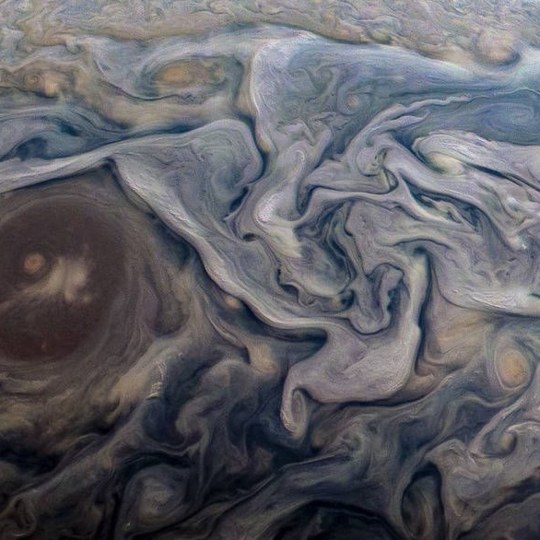
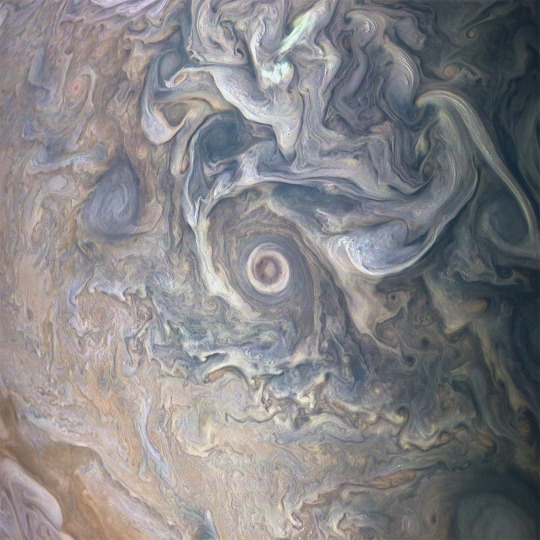
Text

309 notes
·
View notes
Text

1K notes
·
View notes
Text
How does NASA use the constellations?
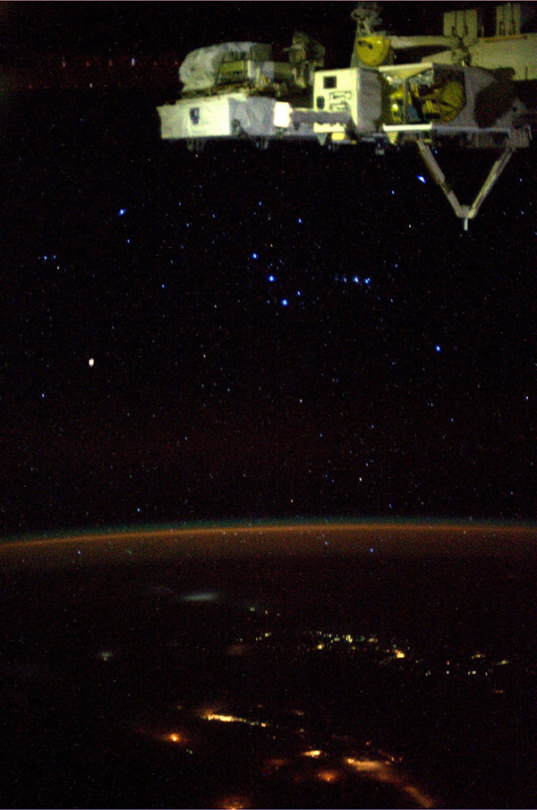

This photo of the constellation Orion was taken by NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg aboard the International Space Station.
Stars and constellations stay in approximately the same spot for many, many years. They only appear to move in the sky during the year because we are on a moving planet. Because the constellations are in a fixed location, they are often used as landmarks in the sky. Many stars, nebulae, and other objects are named after the constellations they are found in.
For example, meteor showers are named for the constellation where the meteors appear to be coming from. So, for example, the Orionids meteor shower, which occurs in October each year, appear to come from the same direction as the constellation Orion the Hunter.
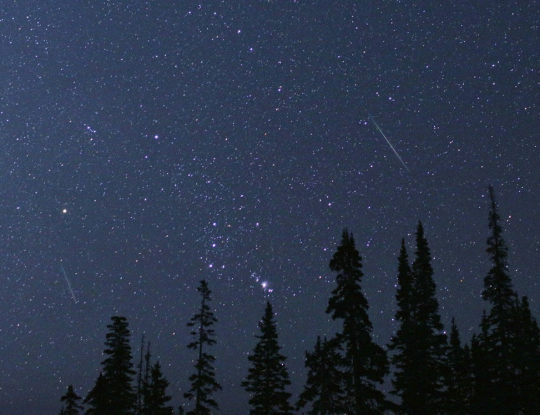

