://www.facebook.com/MNRomano
• IG : @museonazionaleromano
• TW : @MNR_museo
MNR PM | Michael Svetbird phs©msp | 06|23 6000X4100 600 [Set of 3]
The photographed object is the collection item of MNR PM and subject to copyrights.
[non commercial use | sorry for the watermarks]
📸 Part of the "Small Format Sculpture and Miniature Artefacts" MSP Online Photo-gallery:
👉 D-ART:
https://www.deviantart.com/svetbird1234/gallery/69450077/small-format-sculpture-and-miniature-artifacts
👉 FB Album:
https://www.facebook.com/media/set/?set=a.859777984390780&type=3
.
#rome#roman#palazzomassimo#museonazionaleromano#massimo#ancient sculpture#sculpture#artemis#άρτεμις#artemide#artemida#goddess#antiquity#antiquities#archaeology#archeologia#ancient#culture#ancientworld#museology#museum#mythology#heritage#art history#archaeology art#photography#archaeology photography#sculpture photography#museum photography#michaelsvetbird
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today in History- Cleopatra dies.
Cleopatra. An icon. A ruler. A leader. And recently sparked a heated debate worldwide. Who is the person behind the myth?
Friends,
My whiteboard reminded me that it was time for another ‘Today in History’. And I have a story for you! The famous Cleopatra. The woman who is an icon. A ruler. A leader. And recently sparked a heated debate worldwide.
But as I would like to know the whole story, I decided to dig into Cleopatra and the reality of her history. As with many of my historical blogs, this one will share the…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
Exploring Geography with Ptolemy - Geographia

Step into the captivating world of "Geographia," a timeless masterpiece that traces the evolution of geography.
Delve into the ancient era, where the brilliant mind of Claudius Ptolemy, a revered Greek mathematician, astronomer, and geographer, left an indelible mark.
Uncover the significance of his influential book, which illuminates the geography of the Roman Empire and beyond.

Ptolemy. Line engraving. Photo by Wellcome Images. Wikimedia.
Early Life and Work of Ptolemy
Born in Ptolemais Hermiou, a Greek city in Egypt, in 90AD, Ptolemy was a renowned mathematician. Early on, most of his work was centered around mathematics and astronomy.
It was through his observations of the stars and the movements of the planets that Ptolemy found his interest in geography. He believed that the earth was the center of the universe, and everything else, including the heavenly bodies, revolved around it.
Learning from the Past
As he started to explore further, Ptolemy began to compile and synthesize the works of previous geographers, merging knowledge from different civilizations and cultures.
His book laid out his belief in geography as a science, laying out the concept of longitude and latitude. He also divided the earth into smaller sections, with each section containing a map that was more accurate than the previous one.
Mapping and Projections
Ptolemy also explored the concept of mapping and projections, which eventually led to the creation of various projections named after him. These projections were widely used in cartography for centuries until newer and more accurate methods were developed.
His contribution to geography was not just about the maps, but the accuracy of the maps he made, based on the knowledge he gained from combining different cultures and civilizations.
Ptolemy had not only an impact on geography, but his work also influenced many other fields, including astronomy, philosophy, and cartography. His works were translated into several languages, and his theories and ideas were featured in the works of many scholars in the centuries that followed.