The constellation Orion is framed by two Perseid meteors on Aug. 12, 2018, in Cedar Breaks National Monument, Utah. The Perseid meteor showers appear to come from the same direction as the constellation Perseus
If you are curious about the difference between astronomy and astrology, you can access the link below from another post of mine:
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
What’s the difference between astrology and astronomy?

This image of the Orion nebula was captured by the Hubble Space Telescope. It is located in the constellation Orion, below the three stars that form the hunter's belt.
1. Astronomy is the scientific study of everything in outer space. Astronomers and other scientists study stars and galaxies, most of which are many light-years away from Earth. Studying the scientific properties of these objects in space helps us to understand how the universe was made, what else is out there, and how we fit in.
2. Astrology is not the same thing as astronomy. As a science, astronomy follows the scientific process involving evidence and data. Astrology is based on the belief that the location of certain stars and planets in the sky can predict the future or describe what a person is like. While astrology is important to some cultural traditions, its claims are not based on scientific evidence
If you are interested in knowing what a constellation is, I made a post about it:
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Are Constellations?
There are a few different definitions of constellations, but many people think of constellations as a group of stars. The constellations you can see at night depend on your location on Earth and the time of year. Constellations were named after objects, animals, and people long ago. Astronomers today still use constellations to name stars and meteor showers.
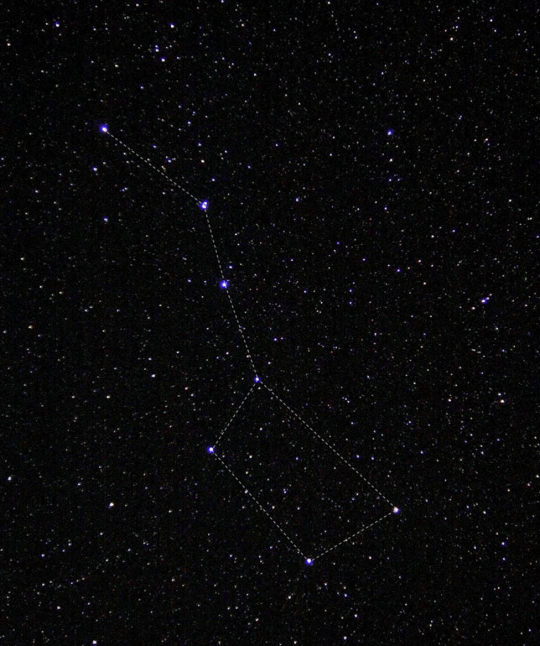

This group of stars is called the "big dipper." If you trace a line between the stars, it looks like a ladle, or dipper, that you'd use to dip soup from a pot. This photo of the big dipper was taken by an astronaut on the International Space Station, but you can often see this group of stars from the ground, too!
What constellations can you see in the night sky?
It can be a little confusing to picture how the night sky changes as we orbit the Sun. You can see how it all works in the illustration below.
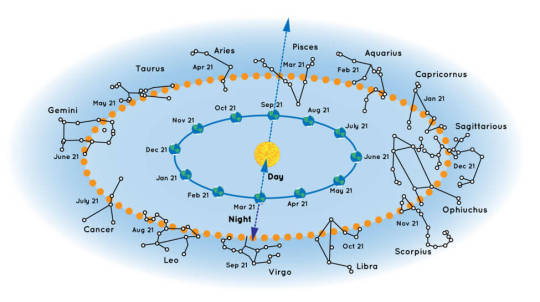
For example, say you’re in the Northern Hemisphere looking into the night sky on September 21. You’ll probably be able to see the constellation Pisces. But you won’t see Virgo because that constellation is on the other side of the Sun. During that time of year, Virgo’s stars would only be visible during the daytime – but you’d never see them because of the brightness of our Sun.
47 notes
·
View notes
Text



M63 - The Sunflower Galaxy
Flocculant spiral galaxies are simply beautiful, the tight arms with intermittent dust lanes and areas of star formation that look like diamonds in wool.
The galaxy is however named more because of the arms in the upper image, which stretch almost 180,000 light years out from the centre and thought to be the results of recent interactions with nearby dwarf galaxies.
The galaxy is actually a similar size to the Milky Way, and sits in the constellation of Canes Venatici some 30 million light years from us.
211 notes
·
View notes
Text

We are back!!
185 notes
·
View notes
Text
I want to thank you for all your support. Today I made 4000 followers and you don't know how much this means to me
Thank you so much and I hope to be more and more
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
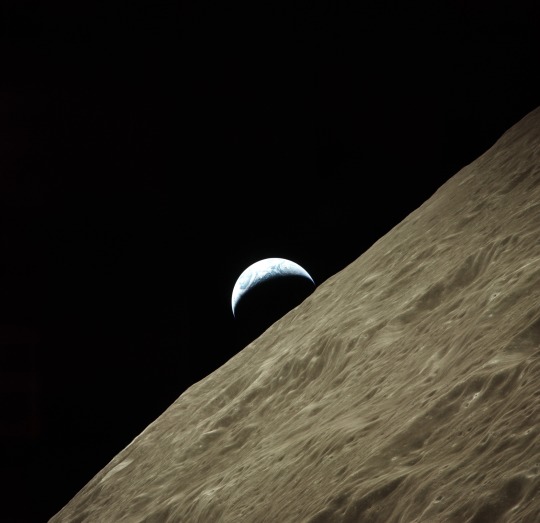
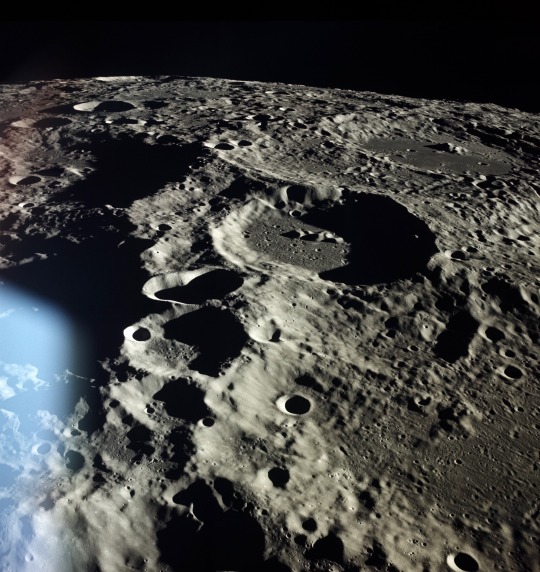
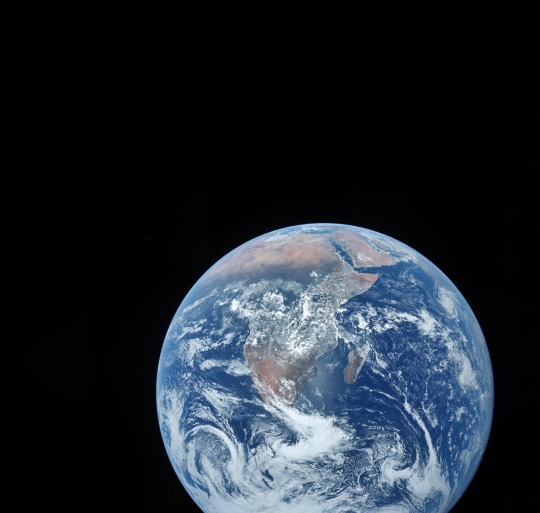
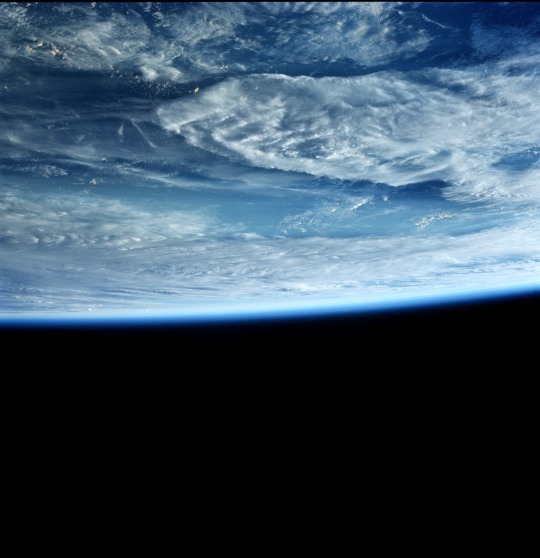
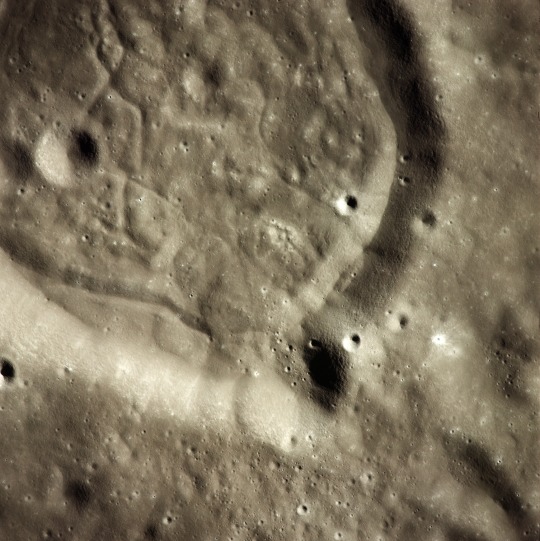