Atlas Ulm with maps by Claudius Ptolemy. Photo by Jennifer Morrow. Flickr.
Ptolemy’s Contribution to Geography
Ptolemy's "Geographia" is a masterpiece that comprises eight books, each with its own perspective on the geography of the ancient world. Book one consists of an introduction, while books two to seven contain maps and geographical descriptions of the ancient world.
Book eight presents instructions on how to construct a world map, take latitude measurements, and more. Ptolemy's maps were unique as they were based on a coordinate system using latitude and longitude, which was groundbreaking.
Defining Geographical Concepts
One of Ptolemy's most significant contributions was introducing several geographical concepts, such as the equator, tropics, and the division of the sphere into 360 degrees of latitude and longitude.
At the time, the precise measurement of longitude and latitude was unknown, and maps were often inaccurate. By introducing the concept of the equator and the tropics, Ptolemy was able to create a more precise representation of the world, leading to more accurate maps.
Ptolemy's work had a profound impact on geography's development, both in his time and for future generations. He created chords that measured angles between cities, and he also used spherical trigonometry which allowed him to measure the distance between different points on the earth. These methods helped him determine the precise location of different cities and create accurate maps.
His Impact on Society
In addition to the development of accurate maps, Ptolemy's work also had a significant impact on the trade and commerce of ancient societies. His maps allowed merchants to navigate the sea and travel safely, making the transportation of goods more efficient.
Ptolemy's work opened up new trading routes around the Mediterranean and beyond, leading to an explosion of wealth and prosperity.
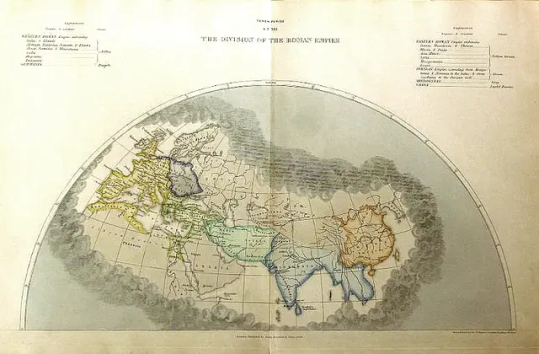
The Division of the Roman Empire AD 395. Photo by THX News. Copyright.
Geography in Ptolemy's Time
During Ptolemy's time, the world was much different from what we see today. Europe was mostly dominated by the powerful Roman Empire, and many of the world's kingdoms existed as tributaries.
This domination made it easy for the Romans to control and collect information about conquered territories through maps.
The trade routes to the East were thriving, causing an increase in the demand for spices, silk, and other exotic goods. Merchants needed accurate maps to traverse the vast lands and seas, and Ptolemy's geographically accurate maps helped them do just that - leading to the development of modern-day cartography.
The Founding of the Modern Map System
Many early civilizations, including the Babylonians and Egyptians, had established cartography as a science. However, Ptolemy's extensive work helped to revolutionize it. He produced world maps and detailed maps of specific areas, especially in Europe, Asia, and Africa.
He was also the first to map latitude and longitude, which made it possible to locate any place on Earth. His maps showed the shape and size of the Earth, and he made extensive calculations on its size to ensure accuracy.
Ptolemy's work revolutionized the measurement of distances. By using the latitude and longitude system, he could calculate the distance between any two points on the surface of the Earth. This invaluable information allowed merchants to plan their routes accurately, saving them time and resources.
Ptolemy's maps also identified the sources of valuable trade goods, which made it easier to explore new trading routes.
Geographia's Impact on Explorers and Educators
Ptolemy's work includes geography, astronomy, and mathematics. His extensive writings include The Geography, which became a major influence on European cartography for centuries.
Scholars used his work as a textbook for many generations, and it guided explorers like Christopher Columbus and Vasco da Gama in their expeditions.
His works were translated into various languages, and his maps were reproduced to ensure the spread of geographically accurate information.

Bronze of Christopher Columbus, City of Westminster, London. Photo by Peter O'Connor. Flickr.
The Legacy of Ptolemy
Ptolemy's Geographia, written in the 2nd century, contained a wealth of information on the geography of the ancient world. His use of grid systems and projections made his maps some of the most beautiful and accurate from the ancient world.
His methods and techniques were used until the 16th century when significant advancements in technology and navigation took place. Ptolemy's legacy is evident in the development of geography and cartography.
His work inspires many modern geographers and historians, who actively integrate his methods and techniques into their research.
His Influence on Astronomy
In addition to geography and cartography, Ptolemy had a significant impact on the development of astronomy. He believed that the Earth was at the center of the universe and that celestial bodies orbited around it.
His theories and calculations were essential in establishing the basis of astronomy during his time. Furthermore, his work was improved upon and built upon by later astronomers, and his legacy can still be seen in the way we understand the universe today.
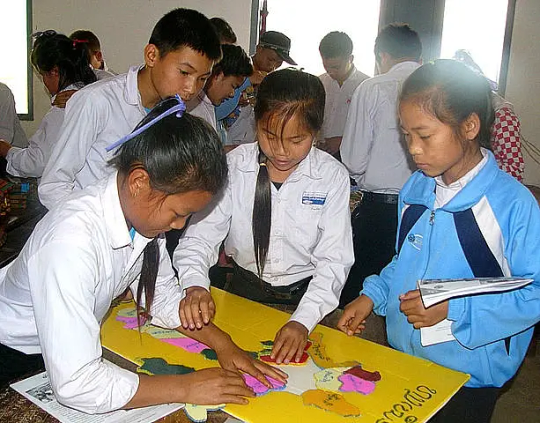