Snapshots from the Apollo 17 mission, December 7-19, 1972. The camera was a Hasselblad 500EL 70mm. (via)
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
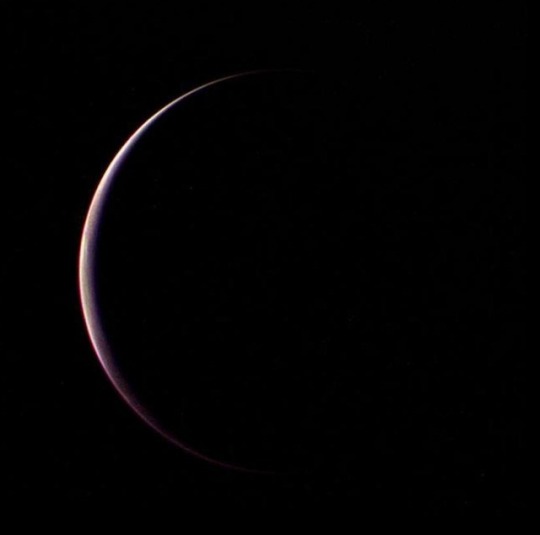
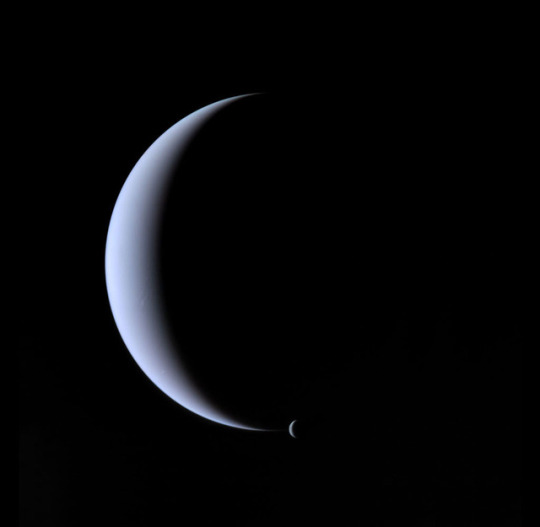
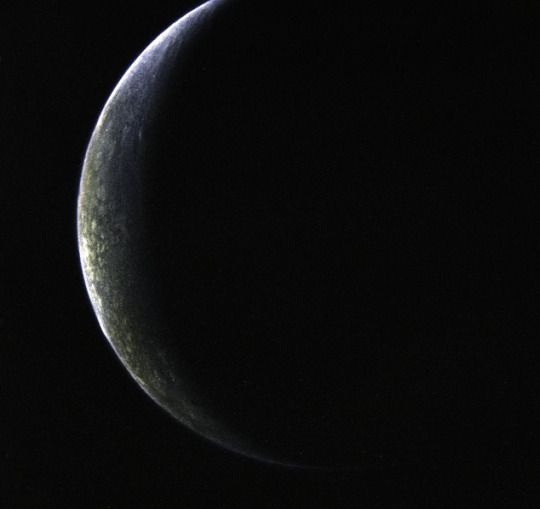
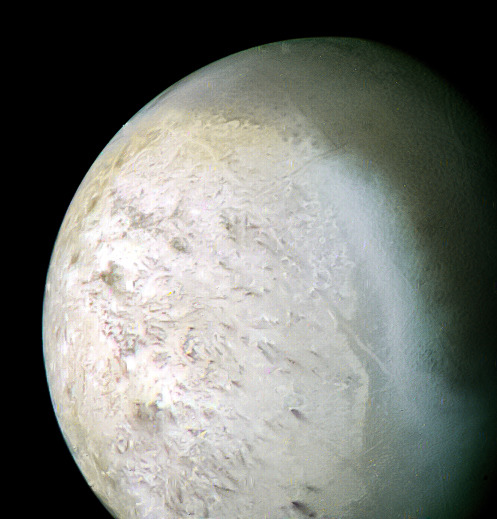