Students learn geography with jigsaw map of Laos.. Photo by Blue Plover. Wikimedia.
Ptolemy's Legacy
Despite the fact that many aspects of Ptolemy's legacy were replaced by newer technologies and theories, his work still holds relevance and significance today. His Geographia serves as a historical document that allows us to gain insight into the knowledge of the ancient world.
Furthermore, his contributions to astronomy laid the groundwork for modern astronomy and physics, making him one of the most important figures in the history of science.
Ptolemy's legacy also extends to the study of geography and culture. His maps contained not only geographical information but also cultural and historical information, making them some of the most valuable sources for understanding the ancient world.
His maps provided valuable insights into the lifestyles, customs, and habits of the people of the ancient world, which have helped scholars and historians to better understand ancient civilizations and cultures.
Conclusion
Learning about the geography of Ptolemy is crucial in understanding the development of geography, cartography, and the ancient world. Ptolemy's works lay the groundwork for geographers and historians, aiding our comprehension of global geography.
Ptolemy's legacy has left a mark on history, as his work was a comprehensive exploration of geography that combined knowledge from diverse civilizations from around the world.
His contribution to geography has undoubtedly shaped the way we learn and study geography, making him an essential figure in the history of geography.
Sources: THX News & University of Houston.
Read the full article
#accuratemaps#ancienttimes#ancientworld#geographer#geography#latitude#longitude#maps#Ptolemy#traderoutes
0 notes
Text
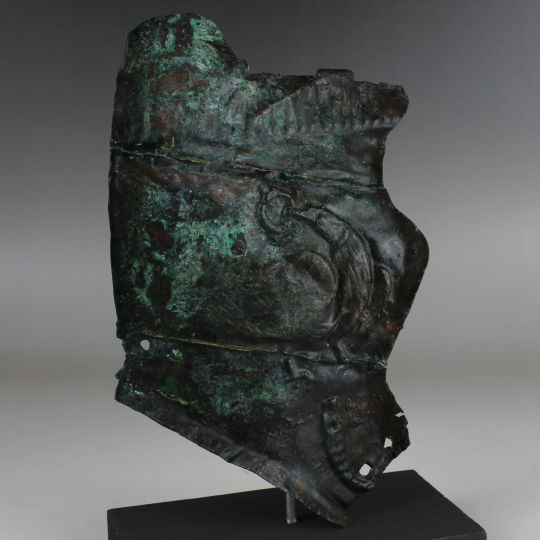
Roman military helmet face mask fragment with Jupiter's eagle

ITEM
Military helmet face mask fragment with Jupiter's eagle
MATERIAL
Bronze
CULTURE
Roman
PERIOD
3rd Century A.D
DIMENSIONS
180 mm x 123 mm
CONDITION
Good condition
PROVENANCE
Ex Alison Barker private collection, a retired London barrister, acquired between 1960s - 1990s
BIBLIOGRAPHY
RUCINSKI, E., Get the picture?: Iconography of cheek pieces on Roman Imperial cavalry helmets, Journal of Roman Military Equipment Studies
Roman military equipment is famous for its abundance of depictions rife with symbolical content. The so-called cavalry sports equipment, which used to be seen as being solely parade armour, can be distinguished from the infantry equipment not only by its function, but also by its design. There are numerous surviving heavily ornamented parts of Roman cavalry equipment and a number of studies have been published on their purpose and decoration. Whether the ornamented equipment belonged to parade armour or was also worn in battle is still under discussion. One of those groups contains the helmets, of which a relatively large number of different variations exist. Apart from the calotte with its neck guard, the loosely attached cheek pieces were also an essential part of the helmet. Cheek pieces as protective elements were used both for infantry and cavalry helmets.
Read the full article
#ancient#ancientart#ancienthistory#artefact#artifact#ancientartifacts#antiquities#antiquity#art#artobject#ancientrome#ancientworld#history#classical#archaeology#roman#military#legion#legionary#helmet#jupiter#eagle#army#mask#face#bronze#arms#armour
9 notes
·
View notes