Triton
It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, an orbit in the direction opposite to its planet’s rotation. At 2,710 kilometres in diameter, it is the seventh-largest moon in the Solar System. Because of its retrograde orbit and composition similar to Pluto’s, Triton is thought to have been a dwarf planet captured from the Kuiper belt. Triton has a surface of mostly frozen nitrogen, a mostly water-ice crust, an icy mantle and a substantial core of rock and metal. The core makes up two-thirds of its total mass.
All detailed knowledge of the surface of Triton was acquired from a distance of 40,000 km by the Voyager 2 spacecraft during a single encounter in 1989. The 40% of Triton’s surface imaged by Voyager 2 revealed blocky outcrops, ridges, troughs, furrows, hollows, plateaus, icy plains and few craters.
Triton is geologically active; its surface is young and has relatively few impact craters. Although Triton’s crust is made of various ices, its subsurface processes are similar to those that produce volcanoes and rift valleys on Earth, but with water and ammonia as opposed to liquid rock.
Triton’s entire surface is cut by complex valleys and ridges, probably the result of tectonics and icy volcanism. The vast majority of surface features on Triton are endogenic—the result of internal geological processes rather than external processes such as impacts. Most are volcanic and extrusive in nature, rather than tectonic
The Voyager 2 probe observed in 1989 a handful of geyser-like eruptions of nitrogen gas and entrained dust from beneath the surface of Triton in plumes up to 8 km high.
Triton is thus, along with Earth, Io, and Enceladus, one of the few bodies in the Solar System on which active eruptions of some sort have been observed. (source)
images: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ISS & Kevin M. Gill
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo

2022 December 9
Mars Rises above the Lunar Limb
Image Credit & Copyright: Tom Glenn
Explanation: On the night of December 7 Mars wandered near the Full Moon. In fact the Red Planet was occulted, passing behind the Moon, when viewed from locations across Europe and North America. About an hour after disappearing behind the lunar disk Mars reappears in this stack of sharp video frames captured from San Diego, planet Earth. With the Moon in the foreground Mars was a mere 82 million kilometers distant, near its own opposition. Full Moon and full Mars were bright enough provide the spectacular image with no exposure adjustments necessary. In the image Mars appears to rise just over ancient, dark-floored, lunar crater Abel very close to the southeastern edge of the Moon’s near side. Humboldt is the large impact crater to its north (left).
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap221209.html
242 notes
·
View notes
Text
Jovian System: Jupiter with its Great Red Spot, and Jupier's four largest moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto

This is a composite of the Jovian system, includes the edge of Jupiter with its Great Red Spot, and Jupiter's four largest moons, known as the Galilean satellites. From top to bottom, the moons shown are lo, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto.
The Great Red Spot, a storm in Jupiter's atmosphere, is at least 300 years old.
Winds blow counterclockwise around the Great Red Spot at about 250 miles an hour. The storm is larger than one Earth diameter from north to south, and more than two Earth diameters from east to west. In this oblique view, the Great Red Spot appears longer in the north-south direction.
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today marks 1 year since I posted on this account. I am extremely happy that I have gathered so many followers, that there are so many people interested in what I post.
I want to thank you very much for all the messages of encouragement, all the questions you asked me and all the nice comments. It has always been a great pleasure to talk to you.
The thought that someone somewhere is reading from their phone or this post or in general that you are reading my posts from this account is wow for me.

56 notes
·
View notes
Note
Ok,
Can you tell me why planets spin ? And, are there planets that do not spin ?
Zehel
To be honest, since you asked me the question, I tried to study the problem. I know this has more to do with physics than astronomy. It has to do with the force of physics inertia. Really because it has more to do with physics than simple astronomy that I'm posting here, it's a topic that's beyond me.
If there is someone here who could explain the concept to us, please, because it is not really simple.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

57 notes
·
View notes








